Download as PDF, PPTX









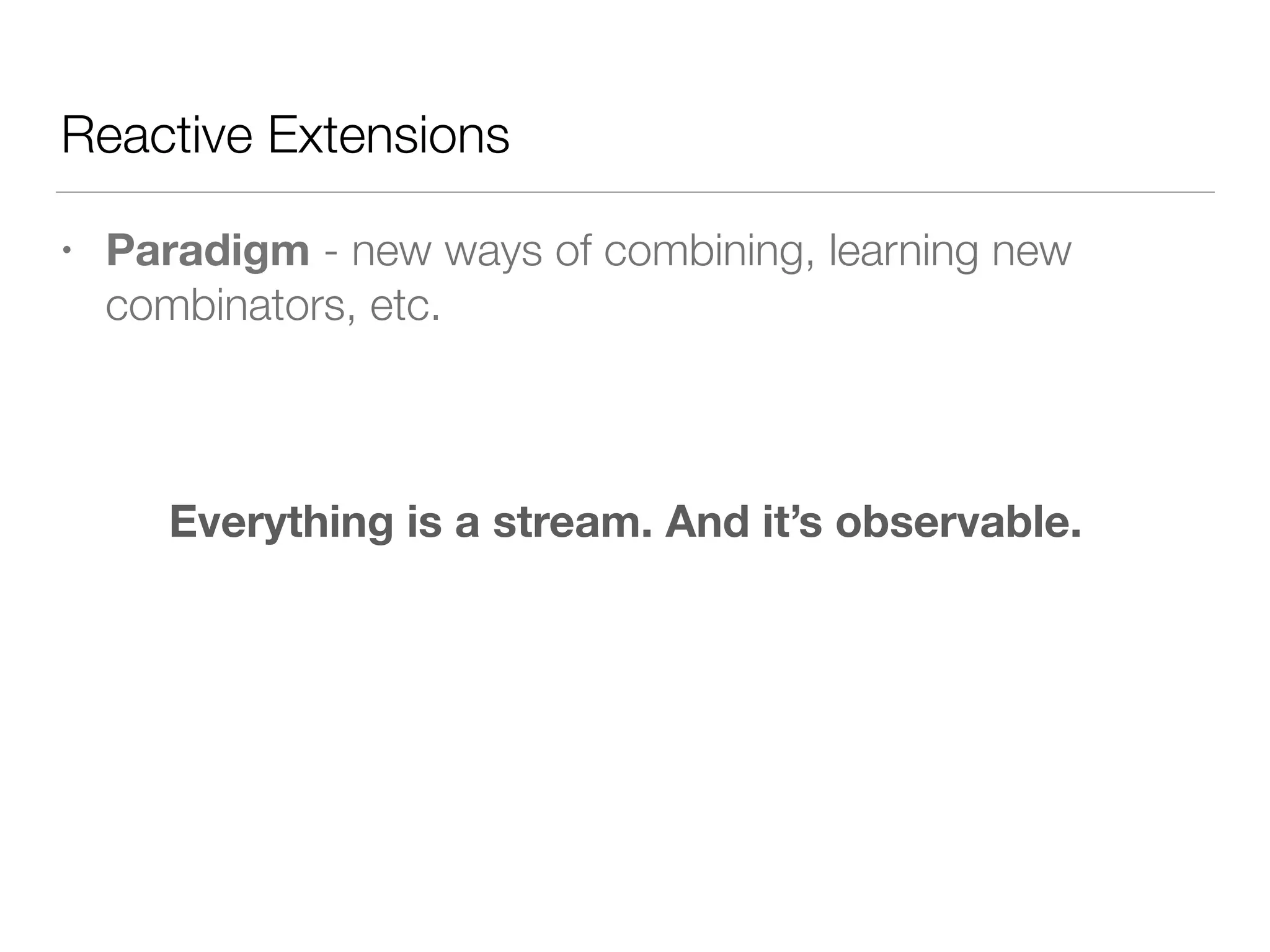










The document discusses various approaches to asynchronous programming including threading, callbacks, promises/futures, reactive extensions, and Kotlin coroutines. It notes challenges with threading like state mutations and limited operating system support. Callbacks are described as complex to handle errors. Promises/futures and reactive extensions introduce new paradigms. Coroutines allow the same way of thinking and code structures for both synchronous and asynchronous operations using suspendable functions.



















