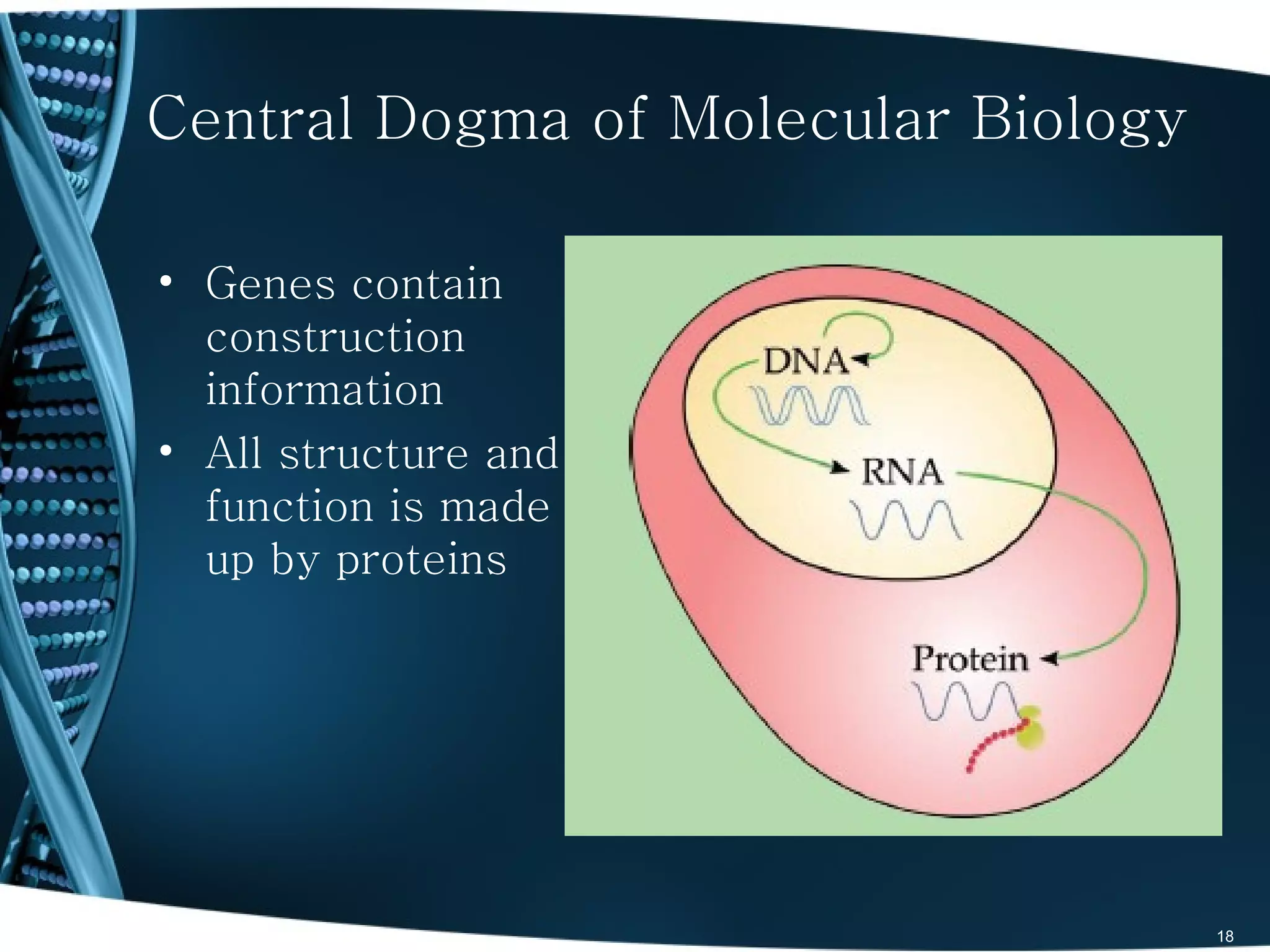
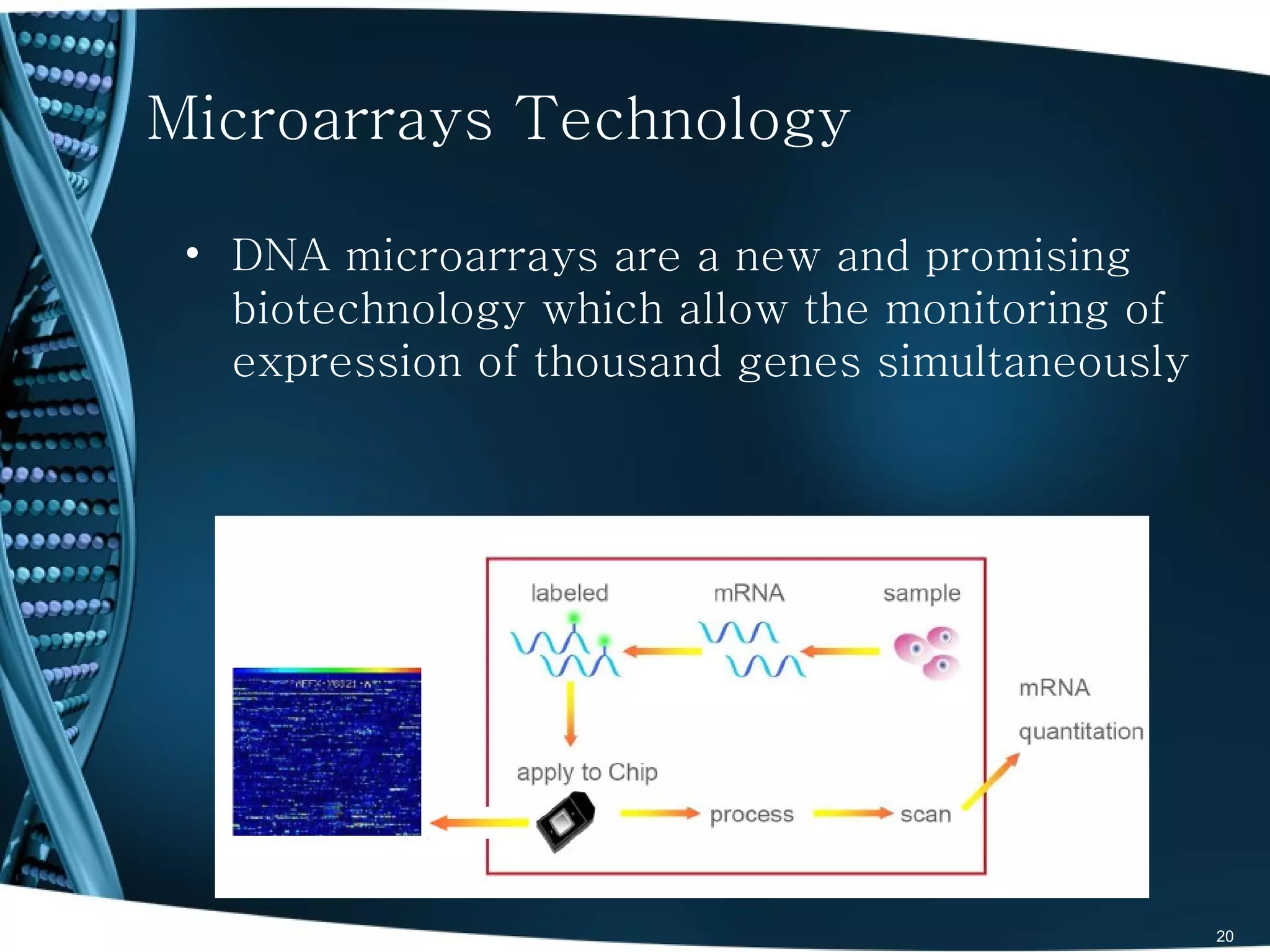
