0% found this document useful (0 votes)
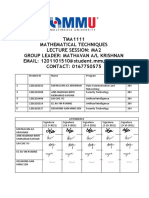
104 views5 pagesFaculty of Information Science and Technology (FIST) : PIM 0245 Introduction To Multimedia Technology
This document provides an introduction to multimedia, including:
1. Definitions of multimedia as the combination of multiple media types like text, graphics, audio, video and animation in a presentation or interactive application.
2. Examples of different types of multimedia products like briefings, references, databases, education/training, kiosks, and entertainment.
3. Guidelines for evaluating multimedia products from both a user and developer perspective in terms of content, usability, performance, and more.
4. An overview of some advantages of using multimedia like improving lives through education and influencing users in both positive and negative ways.
Uploaded by
MATHAVAN A L KRISHNANCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views5 pagesFaculty of Information Science and Technology (FIST) : PIM 0245 Introduction To Multimedia Technology
This document provides an introduction to multimedia, including:
1. Definitions of multimedia as the combination of multiple media types like text, graphics, audio, video and animation in a presentation or interactive application.
2. Examples of different types of multimedia products like briefings, references, databases, education/training, kiosks, and entertainment.
3. Guidelines for evaluating multimedia products from both a user and developer perspective in terms of content, usability, performance, and more.
4. An overview of some advantages of using multimedia like improving lives through education and influencing users in both positive and negative ways.
Uploaded by
MATHAVAN A L KRISHNANCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5