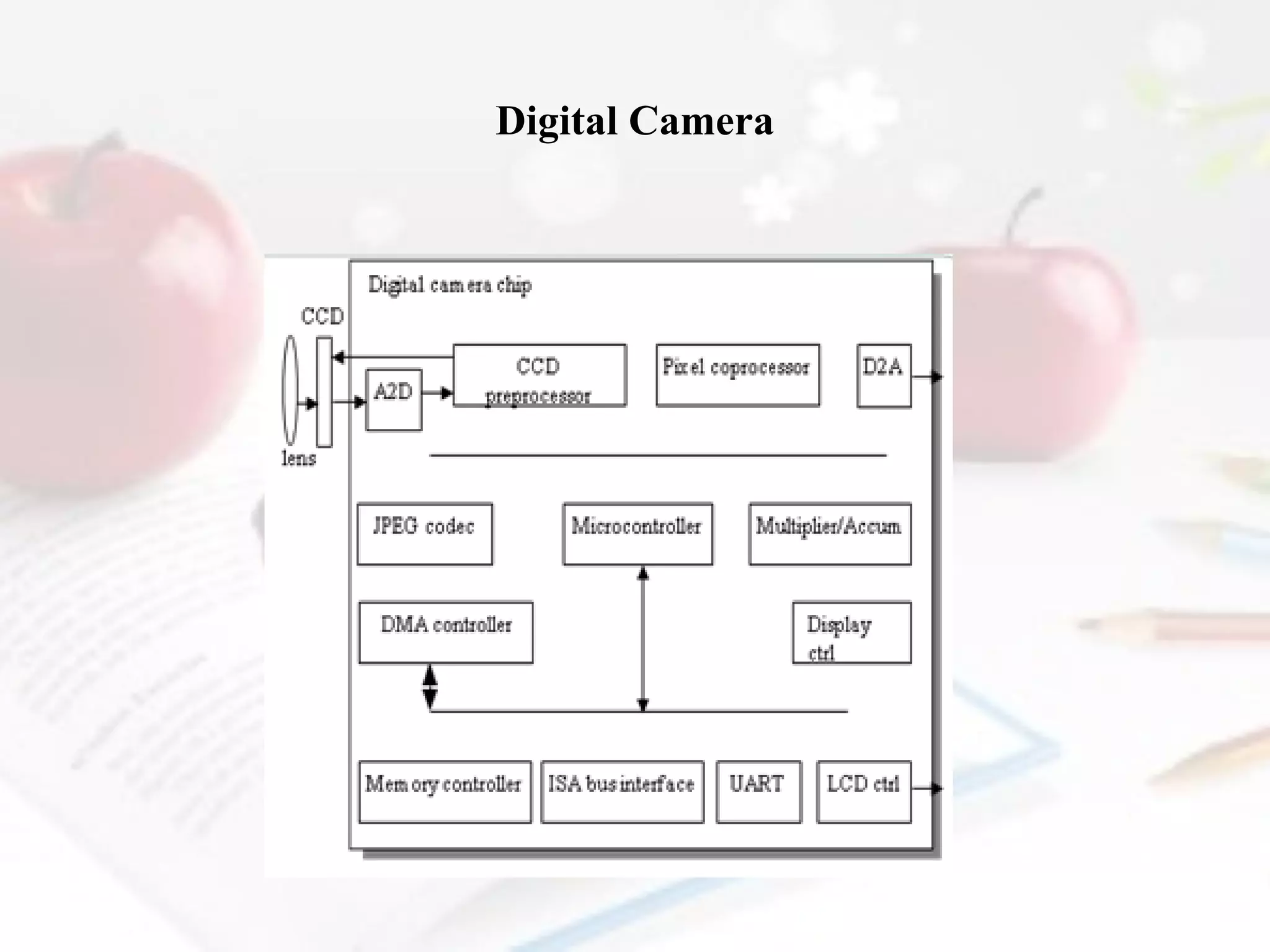
The document discusses several topics related to digital circuits and processors:
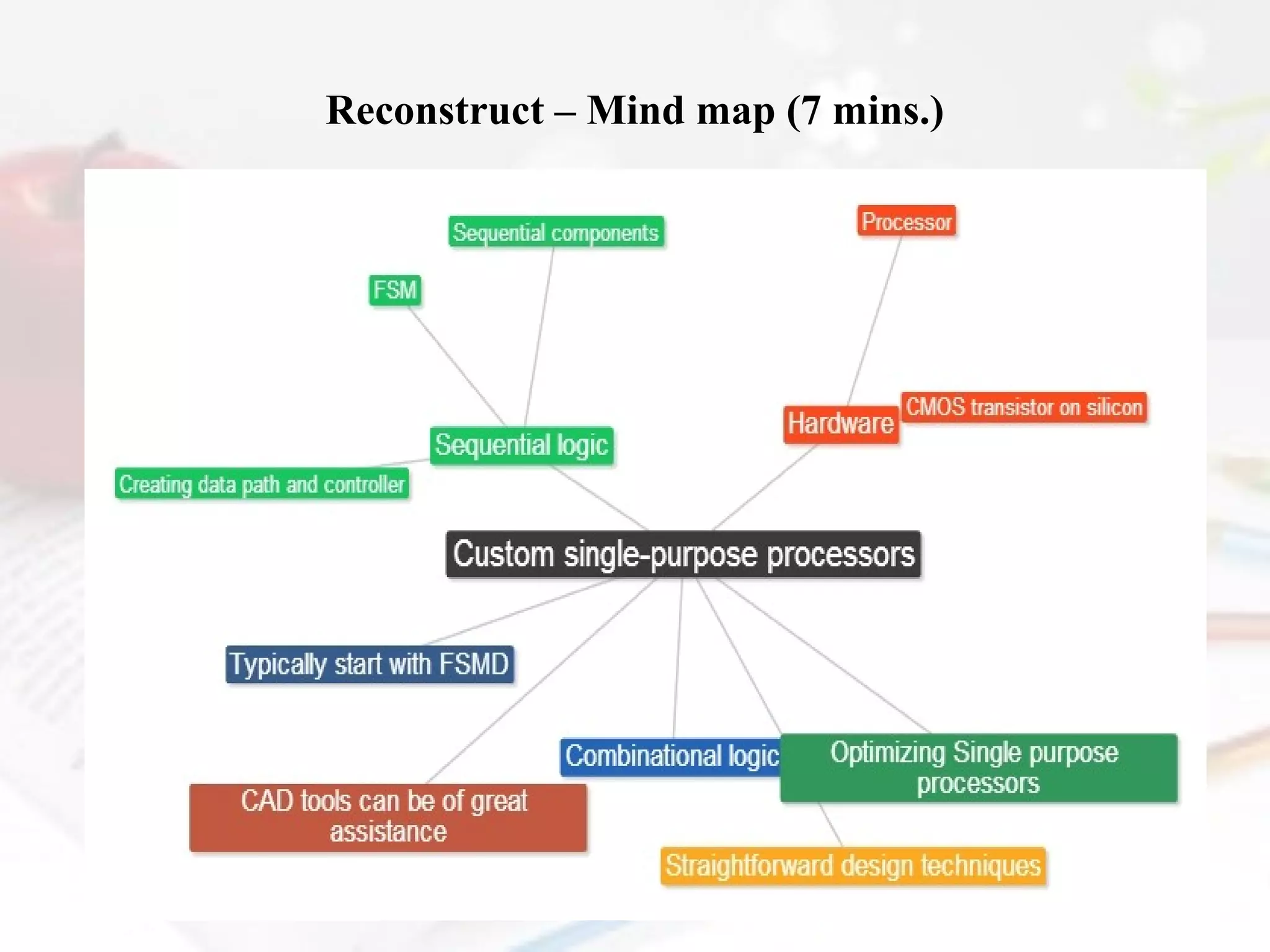
- Custom single-purpose processors are designed for a specific computation task and can be fast, small and low power but require more design time and are less flexible than general purpose processors.
