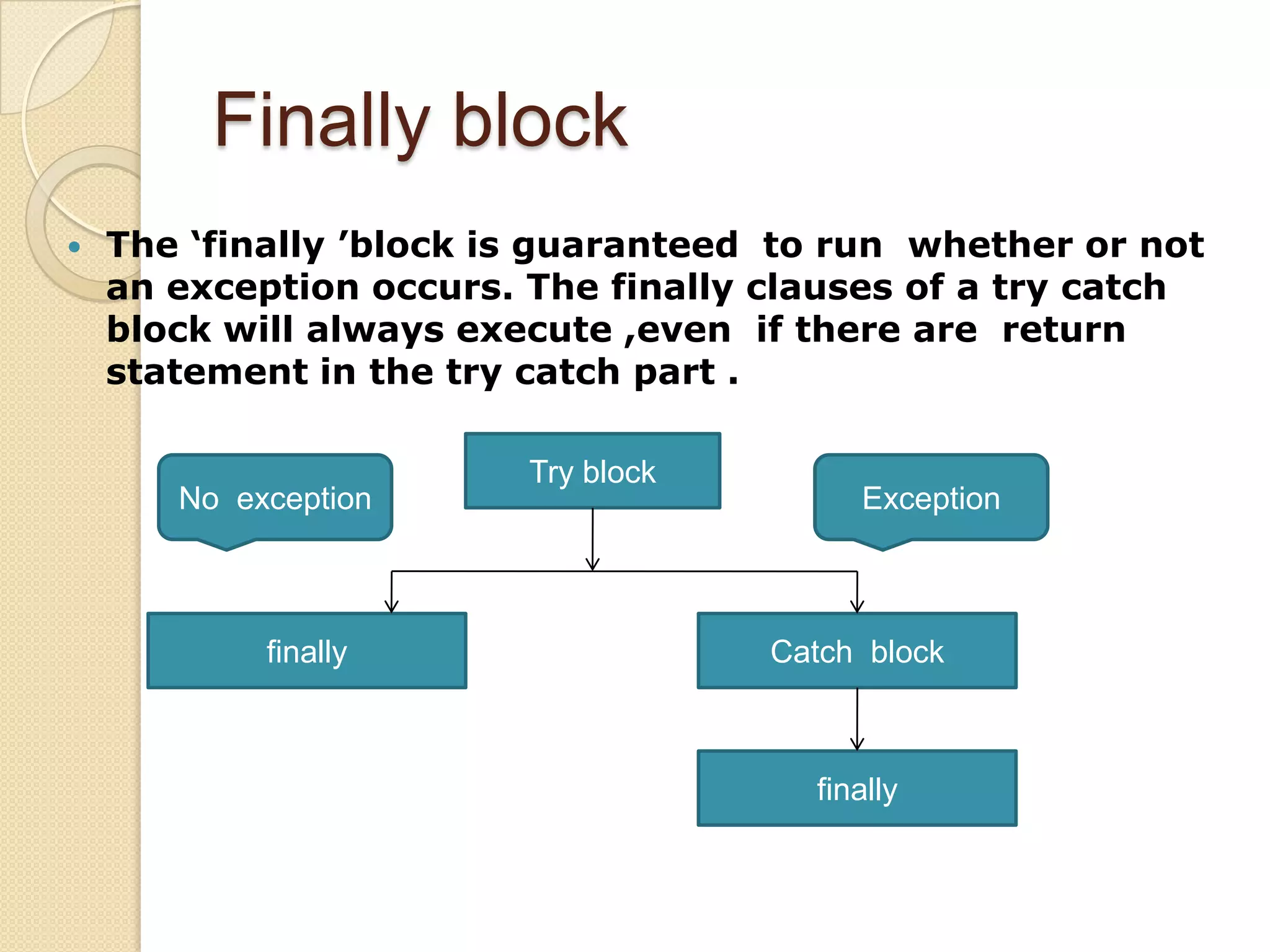
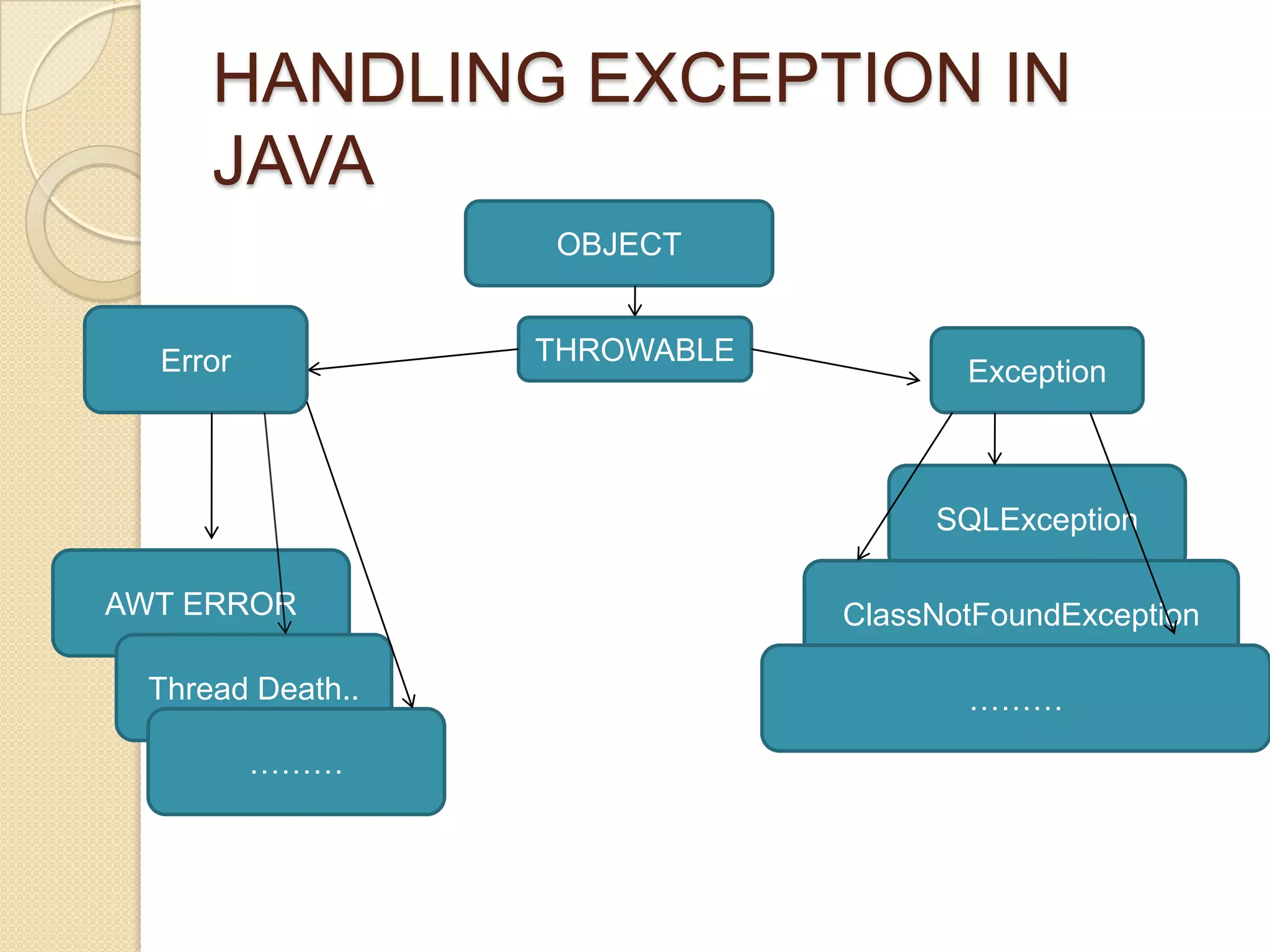
The document discusses exception handling in Java. It defines exceptions as errors encountered during program execution. Exception handling involves using try, catch, and finally blocks. The try block contains code that may throw exceptions. Catch blocks handle specific exception types, while finally blocks contain cleanup code that always executes. Common system-defined exceptions like NullPointerException and user-defined exceptions can be thrown using the throw keyword and handled using try-catch. Nested try-catch blocks and multiple catch blocks are also described.




