Downloaded 213 times



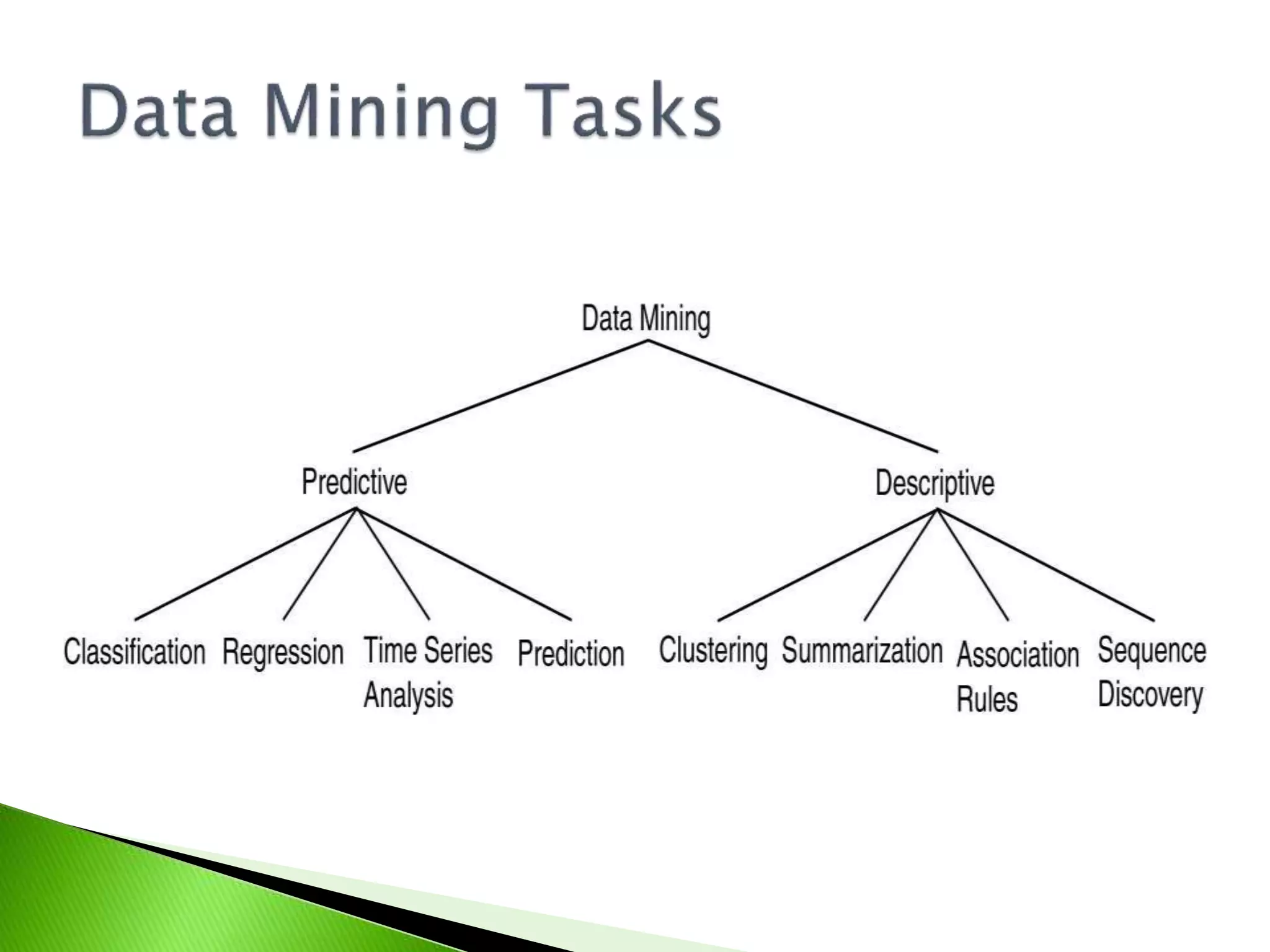



This document discusses data mining and different types of data mining techniques. It defines data mining as the process of analyzing large amounts of data to discover patterns and relationships. The document describes predictive data mining, which makes predictions based on historical data, and descriptive data mining, which identifies patterns and relationships. It also discusses classification, clustering, time-series analysis, and data summarization as specific data mining techniques.
