0% found this document useful (0 votes)
107 views45 pagesLec02 Sequential Circuit
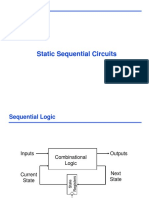
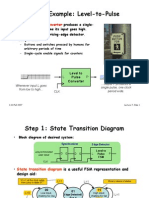
This document provides an outline for a lecture on sequential circuits. Section 1 introduces sequential circuits and their syntax, including flip-flops, non-blocking and blocking assignments, and synchronous reset. Section 2 will cover finite state machines, Section 3 will discuss timing, and Section 4 will cover synthesis and design compiler. The document includes diagrams to illustrate flip-flop operation and coding styles.
Uploaded by
yanjia8161100Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
107 views45 pagesLec02 Sequential Circuit
This document provides an outline for a lecture on sequential circuits. Section 1 introduces sequential circuits and their syntax, including flip-flops, non-blocking and blocking assignments, and synchronous reset. Section 2 will cover finite state machines, Section 3 will discuss timing, and Section 4 will cover synthesis and design compiler. The document includes diagrams to illustrate flip-flop operation and coding styles.
Uploaded by
yanjia8161100Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 45