The document discusses queues as a linear data structure that follows the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle, contrasting it with stacks. It details operations such as enqueue and dequeue, along with their algorithms, and explains the practical applications of queues in CPU scheduling, data transfer synchronization, and real-time systems. Additionally, it outlines the pros and cons of implementing queues using arrays.







![9
Enqueue Algorithm
begin procedure enqueue(data)
if queue is full
return overflow
endif
rear ← rear + 1
queue[rear] ← data
return true
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5queue-210409103157/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Queue-9-2048.jpg)
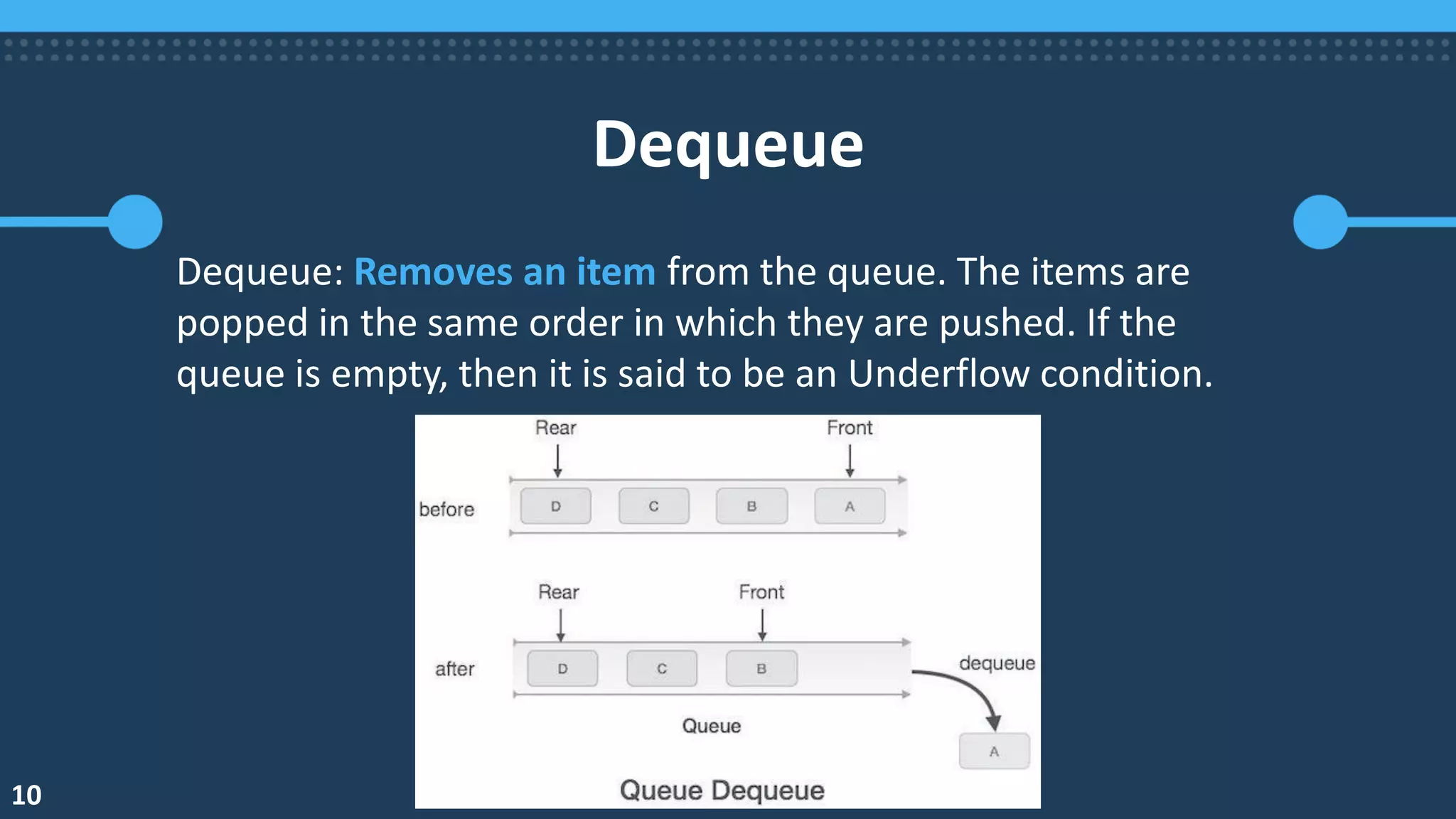

![Dequeue Algorithm
begin procedure dequeue
if queue is empty
return underflow
end if
data = queue[front]
front ← front + 1
return true
end procedure
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5queue-210409103157/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Queue-12-2048.jpg)
![Front
Front: Get the front item from queue.
13
Front Algorithm:
begin procedure front
return queue[top]
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5queue-210409103157/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Queue-13-2048.jpg)
![Rear
Rear: Get the last item from
queue.
Rear Algorithm:
begin procedure rear
return queue[last]
end procedure
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5queue-210409103157/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Queue-14-2048.jpg)