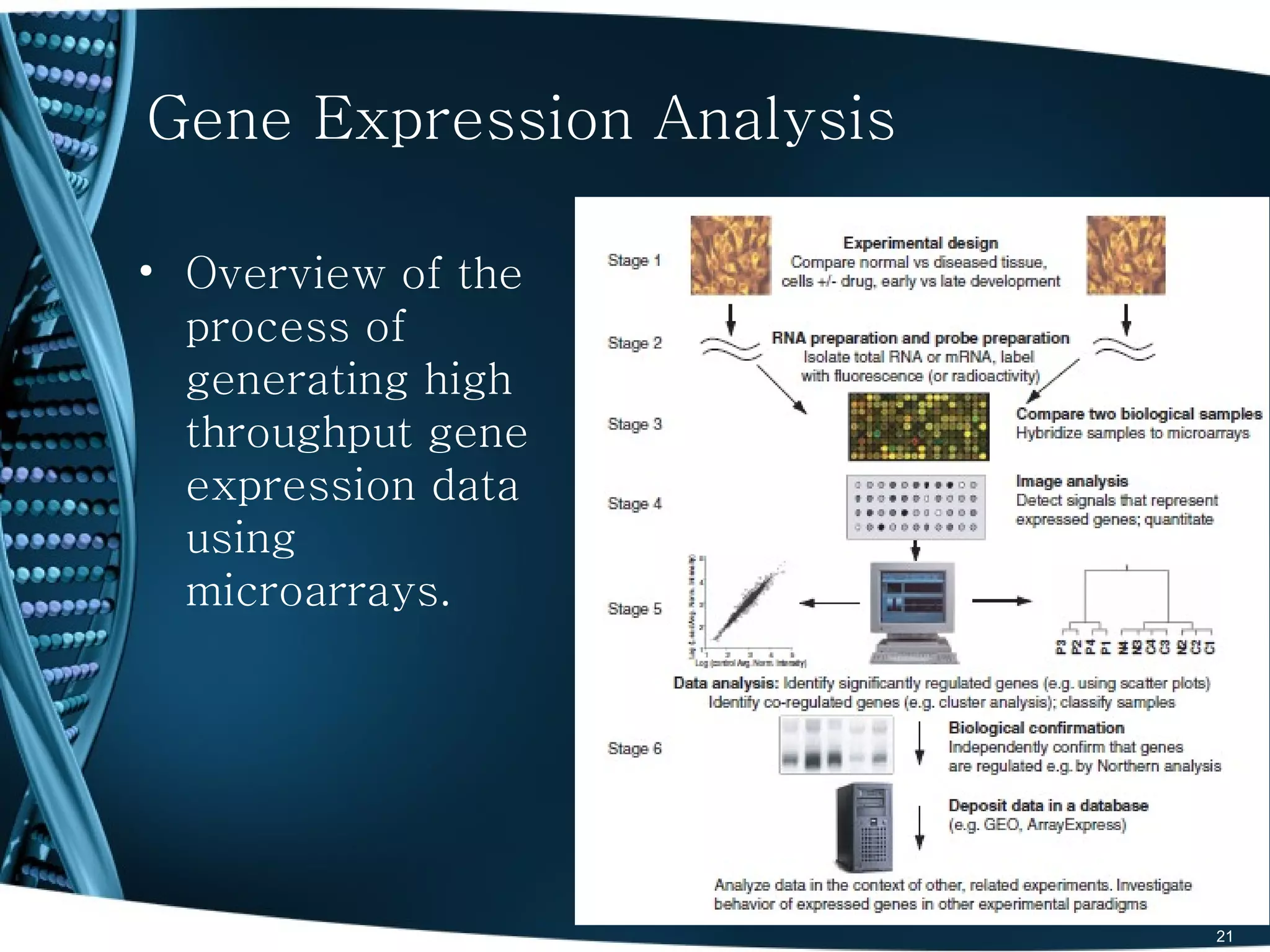
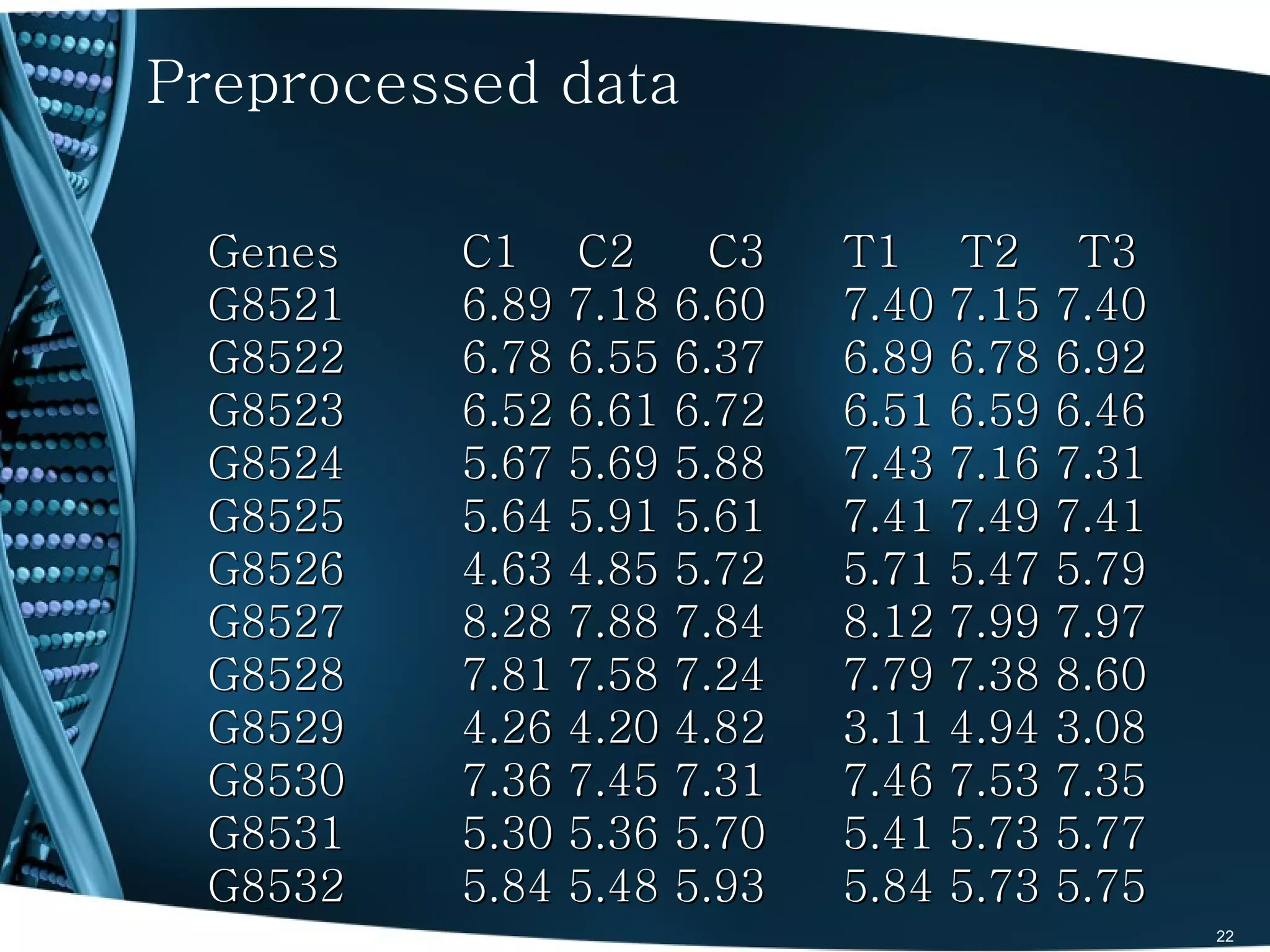
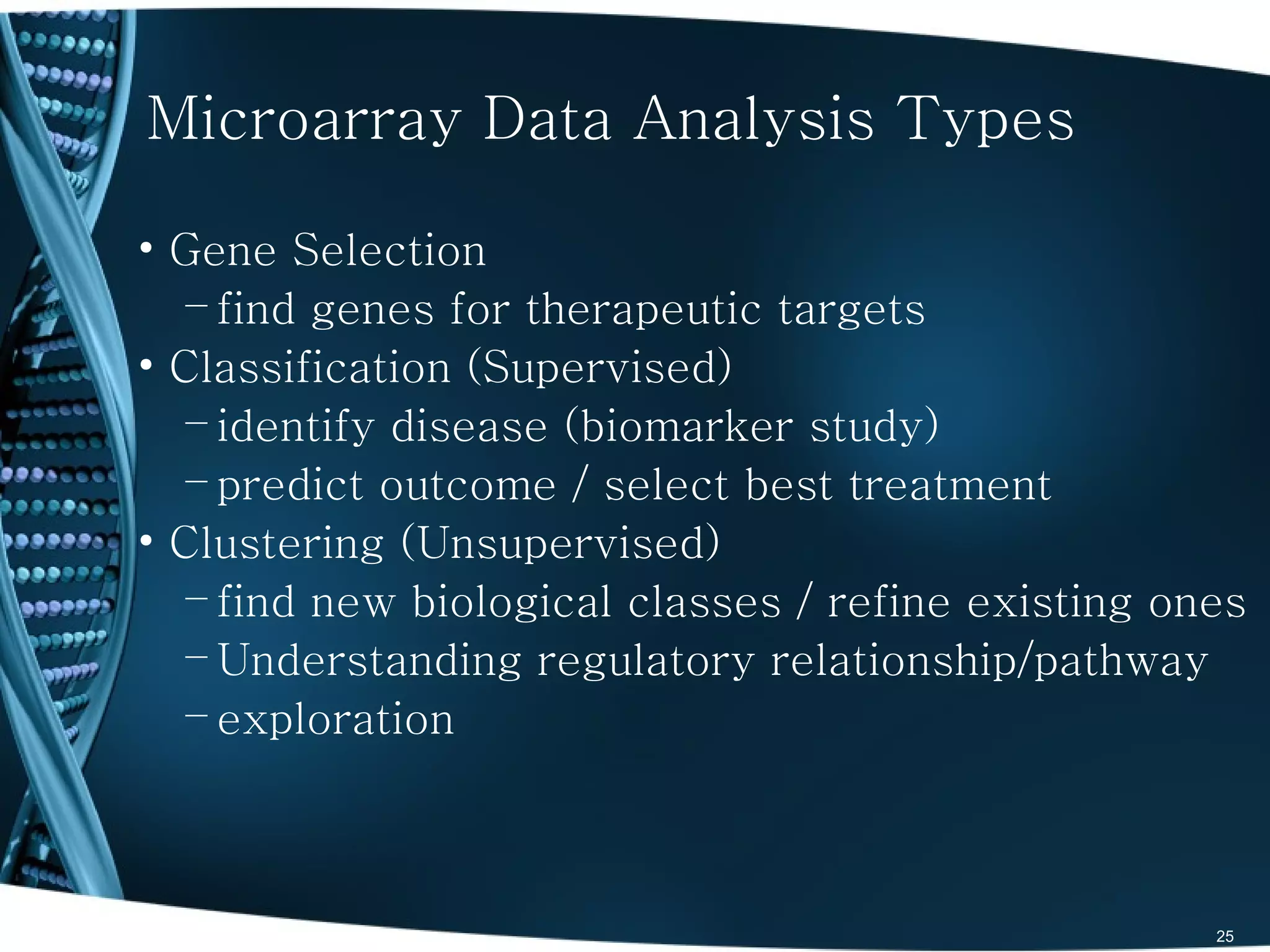
