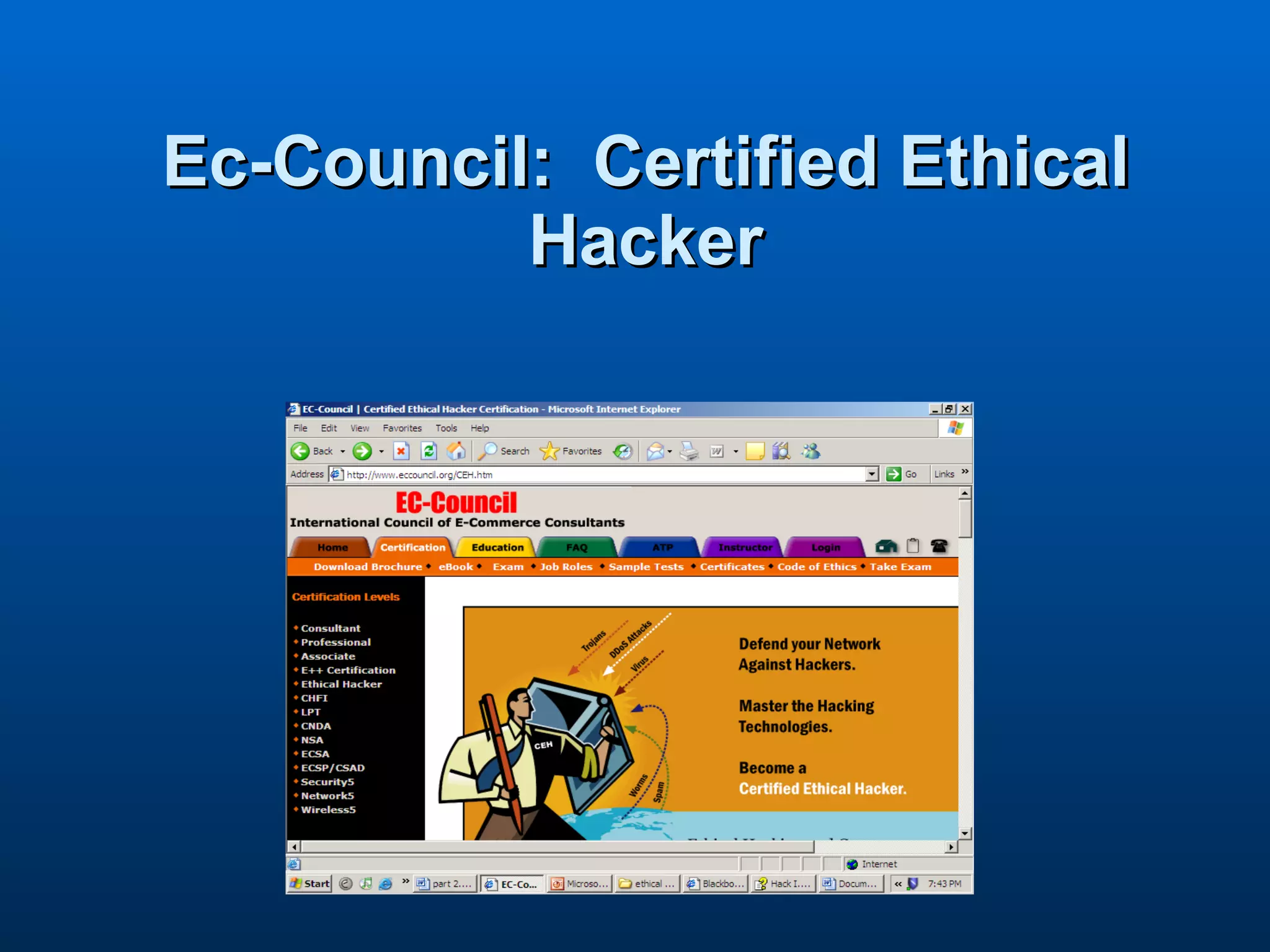
- Ethical hacking involves discovering vulnerabilities in systems through authorized penetration testing to improve security. Ethical hackers have strong technical skills and work to answer questions about what intruders can access and do on targeted systems.
- The Certified Ethical Hacker (C|EH) certification from EC-Council covers topics including reconnaissance, scanning, enumeration, hacking web servers, social engineering, cryptography, and penetration testing to evaluate system defenses.
- Ethical hackers are paid well, with experienced consultants earning over $120,000 annually and freelancers receiving $10,000-$45,000 per project. Many large organizations have certified ethical hackers on staff to test their security.















![2004 March: Myron Tereshchuk is arrested for attempting to extort $17 million from Micropatent . July: North Korea claims to have trained 500 hackers who successfully crack South Korean, Japanese, and their allies' computer systems. [18] 2005 September 13 : Cameron Lacroix is sentenced to 11 months for gaining access to T-Mobile USA's network and exploiting Paris Hilton's Sidekick . [19] November 3 : Jeanson James Ancheta , whom prosecutors say was a member of the "Botmaster Underground", a group of script kiddies mostly noted for their excessive use of bot attacks and propagating vast amounts of spam , was taken into custody after being lured to FBI offices in Los Angeles. [20]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cehpresentationmod-100130062021-phpapp01/75/C-EH-Introduction-17-2048.jpg)
![2006 May: Jeanson James Ancheta receives a 57 month prison sentence, [6] and is ordered to pay damages amounting to $15,000.00 to the Naval Air Warfare Center in China Lake and the Defense Information Systems Agency, for damage done due to DDoS attacks and hacking. Ancheta also had to forfeit his gains to the government, which include $60,000 in cash, a BMW, and computer equipment [7] . May: Largest Defacement in Web History is performed by the Turkish hacker iSKORPiTX who successfully hacked 21,549 websites in one shot. [8] October: Jesus Oquendo releases Asteroid, a SIP Denial of Service testing tool. It broke all versions of Asterisk until 1.2.13. Asteroid is also known to affect certain SIP Softphones, SIP Phones and possibly other products using the SIP protocol. It was used in Henning Schulzrinne 's Columbia University seminars. See MITRE CVE-2006-5444 and CVE-2006-5445](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cehpresentationmod-100130062021-phpapp01/75/C-EH-Introduction-18-2048.jpg)
![2007 May 17: Estonia recovers from massive denial-of-service attack [21] June 13: FBI Operation Bot Roast finds over 1 million botnet victims June 21: A spear phishing incident at the Office of the Secretary of Defense steals sensitive U.S. defense information, leading to significant changes in identity and message-source verification at OSD. August 11: United Nations website hacked by Turkish Hacker Kerem125 October 7: Trend Micro website successfully hacked by Turkish hacker Janizary(a.k.a Utku) November 29: FBI Operation Bot Roast II: 1 million infected PCs, $20 million in losses and 8 indictments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cehpresentationmod-100130062021-phpapp01/75/C-EH-Introduction-19-2048.jpg)