0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views6 pagesProgram 5
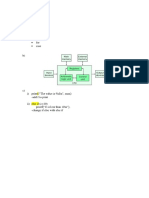
The document outlines a lab experiment for a menu-driven C program that performs basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) based on user input. It details the aim, objectives, theory, working principle, algorithm, flowchart, and includes a sample C code implementation. The program uses conditional statements to execute the chosen operation and handles errors such as division by zero.
Uploaded by
chiragtp452007Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views6 pagesProgram 5
The document outlines a lab experiment for a menu-driven C program that performs basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) based on user input. It details the aim, objectives, theory, working principle, algorithm, flowchart, and includes a sample C code implementation. The program uses conditional statements to execute the chosen operation and handles errors such as division by zero.
Uploaded by
chiragtp452007Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6