Downloaded 79 times




![Algorithm
public insertionSort(int[] arr)
{
for (int i = 1; i < arr.Length;i++)
{
int temp = arr[i];
int pos = i;
while (arr[pos-1] > temp && pos > 0)
{
arr[pos] = arr[pos-1];
pos--;
}
arr[pos] = temp;
}
}
Select
Comparing
Shift
Insert](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort1-150129075741-conversion-gate02/75/Insertion-sort-5-2048.jpg)






This document discusses insertion sort, including its mechanism, algorithm, runtime analysis, advantages, and disadvantages. Insertion sort works by iterating through an unsorted array and inserting each element into its sorted position by shifting other elements over. Its worst case runtime is O(n^2) when the array is reverse sorted, but it performs well on small, nearly sorted lists. While simple to implement, insertion sort is inefficient for large datasets compared to other algorithms.




![Algorithm
public insertionSort(int[] arr)
{
for (int i = 1; i < arr.Length;i++)
{
int temp = arr[i];
int pos = i;
while (arr[pos-1] > temp && pos > 0)
{
arr[pos] = arr[pos-1];
pos--;
}
arr[pos] = temp;
}
}
Select
Comparing
Shift
Insert](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertionsort1-150129075741-conversion-gate02/75/Insertion-sort-5-2048.jpg)






Introduction of Insertion Sort by B.Raj Shekhar, Monalisa Patel, and Smrutirekha Nath. Agenda includes Introduction, Mechanism, Algorithm, Example, Runtime Analysis, and Advantages & Disadvantages.
Explanation of Insertion Sort mechanism through selecting and comparing, along with shifting and inserting elements using two loops.
Presentation of Insertion Sort algorithm in Java, outlining the process of selecting, comparing, shifting, and inserting elements.
Illustration of Insertion Sort with a detailed example to clarify its practical application.
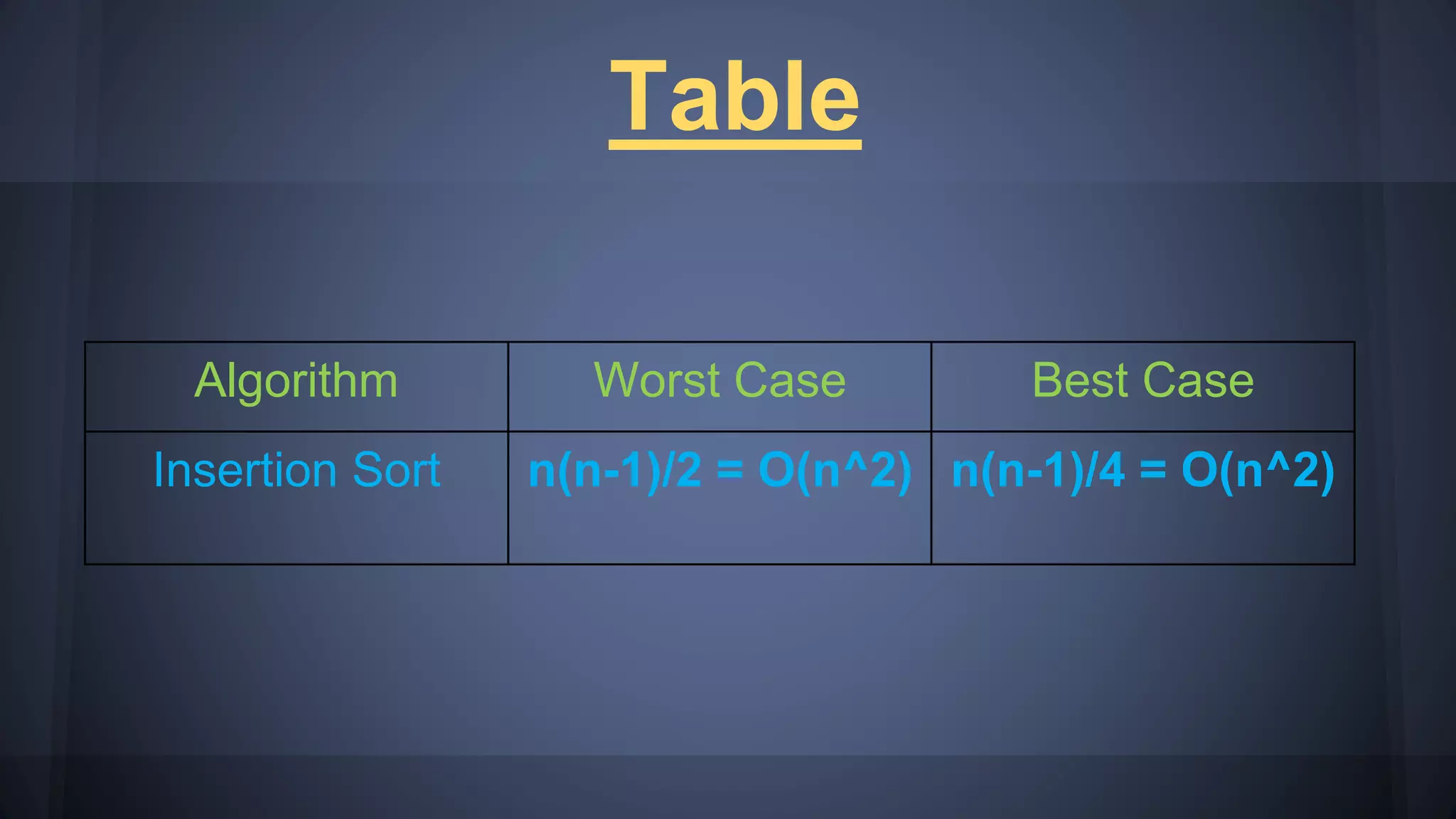
Runtime analysis shows worst and average case complexities, f(n) for worst case as O(n^2) and O(n^2) for average case.
Advantages include simplicity, good performance on small or nearly sorted lists, and memory efficiency.
Disadvantages highlight inefficiency on large datasets and poor performance compared to advanced sorting algorithms.