Introduction of Khwaja Aamer.
Discusses data collection, the need for advanced analysis due to data growth, and the limitations of traditional techniques.
Differentiates between predictive and descriptive data analysis.
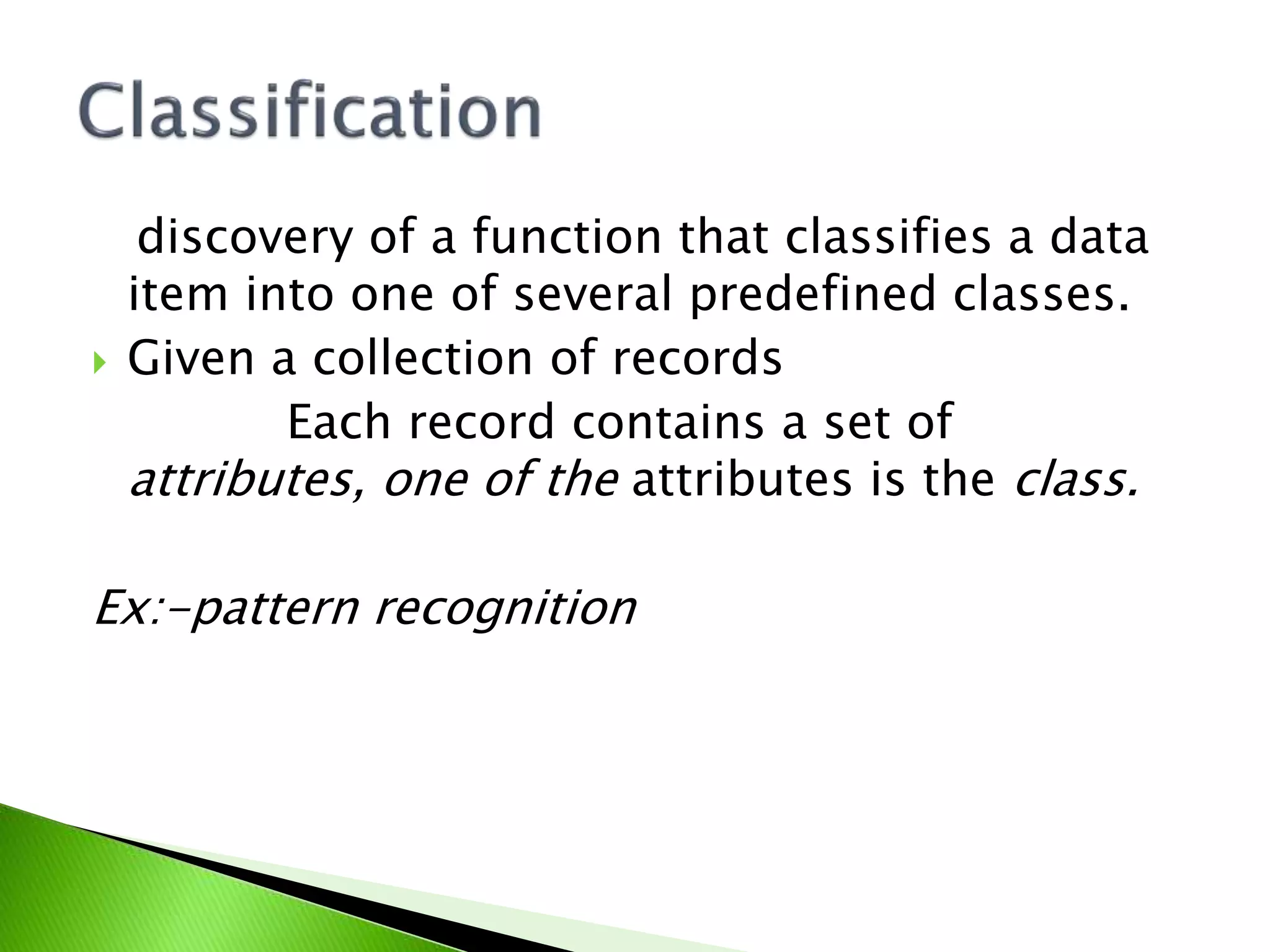
Explains classification functions in data analysis, focusing on attribute examination and patterns.
