0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesSection 2 Objective 1
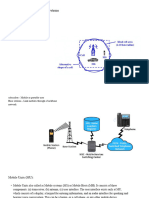
The document outlines four main types of networks: Local Area Networks (LAN), Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), and Mobile Networks, detailing their characteristics and functions. It provides an overview of mobile networks from 1G to 4G, highlighting advancements in speed, technology, and services offered. Additionally, it explains the concepts of intranet and extranet in relation to privacy levels on networks.
Uploaded by
RhanikaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesSection 2 Objective 1
The document outlines four main types of networks: Local Area Networks (LAN), Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), and Mobile Networks, detailing their characteristics and functions. It provides an overview of mobile networks from 1G to 4G, highlighting advancements in speed, technology, and services offered. Additionally, it explains the concepts of intranet and extranet in relation to privacy levels on networks.
Uploaded by
RhanikaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4