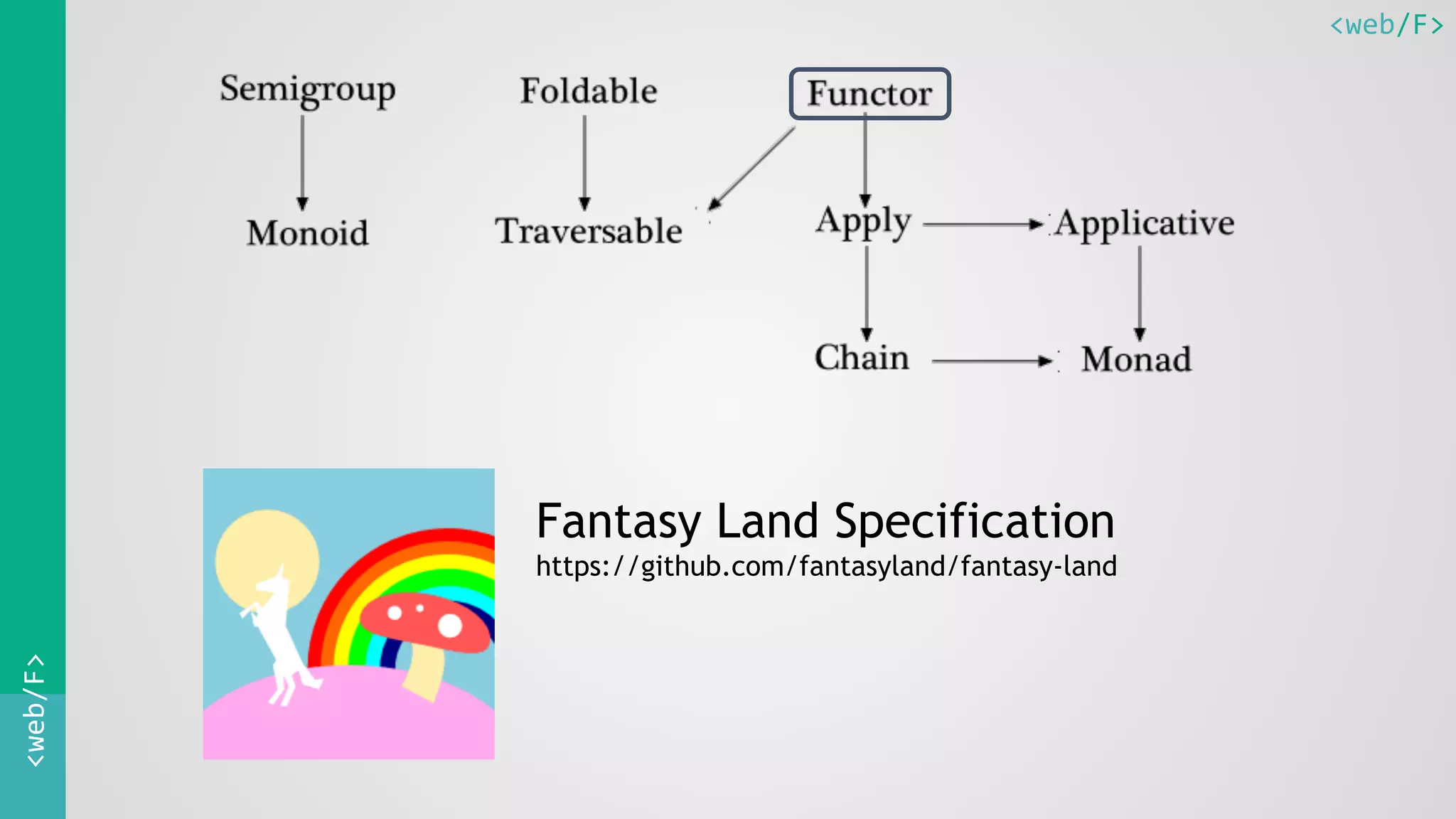
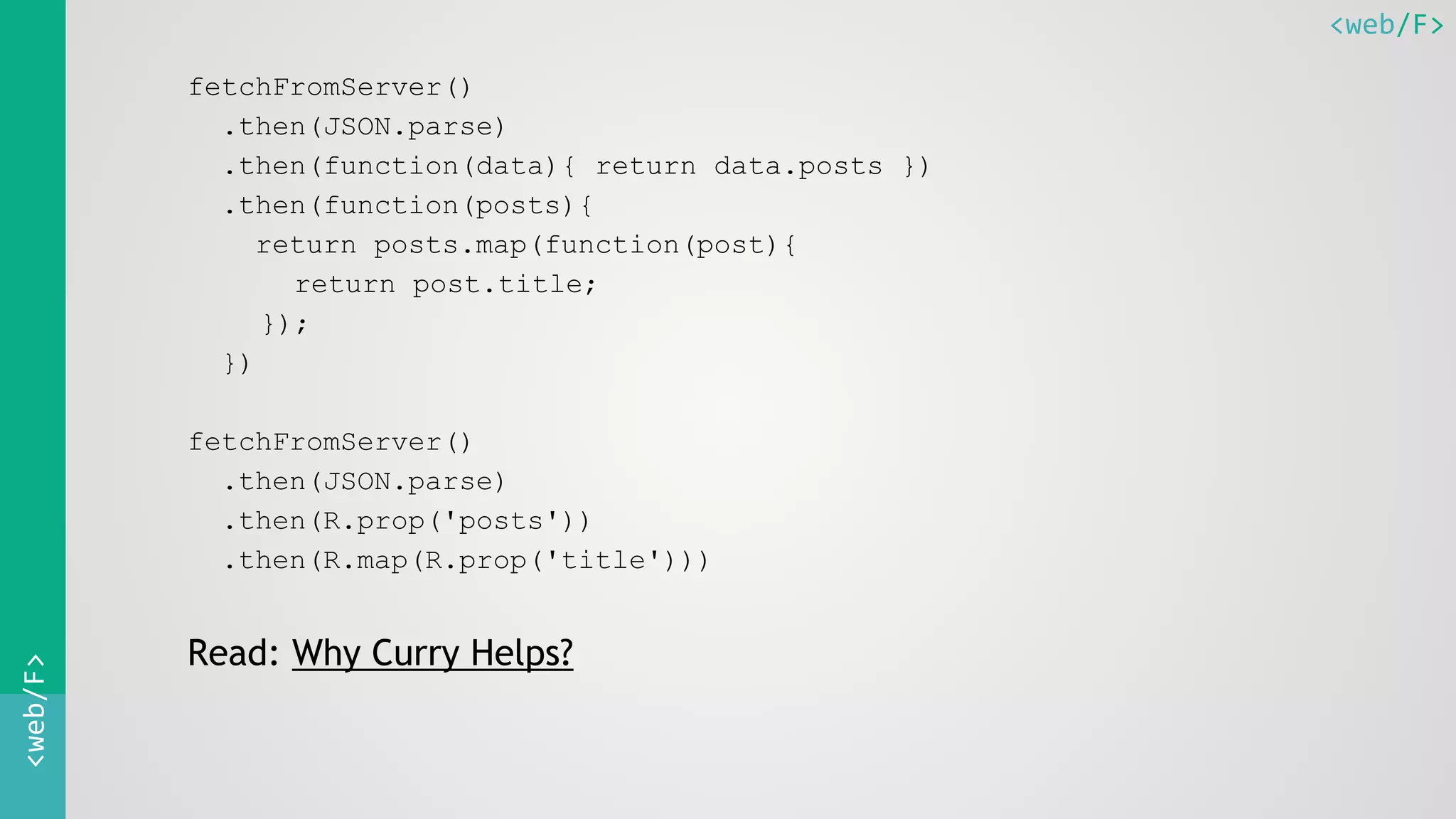
This document discusses functional programming with JavaScript. It begins with an introduction to functions and functional programming. It then covers topics like first-class functions, higher-order functions, function composition, currying, and partial application. It also discusses common functional utilities like map, filter, and reduce. The document emphasizes writing pure and simple functions and gluing them together with other functions. It provides examples of functional programming patterns in JavaScript and recommends libraries like Ramda.js that facilitate a functional style.