![System-Defined ExceptionRaised implicitly by system because of illegal execution of program When cannot continue program execution any more Created by Java System automatically Exception extended from Error class and RuntimeException class [DivByZero.java] IndexOutOfBoundsException: When beyond the bound of index in the object which use index, such as array, string, and vector ArrayStoreException : When assign object of incorrect type to element of array NegativeArraySizeException : When using a negative size of array NullPointerException :When refer to object as a null pointerSecurityException : When violate security. Caused by security managerIllegalMonitorStateException : When the thread which is not owner of monitor involves wait or notify method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/233228633874018300205000-100427111019-phpapp01/75/Exception-handling-in-Java-6-2048.jpg)

![Multiple catch blockClass catch22{ public static void main(String args[]) { try { String num=args[0];intnumValue=Interger.parseInt(num);System.out.println(“The squre is ”+numValue*numvalue”); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException e1) {System.out.println(“No argument is given!”); } catch(NumberFormatException e2) { System.out.println(“Not a number “); } }}C:>javac catch22 No argument is given!C:>javac catch22 aNot a numberC:>javac catch22 3The squre is 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/233228633874018300205000-100427111019-phpapp01/75/Exception-handling-in-Java-9-2048.jpg)
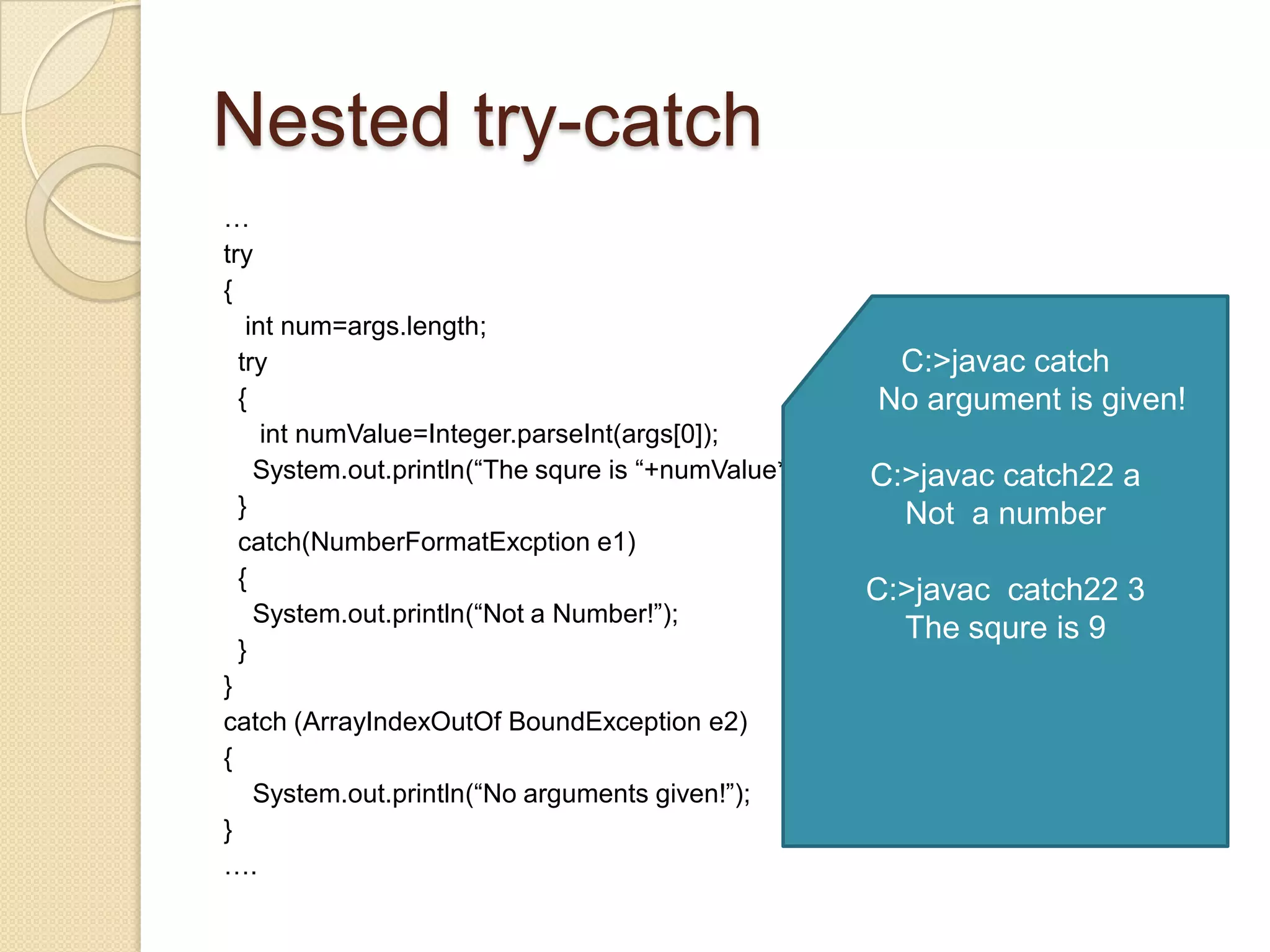
![Nested try-catch …try{int num=args.length; try {intnumValue=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);System.out.println(“The squre is “+numValue*numValue); } catch(NumberFormatExcption e1) {System.out.println(“Not a Number!”); }}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException e2){System.out.println(“No arguments given!”);}….C:>javac catch No argument is given!C:>javac catch22 aNot a numberC:>javac catch22 3The squre is 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/233228633874018300205000-100427111019-phpapp01/75/Exception-handling-in-Java-10-2048.jpg)