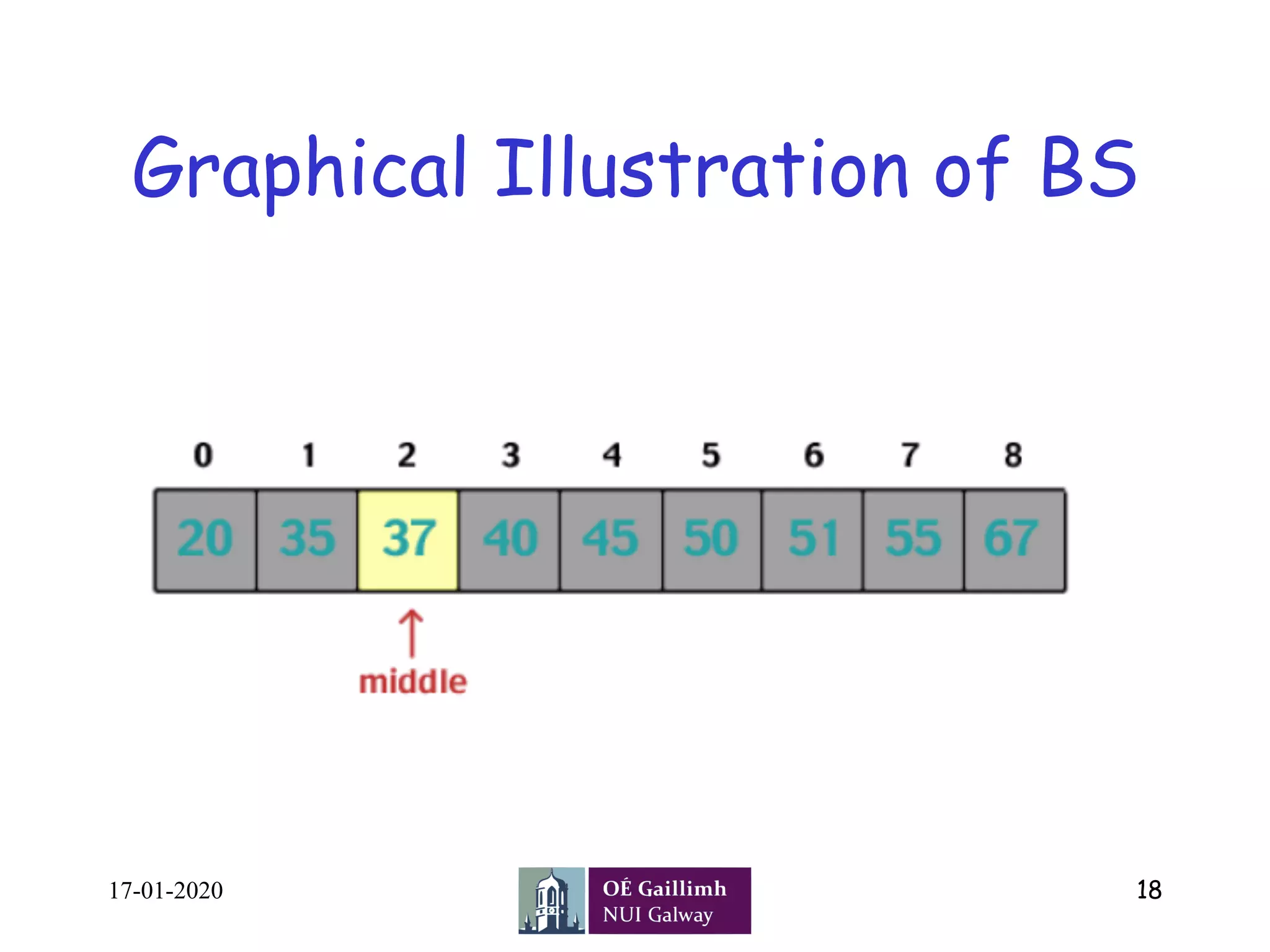
The document outlines a lecture on search algorithms presented by Dr. Zia Ush Shamszaman, covering linear and binary search techniques. Linear search sequentially checks elements until a match is found, while binary search efficiently narrows down the search space in a sorted array by halving it at each step. The lecture also includes pseudocode for both algorithms along with their advantages and disadvantages.




