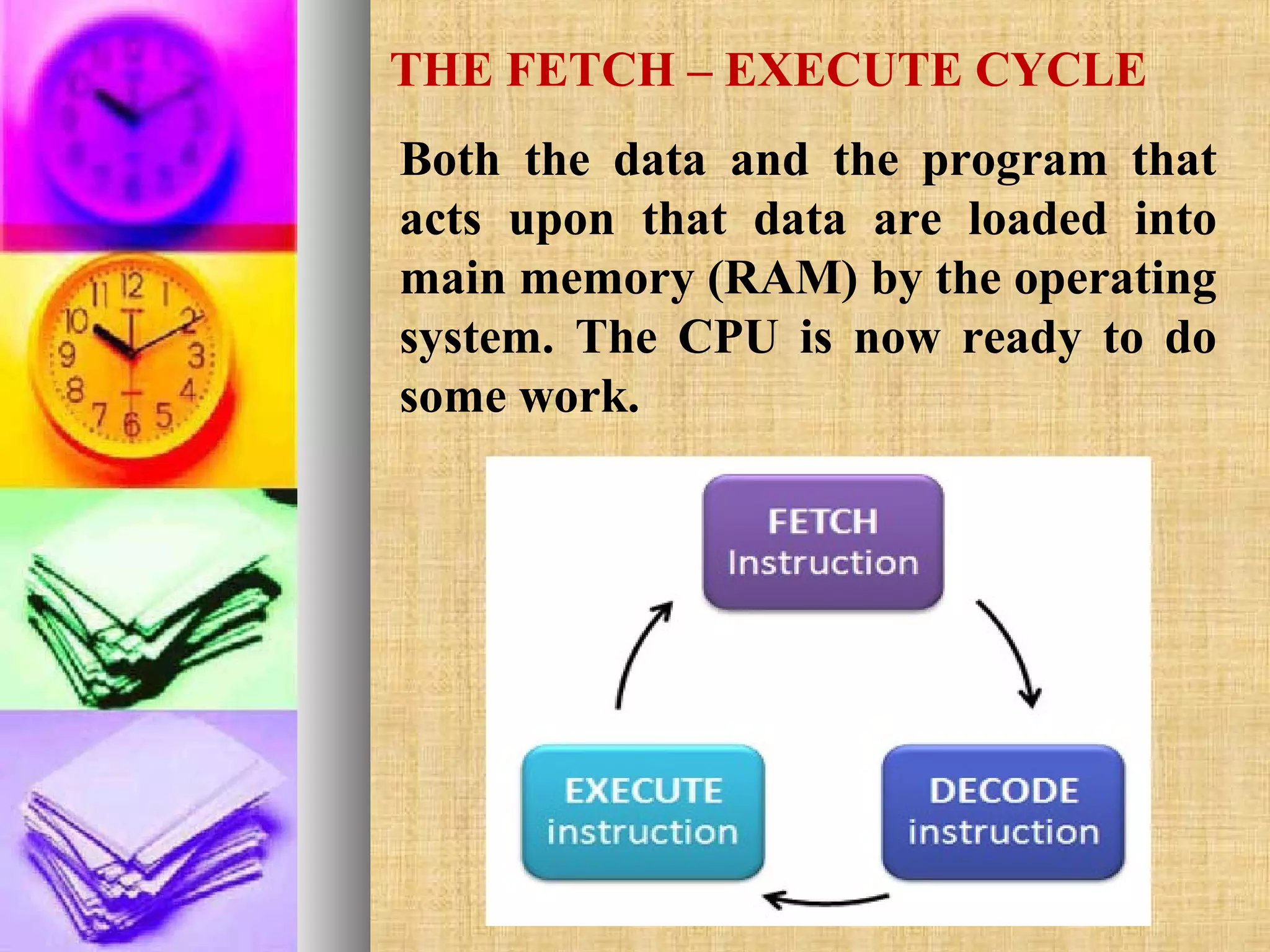
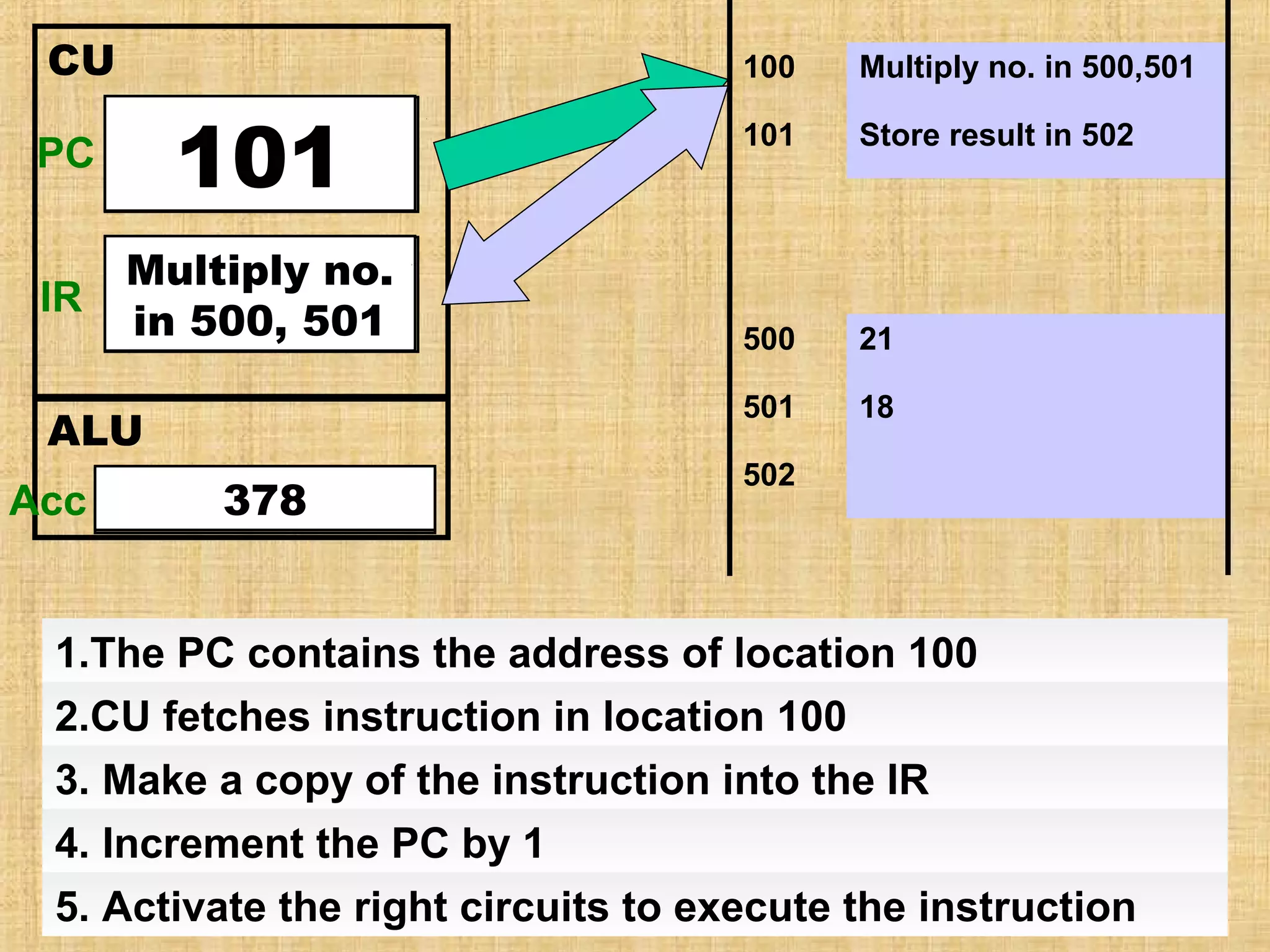
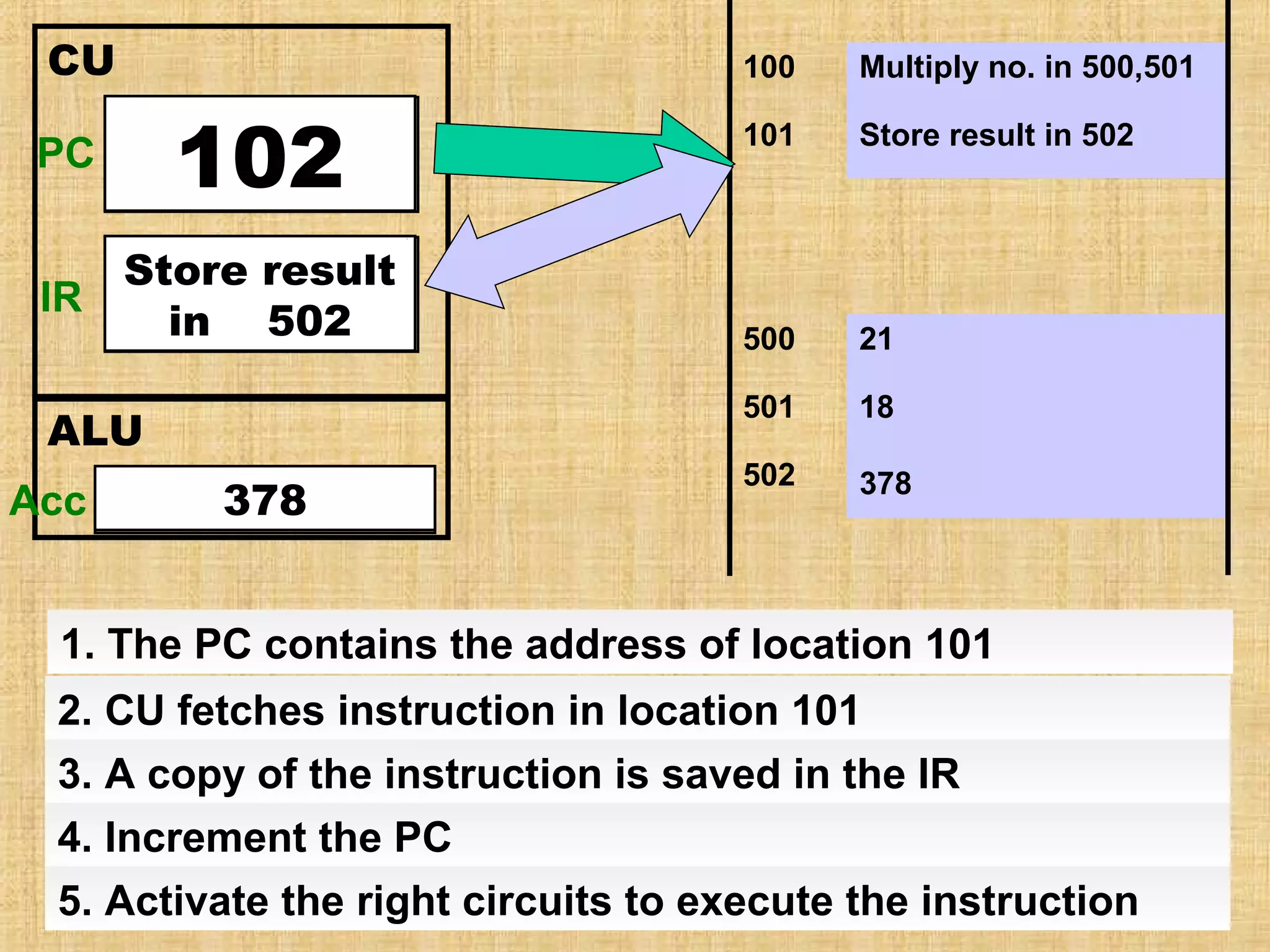
The document describes the fetch-decode-execute cycle of a CPU. It has two main parts: the fetch cycle and the execute cycle. In the fetch cycle, the program counter contains the address of the next instruction to fetch. It is copied to the memory address register to retrieve the instruction from memory and place it in the current instruction register. The program counter is then incremented. In the execute cycle, the instruction is decoded and executed. The processor checks for interrupts and repeats the cycle billions of times per second.