Binary search is a fast search algorithm that works by dividing a sorted collection in half at each step to locate a target value. It compares the middle element to the target and eliminates half of the remaining elements based on whether the middle element is greater than or less than the target. This process continues recursively on smaller sub-arrays until the target is found or the sub-array is empty, with an average time complexity of O(log n). The pseudocode shows initializing lower and upper bounds and calculating the mid-point to compare to the target at each step until the target is found or not present.
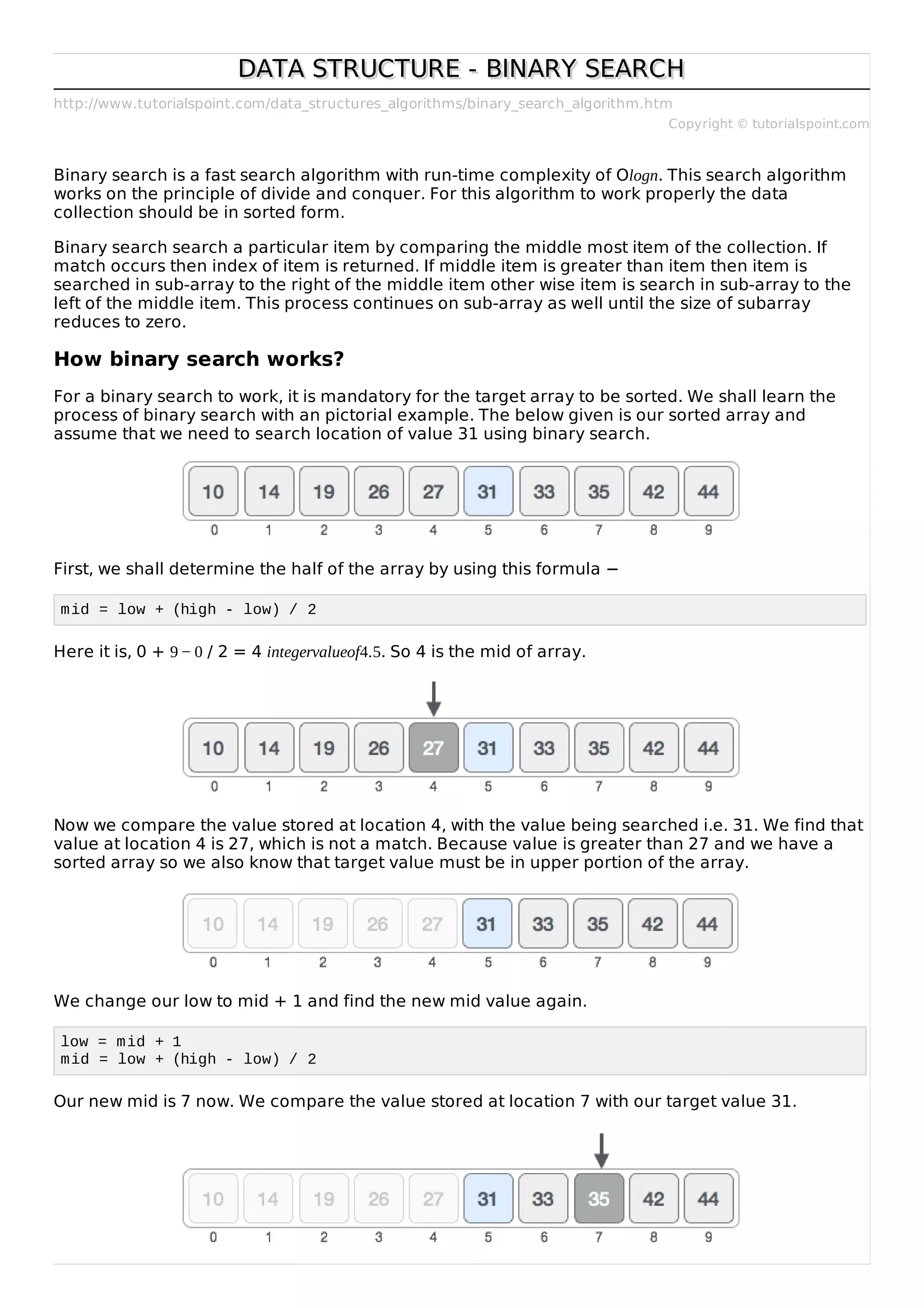
![The value stored at location 7 is not a match, rather it is less that what we are looking for. So the
value must be in lower part from this location.
So we calculate the mid again. This time it is 5.
We compare the value stored ad location 5 with our target value. We find that it is a match.
We conclude that the target value 31 is stored at location 5.
Binary search halves the searchable items and thus reduces the count of comparisons to be made
to very less numbers.
Pseudocode
The pseudocode of binary search algorithm should look like this −
Procedure binary_search
A ← sorted array
n ← size of array
x ← value ot be searched
Set lowerBound = 1
Set upperBound = n
while x not found
if upperBound < lowerBound
EXIT: x does not exists.
set midPoint = lowerBound + ( upperBound - lowerBound ) / 2
if A[midPoint] < x
set lowerBound = midPoint + 1
if A[midPoint] > x
set upperBound = midPoint - 1
if A[midPoint] = x
EXIT: x found at location midPoint
end while
end procedure
To see binary search implementation using array in C programming language, please click here.
Loading [MathJax]/jax/output/HTML-CSS/jax.js](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binarysearchalgorithm-161223151828/75/Binary-search-algorithm-2-2048.jpg)