![Linear Search Algorithm
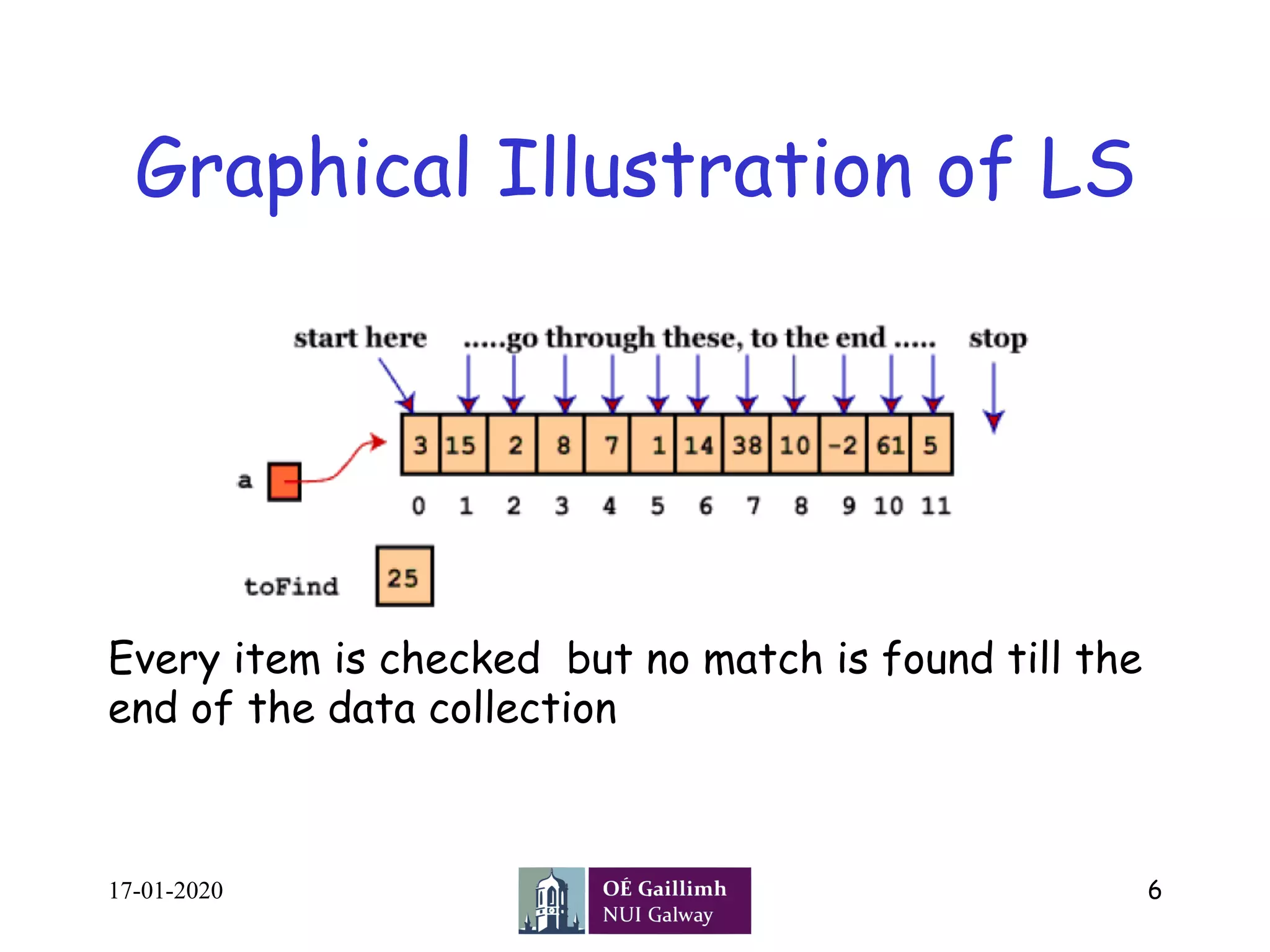
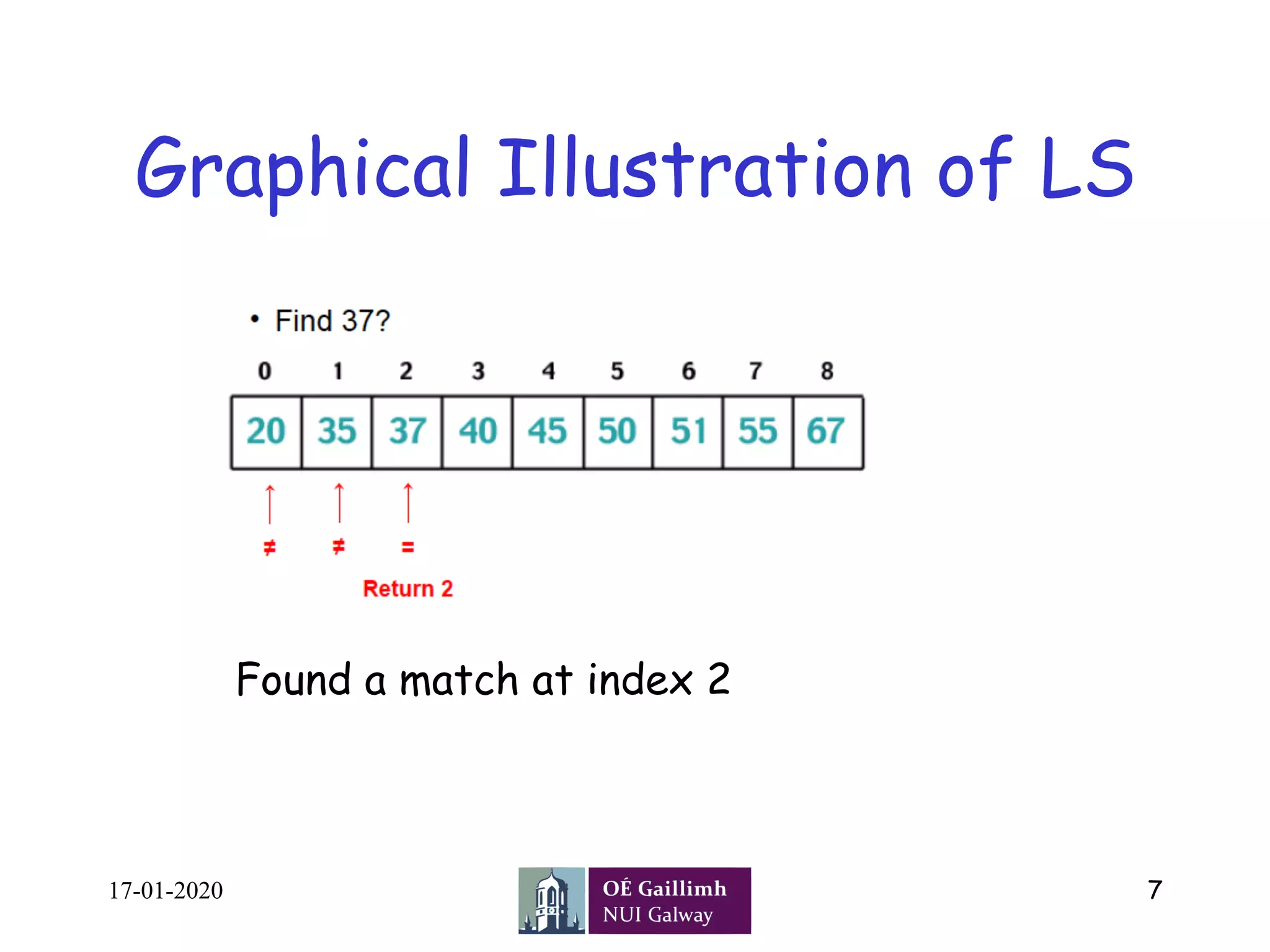
• Linear Search ( Array A, Value x)
• Step 1: Set i to 1
• Step 2: if i > n then go to step 7