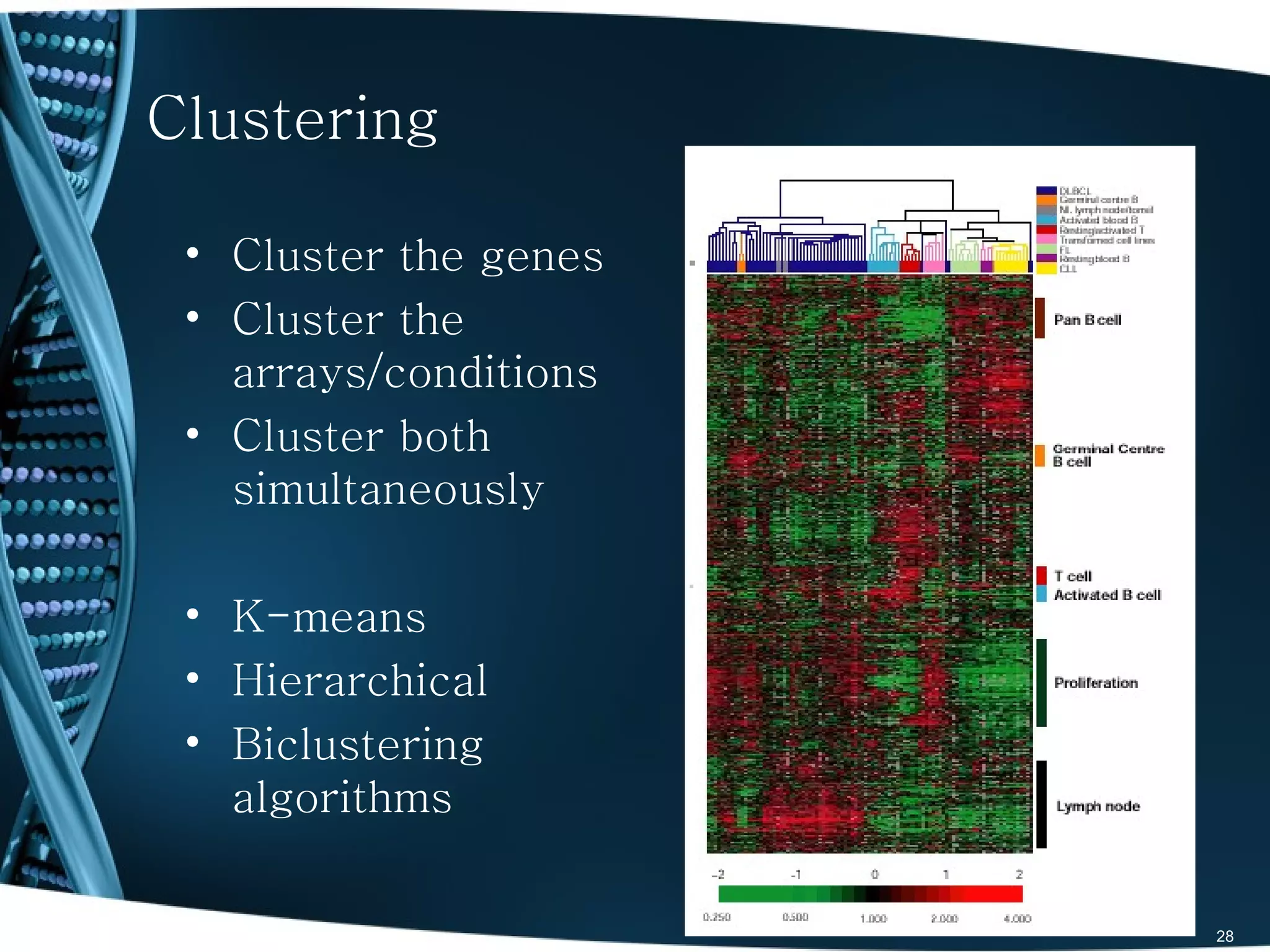
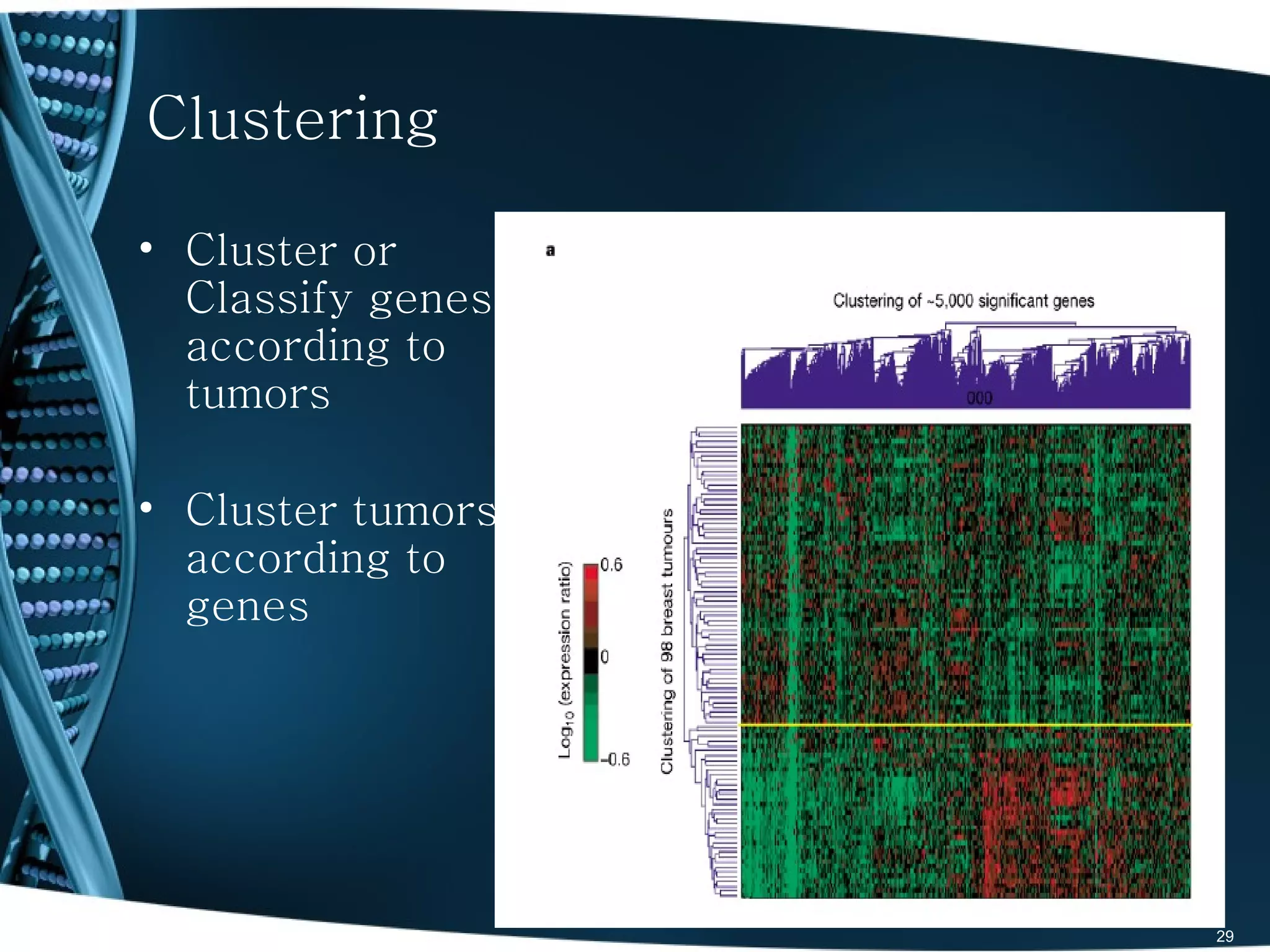
