The document provides an overview of Arduino boards and microcontrollers. It discusses:
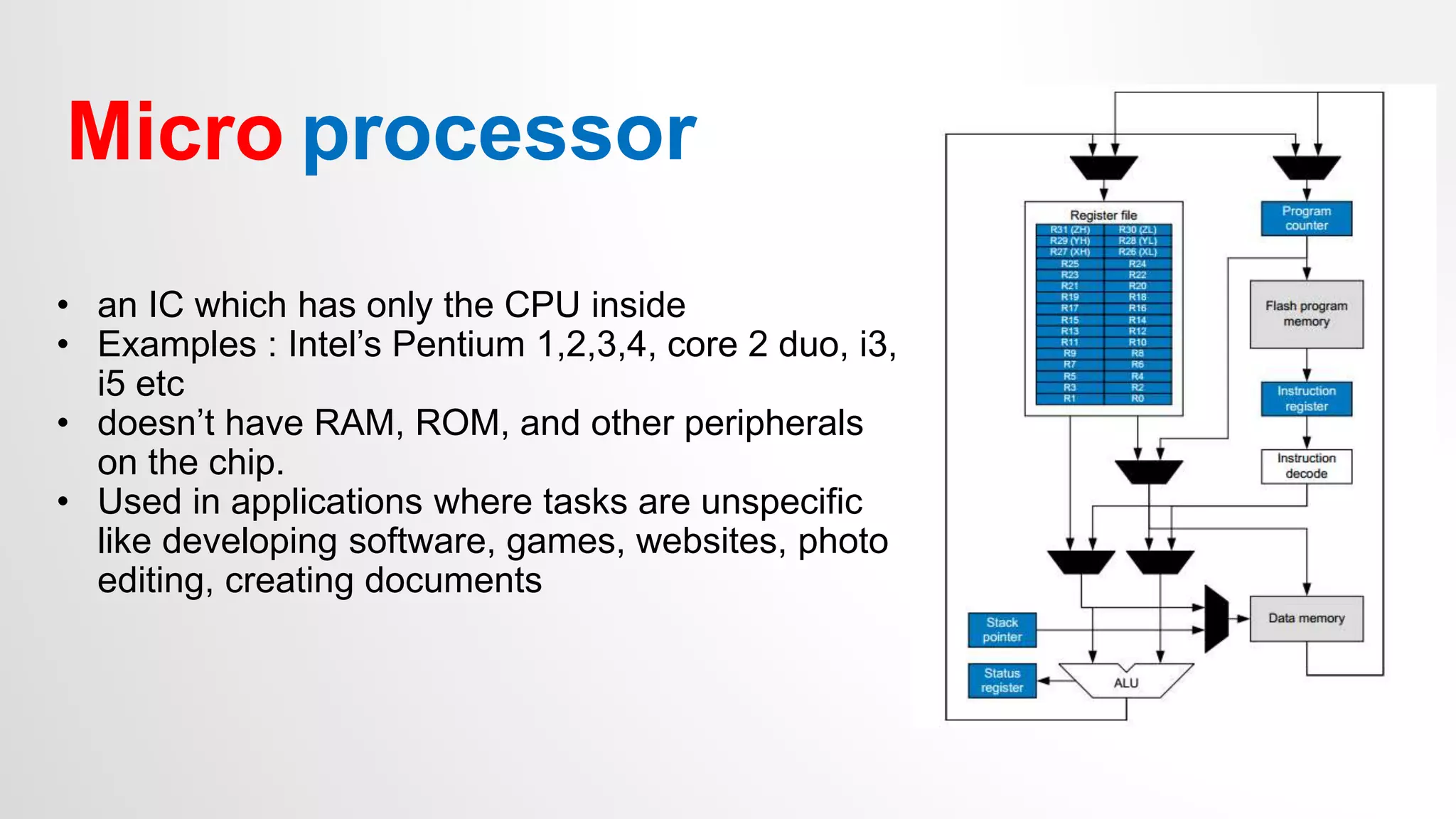
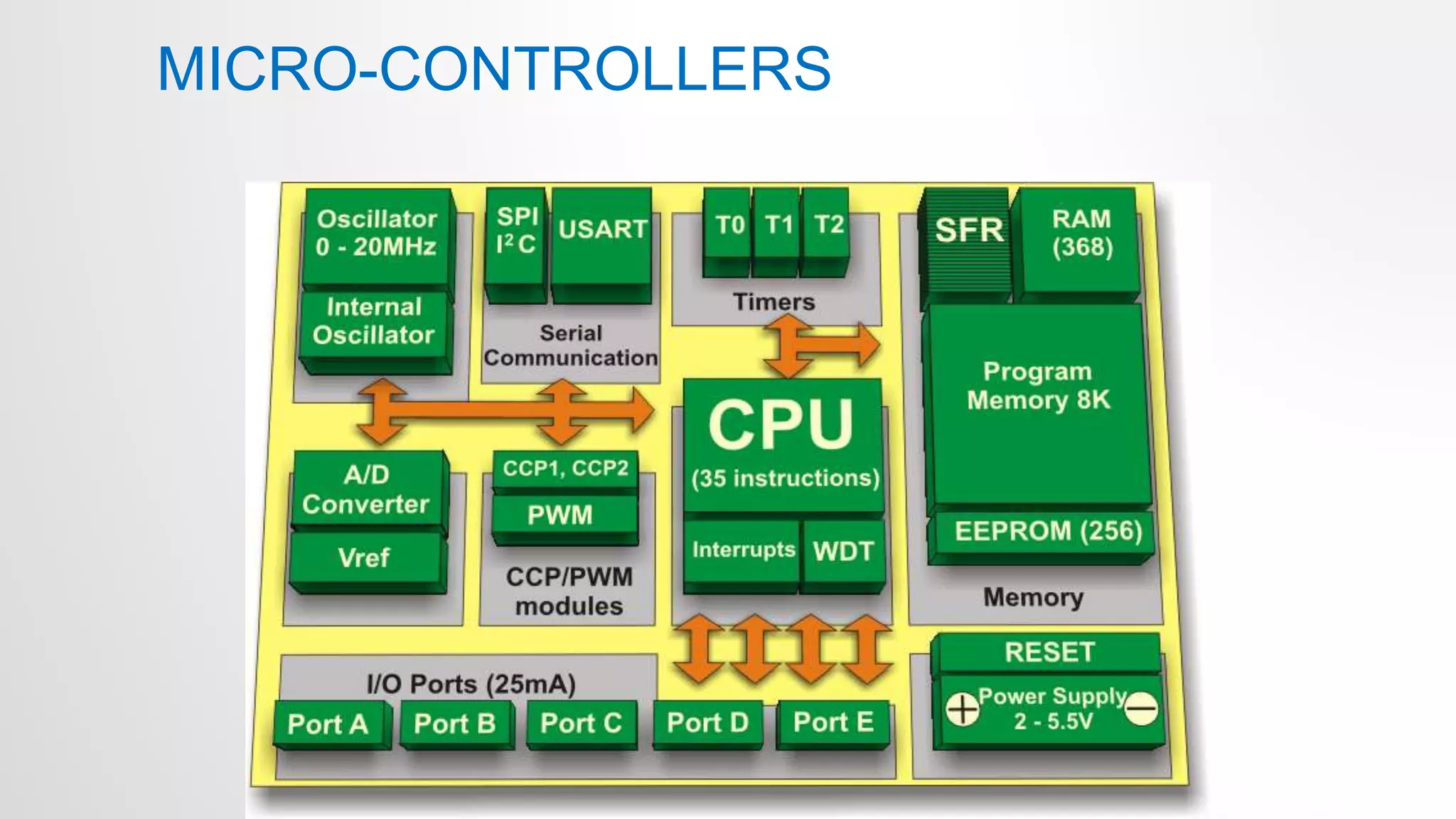
- The differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers, with microcontrollers having CPU, RAM, ROM and peripherals on a single chip to perform dedicated tasks.