• Step 3: if A[i] = x then go to step 6
• Step 4: Set i to i + 1
• Step 5: Go to Step 2
• Step 6: Print Element x Found at index i and go to step 8
• Step 7: Print element not found
• Step 8: Exit
17-01-2020 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-13linearandbinarysearch-200121041434/75/linear-search-and-binary-search-8-2048.jpg)




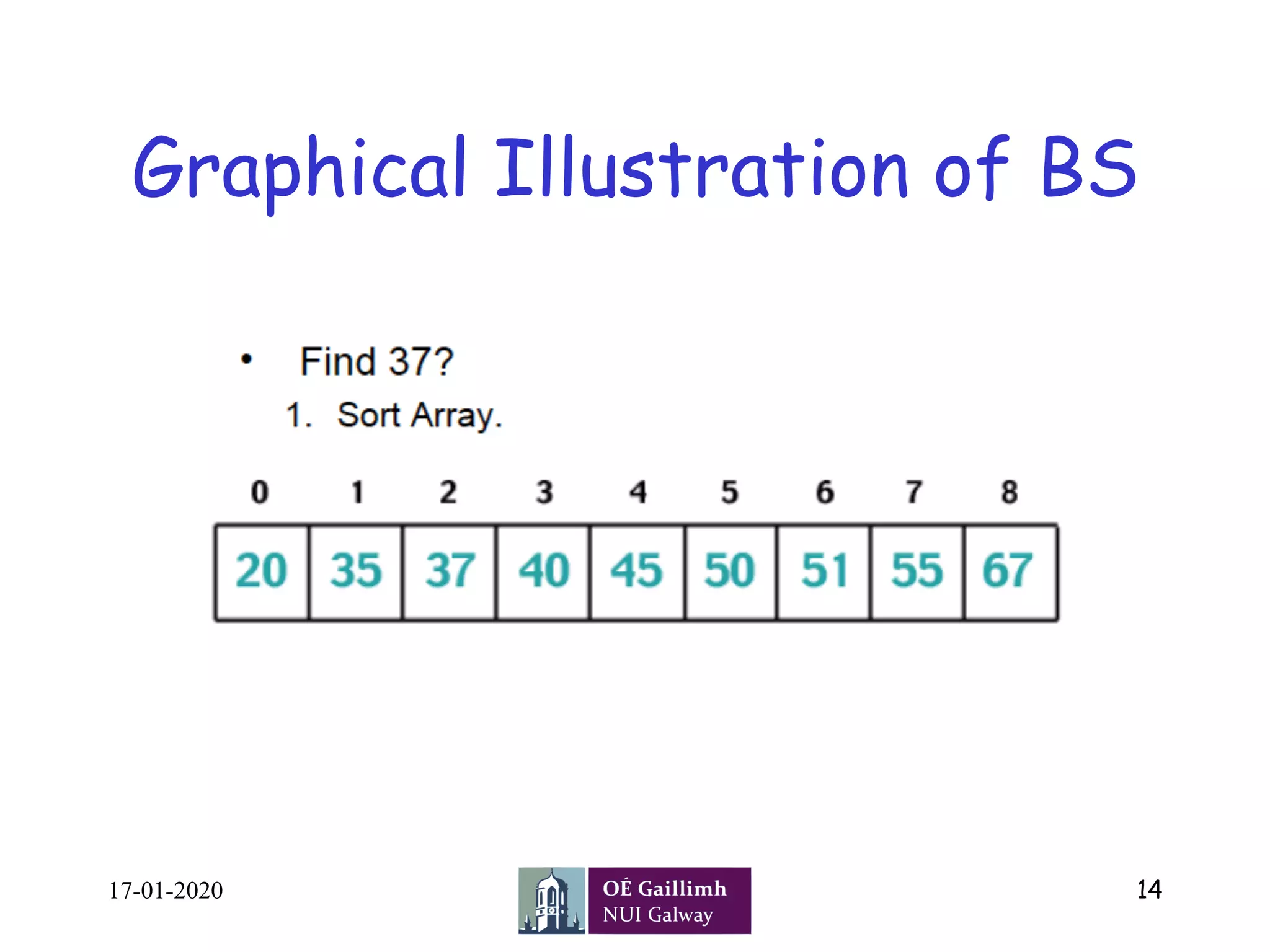
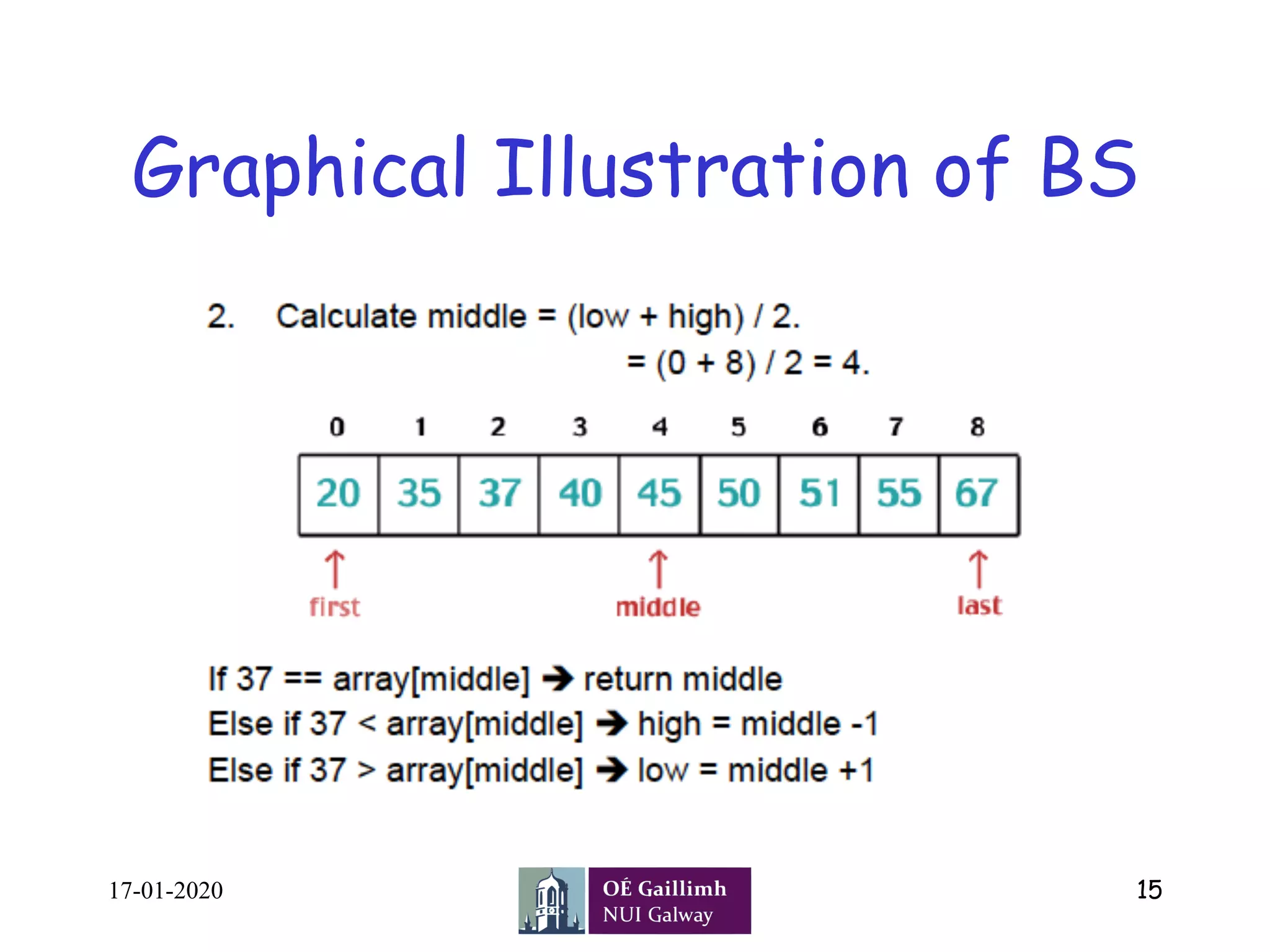
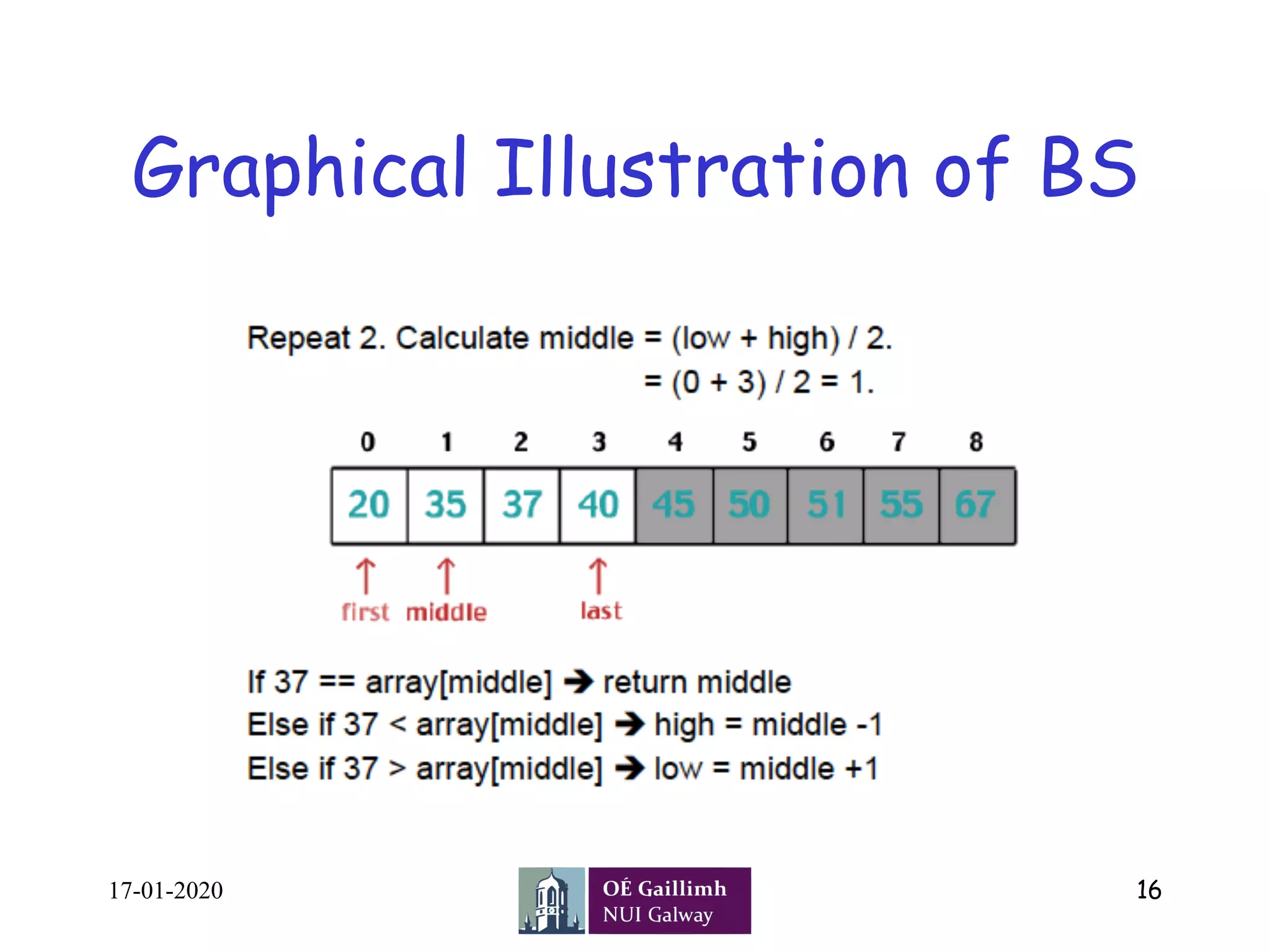
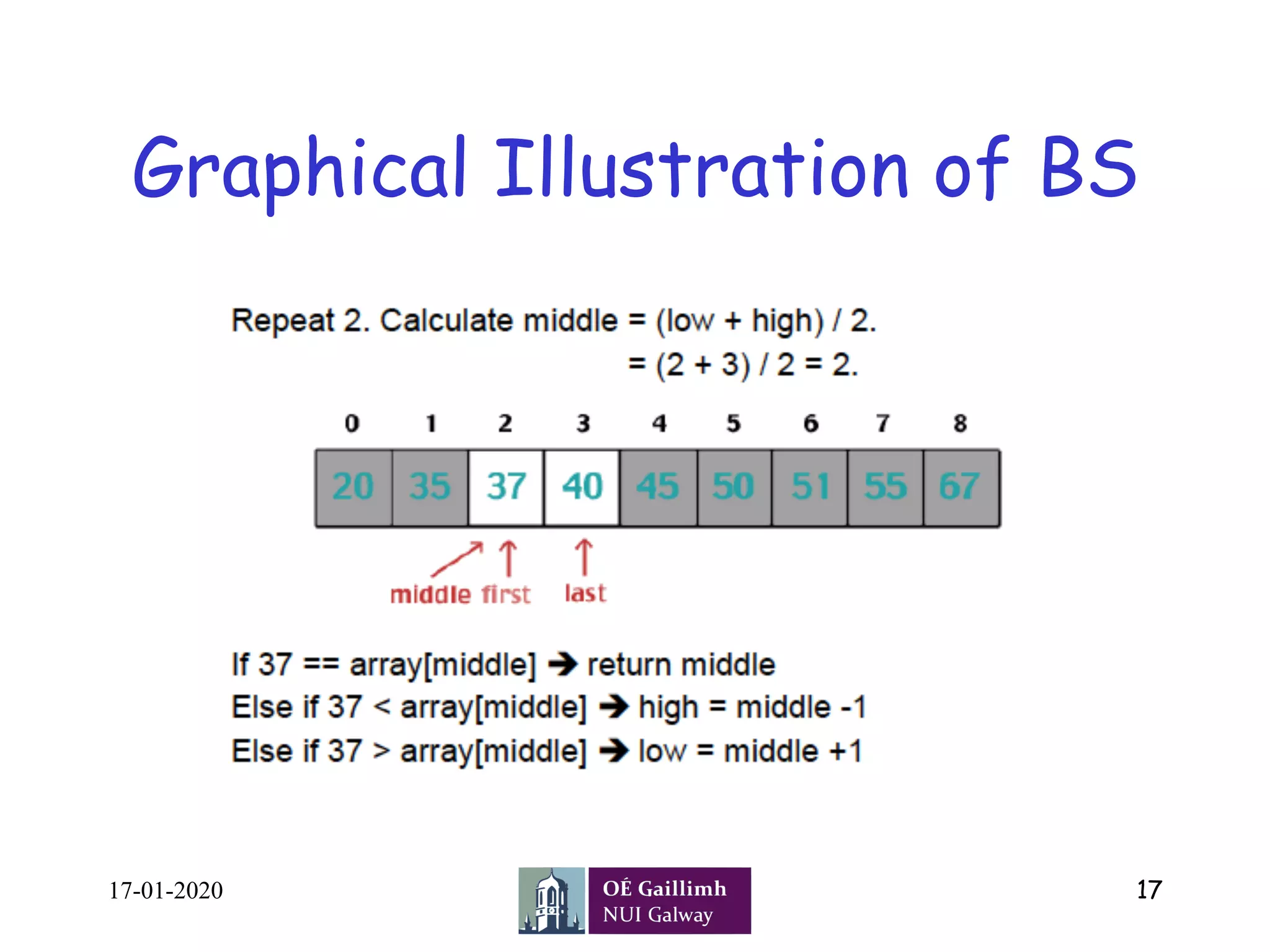

![Pseudocode
17-01-2020 20
