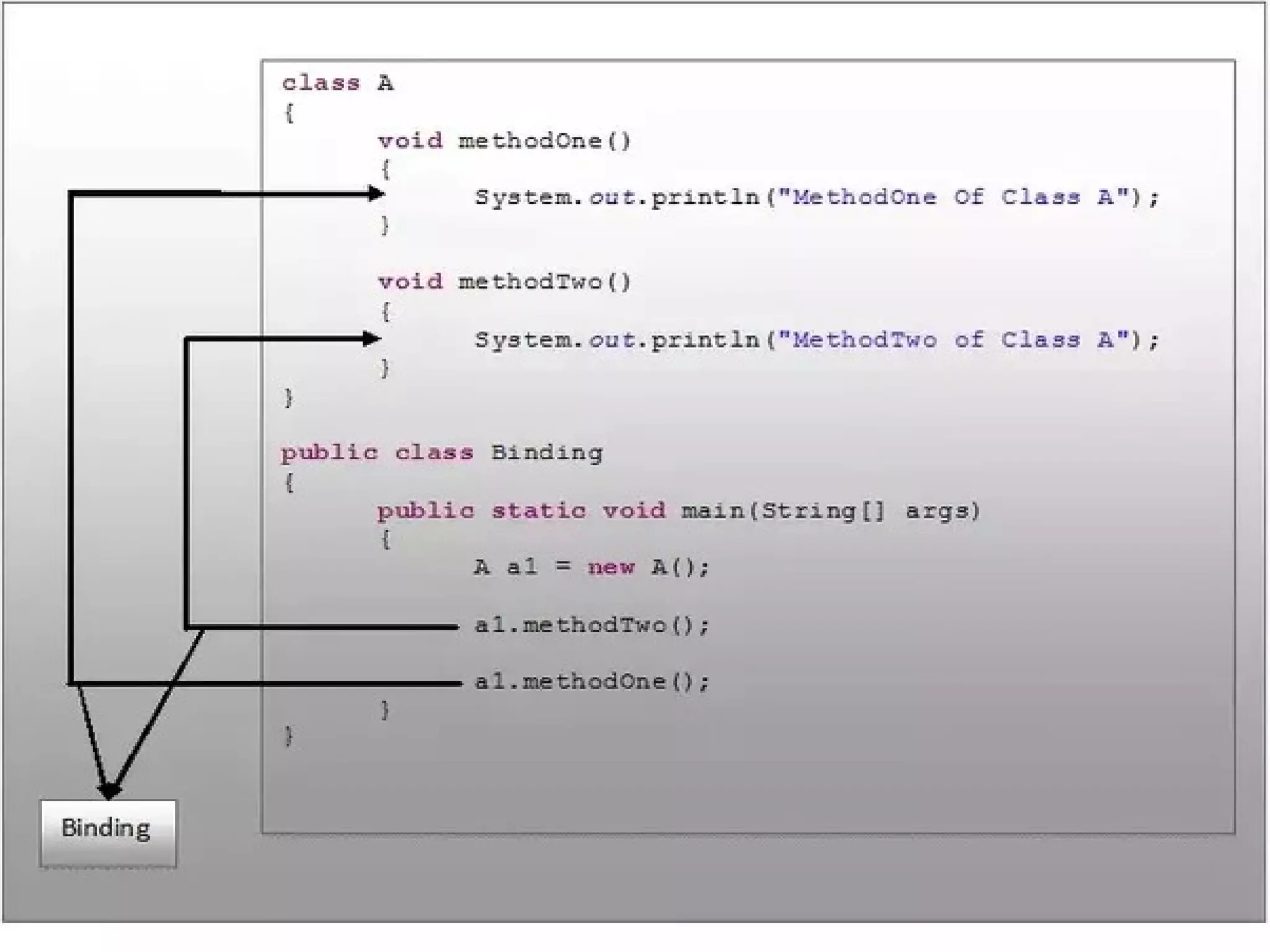
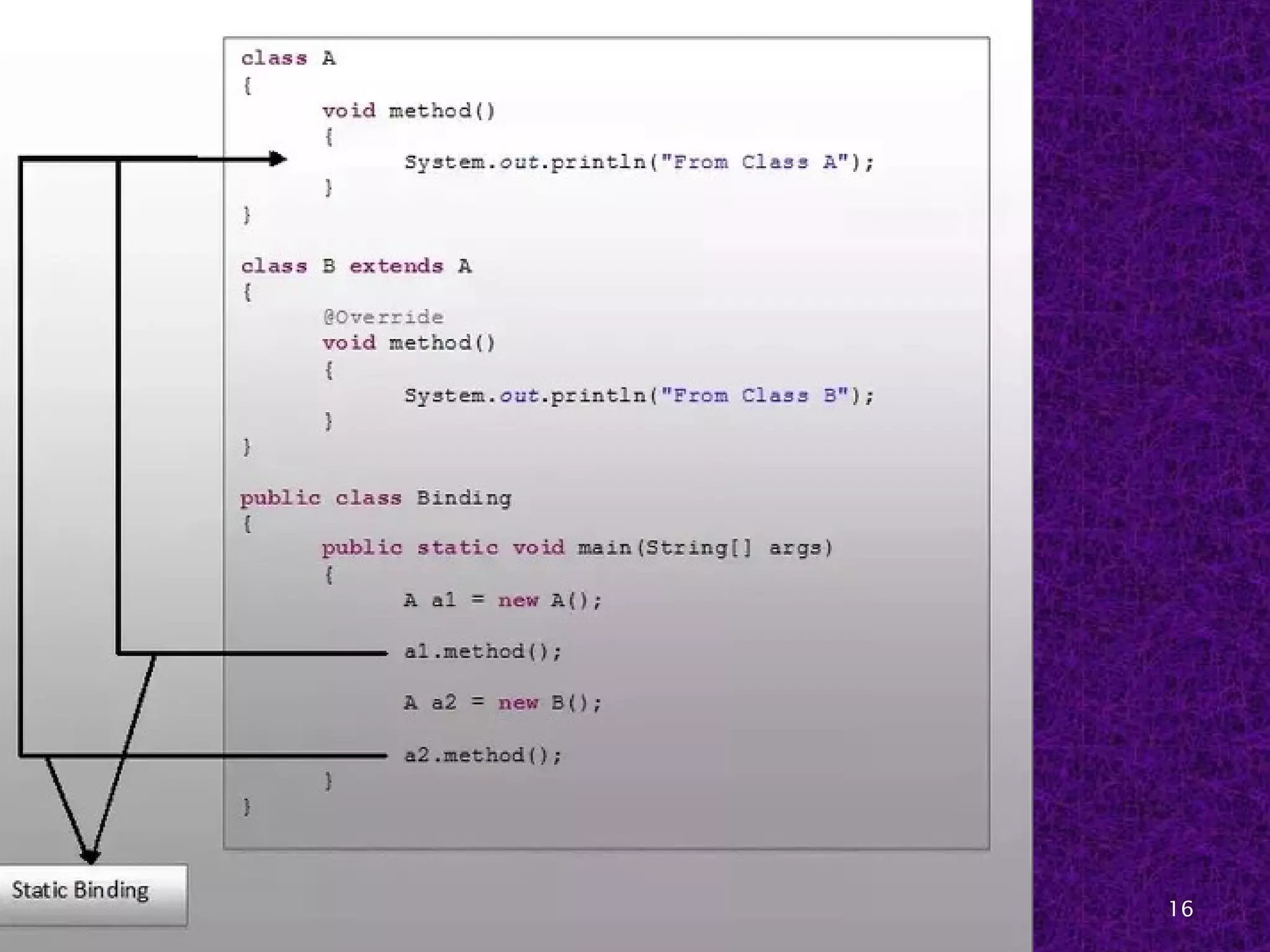
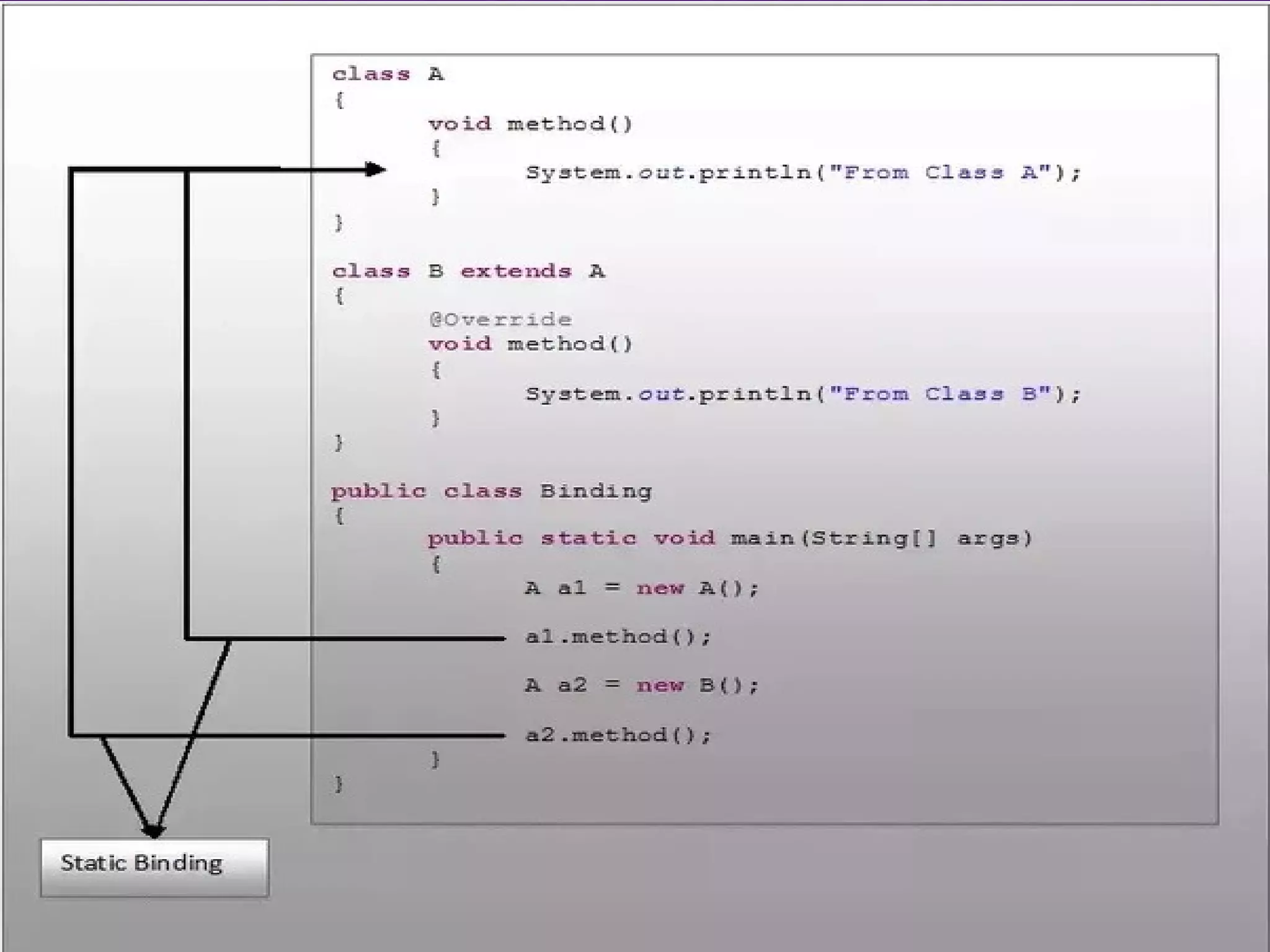
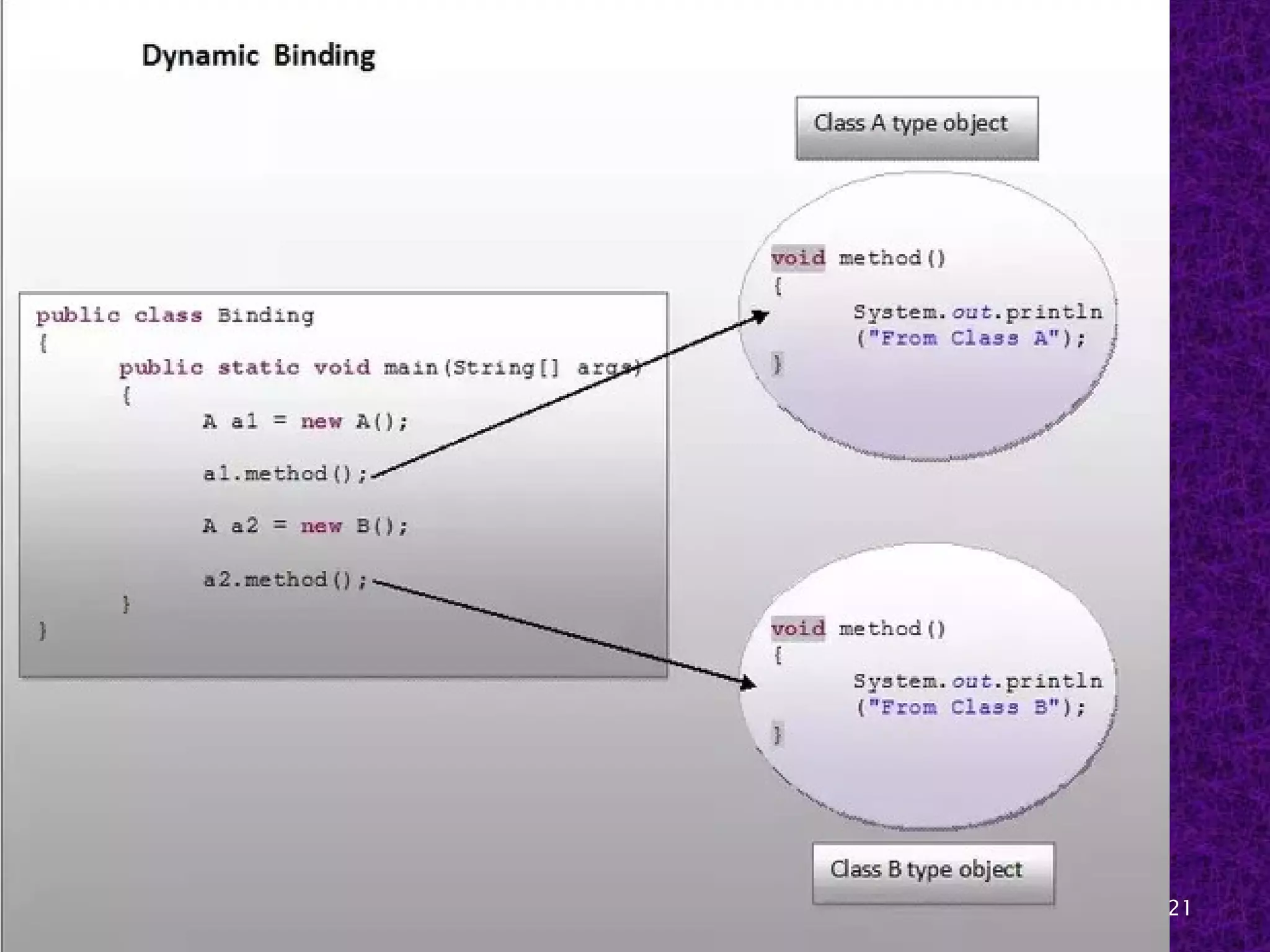
The document discusses early and late binding in functions. Early or static binding occurs when the function being called can be resolved at compile time by the compiler. For direct function calls, the compiler replaces the call with machine code instructions to jump to the function's address. Late or dynamic binding occurs when the function called cannot be determined until runtime, such as with function pointers, requiring an extra level of indirection. Late binding is more flexible but slower, while early binding is faster but less flexible. The document provides examples of each type of binding in code.