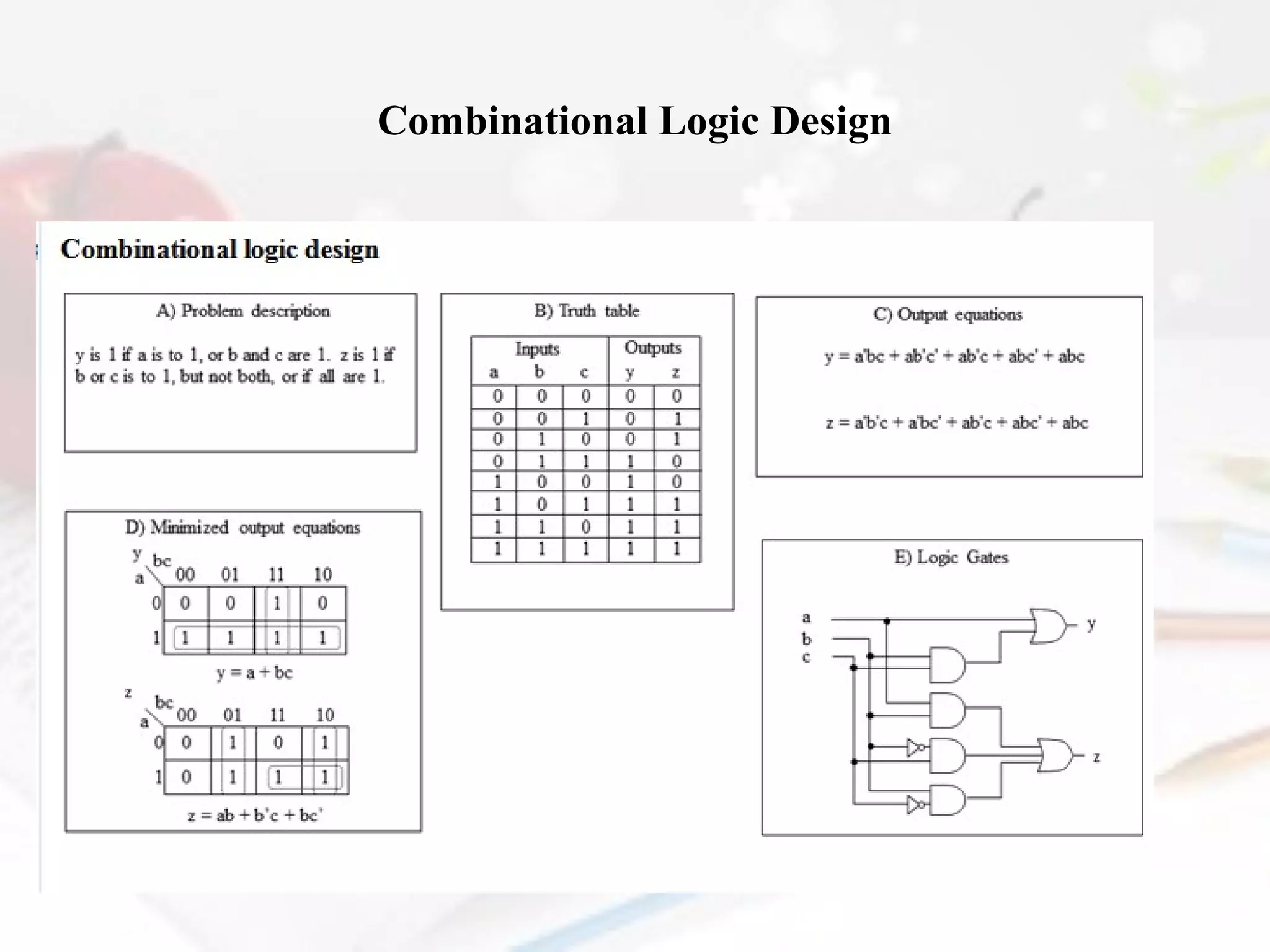
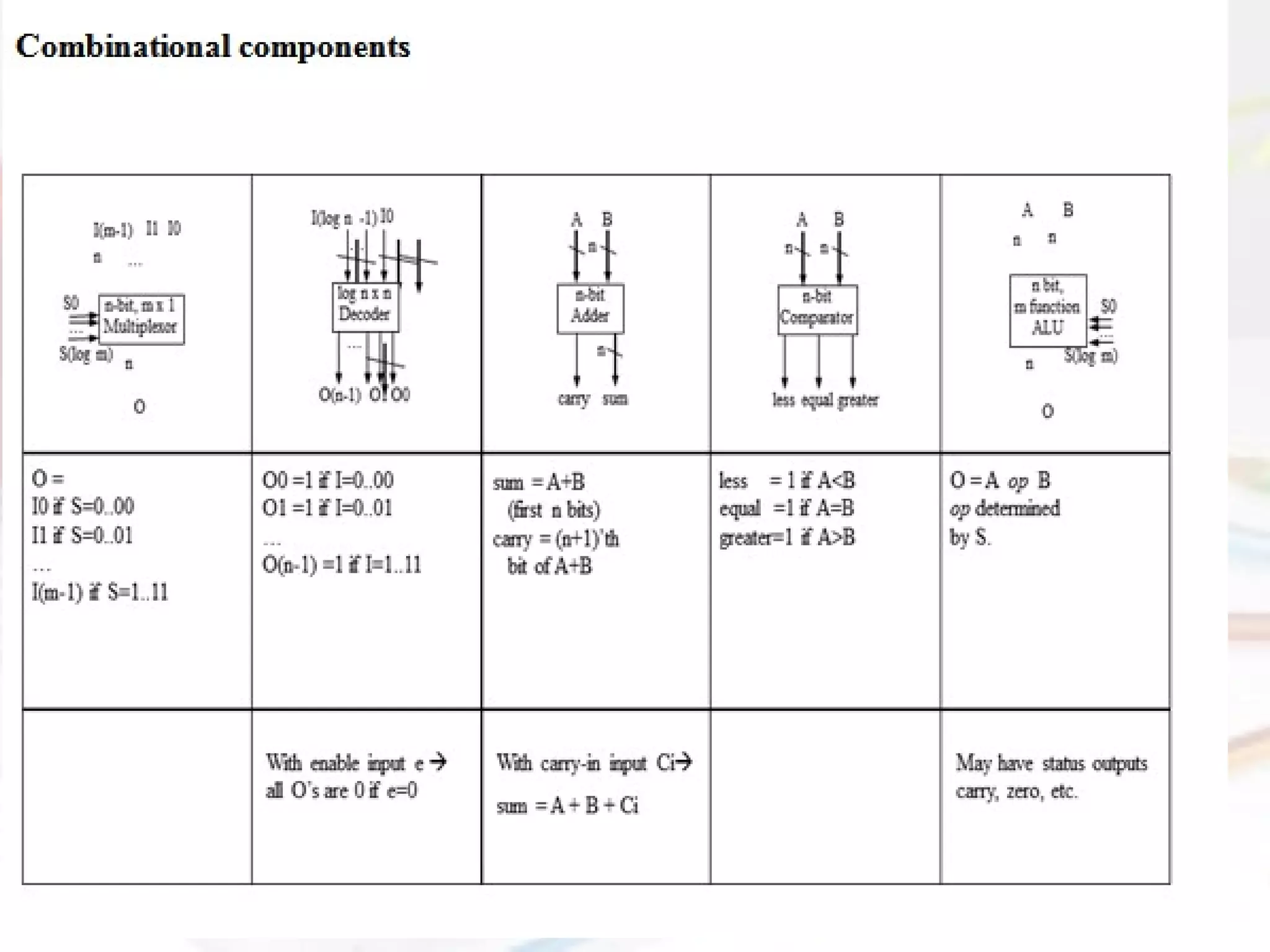
