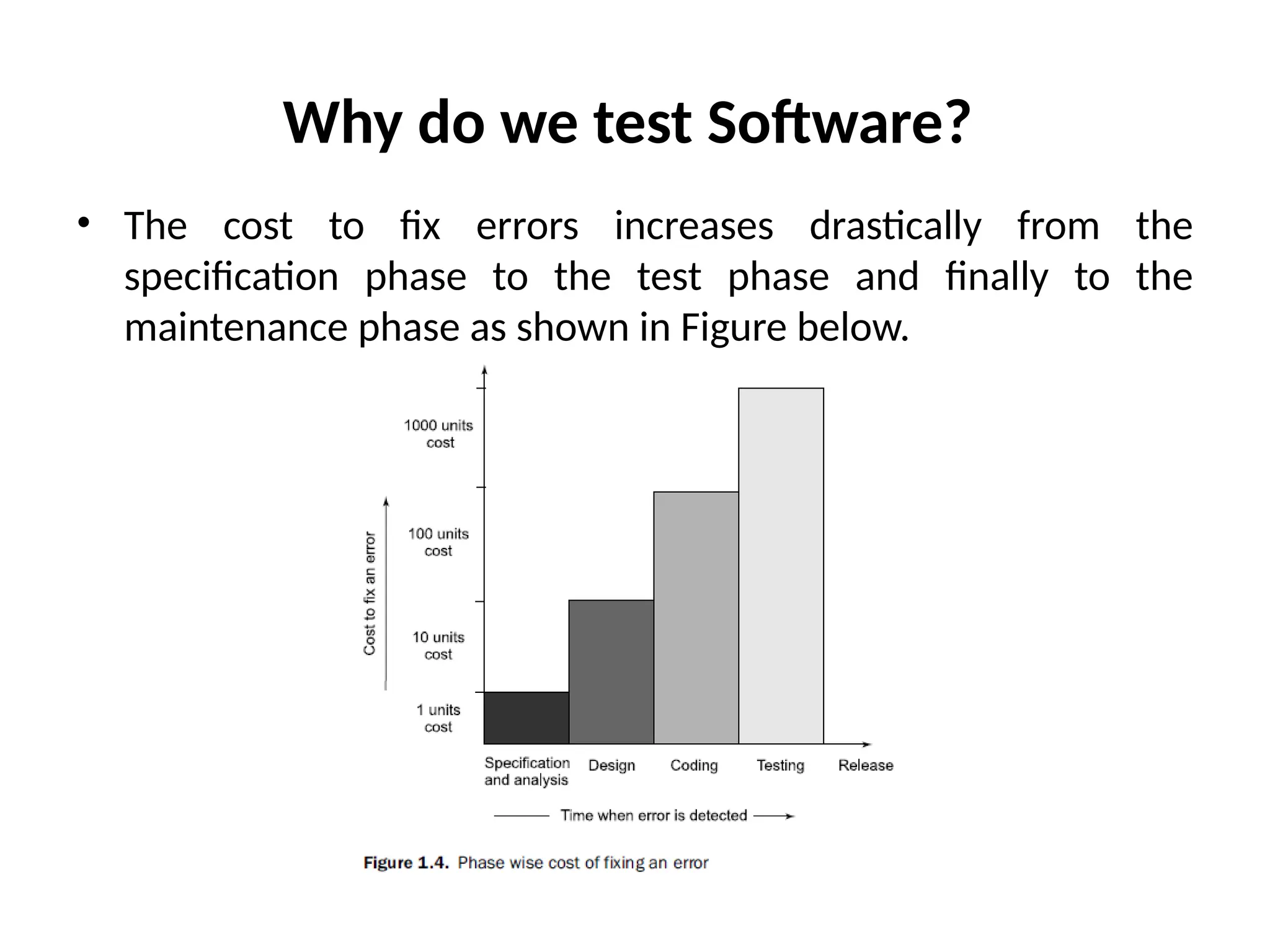
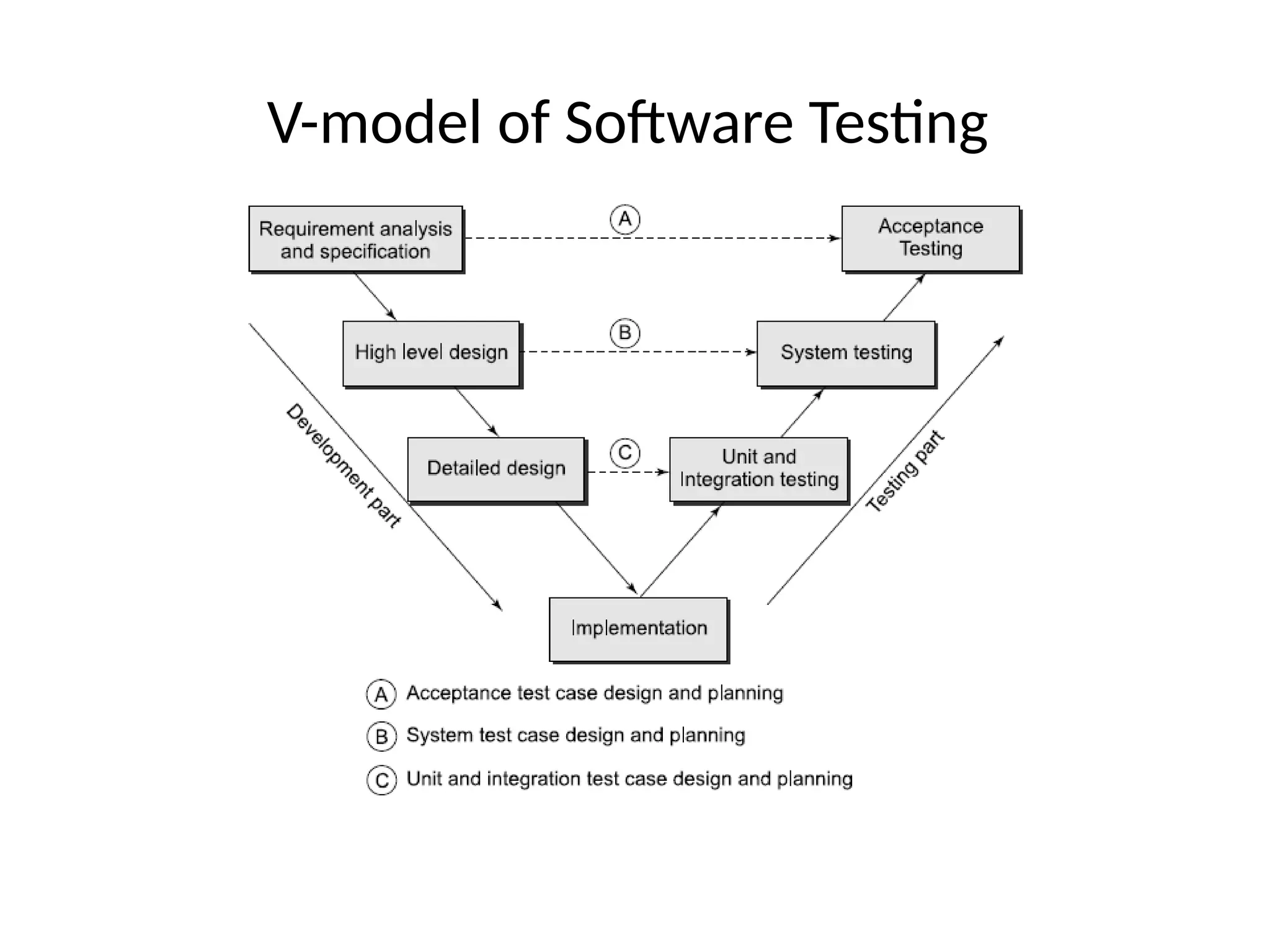
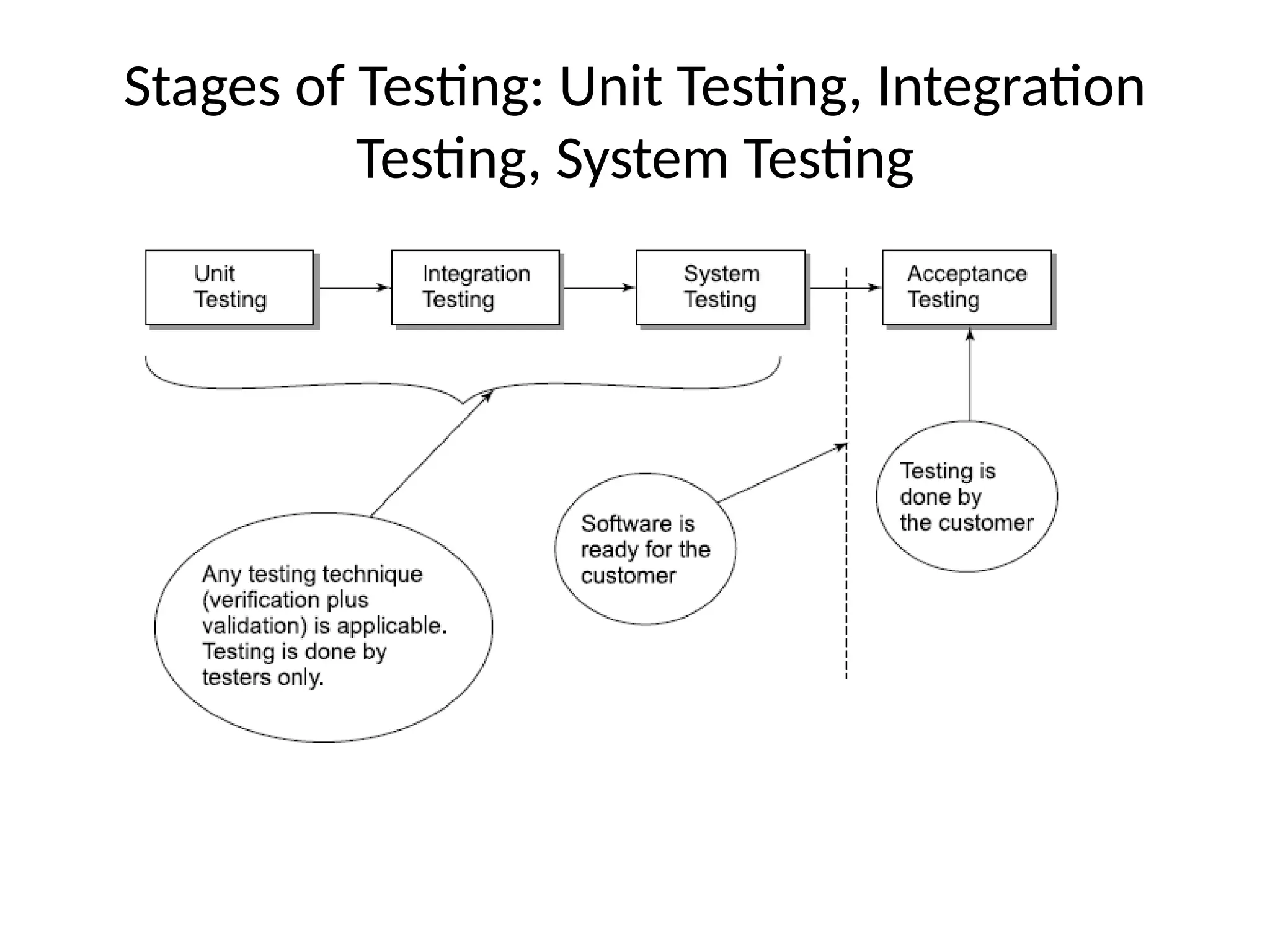
