This document summarizes an ethical hacking seminar that was presented. It discusses the following key points:
- Ethical hacking involves using the same tools and techniques as hackers but in a legal manner to test security vulnerabilities.
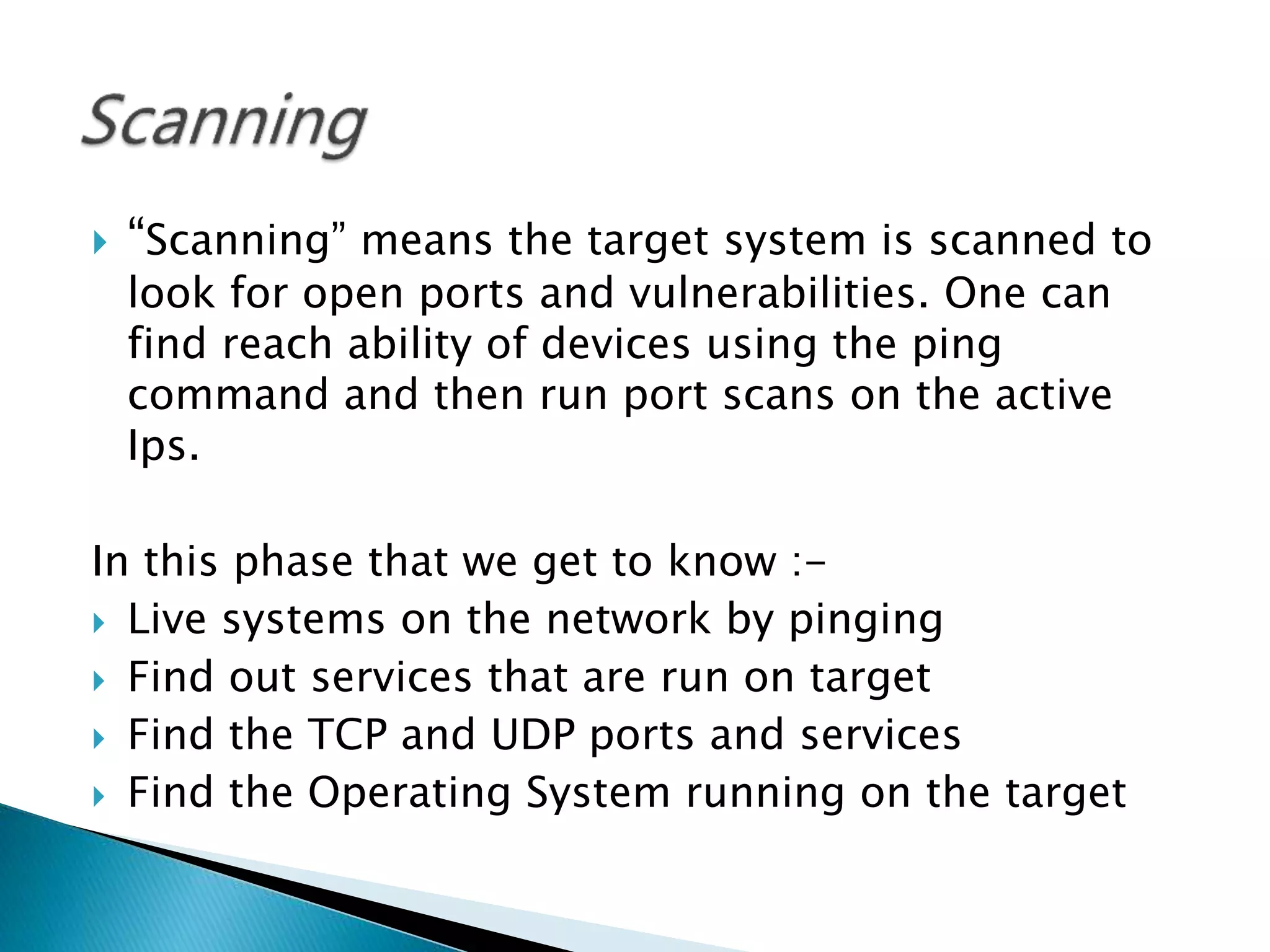
- The hacking process involves footprinting, scanning, gaining access, and maintaining access. Footprinting gathers information, scanning finds open ports and services, and gaining access exploits vulnerabilities.
