0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views27 pagesINTERNET - Meaning and Concept
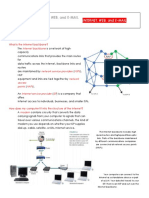
The Internet is a decentralized global network that connects millions of devices, facilitating seamless communication and data exchange through standardized protocols. It serves as a vital infrastructure for modern society, enabling access to information and driving innovation. Key components of the Internet include the World Wide Web, email systems, and protocols like HTTP and FTP, which support various functionalities and data transfers.
Uploaded by
srivastavb600Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views27 pagesINTERNET - Meaning and Concept
The Internet is a decentralized global network that connects millions of devices, facilitating seamless communication and data exchange through standardized protocols. It serves as a vital infrastructure for modern society, enabling access to information and driving innovation. Key components of the Internet include the World Wide Web, email systems, and protocols like HTTP and FTP, which support various functionalities and data transfers.
Uploaded by
srivastavb600Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 27