0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesLinux Features
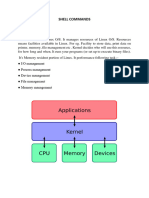
Linux is a versatile and open-source operating system known for its robustness, security, and flexibility. Key features include multi-user support, multi-tasking capabilities, strong security measures, and extensive customizability. It is widely used in various environments, from personal computing to enterprise-level infrastructure, and is favored for its cost-effectiveness and community support.
Uploaded by
manvi0318Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesLinux Features
Linux is a versatile and open-source operating system known for its robustness, security, and flexibility. Key features include multi-user support, multi-tasking capabilities, strong security measures, and extensive customizability. It is widely used in various environments, from personal computing to enterprise-level infrastructure, and is favored for its cost-effectiveness and community support.
Uploaded by
manvi0318Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3