![<web/F><web/F>
Example: Searching a list
Declarative
var nameEquals = R.compose(
R.match(new RegExp(value, 'i')), R.prop('name')
);
var filtered = R.filter(nameEquals, list);
Imperative
var filtered = [], i = 0, pattern = new RegExp(value, 'i');
for (i = 0; i < list.length; i += 1) {
if (list[i].name.match(pattern)) filtered.push(list[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-150811175029-lva1-app6891/75/Functional-Programming-with-JavaScript-11-2048.jpg)


![<web/F><web/F>
If the input and output collections are always
going to be same length, you probably need map.
var double = (x) => x * 2;
R.map(double, [1, 2, 3]); //=> [2, 4, 6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-150811175029-lva1-app6891/75/Functional-Programming-with-JavaScript-14-2048.jpg)
![<web/F><web/F>
If the output collection can have lesser or equal
number of items, you probably need filter.
var isEven = (n) => n % 2 === 0;
R.filter(isEven, [1, 2, 3, 4]); //=> [2, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-150811175029-lva1-app6891/75/Functional-Programming-with-JavaScript-15-2048.jpg)
![<web/F><web/F>
You probably need reduce when the input is a
collection and the output is a single value.
Reduce is also known as fold.
R.reduce(R.add, 0, [1, 2, 3]); //=> 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-150811175029-lva1-app6891/75/Functional-Programming-with-JavaScript-16-2048.jpg)

![<web/F><web/F>
Example: Given an array of objects, get only the
‘name’ property values in an array.
R.map(R.prop('a'), [{a: 1}, {a: 2}]);
// pluck :: k -> [{k: v}] -> v
R.pluck('a', [{a: 1}, {a: 2}]); //=> [1, 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-150811175029-lva1-app6891/75/Functional-Programming-with-JavaScript-18-2048.jpg)




















![<web/F><web/F>
Functional null checking
if (x !== null && x !== undefined) {
f(x);
}
R.map(addOne, Maybe(2)); //=> Maybe(3)
R.map(addOne, [2]) //=> [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-150811175029-lva1-app6891/75/Functional-Programming-with-JavaScript-41-2048.jpg)