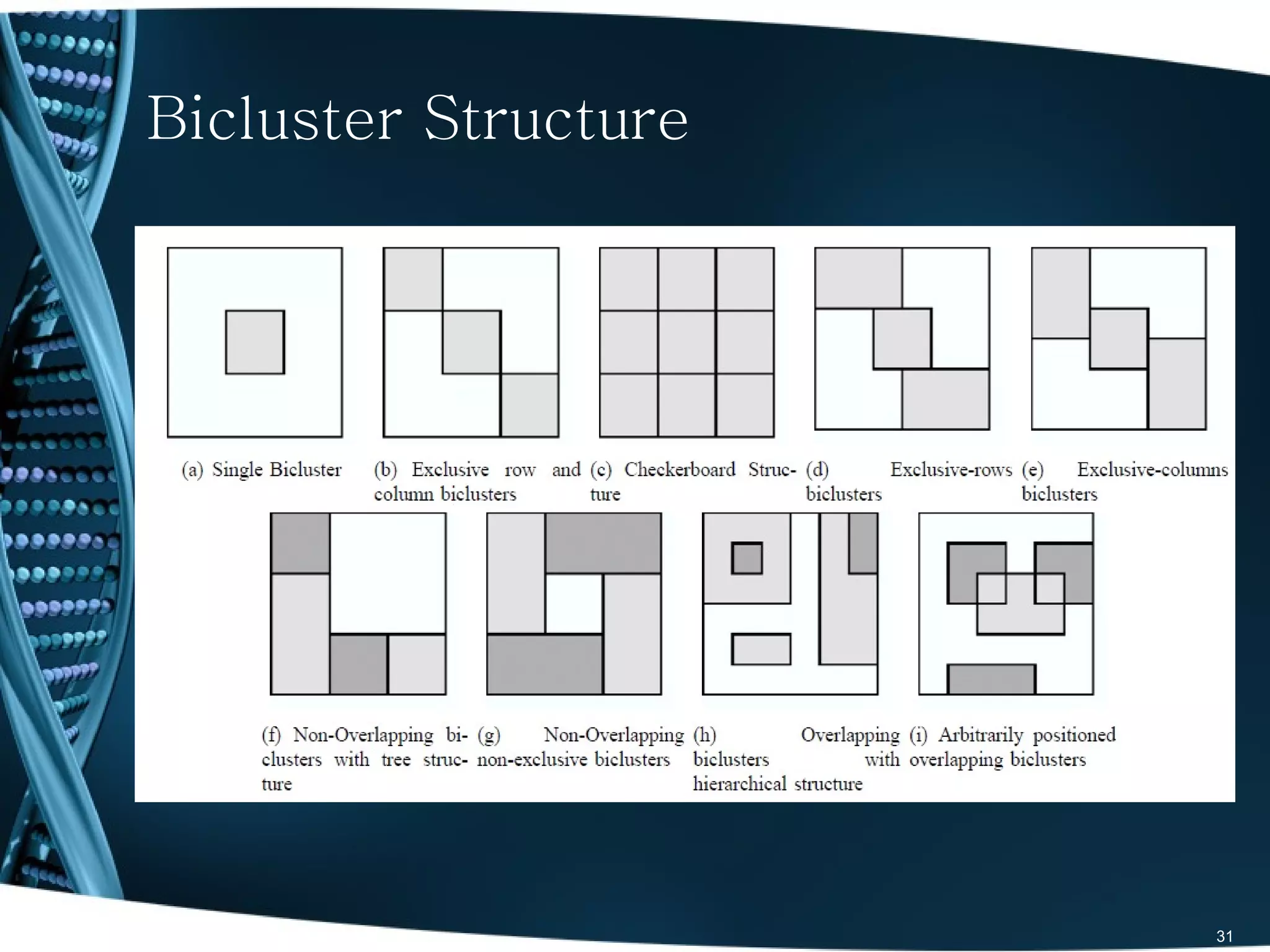
The document discusses the role and significance of biostatistics and statistical bioinformatics in various fields such as public health, drug development, and genomics. It highlights the involvement of statisticians in clinical trials, data analysis, and the use of bioinformatics for biological discoveries. The document emphasizes the opportunities for biostatisticians in multiple sectors, including healthcare and pharmaceutical industries.