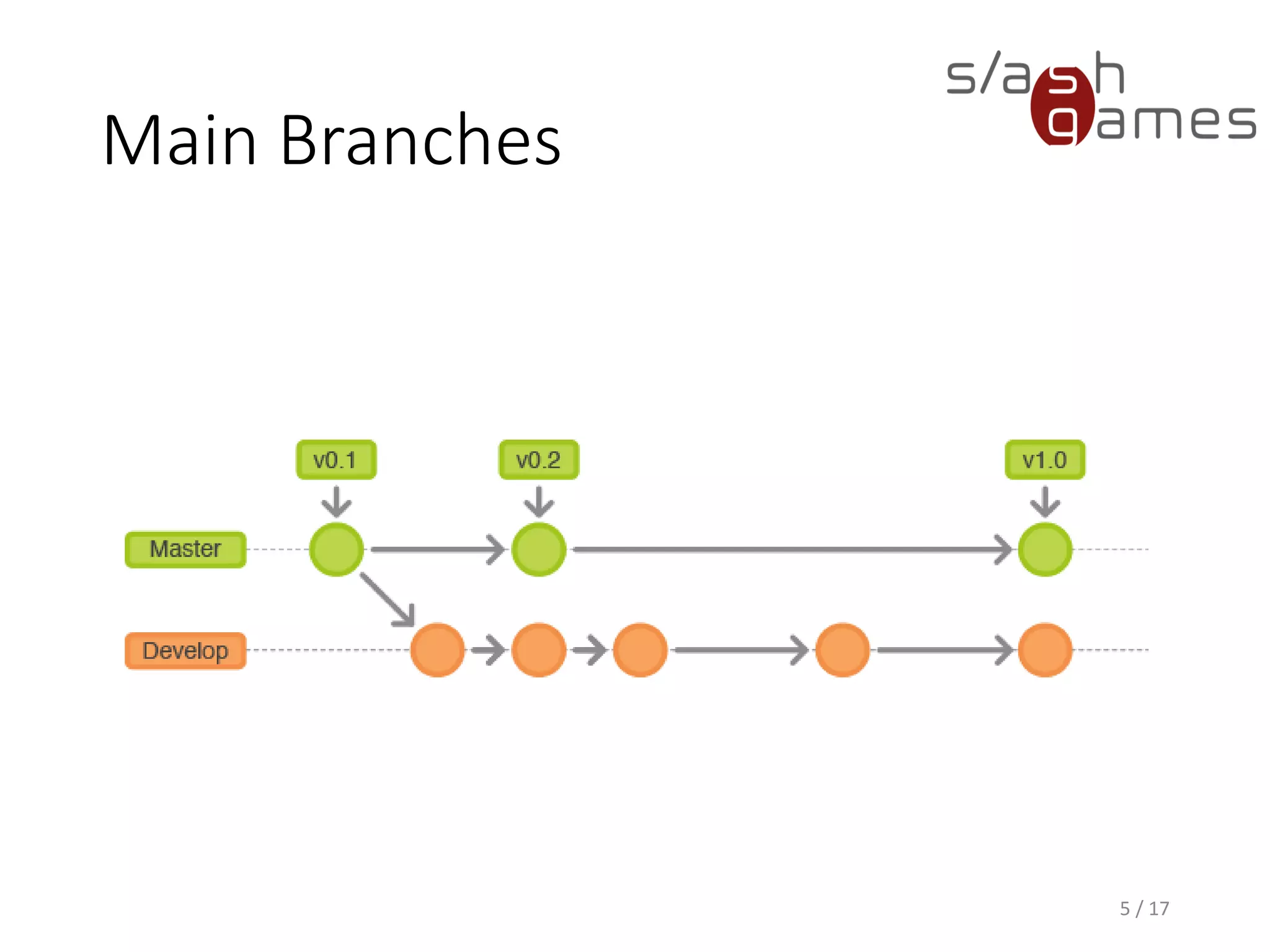
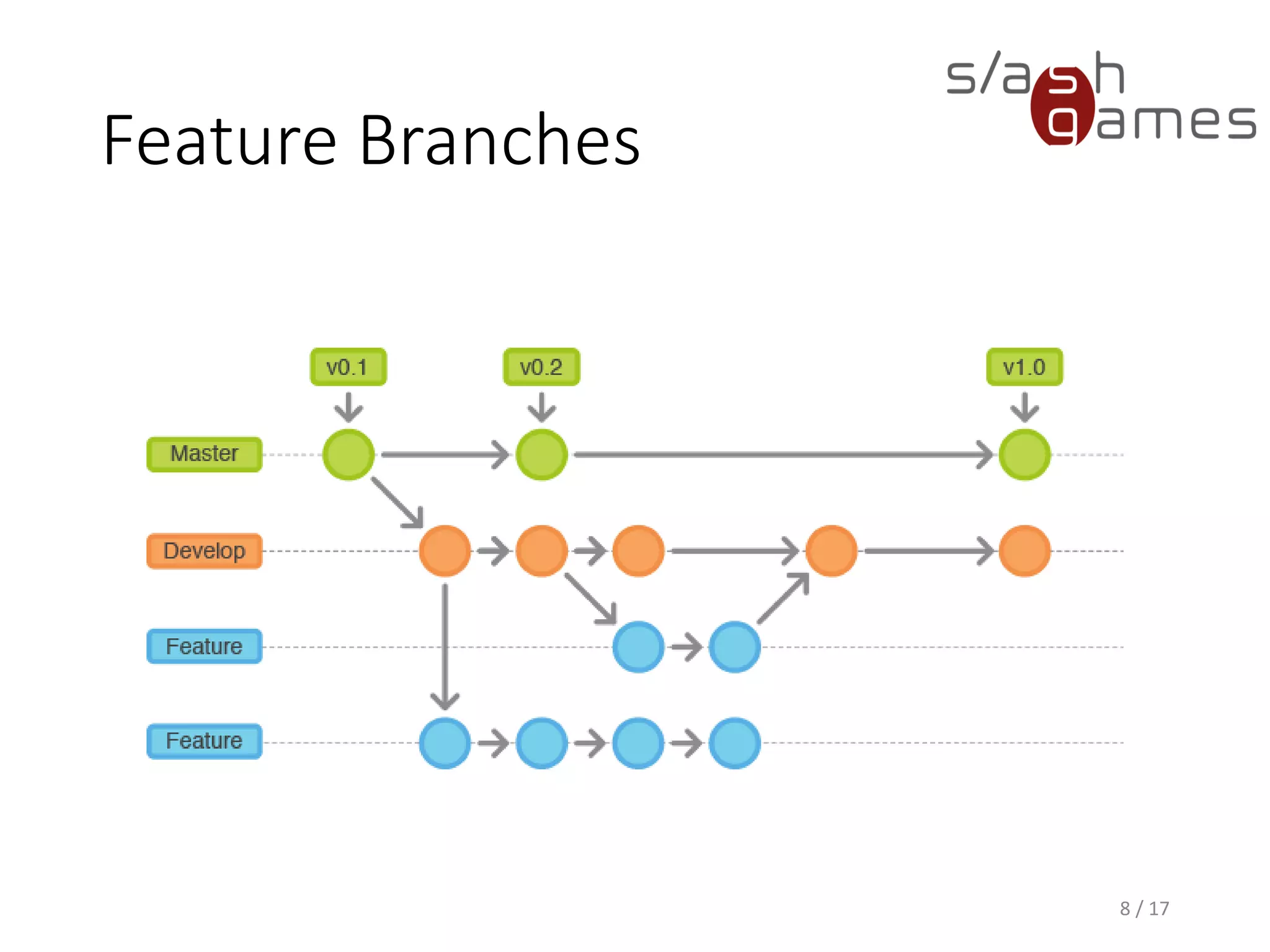
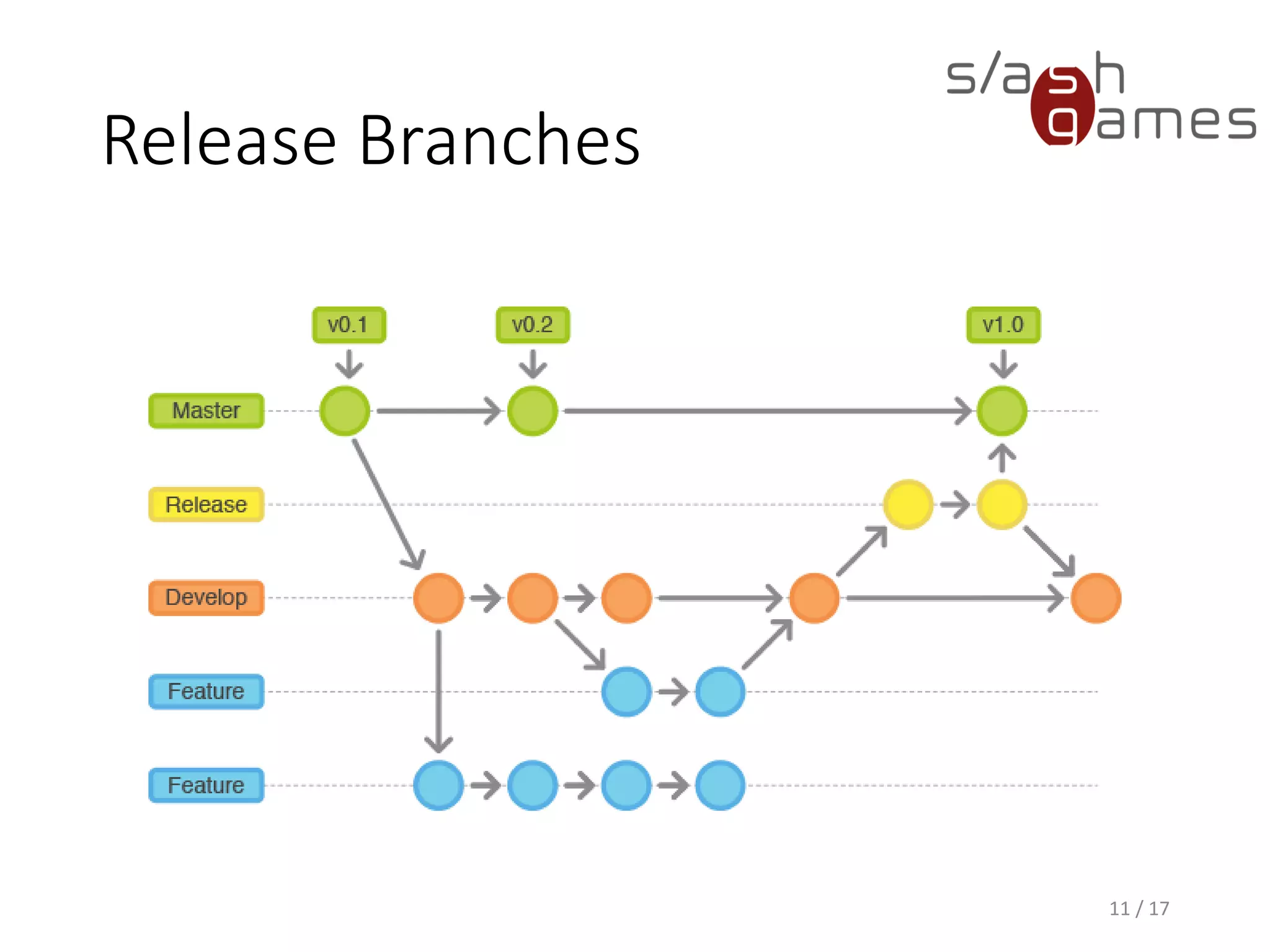
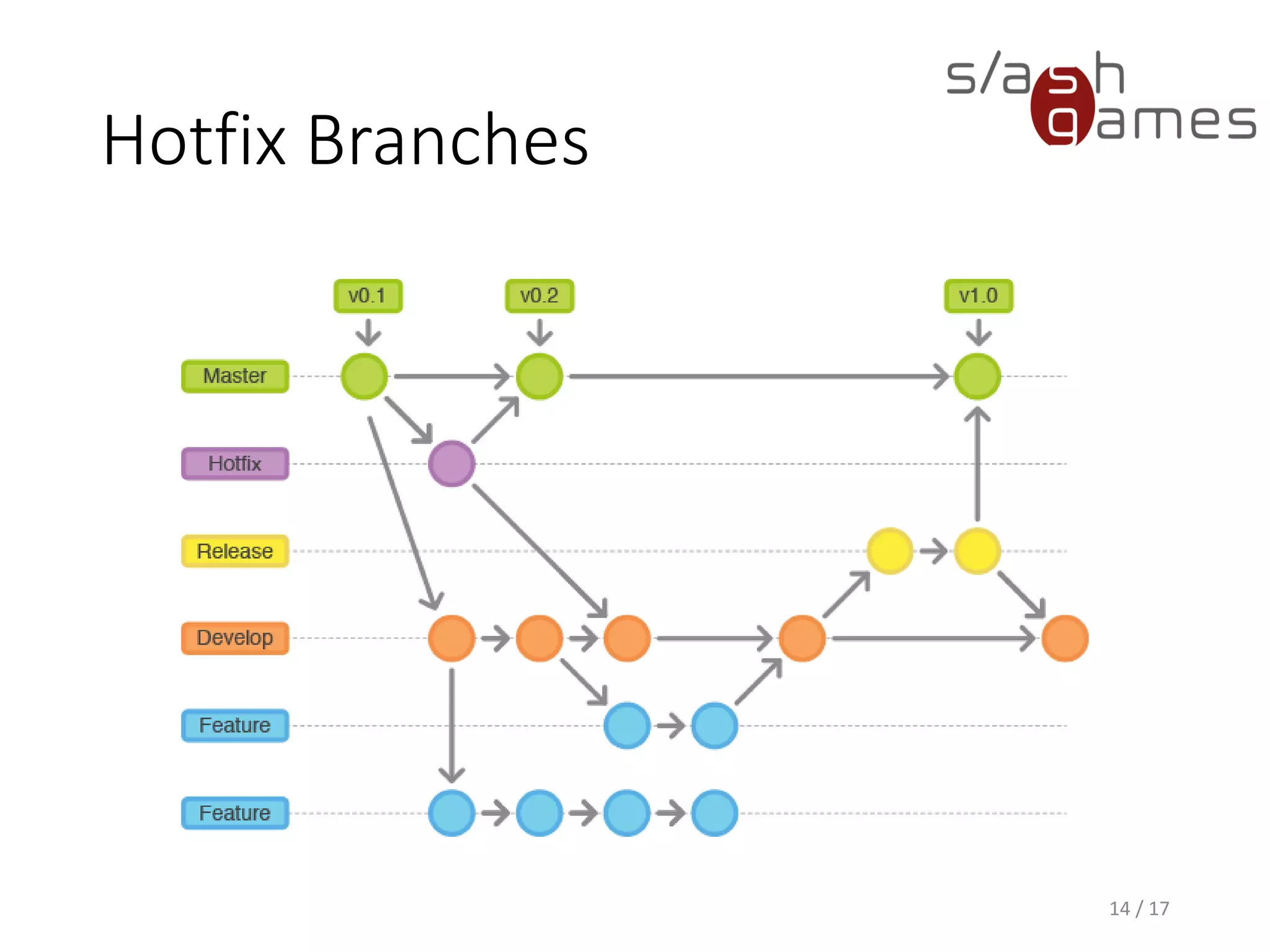
The document outlines the Git Flow methodology for game programming, emphasizing the management of separate branches for features, releases, and hotfixes to streamline collaborative development. It describes the roles of main branches, such as 'master' and 'develop', and the purpose of supporting branches like feature, release, and hotfix branches. Key practices include merging strategies and maintaining clear workflows to facilitate efficient development and integration.