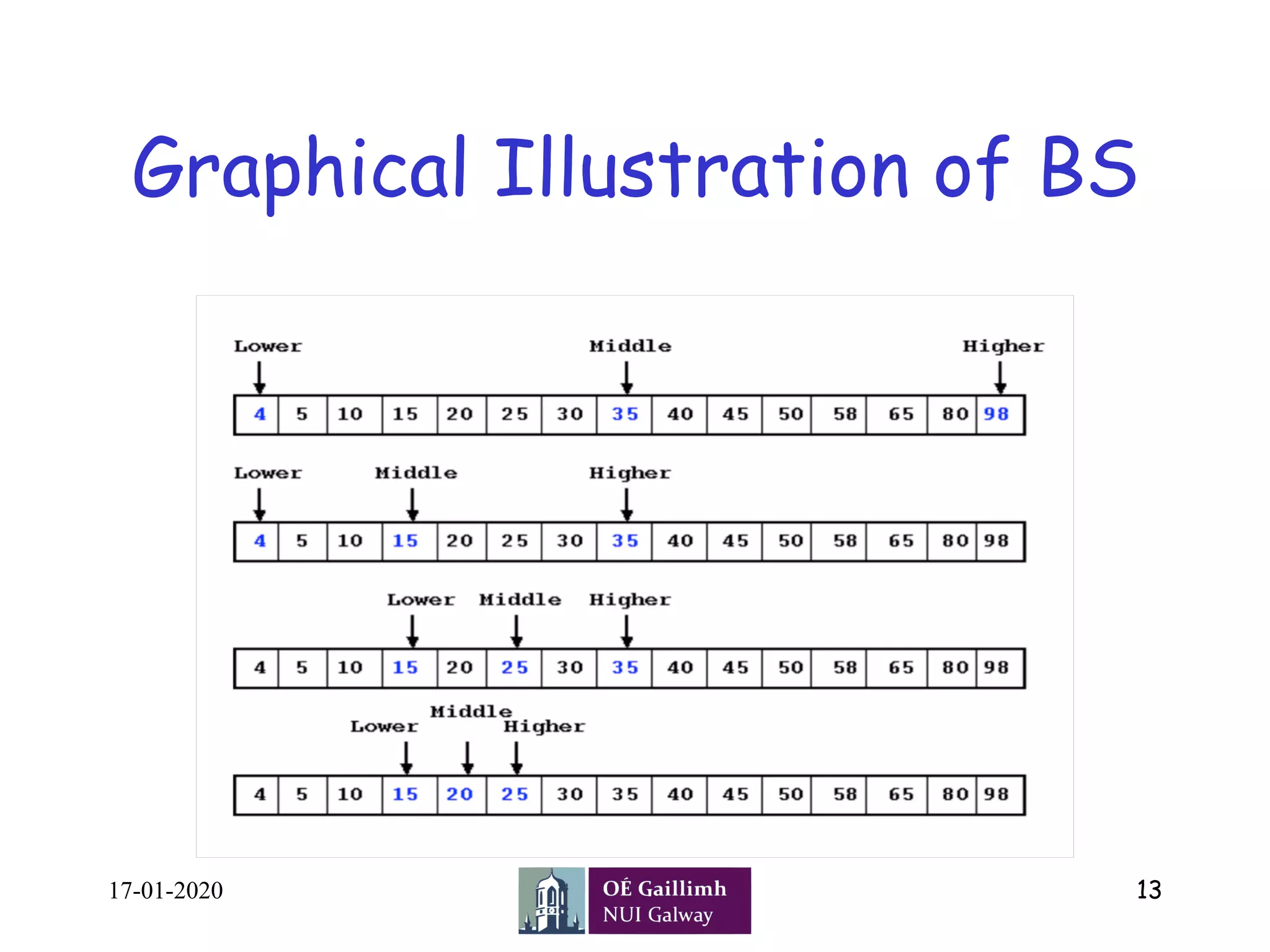
Procedure binary_search
A ← sorted array
n ← size of array
x ← value to be searched
Set lowerBound = 1
Set upperBound = n
while x not found
if upperBound < lowerBound
EXIT: x does not
exists.
set midPoint =
lowerBound + ( upperBound -lowerBound )/2
if A[midPoint] < x
set lowerBound = midPoint + 1
if A[midPoint] > x
set upperBound = midPoint - 1
if A[midPoint] = x
EXIT: x found at location midPoint
end while
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-13linearandbinarysearch-200121041434/75/linear-search-and-binary-search-20-2048.jpg)