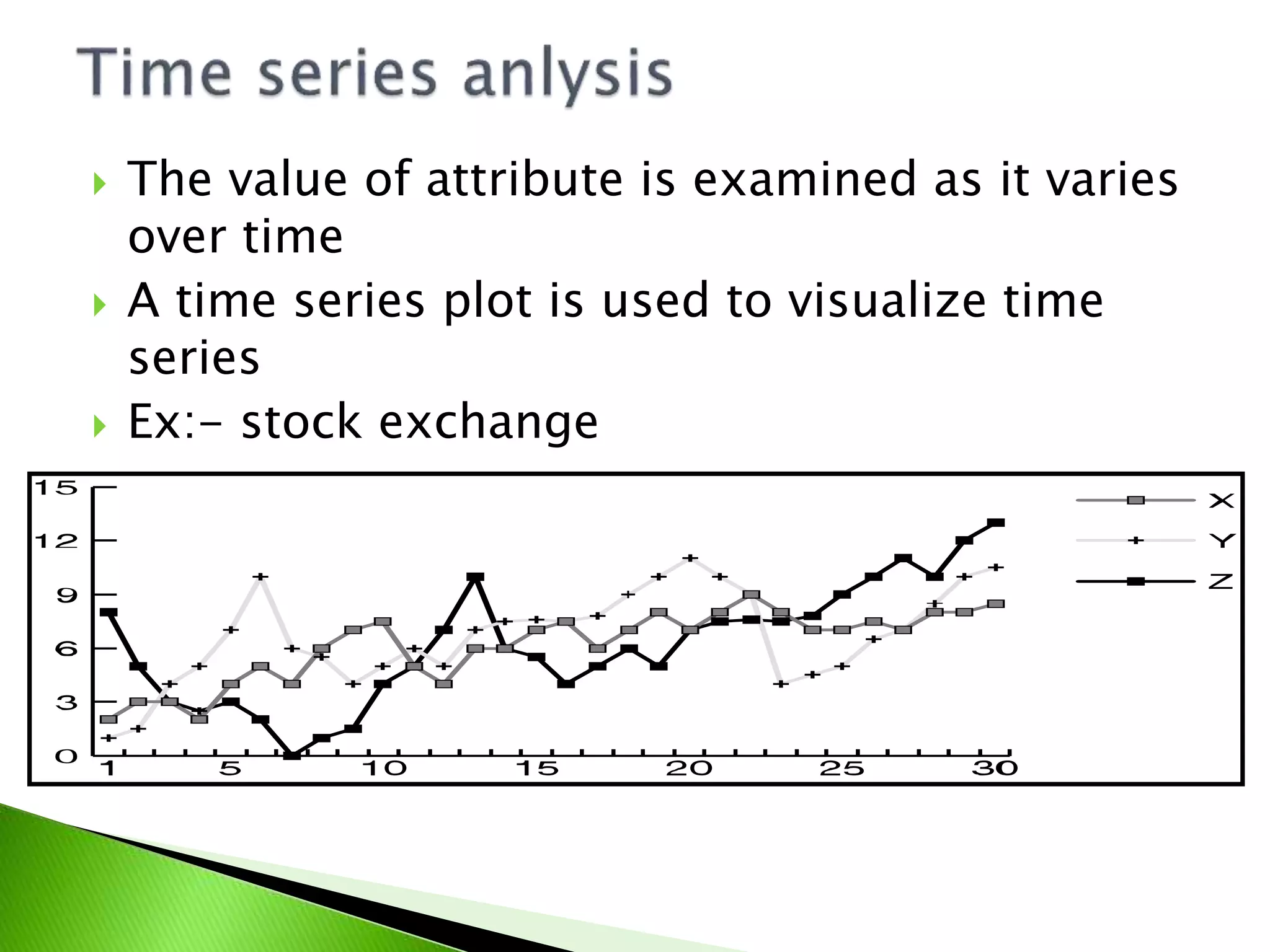
Describes the analysis of changing attributes over time using time series plots.
