0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views21 pagesARM Lecture 1
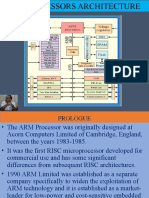
The document outlines the history and development of ARM, starting from its formation in 1990 as a joint venture and the introduction of the ARM6 processor. It highlights key milestones such as the ARM7's role in the first ARM-powered GSM phone and the evolution of ARM architectures leading to the Cortex series. Additionally, it discusses the AMBA bus architecture and provides specifications for the ARM Cortex-M3 processor.
Uploaded by
ahmed.hecham307Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views21 pagesARM Lecture 1
The document outlines the history and development of ARM, starting from its formation in 1990 as a joint venture and the introduction of the ARM6 processor. It highlights key milestones such as the ARM7's role in the first ARM-powered GSM phone and the evolution of ARM architectures leading to the Cortex series. Additionally, it discusses the AMBA bus architecture and provides specifications for the ARM Cortex-M3 processor.
Uploaded by
ahmed.hecham307Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 21