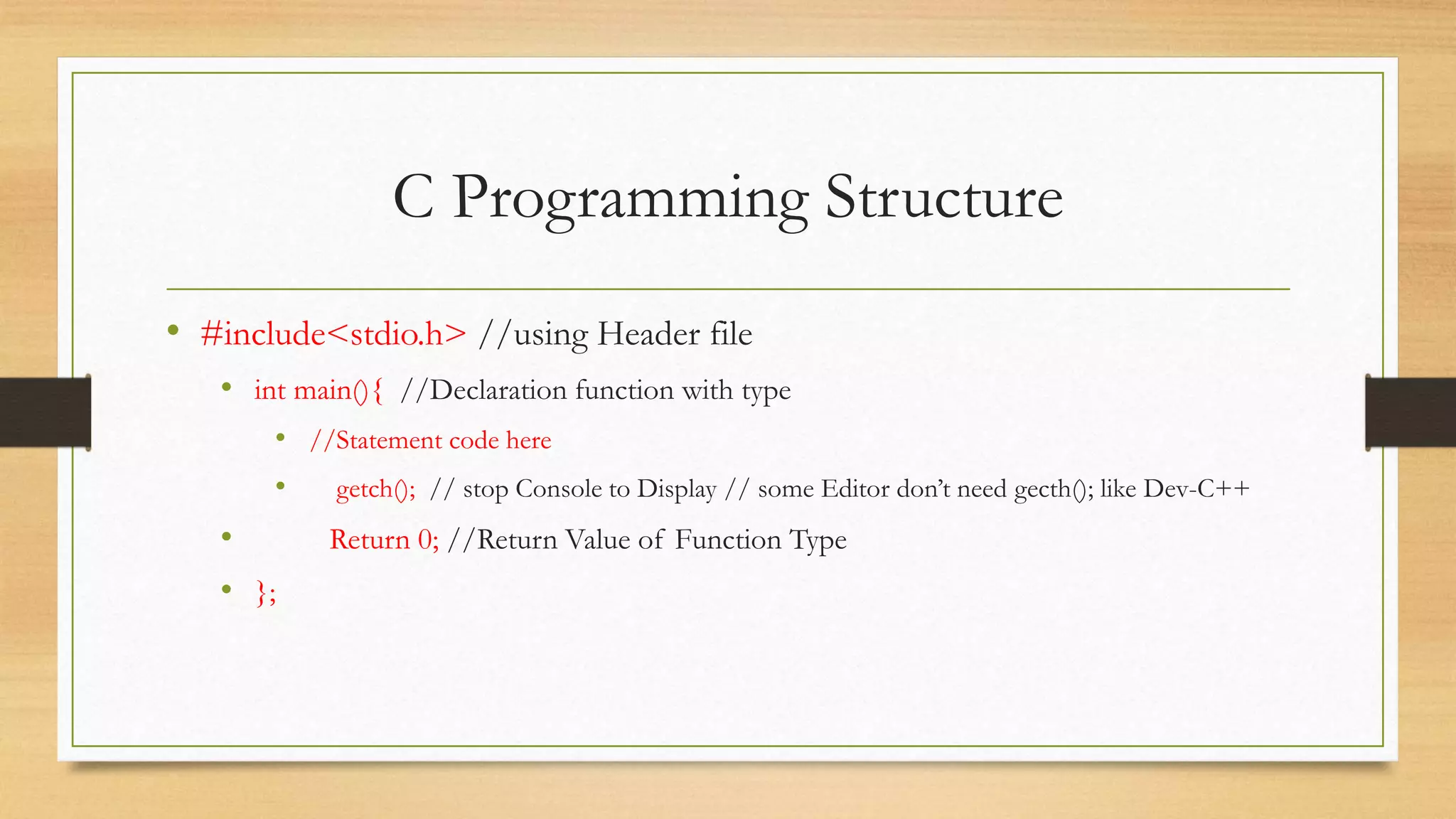
C is a general-purpose programming language initially developed for system development like operating systems. It produces efficient code nearly as fast as assembly language. The document provides an overview of basic C programming concepts including data types, variables, functions, arrays, structures, pointers, strings, input/output operations, and preprocessor directives. It also gives examples of basic "Hello World" program structure and syntax.