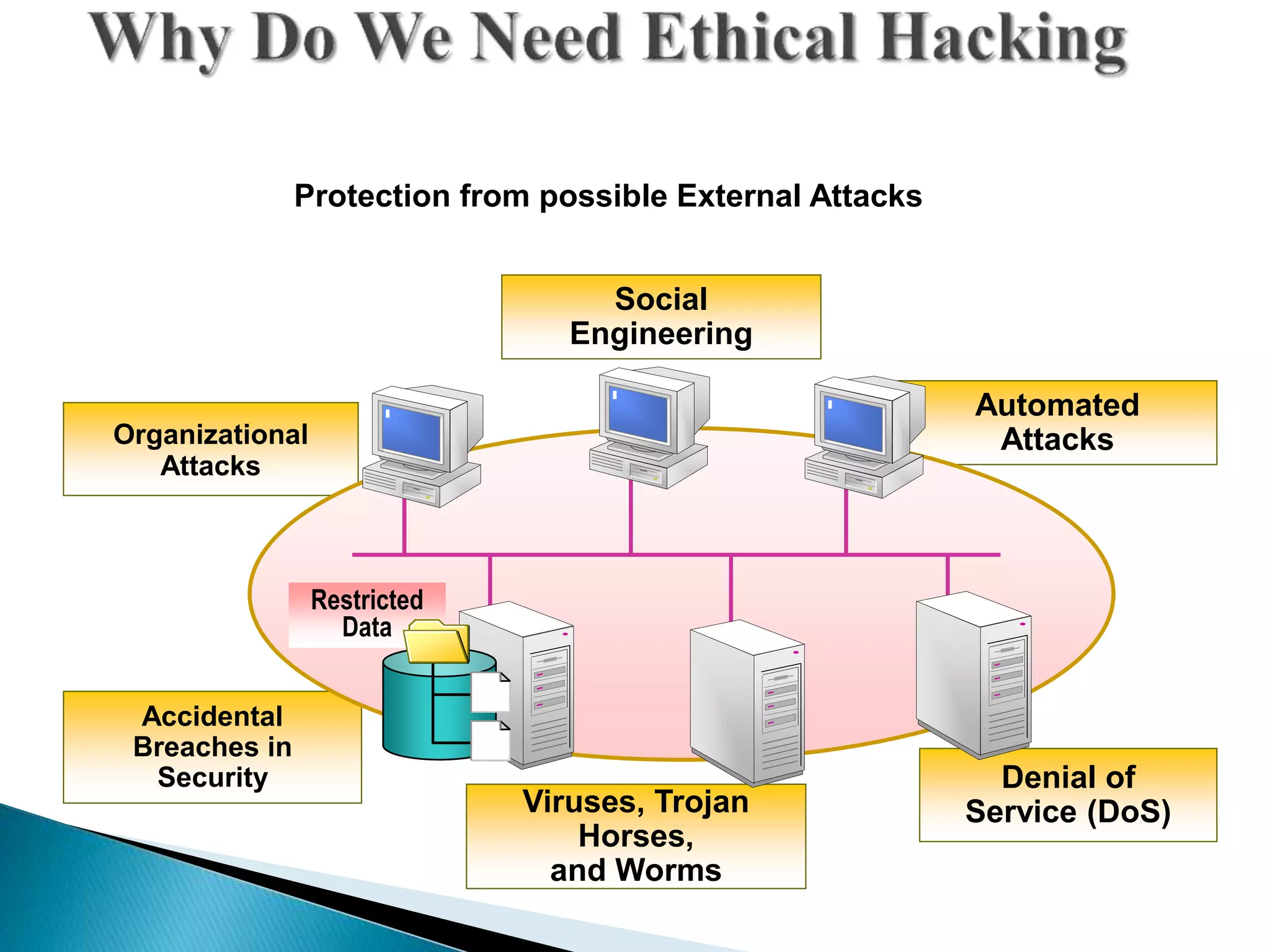
- Ethical hackers are independent security professionals who evaluate systems without damaging them or stealing data. They find vulnerabilities and report them to owners.
- Skills needed for ethical hacking include knowledge of operating systems, firewalls, networking protocols, and project management. Understanding how hackers think is important to catch security