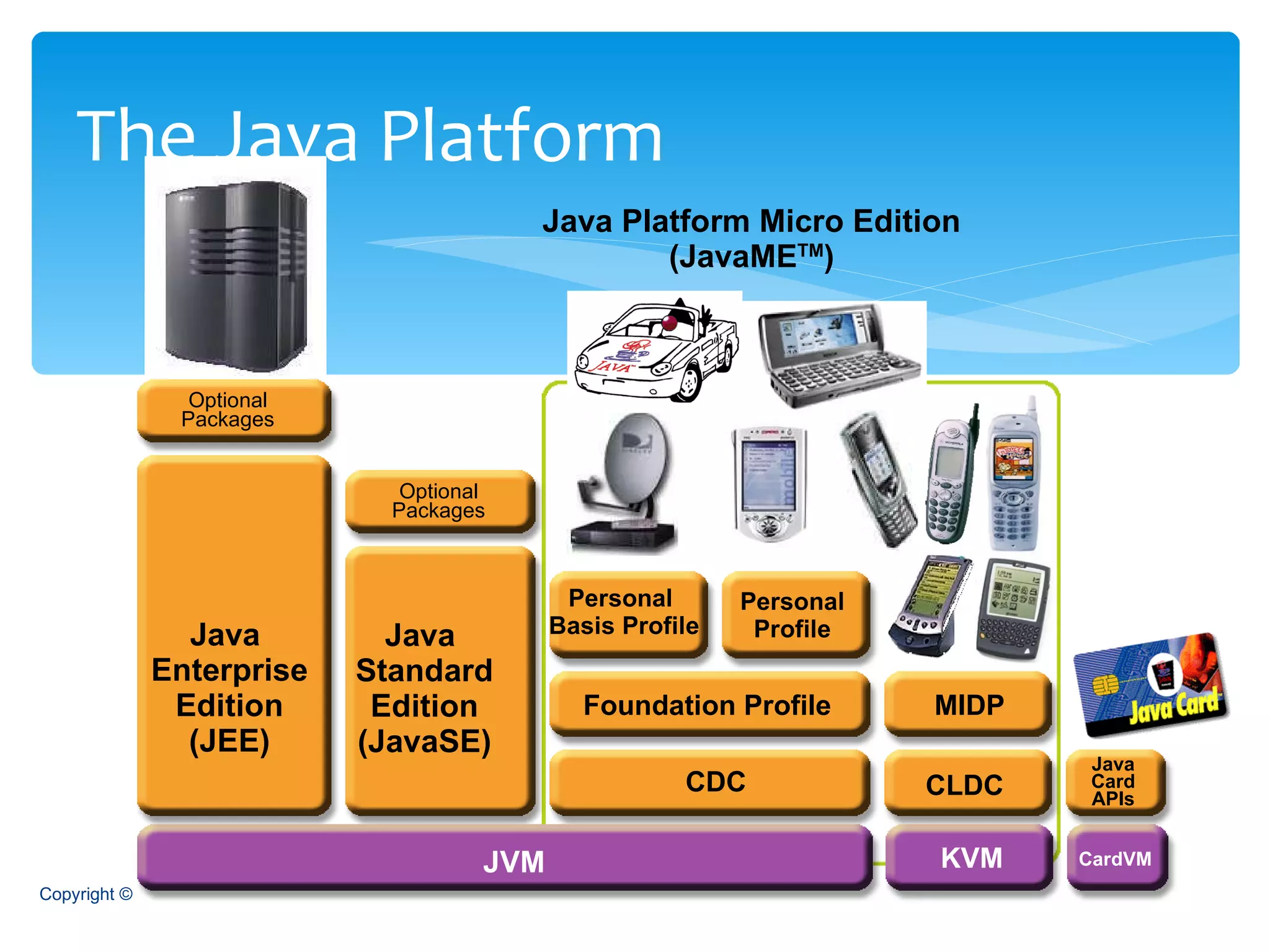
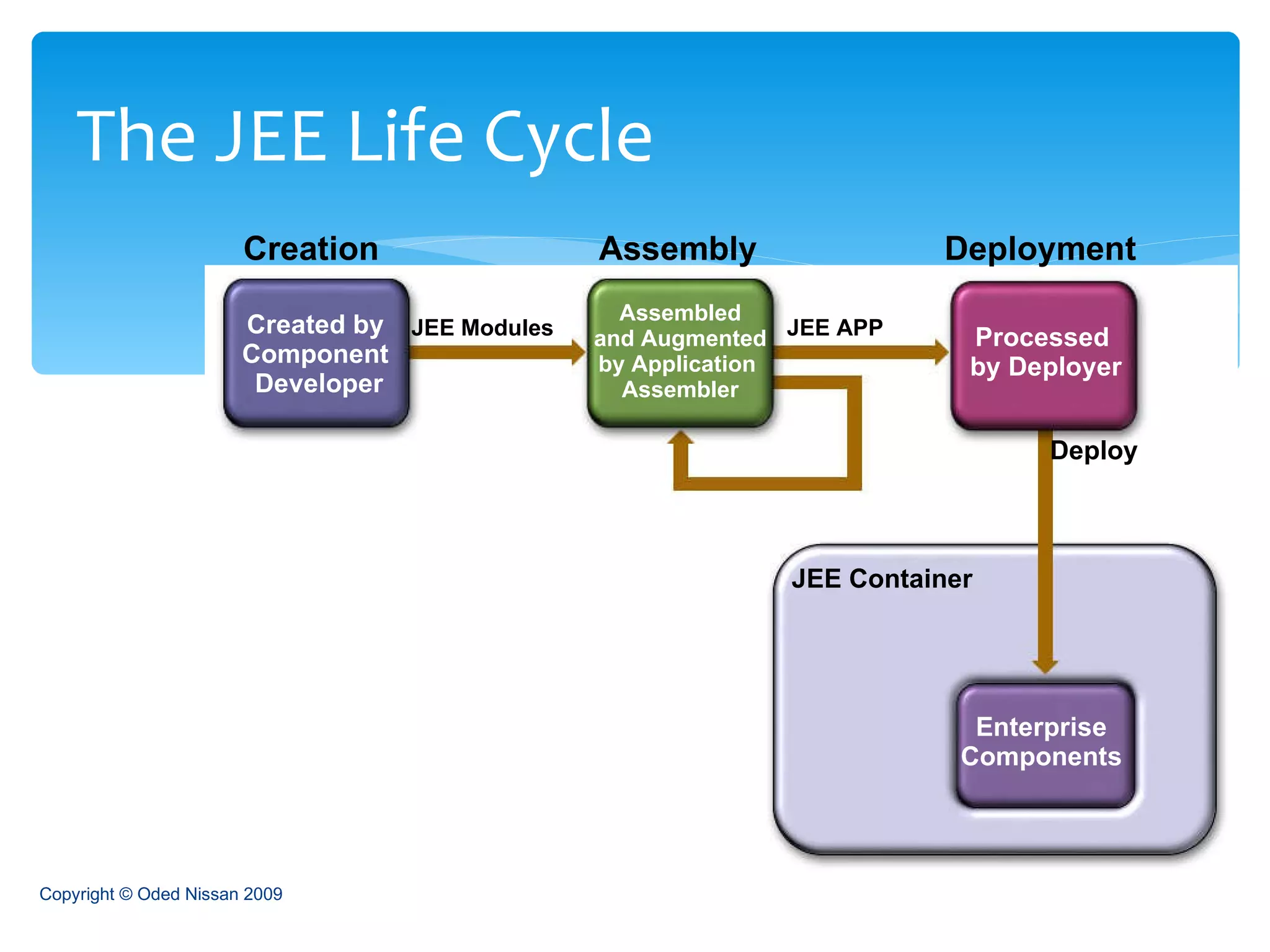
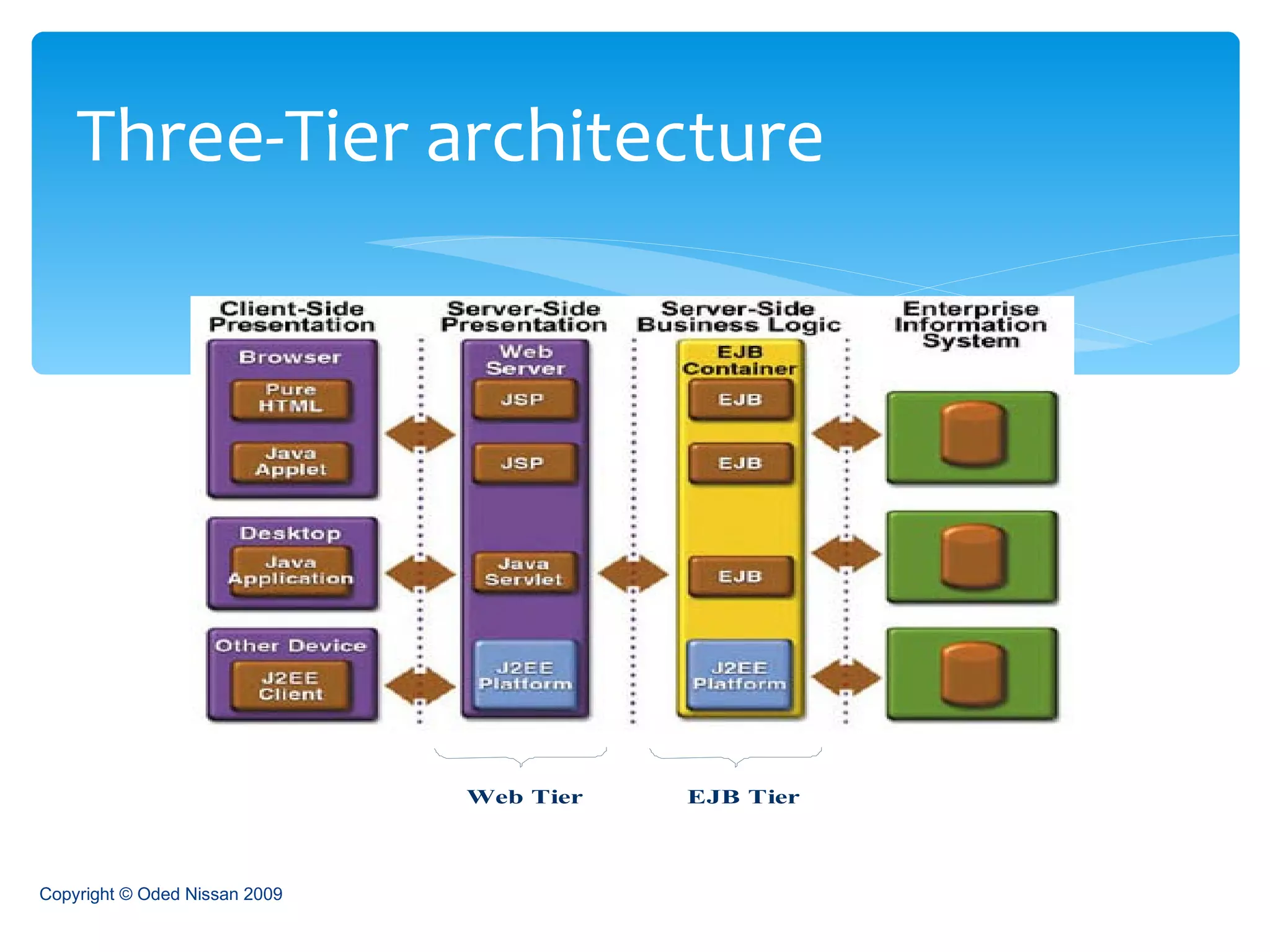