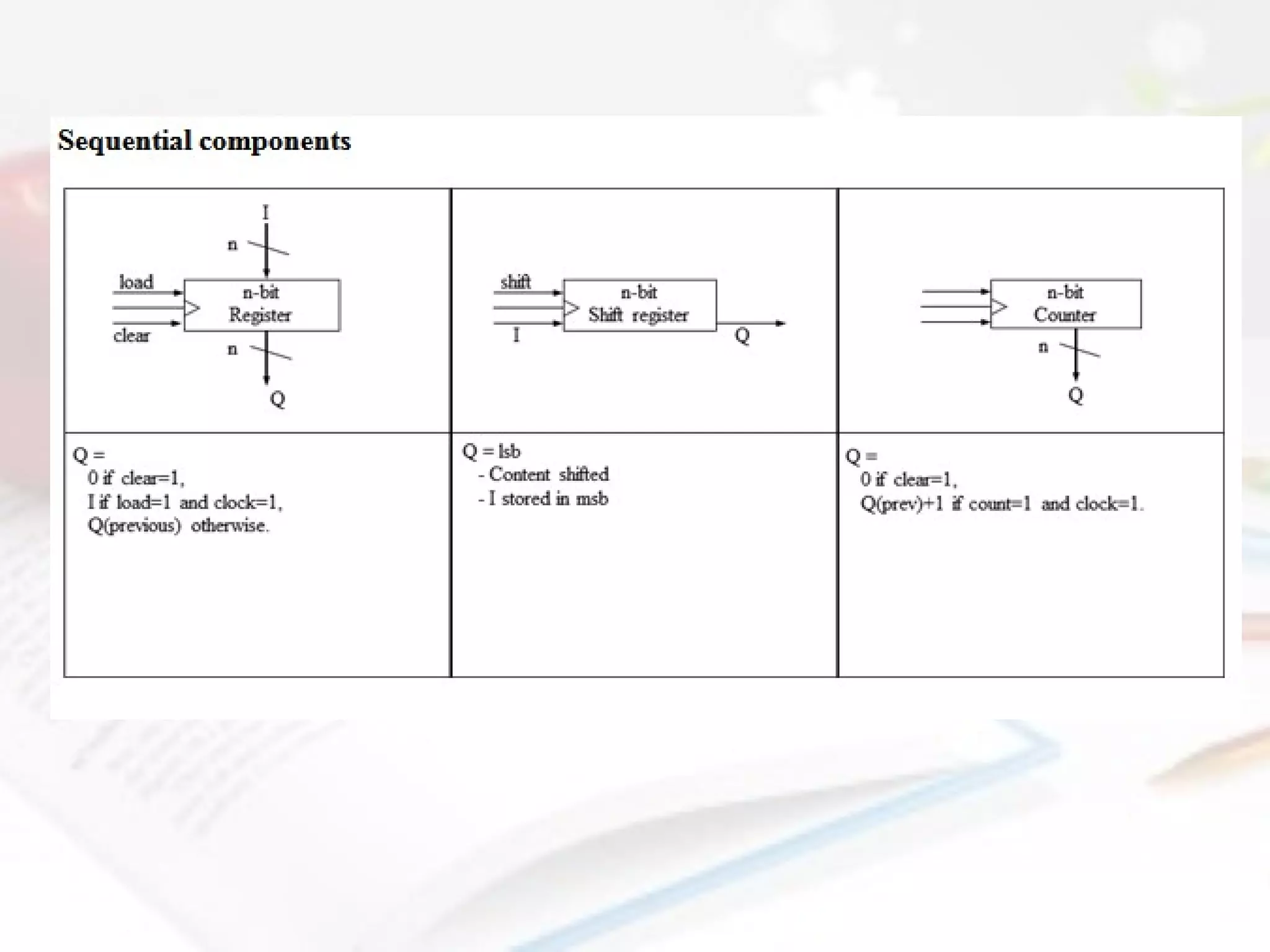
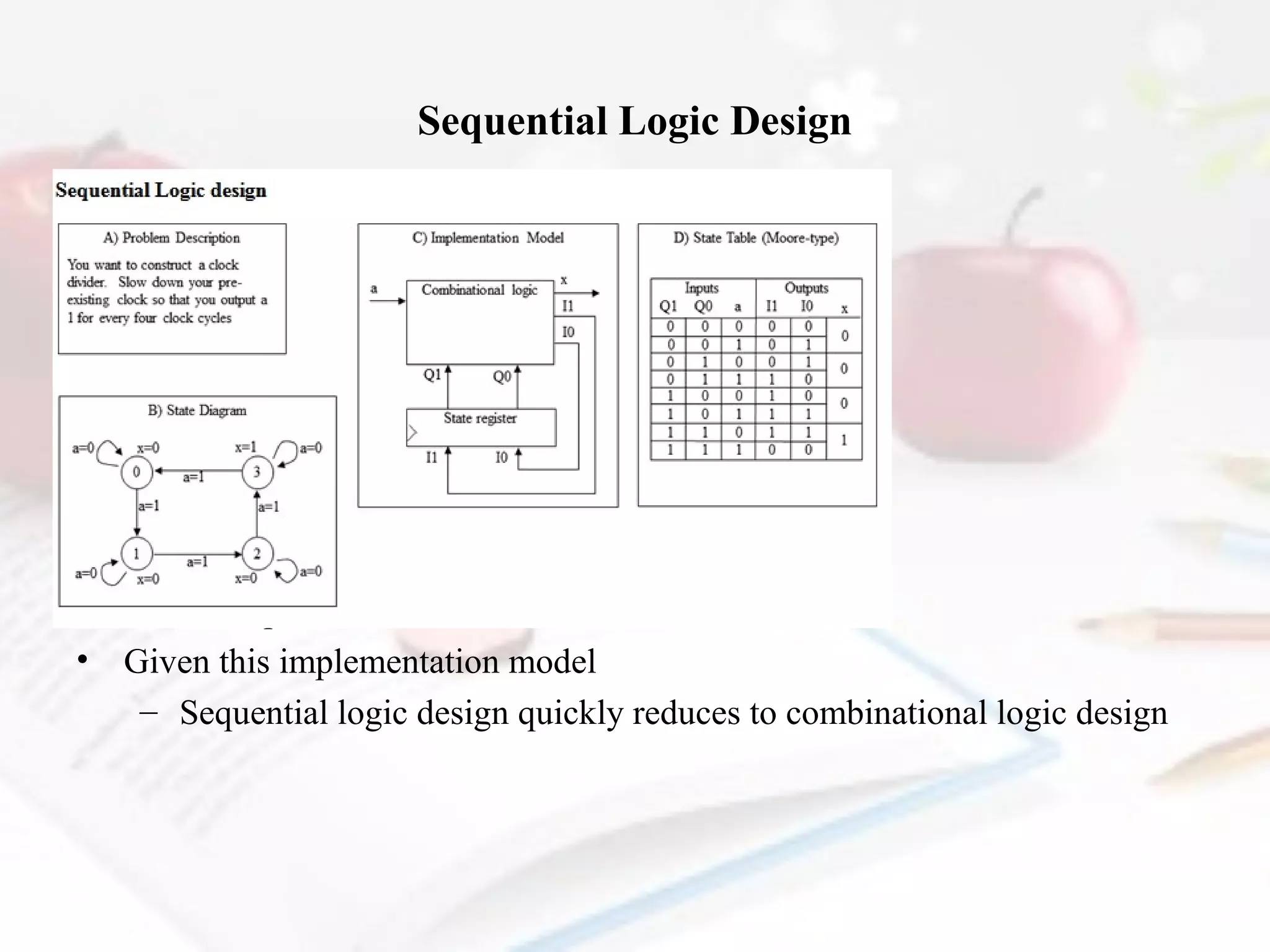
