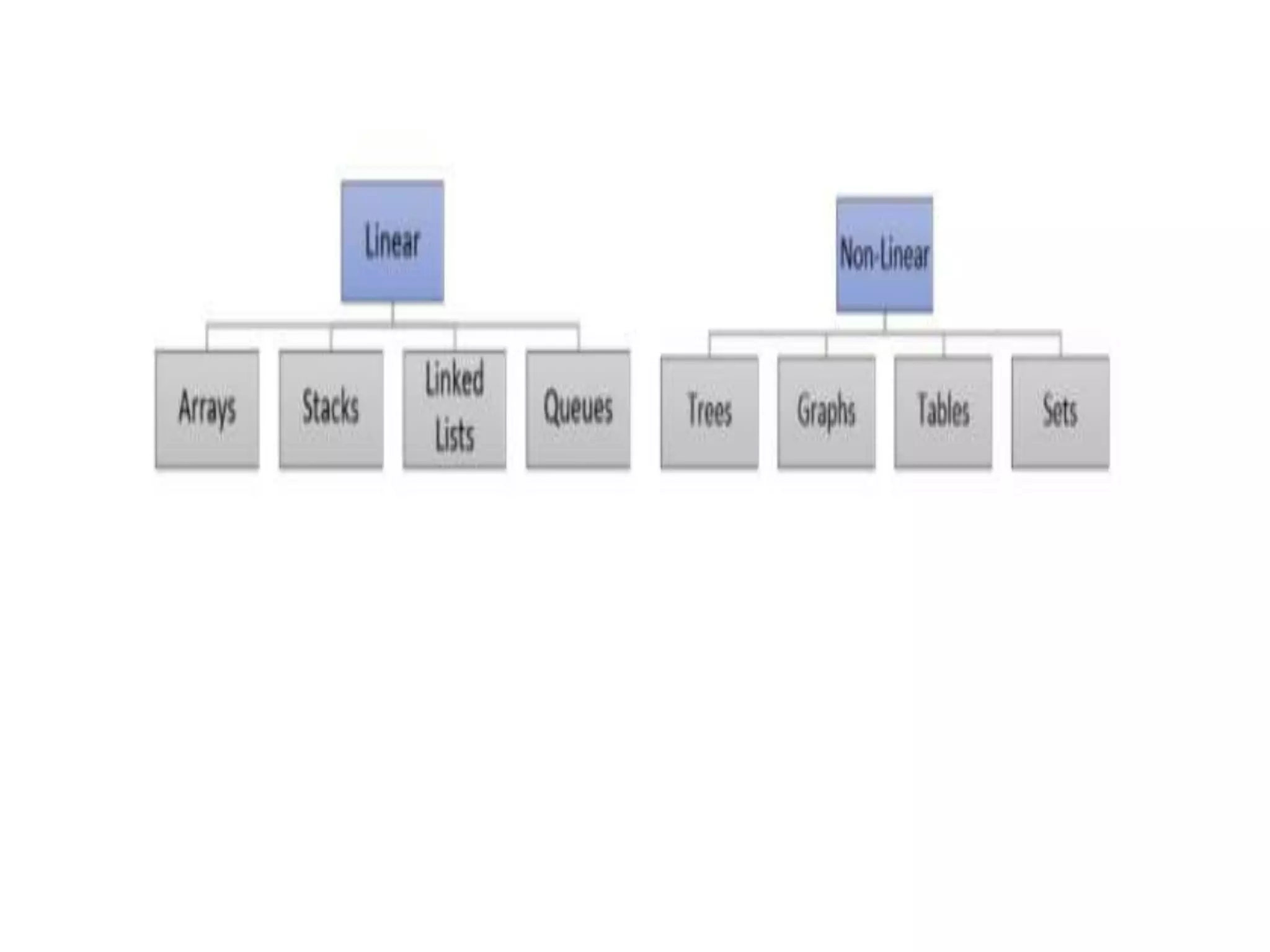
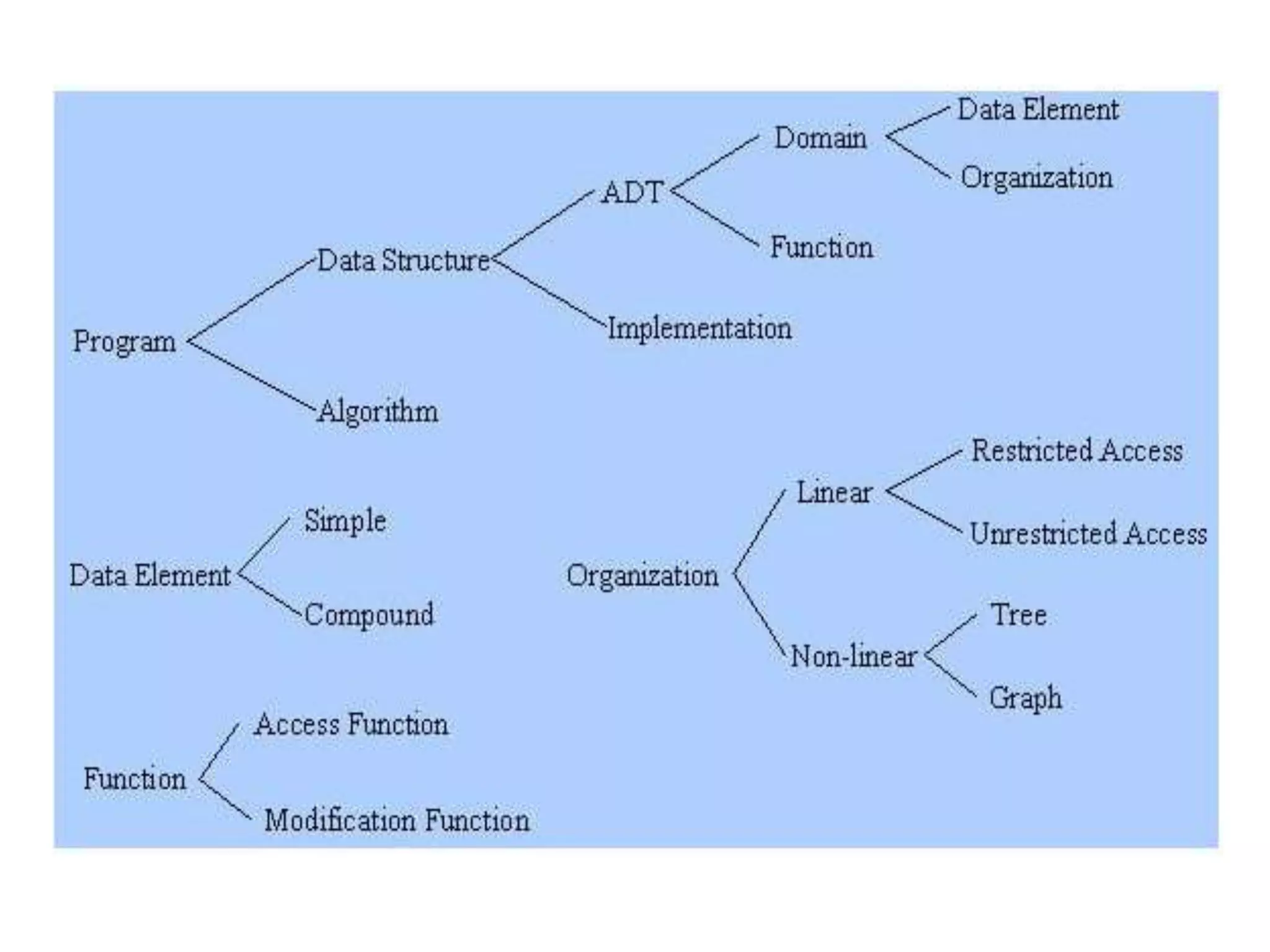
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be accessed and manipulated efficiently. The document discusses how data structures help handle complex algorithms and data volumes, optimize memory usage, and allow code reuse through libraries. Common linear data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues, while non-linear structures include trees. Data structures are a fundamental part of computer science and are used widely in areas like artificial intelligence, operating systems, and graphics.