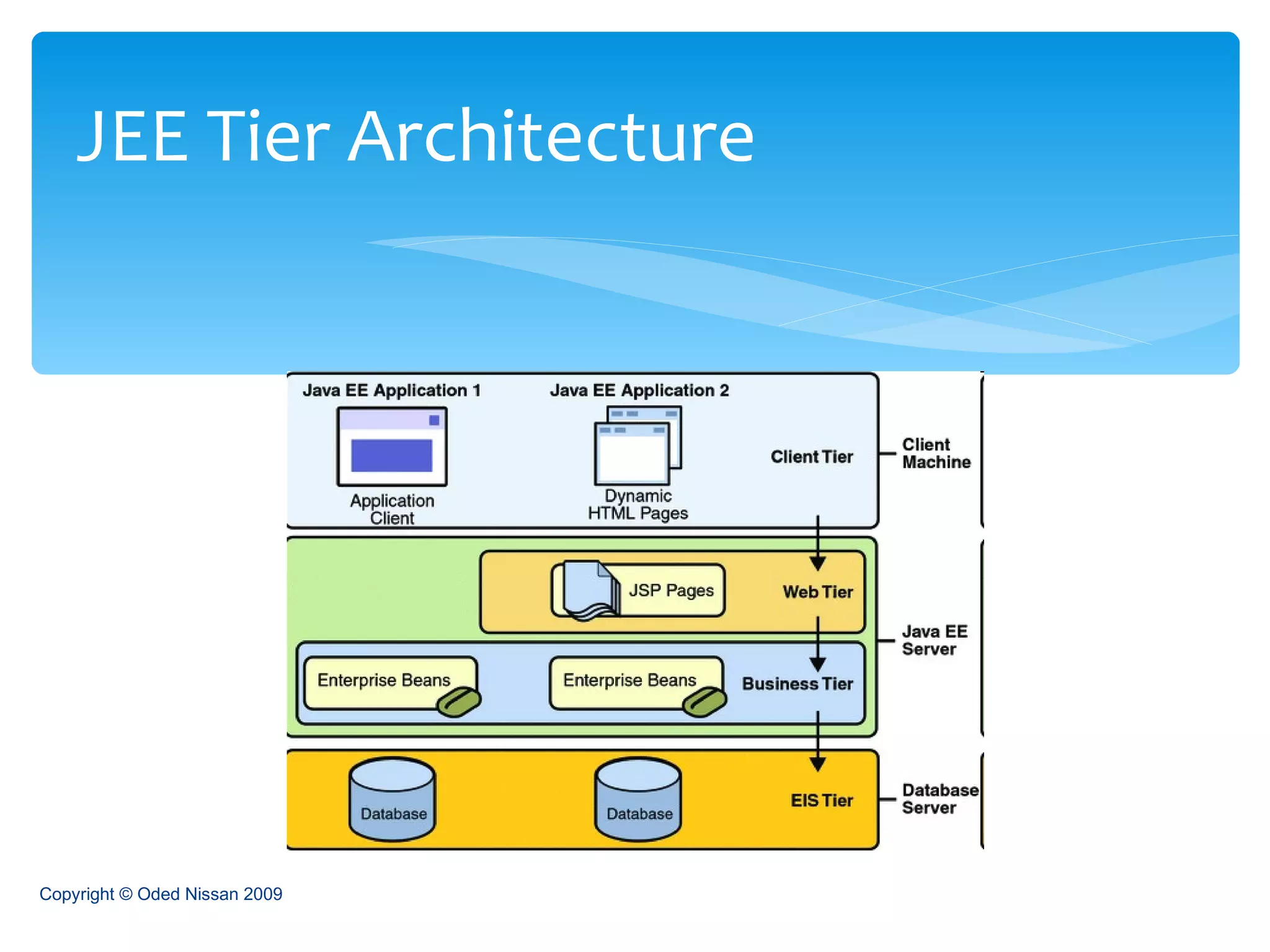
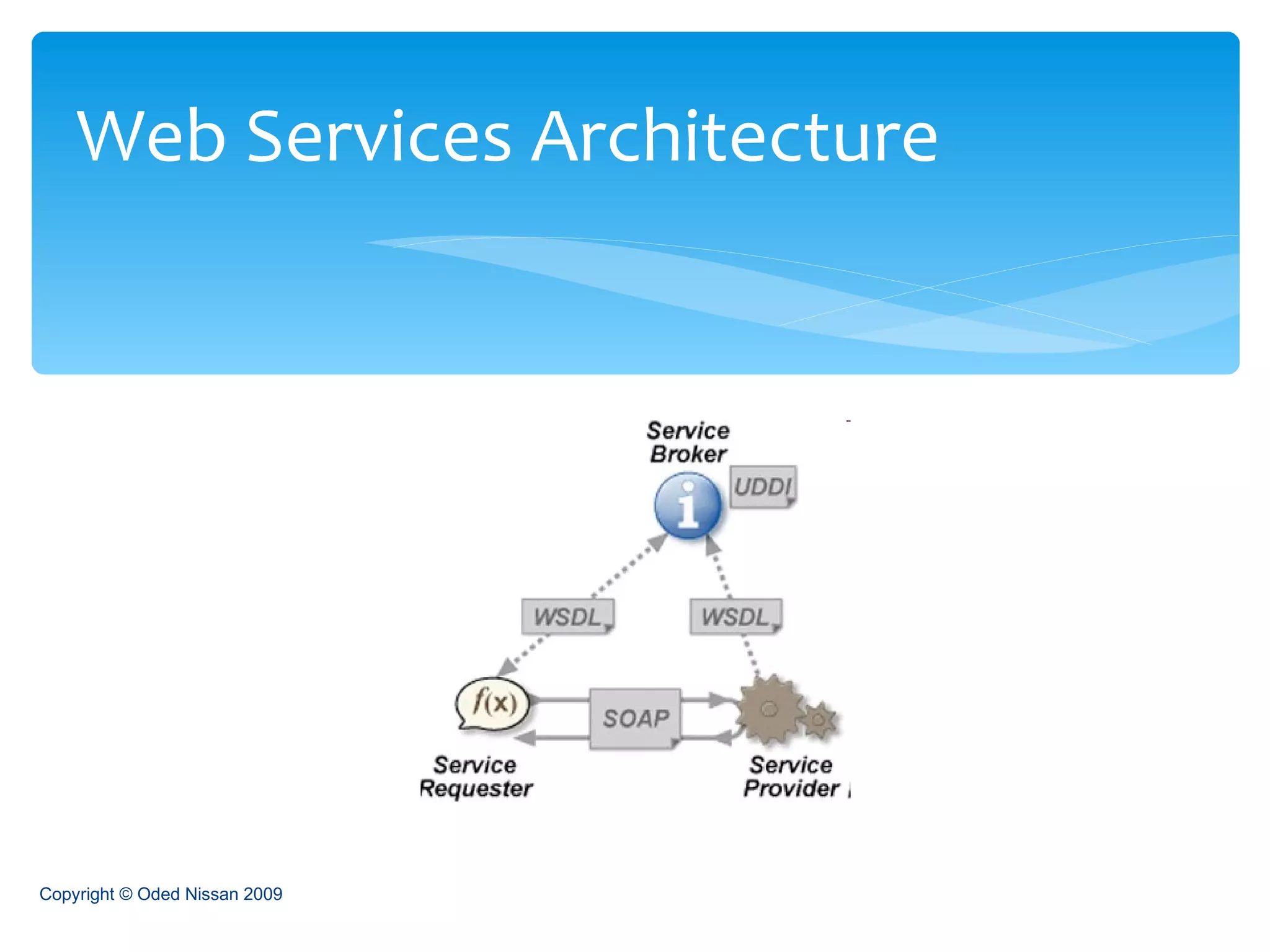
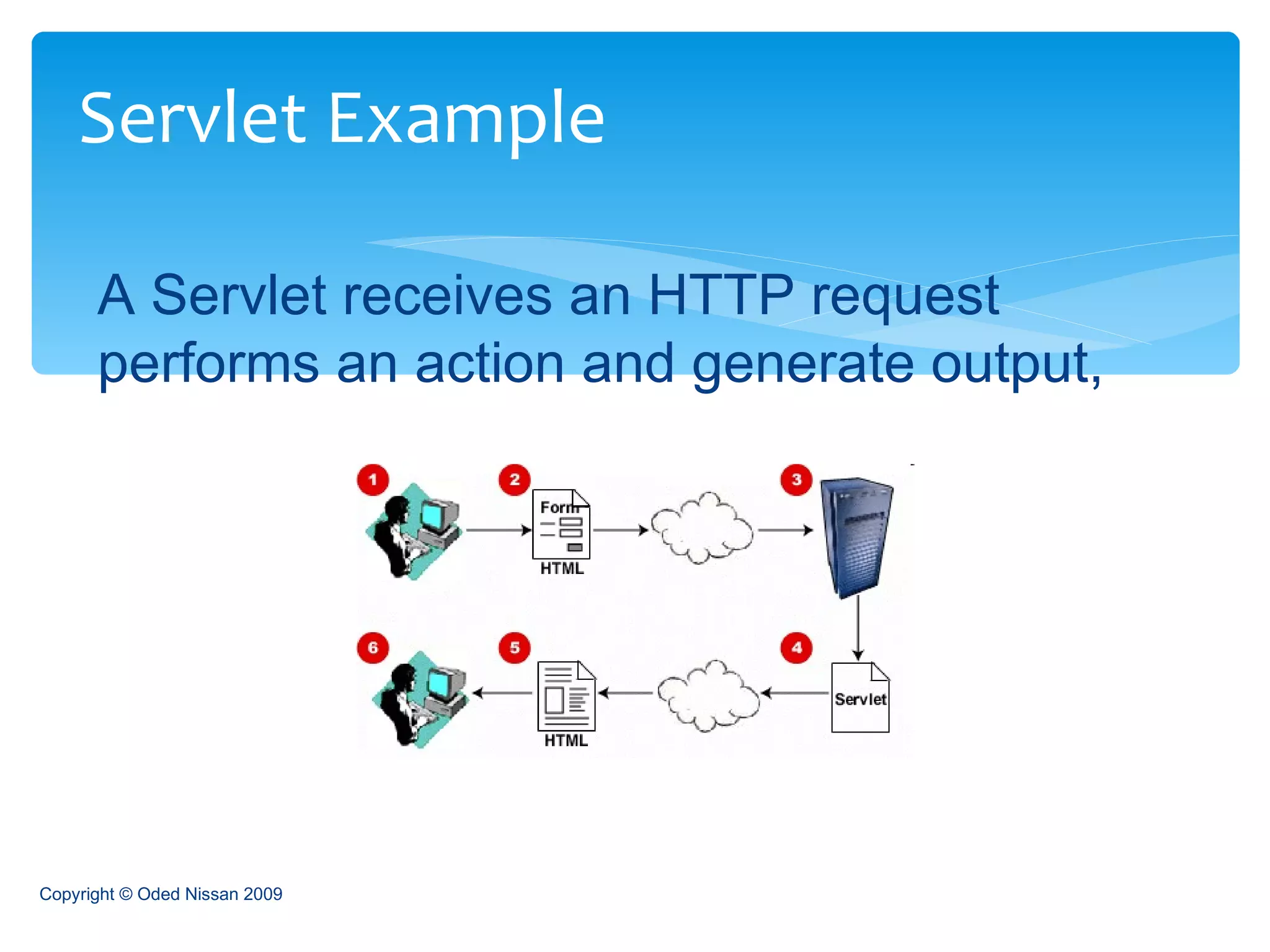
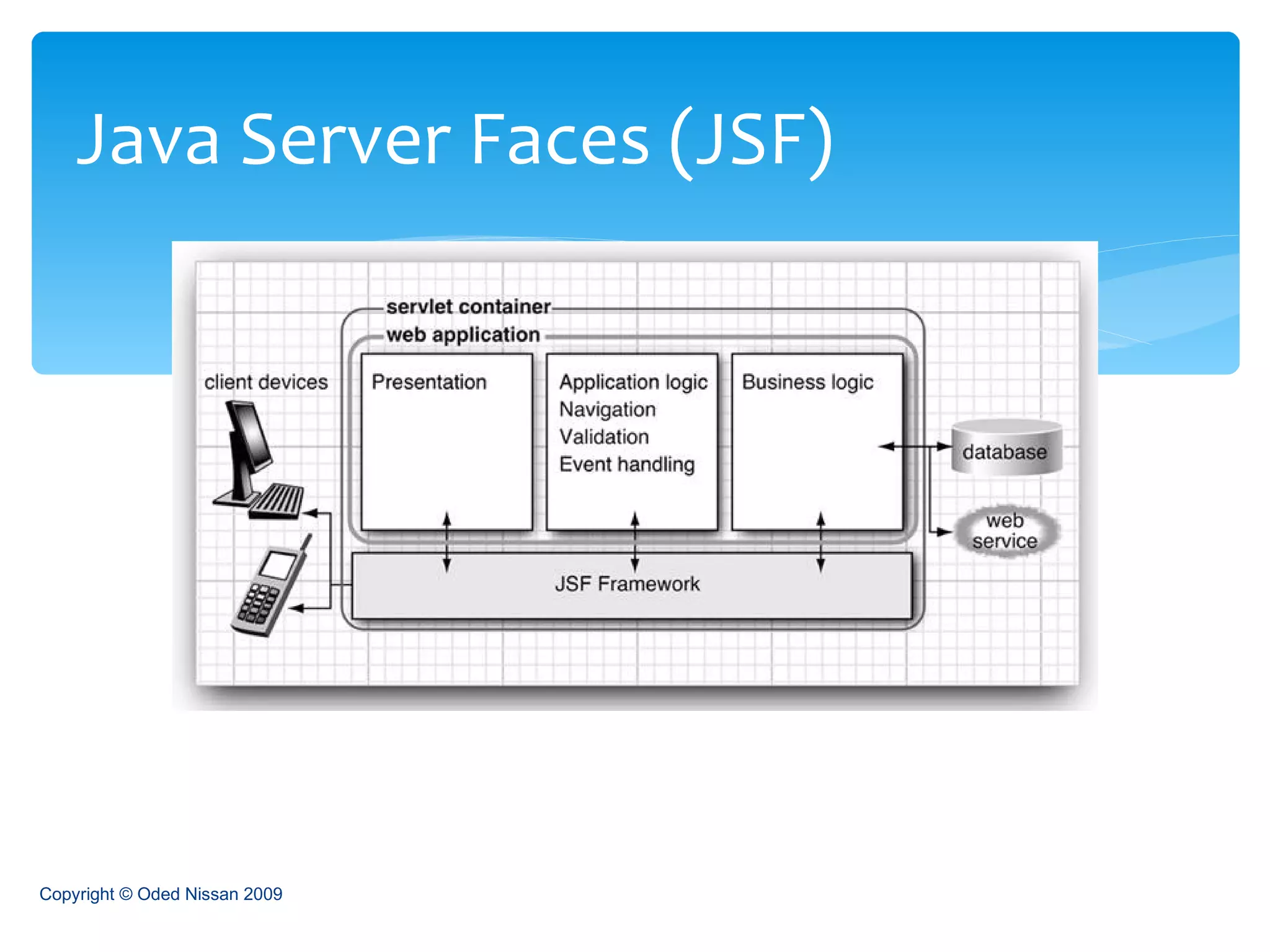