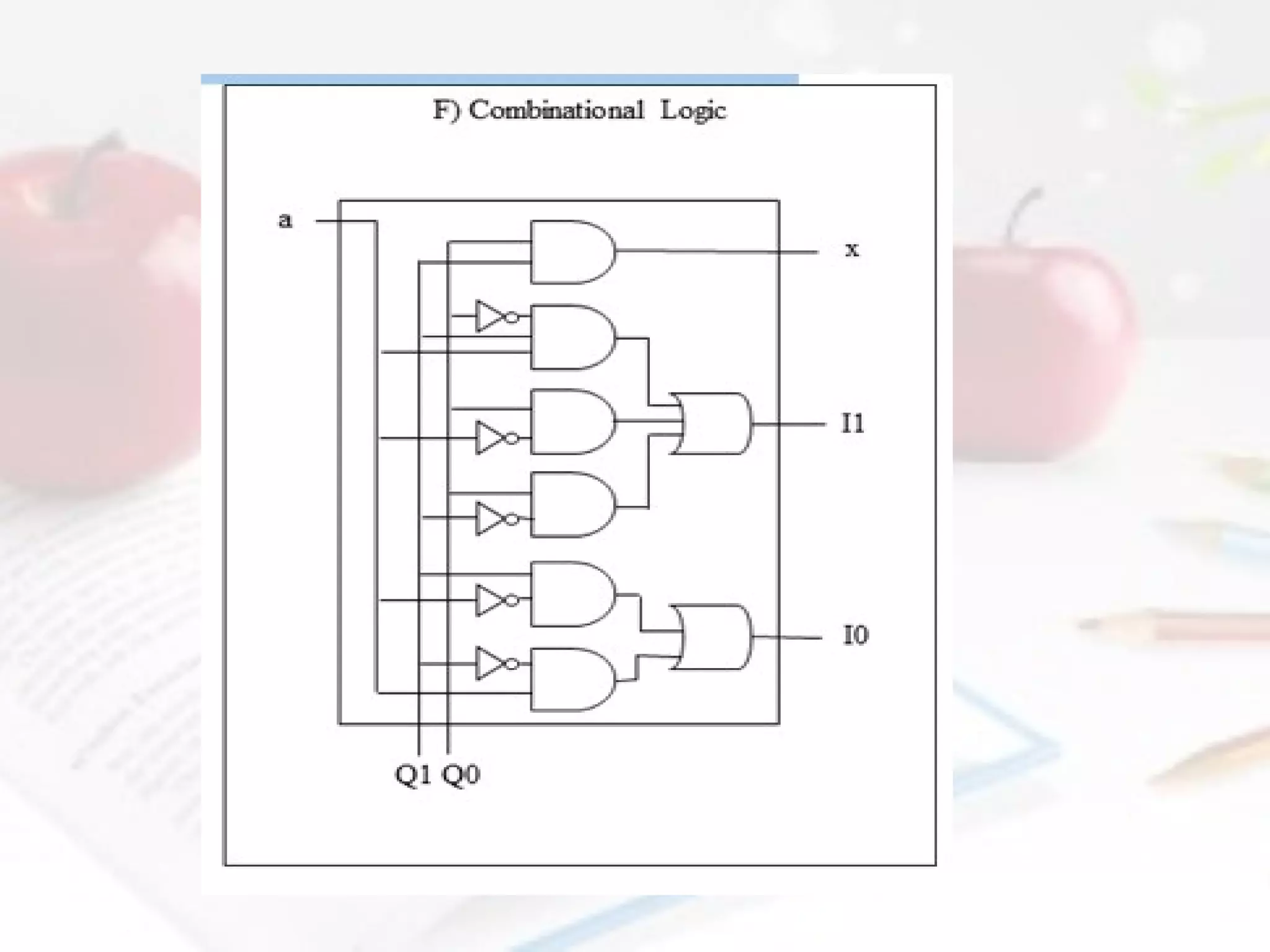
- Combinational logic circuits have outputs determined solely by current inputs while sequential logic circuits have memory of past inputs.