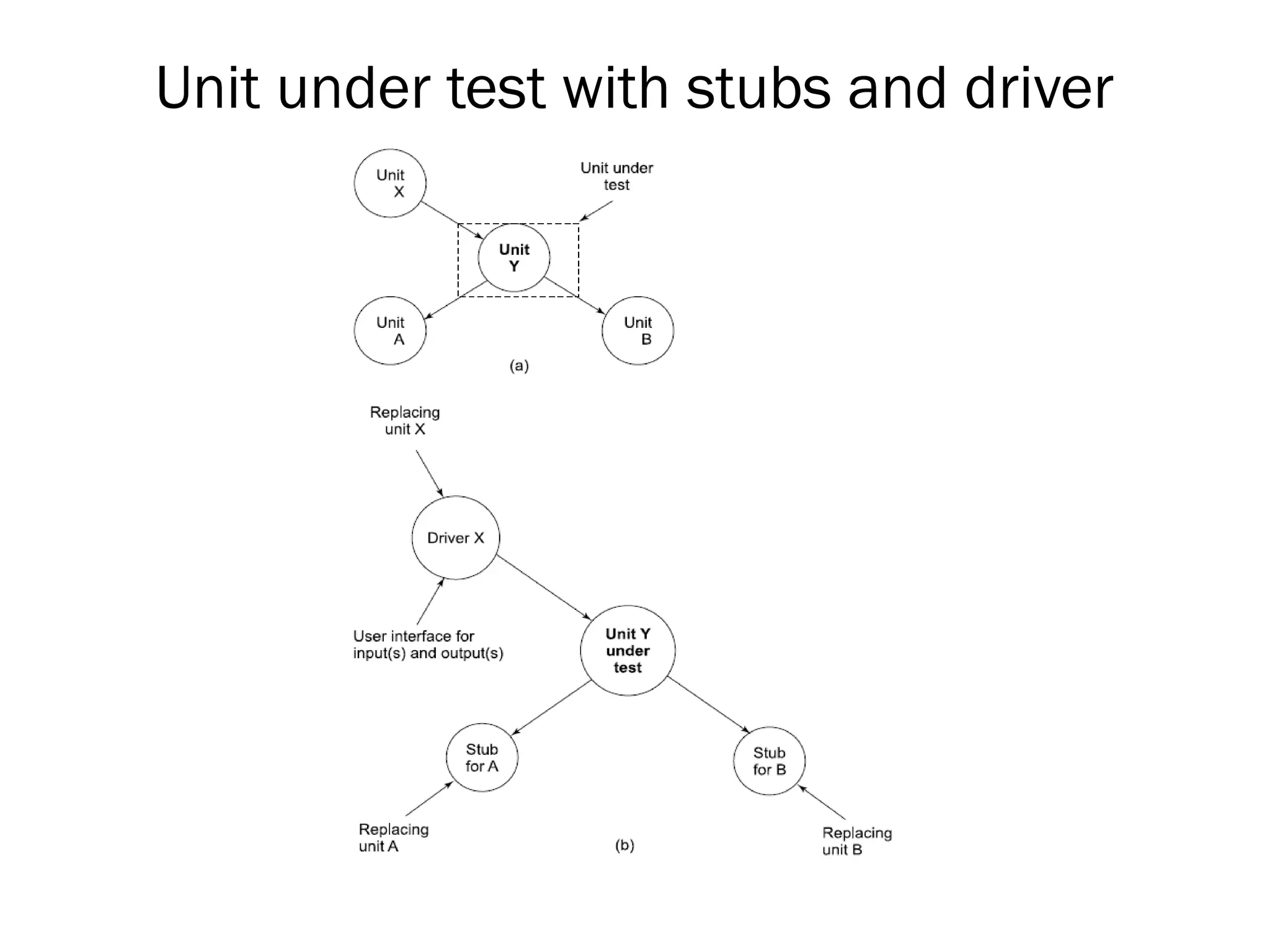
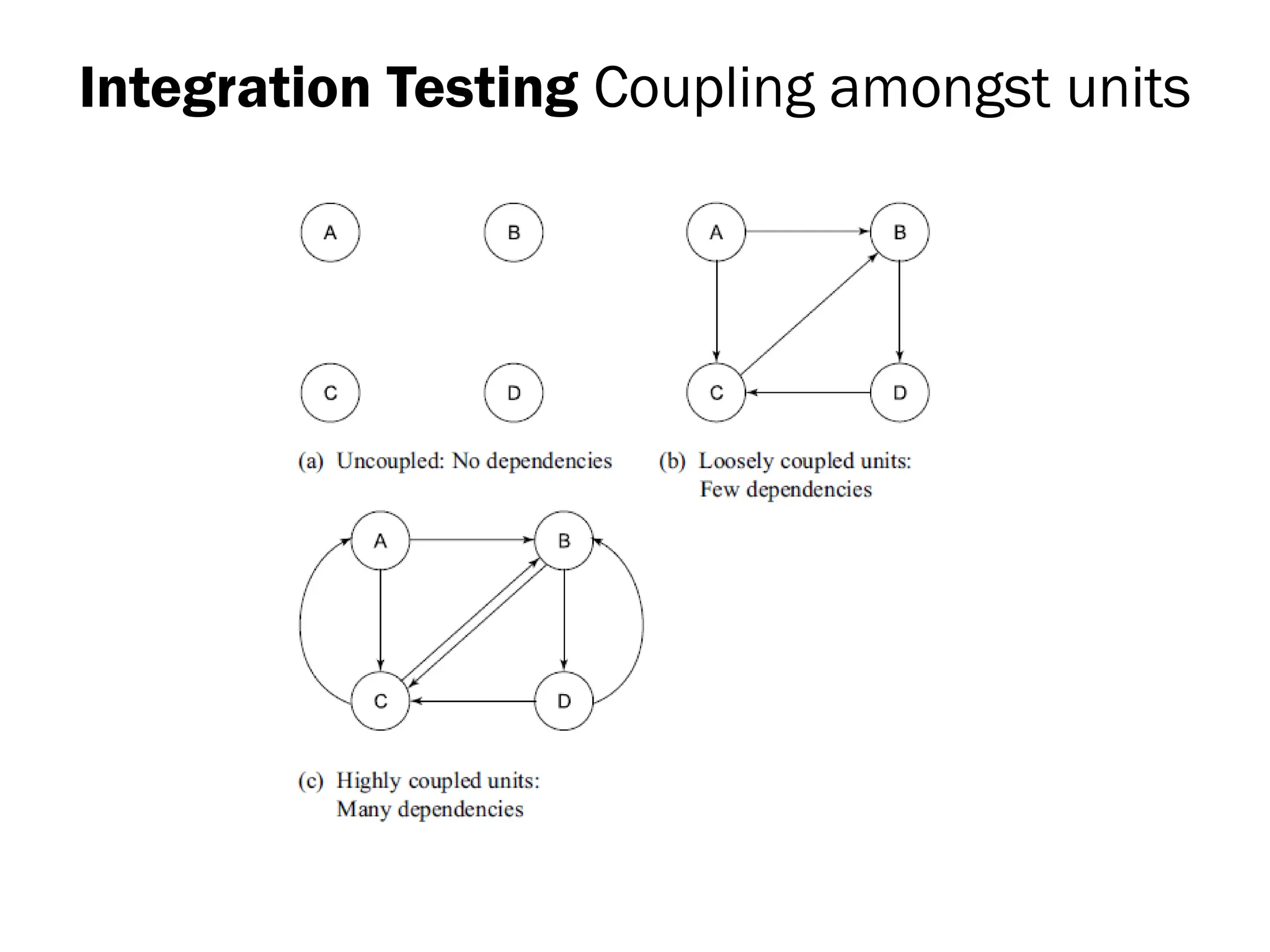
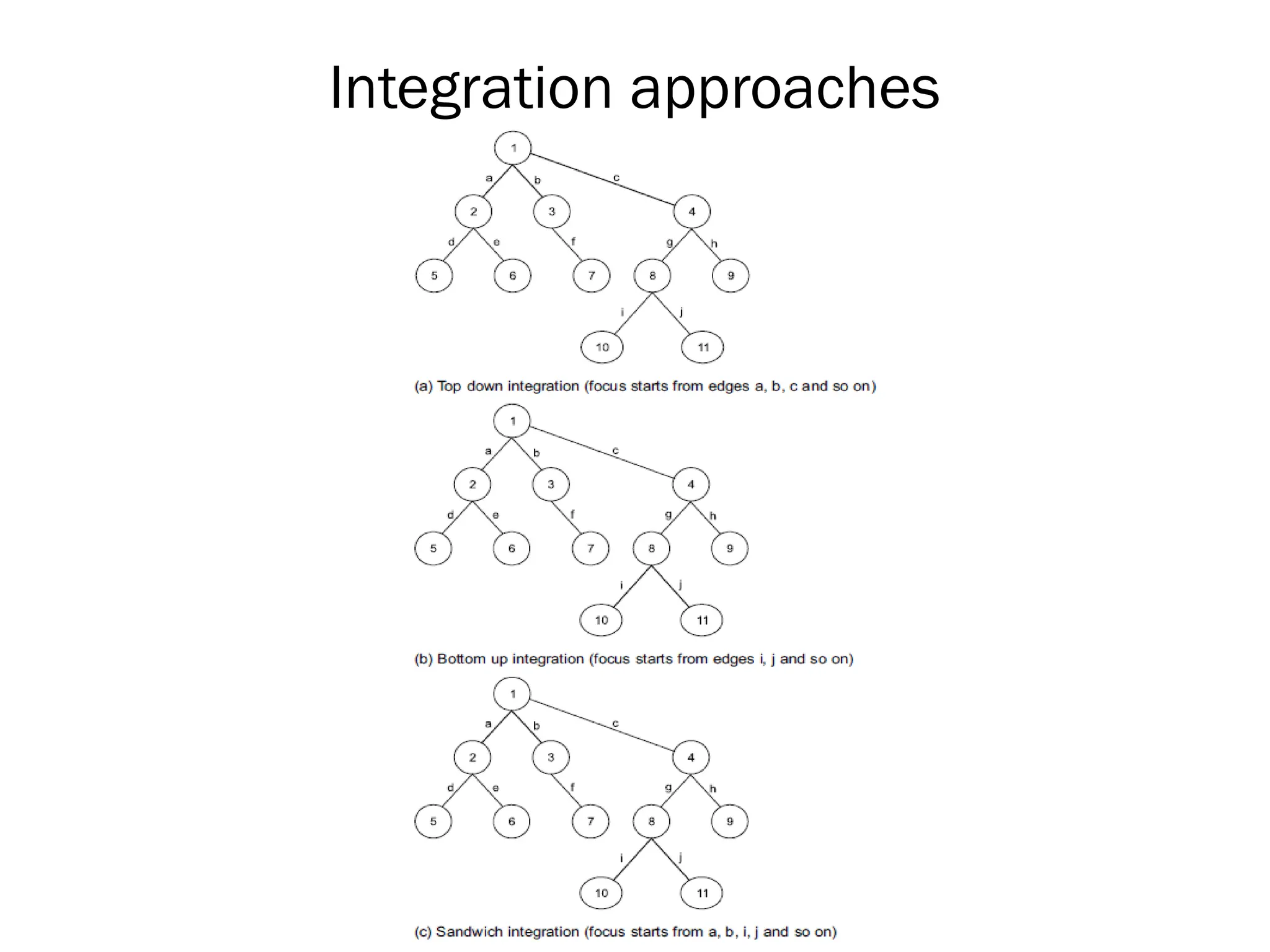
The document outlines the foundations and importance of software testing, addressing the challenges of producing error-free software and the critical need for systematic testing to ensure quality and reliability. It details various stages of testing including unit, integration, system, and acceptance testing, as well as the software testing life cycle (STLC) and the associated costs of error correction throughout the development process. Additionally, it emphasizes the necessity of thorough planning, resource allocation, and different testing strategies such as alpha and beta testing.