0% found this document useful (0 votes)
287 views6 pagesSAP System Refresh Activity
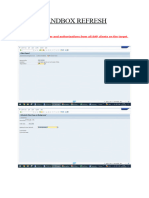
SAP System Refresh is the process of copying data from a production system to quality or development systems to maintain up-to-date testing and training environments. The refresh involves pre-refresh activities like notifying users and backing up systems, execution steps including restoring data and configuring systems, and post-refresh activities for validation and user access. This ensures that QA/DEV systems reflect current production data and function correctly after the refresh.
Uploaded by
Tariq TunioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
287 views6 pagesSAP System Refresh Activity
SAP System Refresh is the process of copying data from a production system to quality or development systems to maintain up-to-date testing and training environments. The refresh involves pre-refresh activities like notifying users and backing up systems, execution steps including restoring data and configuring systems, and post-refresh activities for validation and user access. This ensures that QA/DEV systems reflect current production data and function correctly after the refresh.
Uploaded by
Tariq TunioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6