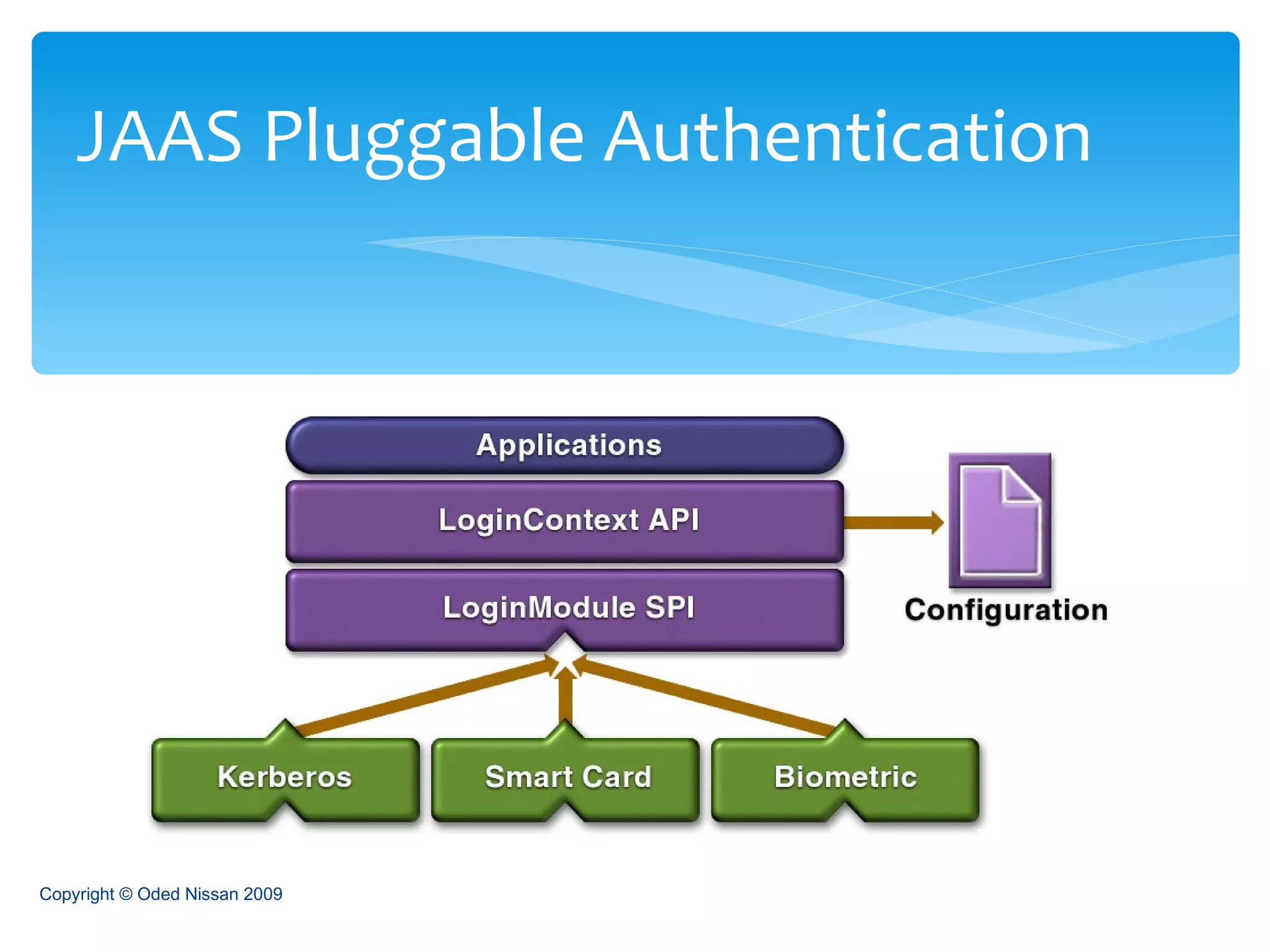
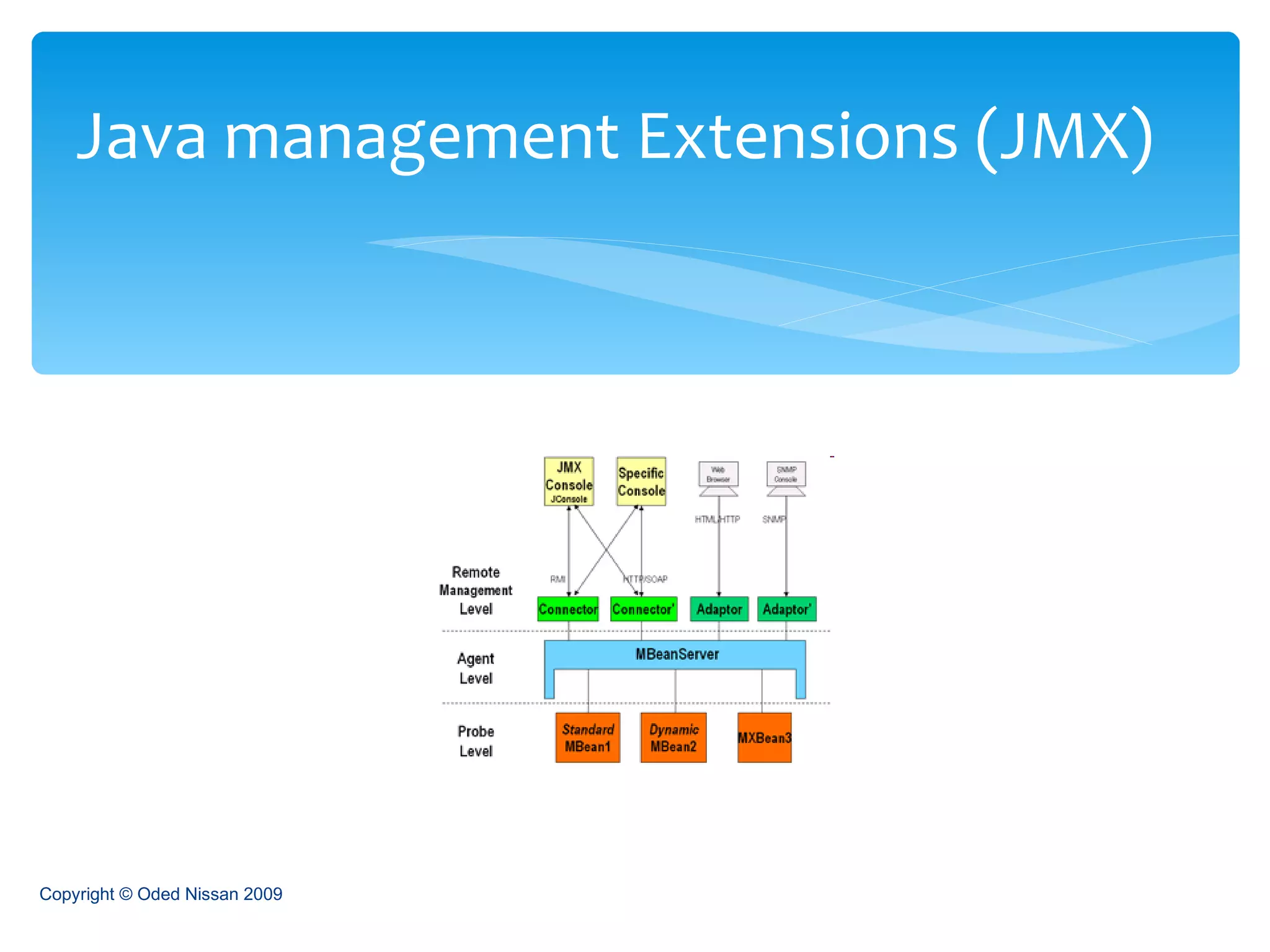
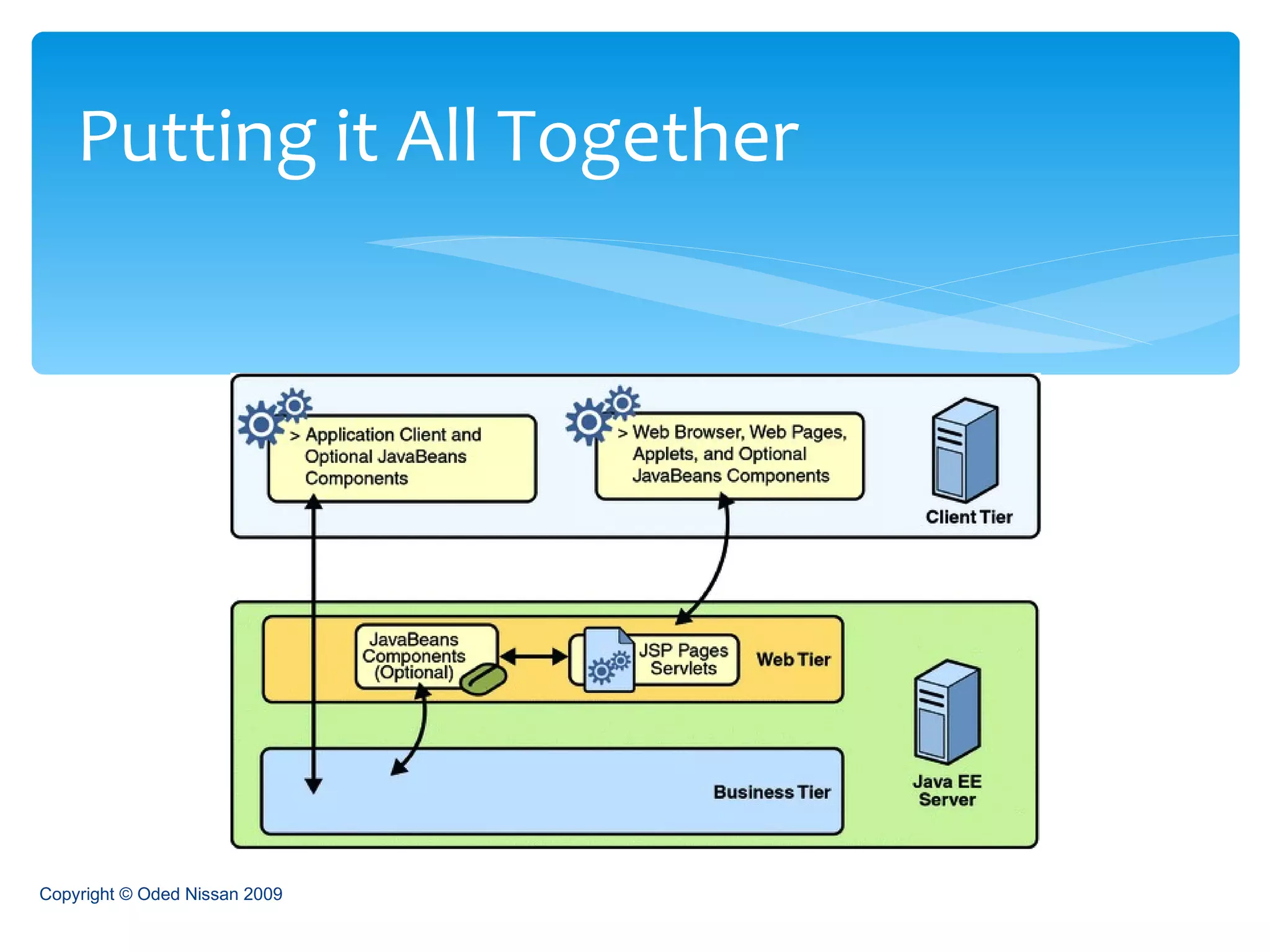
