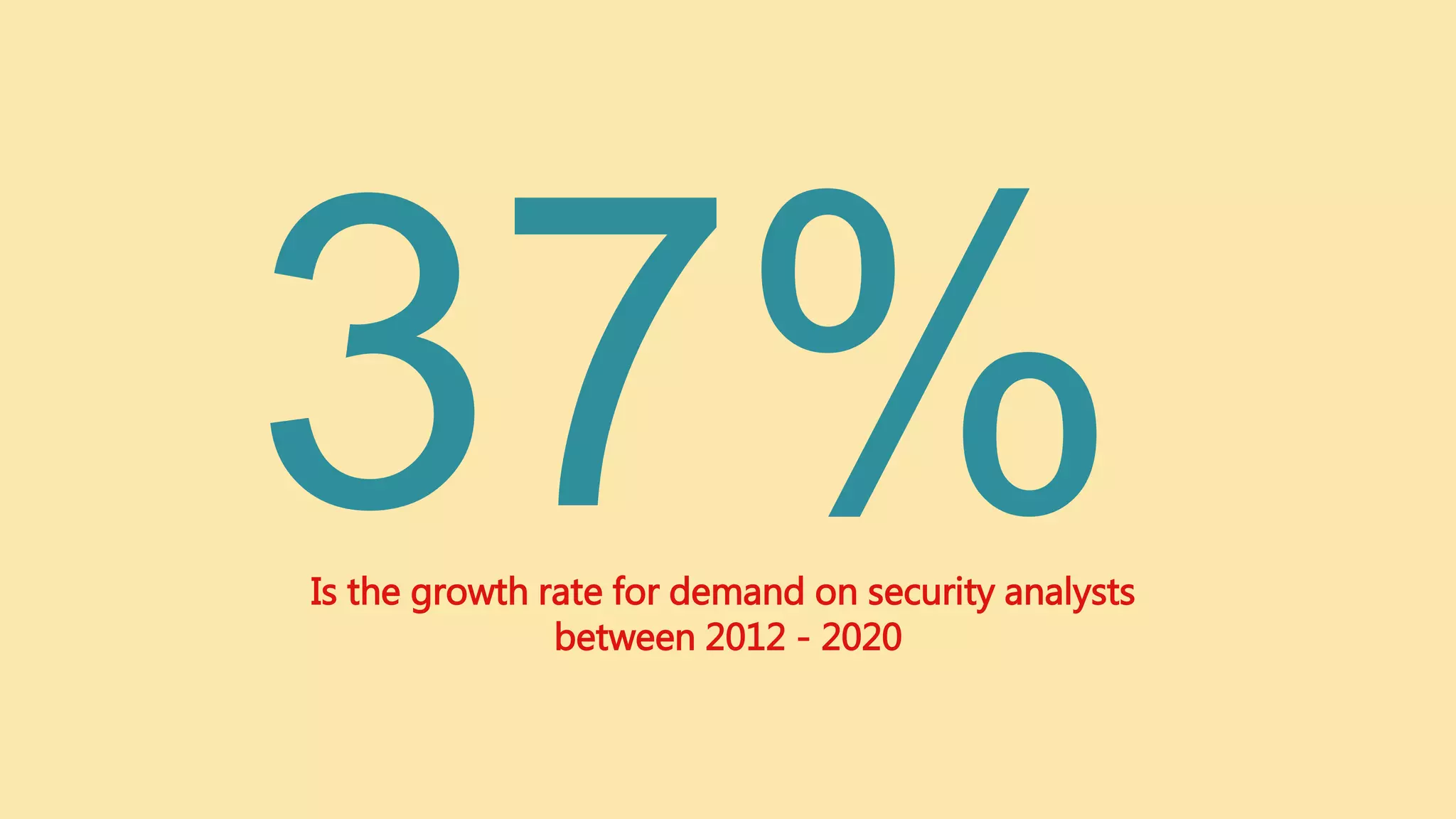
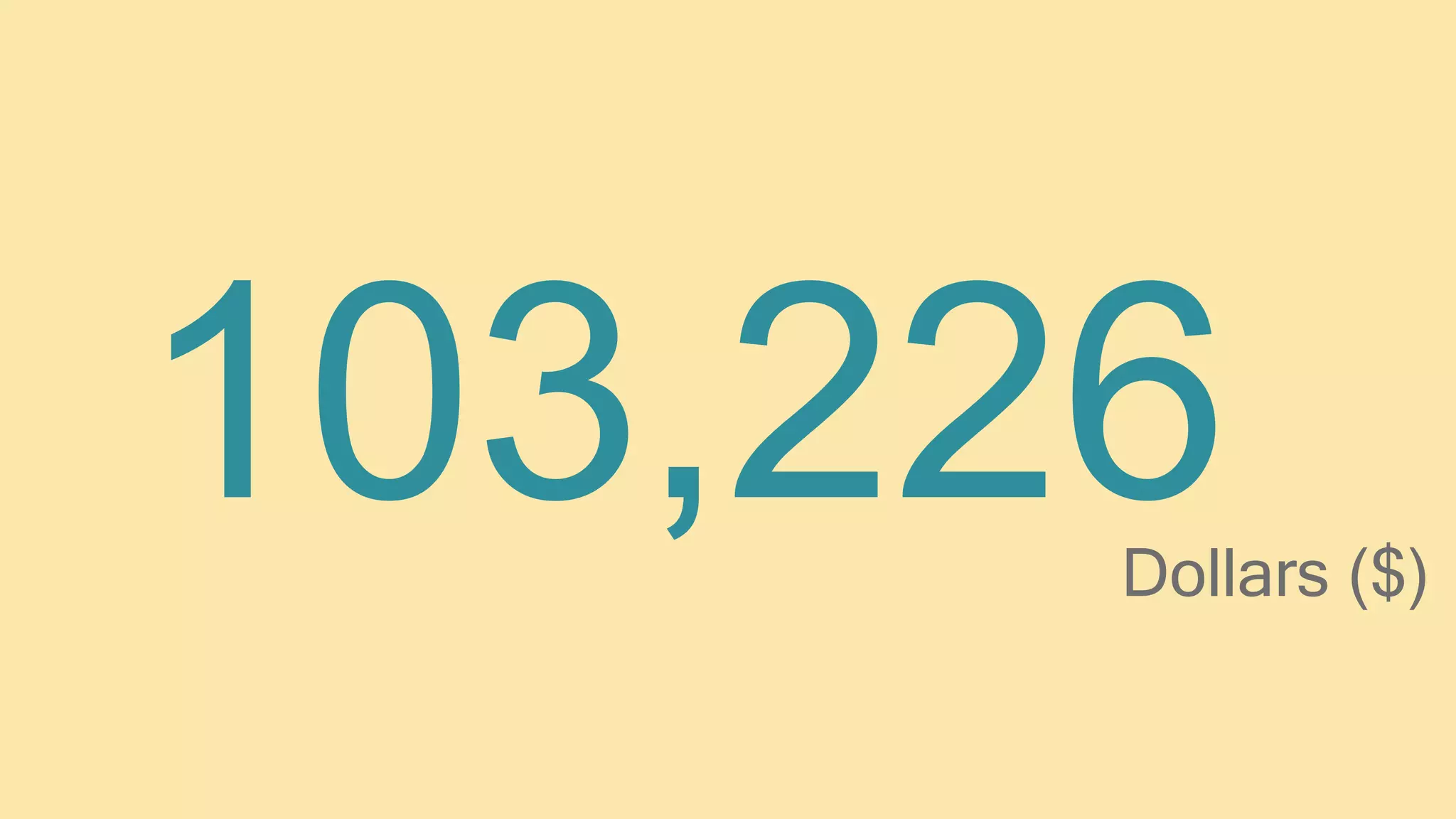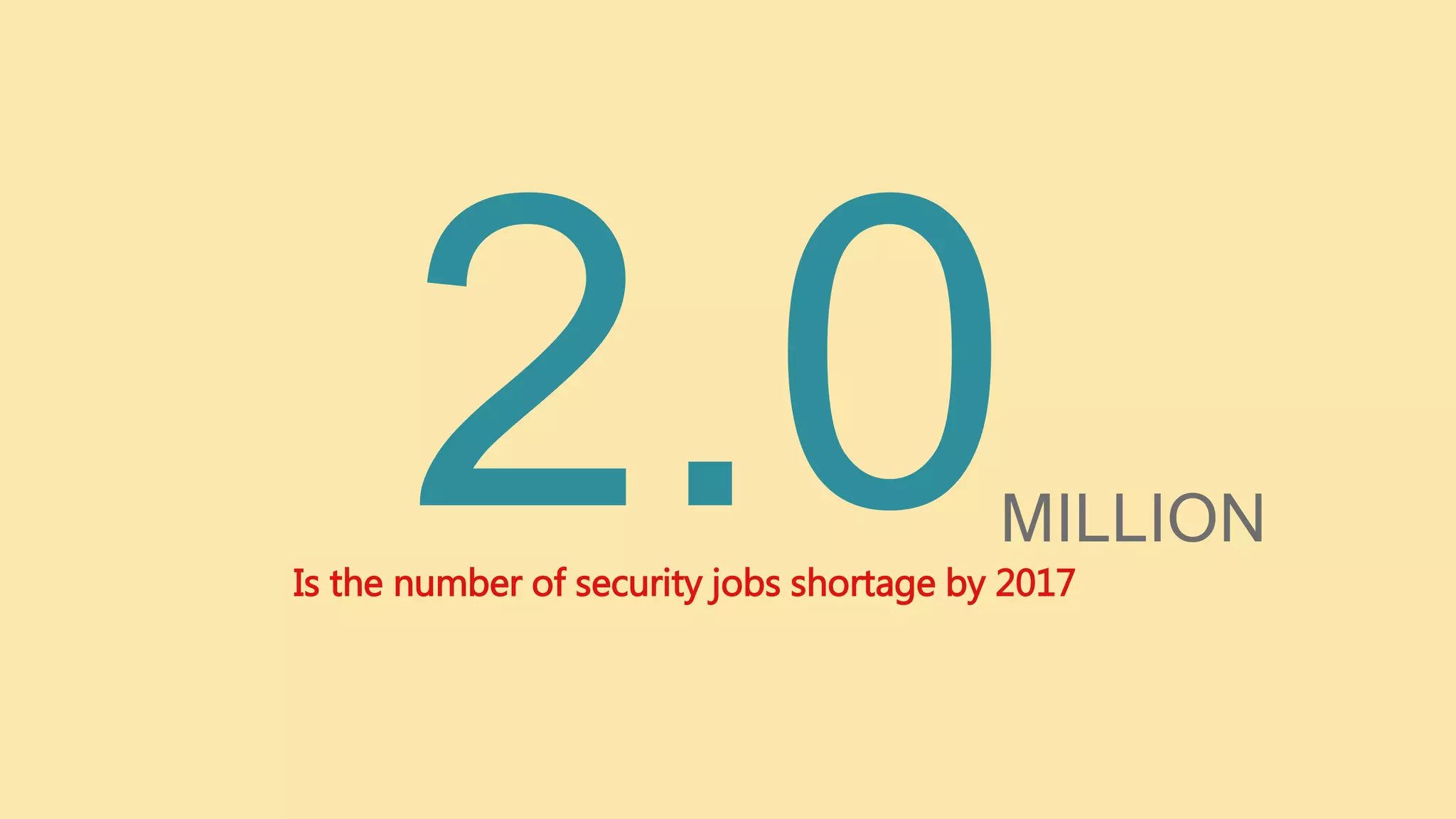The document outlines the current state of information security, highlighting a significant demand for qualified professionals amid a growing skills shortage in cybersecurity. It details various roles in the field, such as security analysts, penetration testers, and security auditors, along with the essential skills and knowledge required for each position. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of risk analysis, compliance assessments, and the necessity for organizations to bolster their security measures against anticipated attacks.