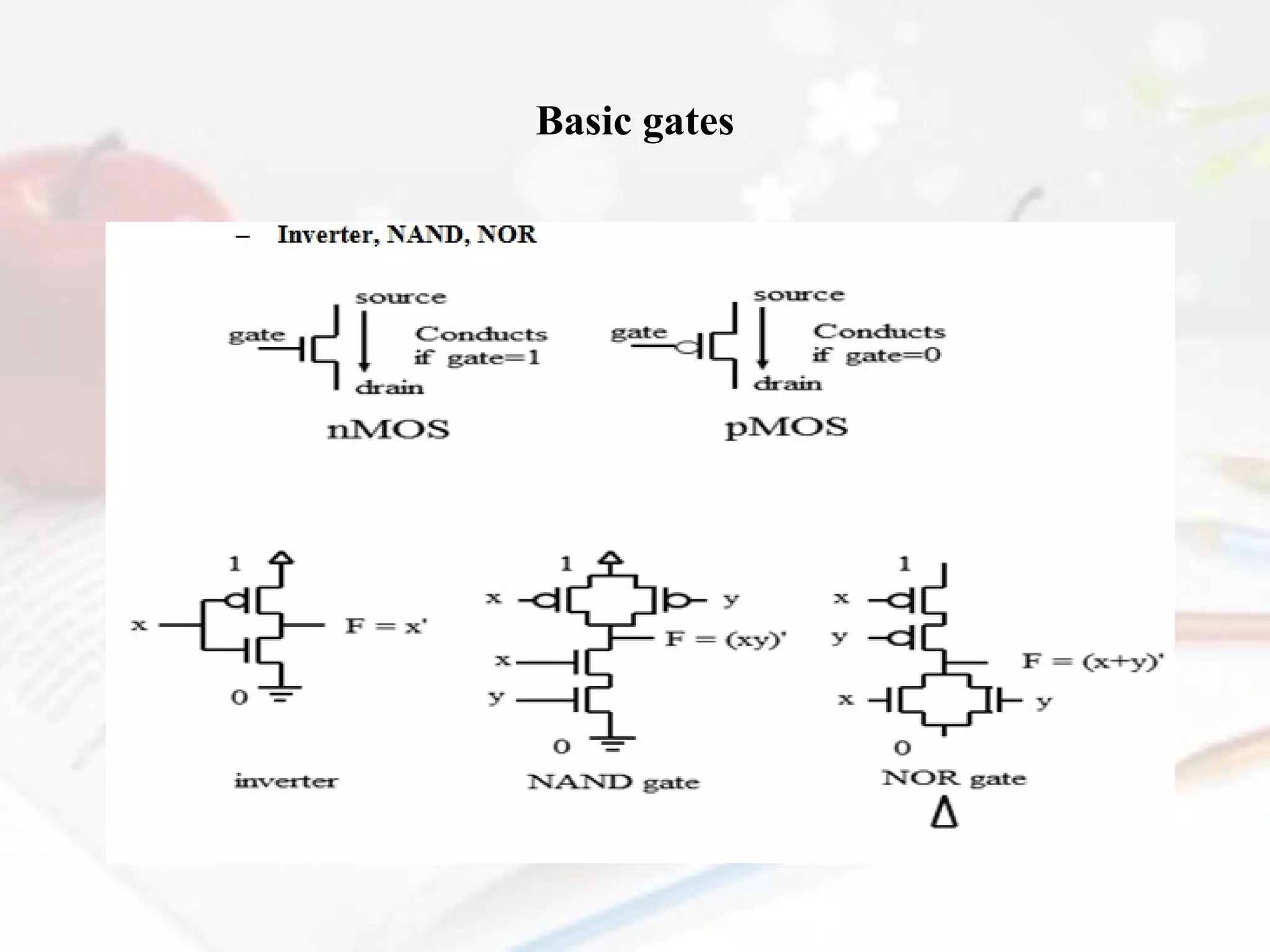
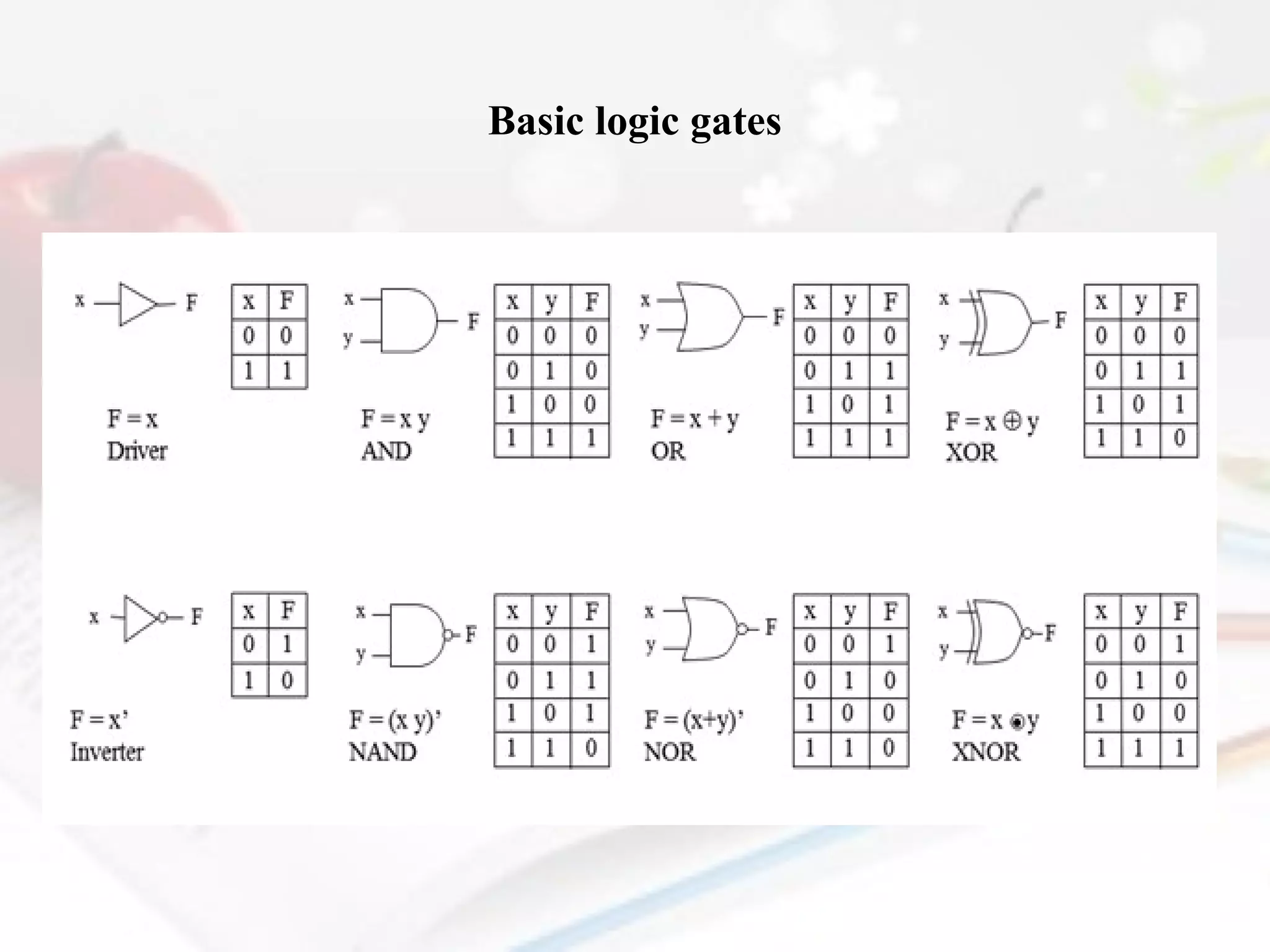
- The document also discusses CMOS transistors, basic logic gates, and the design of combinational and sequential logic circuits.















![Two mark Questions:
State the benefits of custom single purpose processors.
Mention some of the combinational logic gates.
Define combinational logic design.
Mention the advantages and disadvantages in CMOS transistors.
Define the performance metric for throughput and time in embedded system.
[C] Descriptive Questions:
Explain combinational logic.
Differentiate the features of pMOs, CMOS and nMOS transistors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chp04customsinglepurposeprocessors-131222120237-phpapp01/75/Embedded-system-custom-single-purpose-processors-27-2048.jpg)