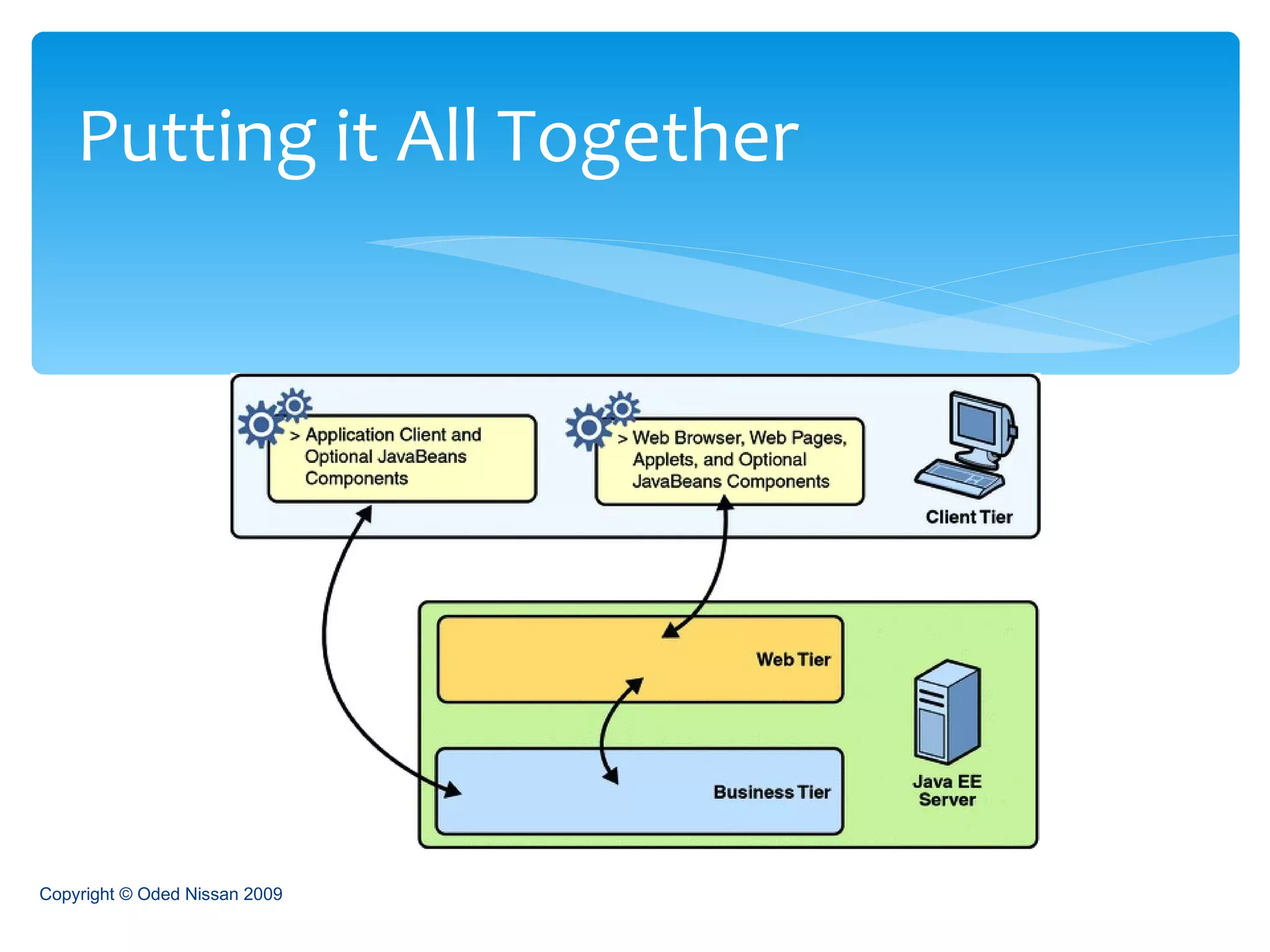
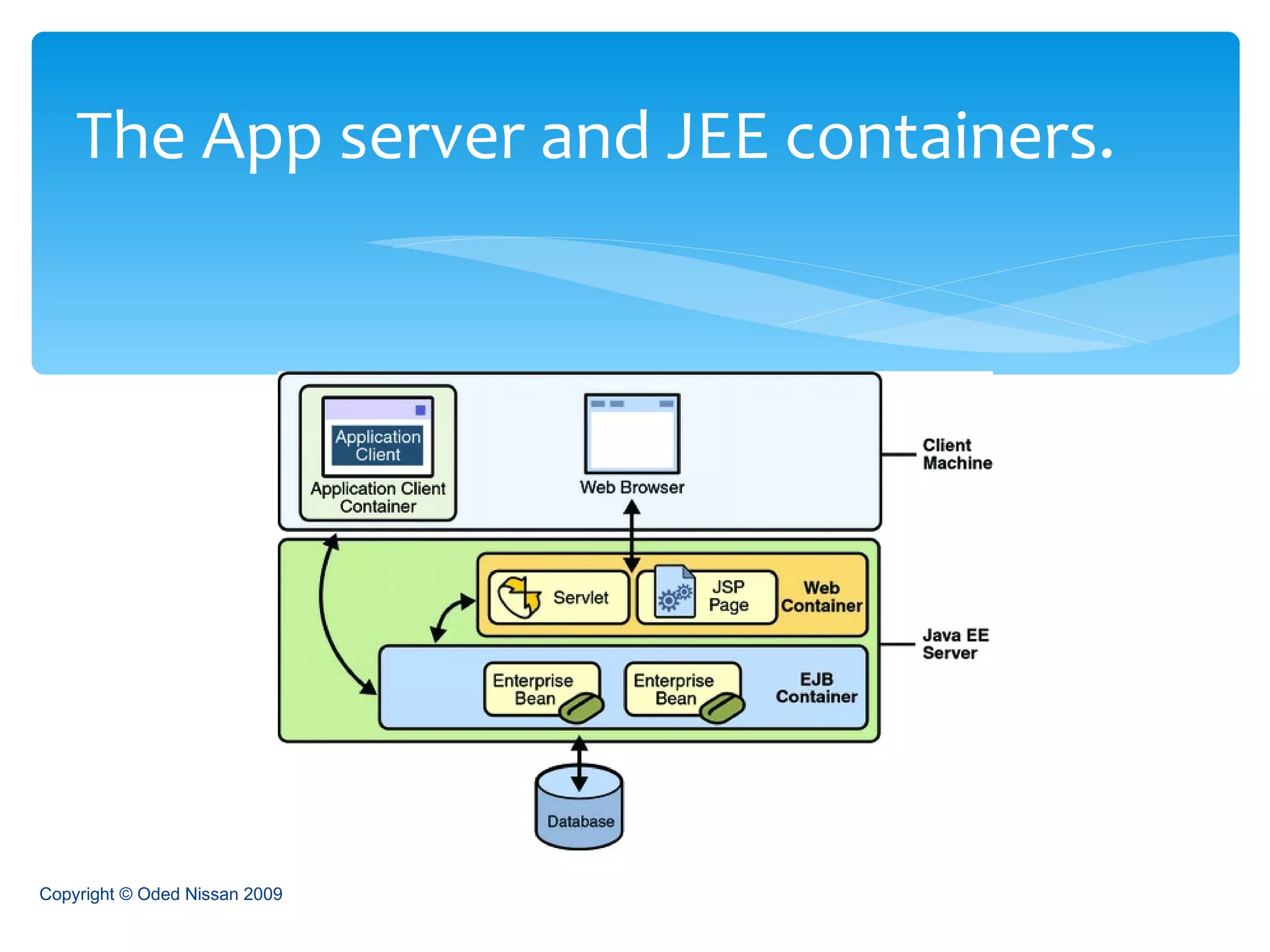
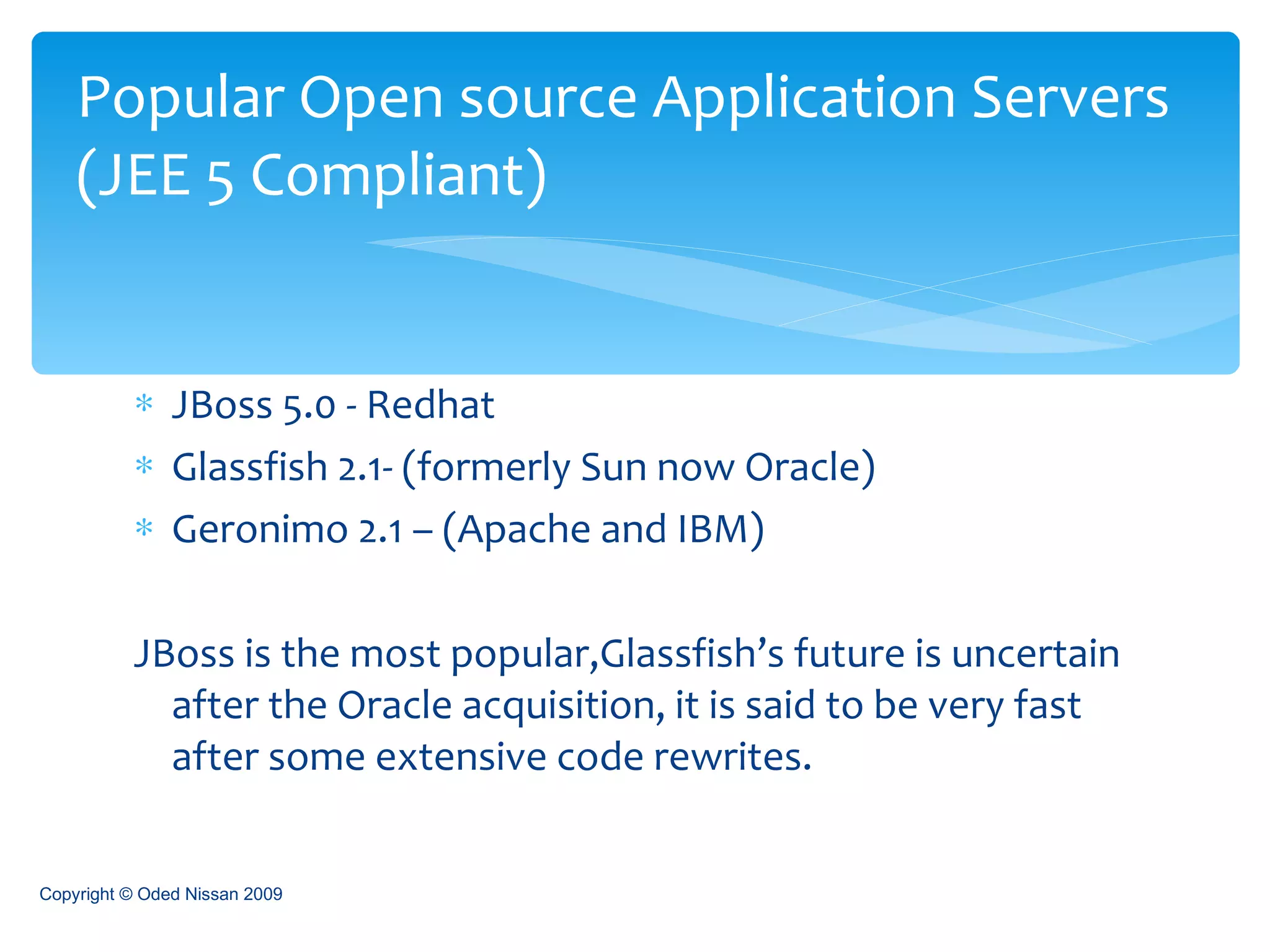
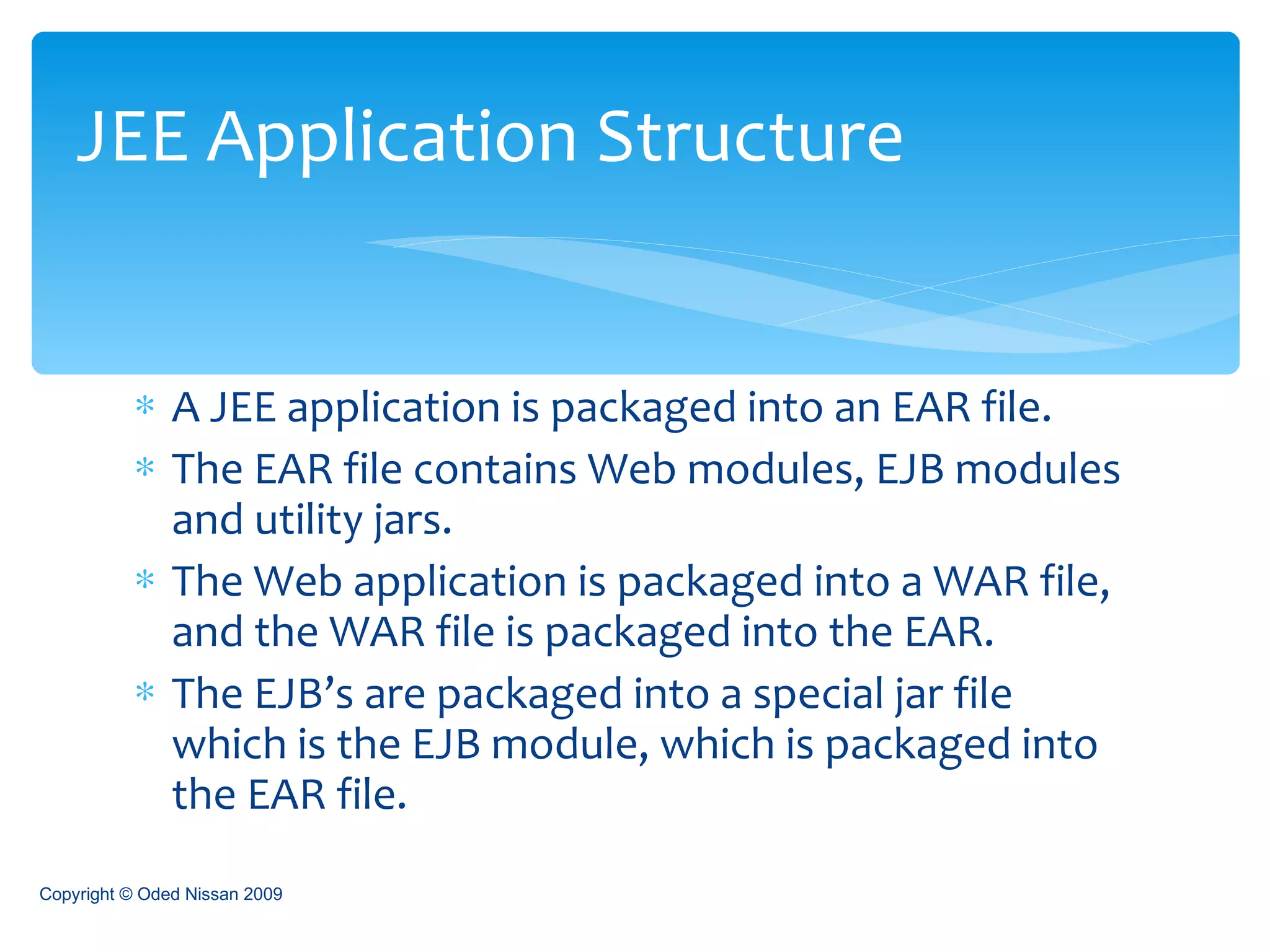
