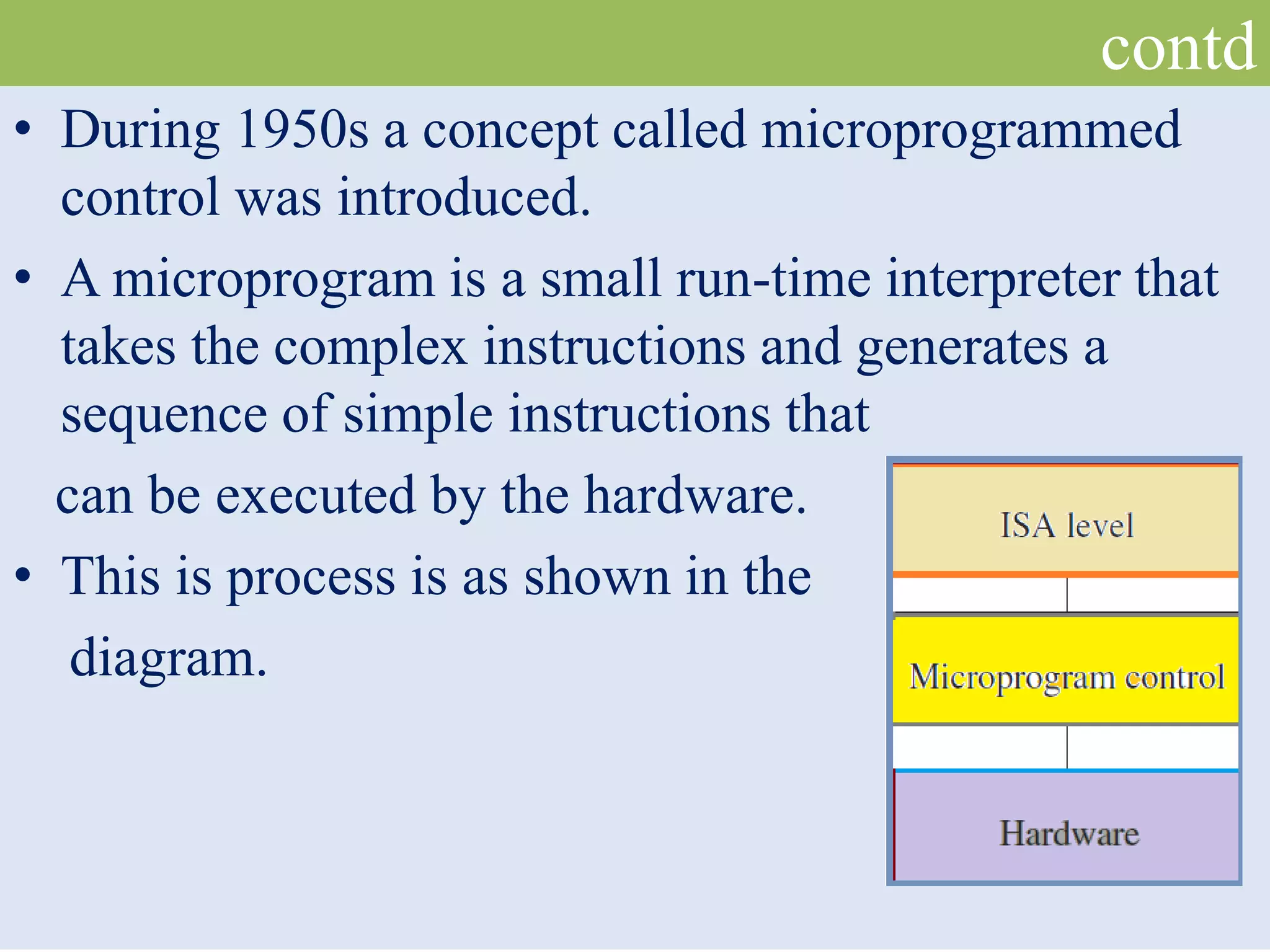
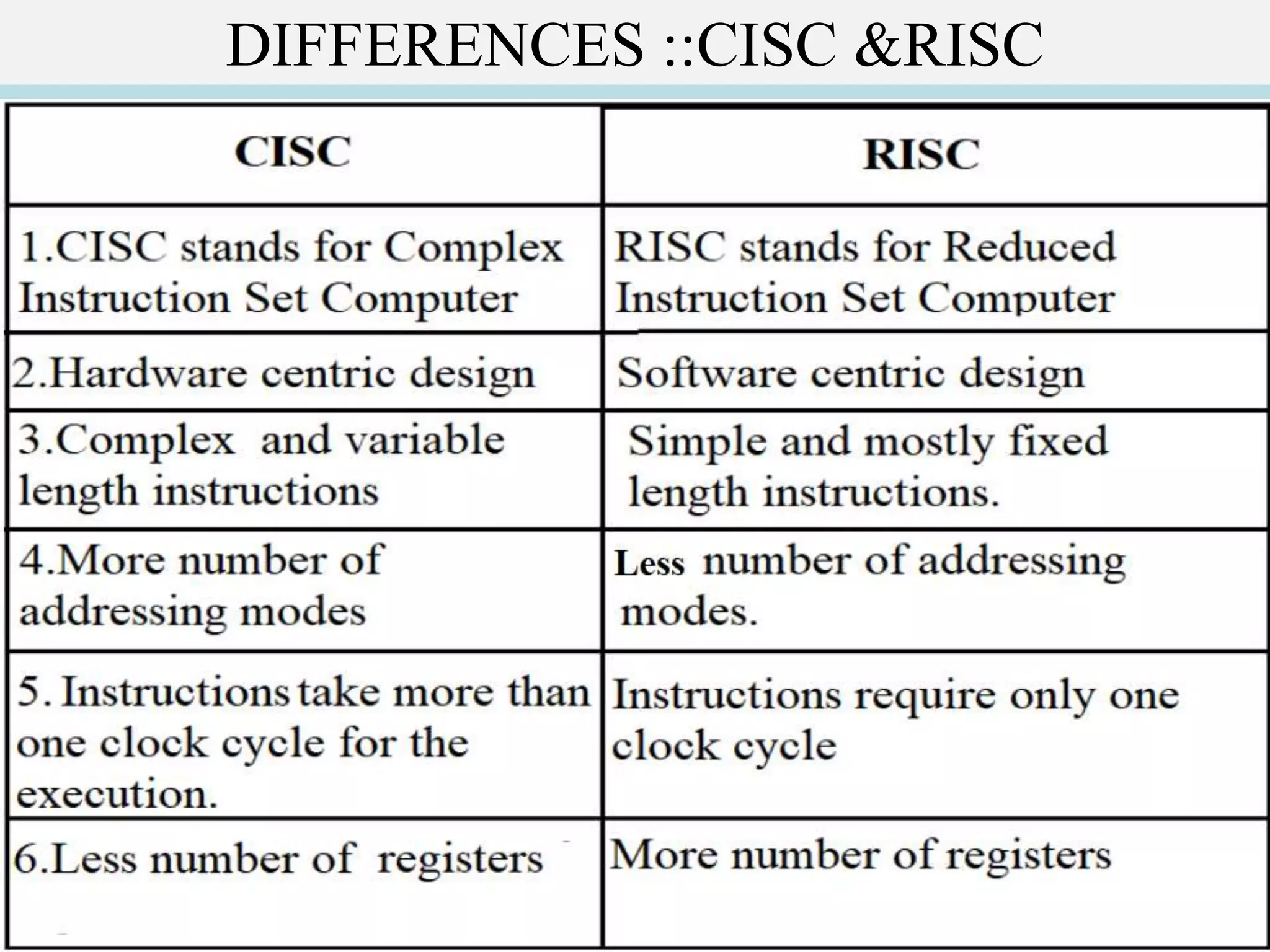
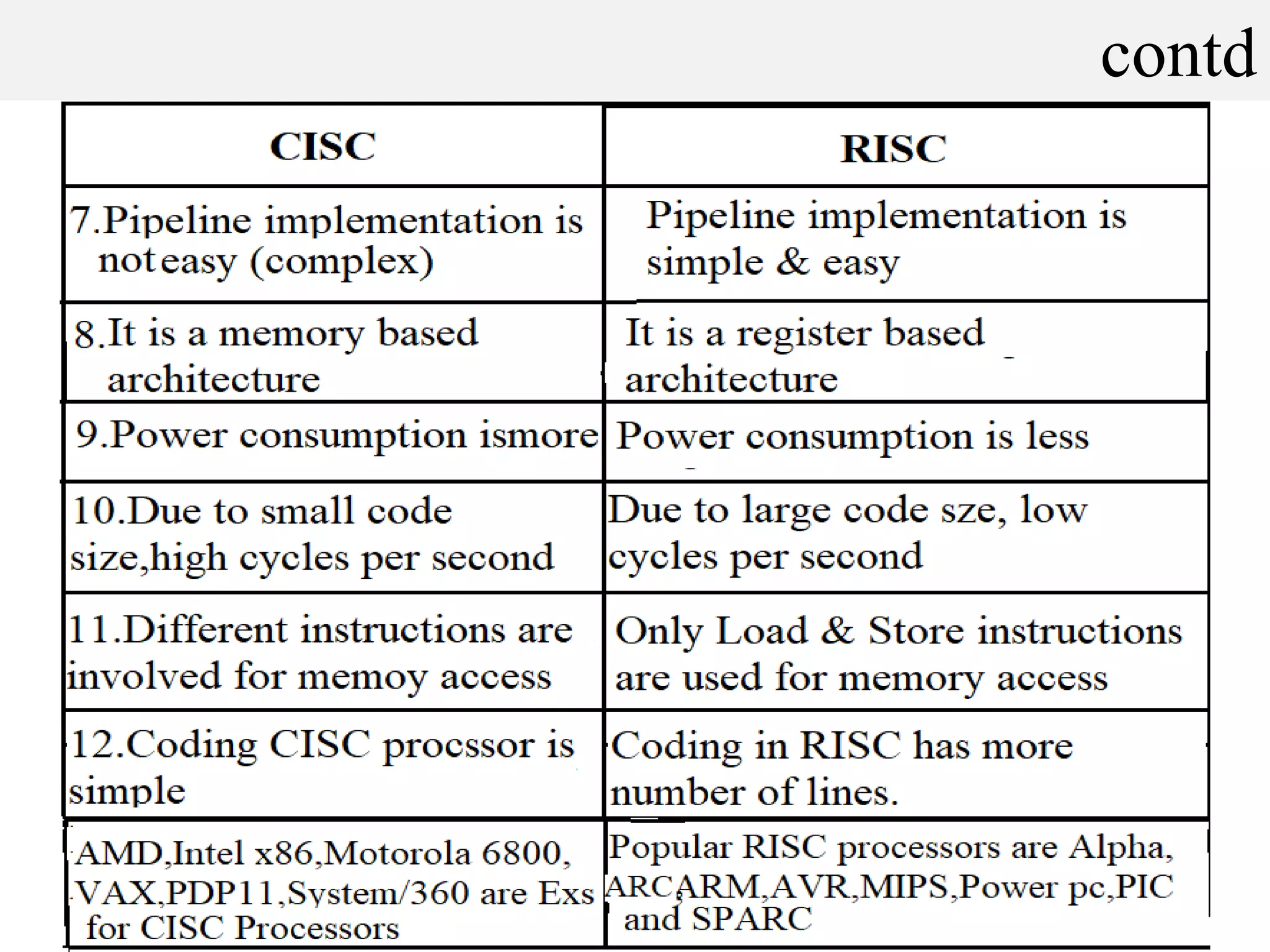
The document discusses the two main processor architectures: Complex Instruction Set Computers (CISC) and Reduced Instruction Set Computers (RISC). It highlights the shift from CISC to RISC designs, particularly in popular processors such as ARM, due to advantages in performance, design simplicity, and rapid development. The summary outlines differences in instruction complexity, execution speed, and architectural focus between the two approaches.