Defines clustering as segmenting diverse groups into similar subgroups, with an example of bank customers.
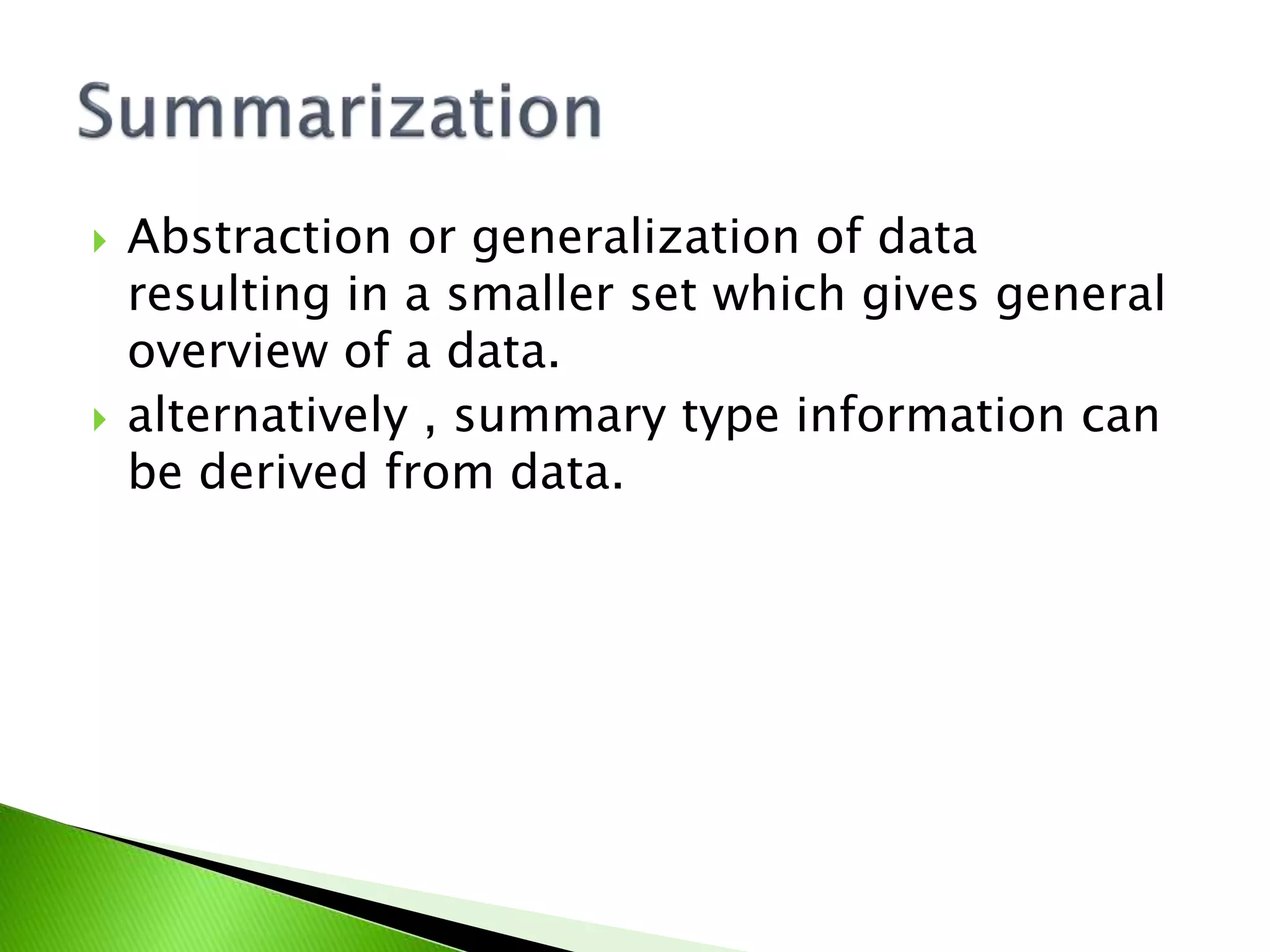
Details the process of data abstraction that simplifies data into a more general overview.