![Array in C
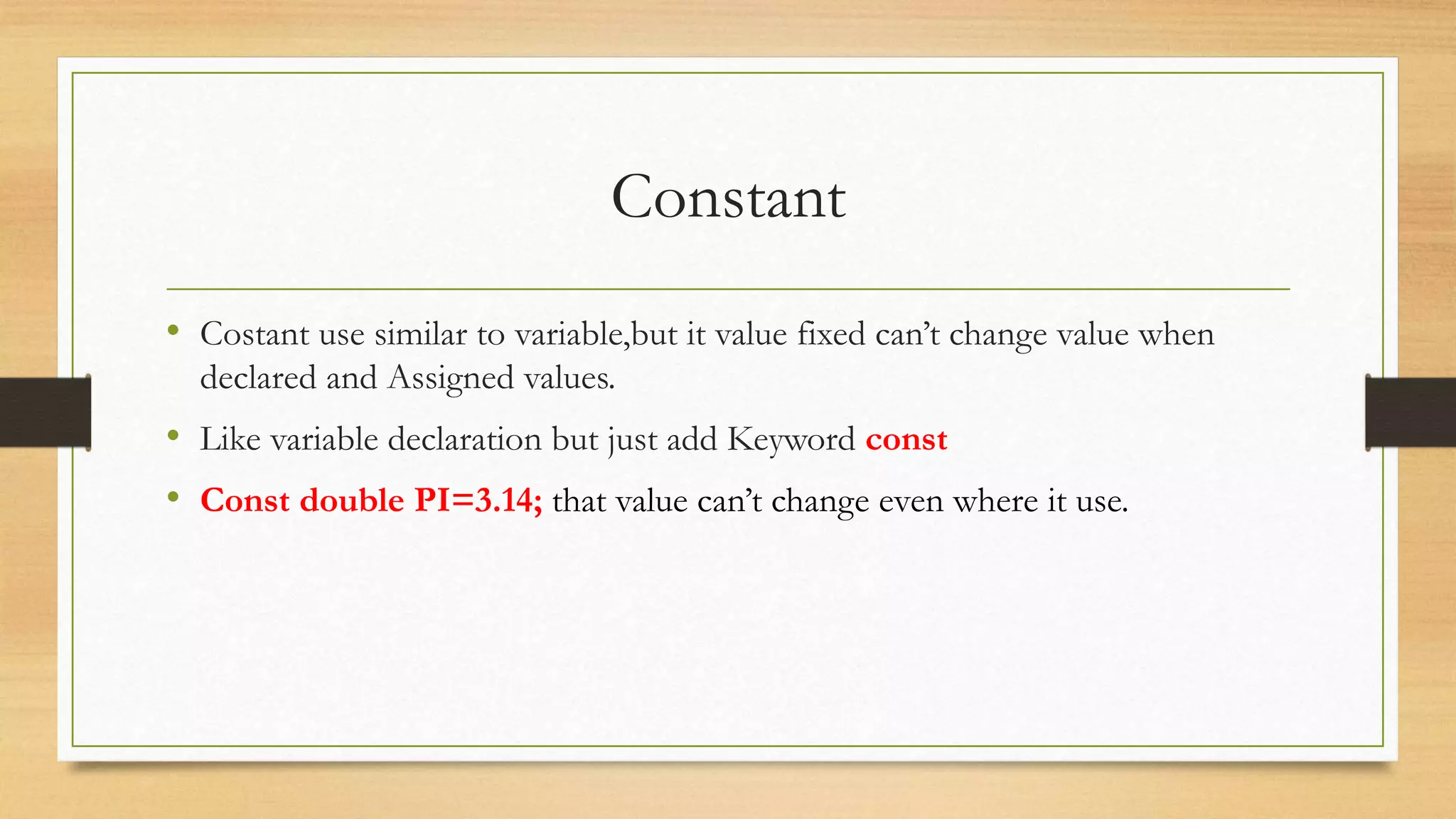
• Array is a variable but contain Multiple values with same type call collection of Elements.
Array are divide two type:
1. One dimensional array
2. Multi-dimensional array
Also are two class : bound index and unbound index array.
Declare one dimensional- array with unbound index : int a[ ]; char s[ ];
Declare one dimensional- array with bound index : int a[5 ]; char s[ 15];
Example: int a[ ]={4,5,6,12};
char str[ ]={‘A’,’B’,’C’};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-211114144637/75/C-programming-tutorial-for-Beginner-30-2048.jpg)
![Using array(conti.)