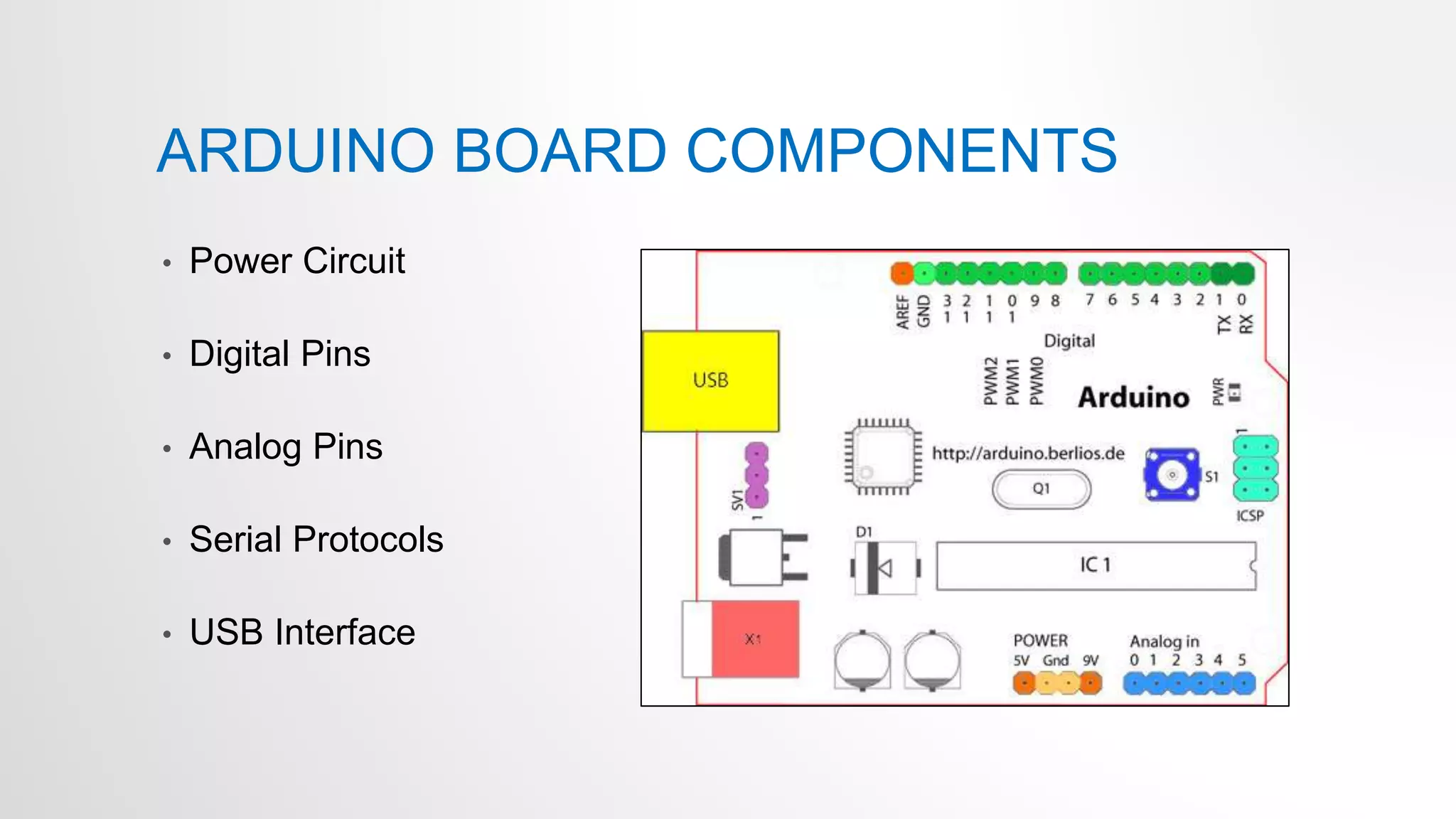