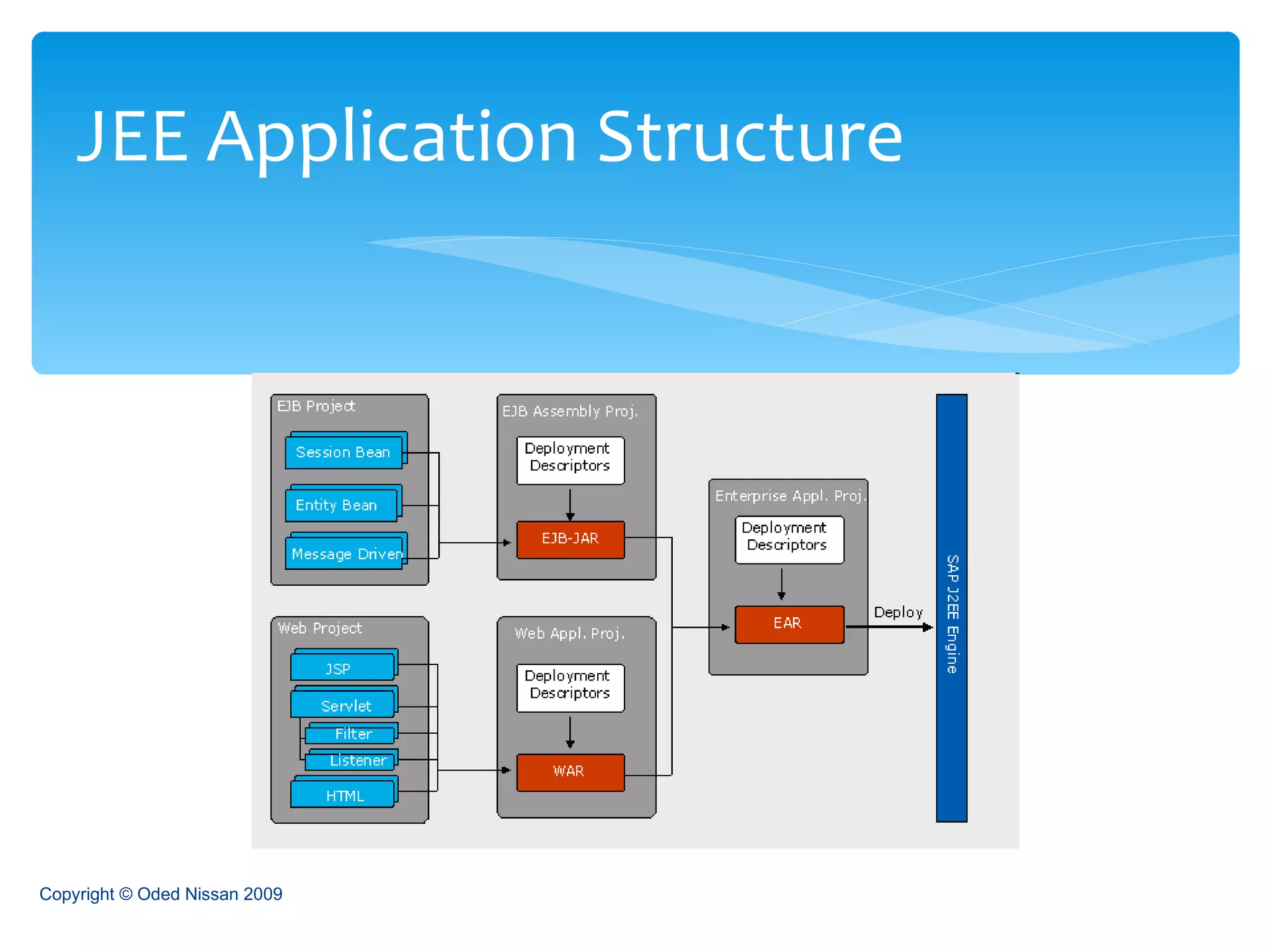
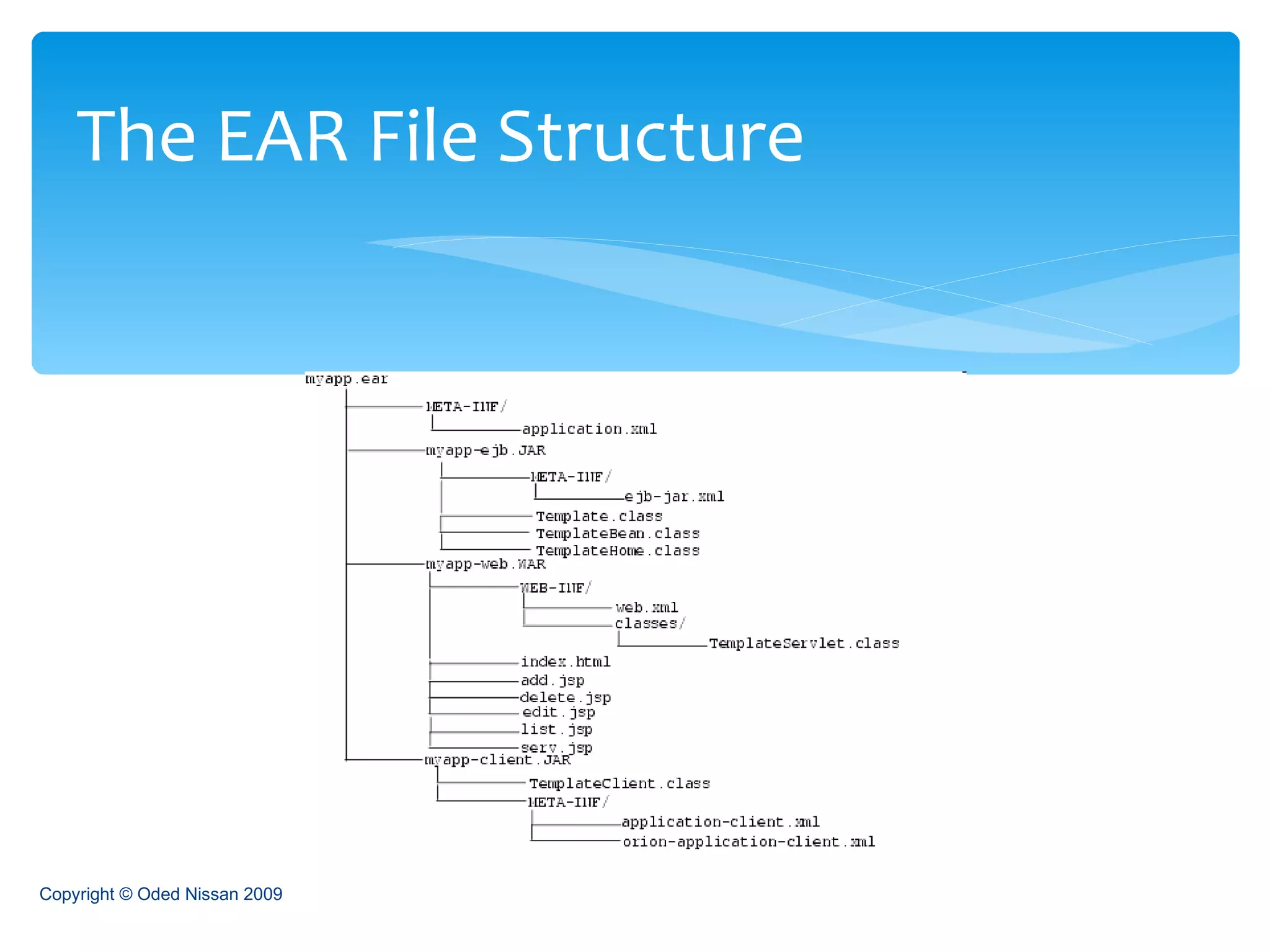
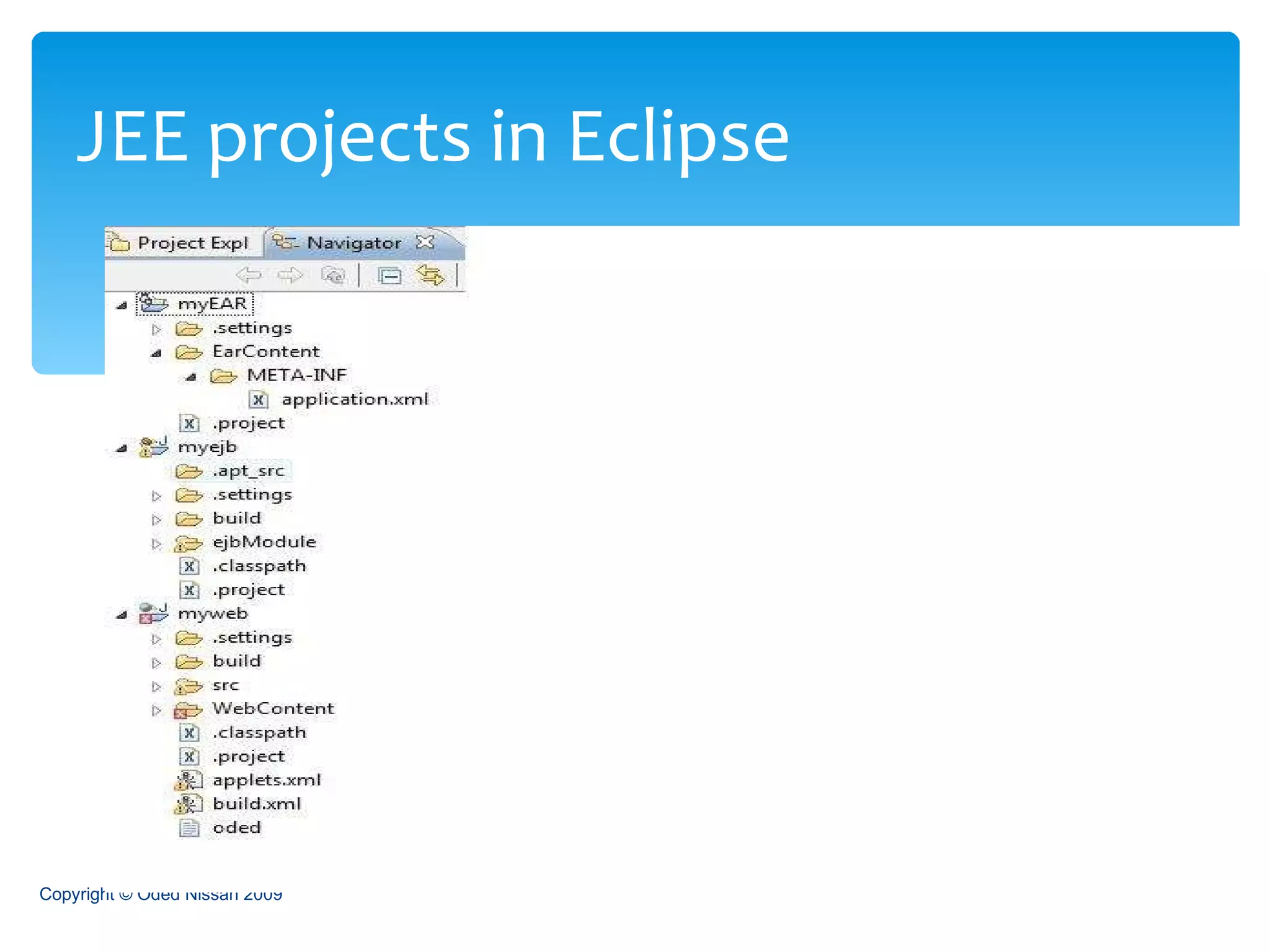
