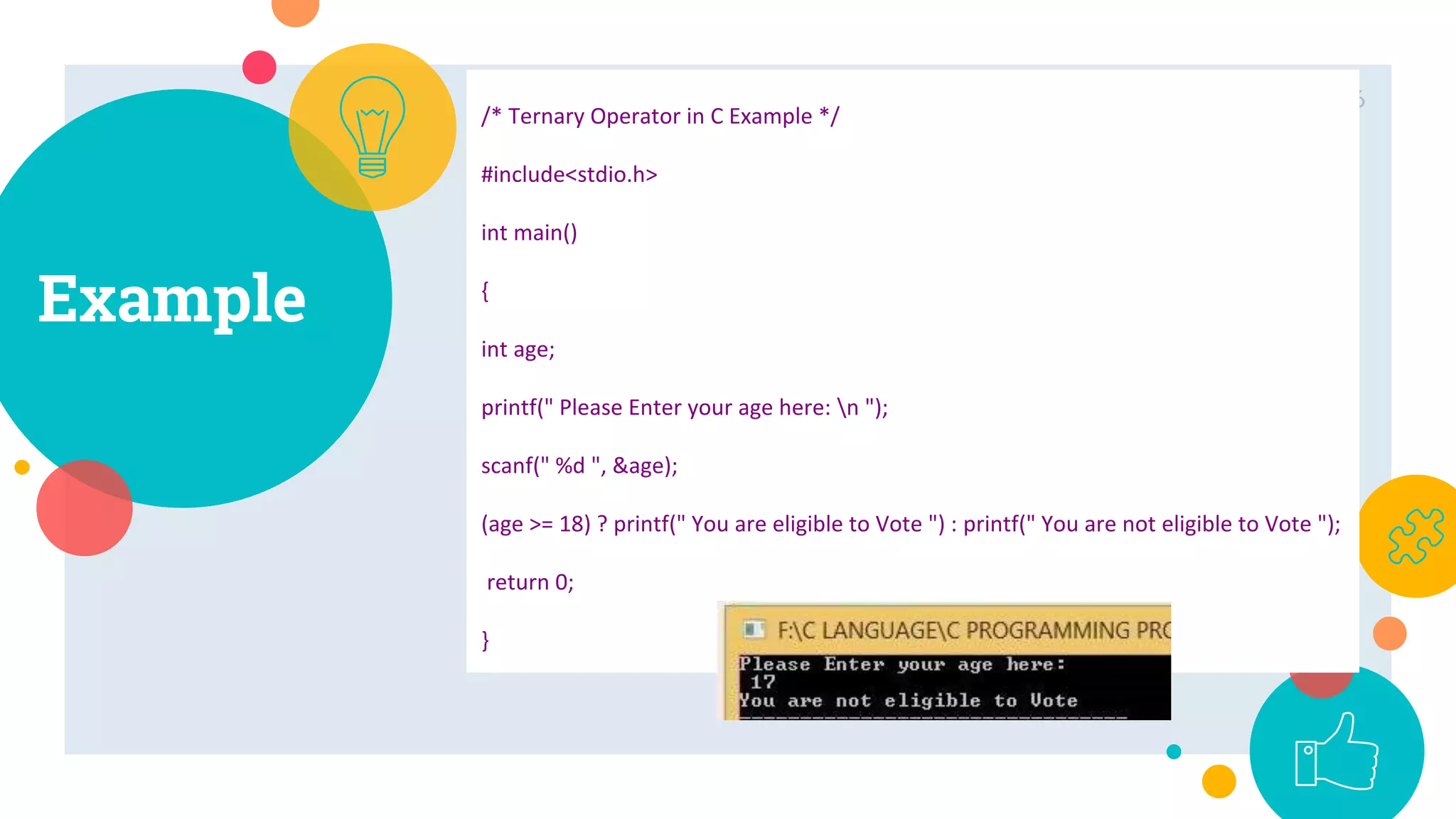
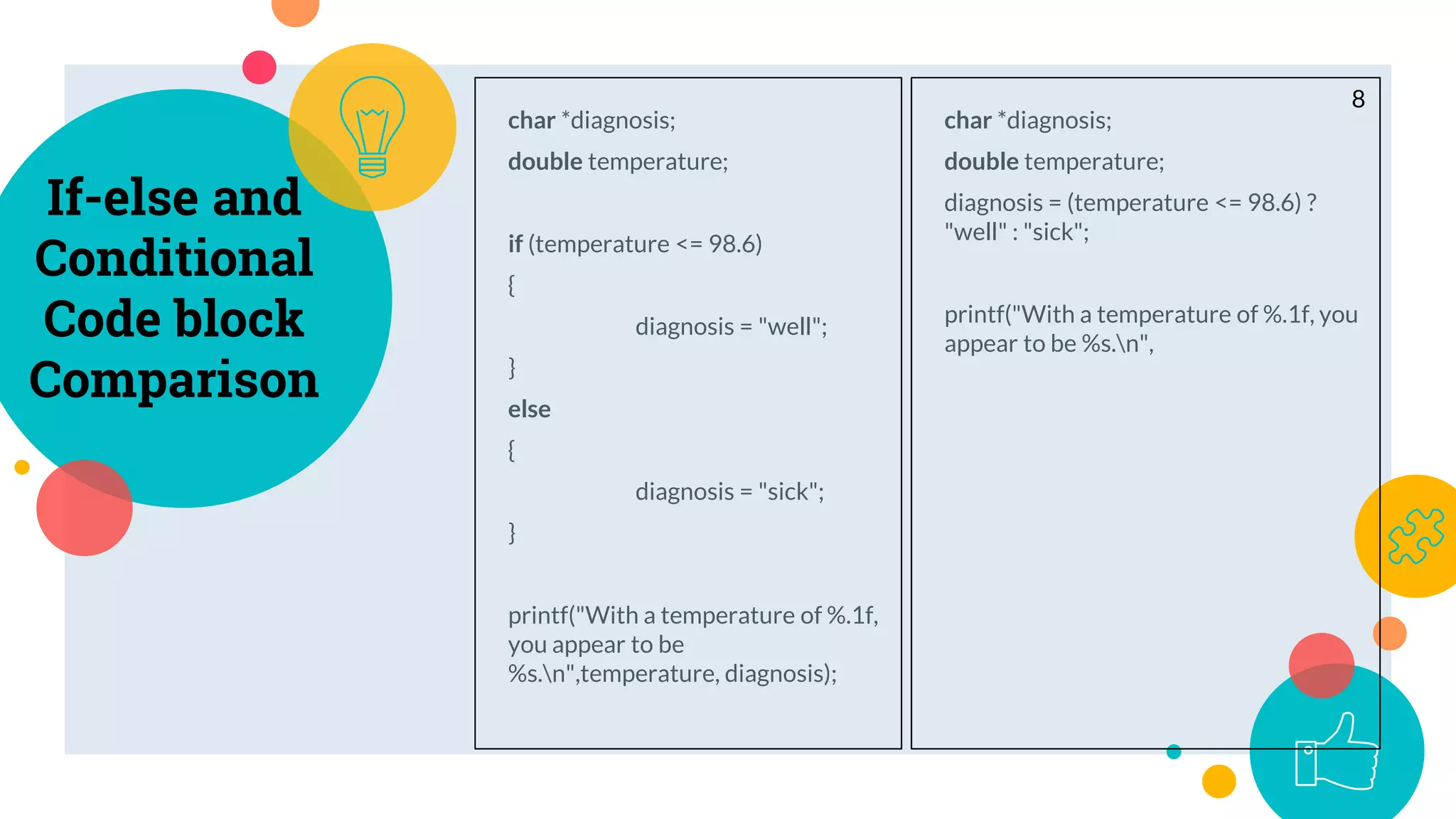
The conditional operator, also known as the ternary operator, allows an expression to take on one of two values based on whether a condition is true or false. It requires three operands - a condition, a value if the condition is true, and a value if the condition is false. The conditional operator provides a shorthand for a basic if-else statement where a variable is assigned one of two values based on a condition. While it can be nested, doing so reduces readability, so conditional operators are best used only in place of simple if-else assignments rather than complex nested logic.