0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views27 pagesSYSTEM SOFTWARE (Midterm)
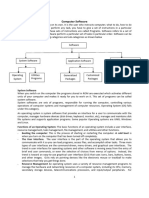
The document discusses different types of systems software. There are three main types: operating systems, utility programs, and language translators. Operating systems manage computer resources and allow users to run applications. Common utilities include backup programs, antivirus software, and screen savers. Language translators convert programs written by programmers into machine-readable code that computers can execute.
Uploaded by
api-3765549Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views27 pagesSYSTEM SOFTWARE (Midterm)
The document discusses different types of systems software. There are three main types: operating systems, utility programs, and language translators. Operating systems manage computer resources and allow users to run applications. Common utilities include backup programs, antivirus software, and screen savers. Language translators convert programs written by programmers into machine-readable code that computers can execute.
Uploaded by
api-3765549Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 27