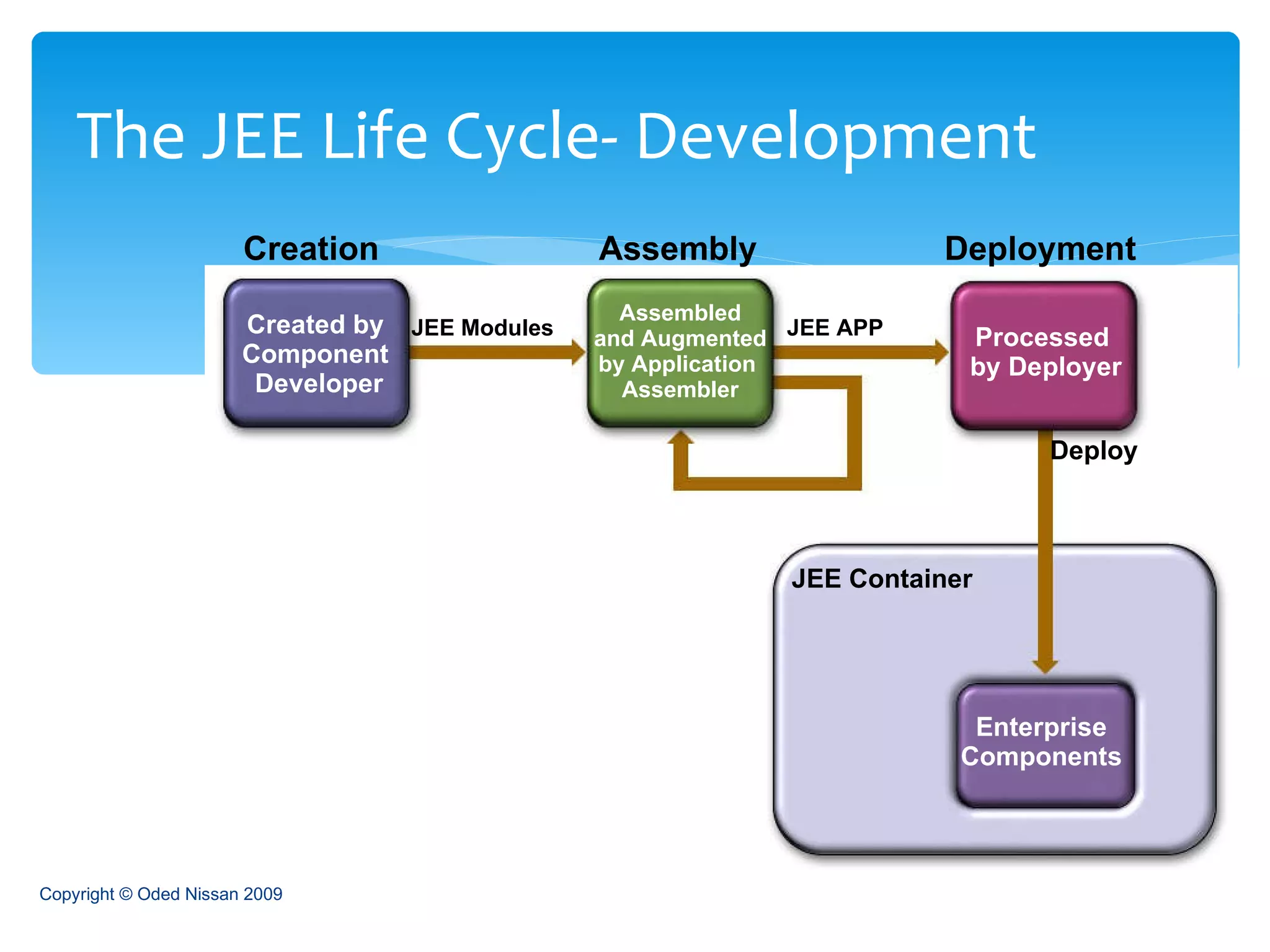
The document provides an overview of the Java Enterprise Edition (JEE) architecture and technologies. It describes JEE as a set of standards for developing scalable, secure, and transactional Java applications. The key components of JEE include web containers, enterprise beans, JavaServer Pages, servlets, and other technologies that allow separation of concerns and portability across application servers.