THE INTERNET
History
It’s hard to say exactly when The Internet was created. The research that led to what we now know as
the Internet was begun in the 1960s. The initial research was carried out by the Advanced Research
Projects Agency in America, funded by the US government. It took many years for the Internet to
become popular around the world. It’s only really since the mid-90s that the Internet has been a part of
our daily lives.
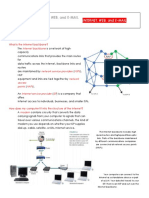
The Internet is a global network of computer networks, which allows users to share all kinds of
information and computer resources. The system is made up of networks interconnected all over the
world, from universities and large corporations to commercial online systems and non-profit
organizations.
Getting Online, Broadband, IP address
To get connected, you need a computer, the right connection software and a modem connected to the
phone line. A modem (modulator/demodulator) converts digital signals into analogue signals so that data
can be transmitted across the phone or cable network. You also need an account with an Internet
Service Provider (ISP), which acts as a gate way between your PC and the rest of the Net. Today ISPs
offer a broadband , high-speed connection.
The language used for data transfer on the Internet is known as TCP/IP (transmission control
protocol/Internet protocol). This is like the Internet operating system. Every computer connected to the
Net is identified by a unique IP address. An IP address consists of 32 bits, often shown as 4 octets of
numbers from 0-255 represented in decimal form instead of binary form. For example, the IP address
can be - 168.212.226.204.
Wi-Fi, hotspots, Web Browsers
Other ways of accessing the Internet include Wi-Fi, satellite, mobile phones and TV sets equipped with a
modem. Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) enabled laptops or tablets smart phones allow you to connect to the
Net if you are near a wireless access point in locations called hotspots (a Wi-Fi café, park, campus). The
Wi-Fi technology uses radio waves to communicate data over medium range distances.
Satellite services are used in places where terrestrial access is not available (ships at sea). High-end
mobile phones provide access through the phone network.
Web browsers include Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox (free, opensource), Safari,
Netscape and Opera.
Email, Email Features
Email lets you exchange messages with people all over the world. Optional attached files can include
text, pictures and even audio and animation. A mailing list uses email to communicate messages to all its
subscribers – that is, everyone that belongs to the list. One of the most popular web-based email is
seznam.cz, gmail.com, centrum.cz, post.cz etc.When you set up an account with ISP (Internet Service
Provider), you are given an email address and a password. The mail you receive is stored on the mail
server of your ISP-in a simulated mail box- until you next connect and download it to your hard drive.
�There are two ways to get email over the Internet. One is by using a mail program (known as an email
client) installed on your computer, for example Outlook Express. The other way is to use web-based
email, accessible from any web browser. The name given to unsolicited email messages is spam.
Anatomy of an Email
In an e-mail, header lines that identify particular routing information of the message, including the
sender, recipient, date and subject goes before the body (content text).
Header
To: name and address of the recipient
From: name and address of the sender
Cc: carbon copy
Bcc: blind carbon copy
Subject: topic of the message
Attachment: files added to the message
Jhartley234@btinternet.com - user name, et symbol, domain name or network address