• Multi-dimensional array: int num [ ,] ={{2,3,5},{6,7,12,9}};
• Another way to declare multi dimensional with bound index
• Int num[2][ 3]={{2,3},{4,6,5}};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-211114144637/75/C-programming-tutorial-for-Beginner-31-2048.jpg)

![String
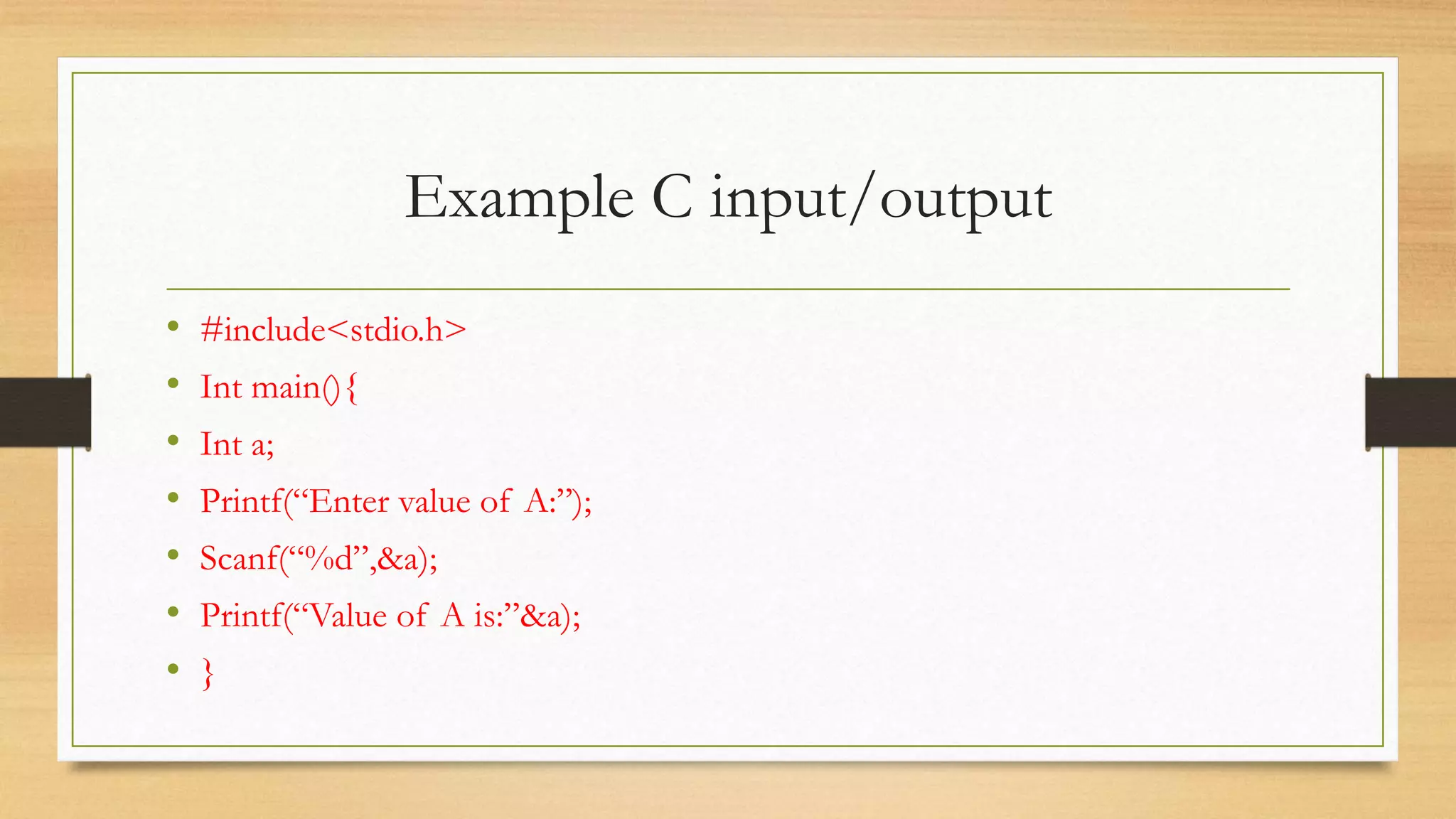
• String is define as the sequence of characters that contain Unicode characters
• Example: char str[ ]=“Hello C”;
• String is allocated to memory address by index and pointer address.
• see example…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-211114144637/75/C-programming-tutorial-for-Beginner-33-2048.jpg)

![Structure(conti.)
• Syntax:
struct(Keyword) [struct tag]{ struct book{
member definition; int book_id[10];
member definition; char book_name[50];
}[one or more structure variables]; char date[20];
float prize[10];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-211114144637/75/C-programming-tutorial-for-Beginner-35-2048.jpg)