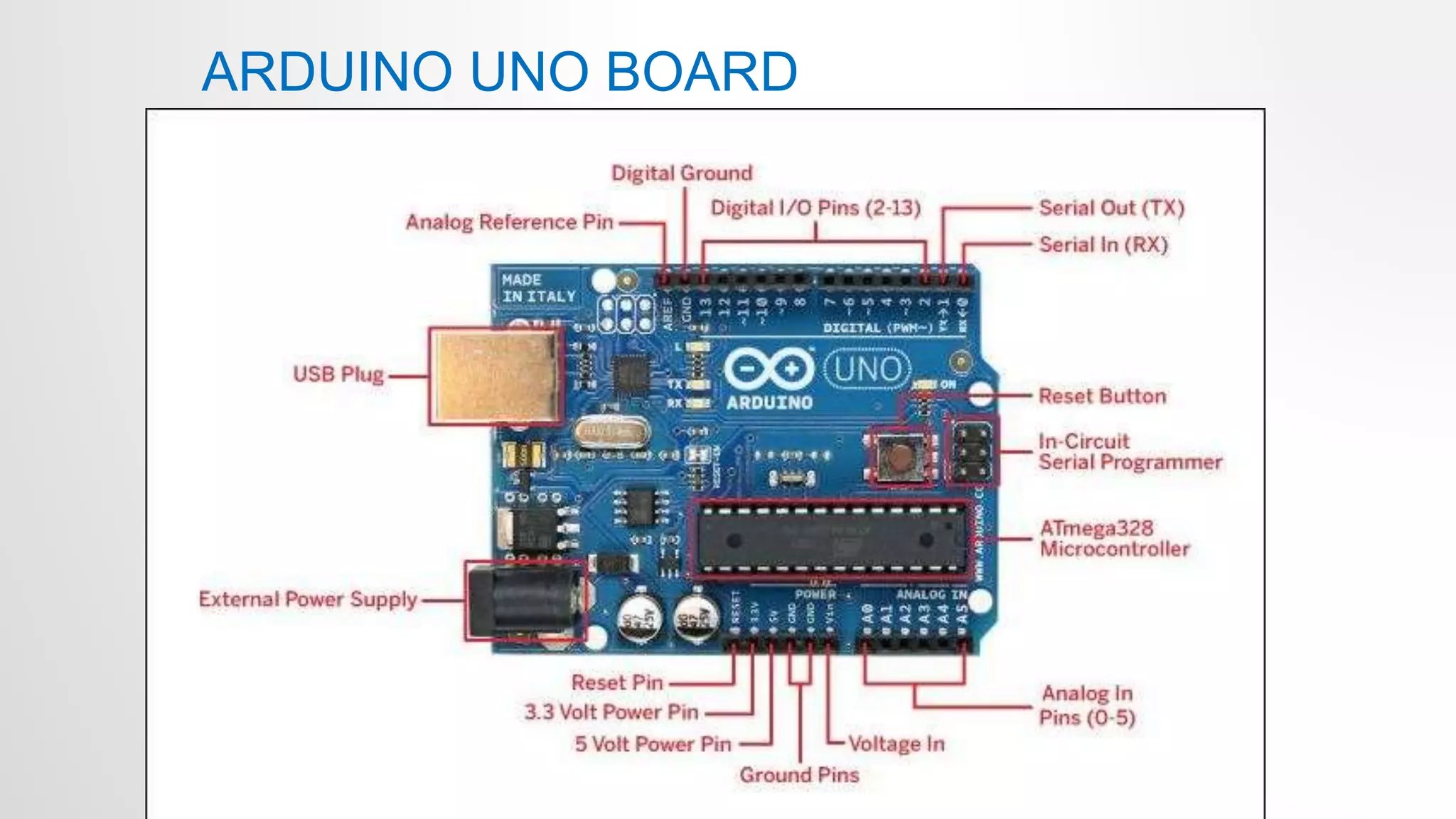
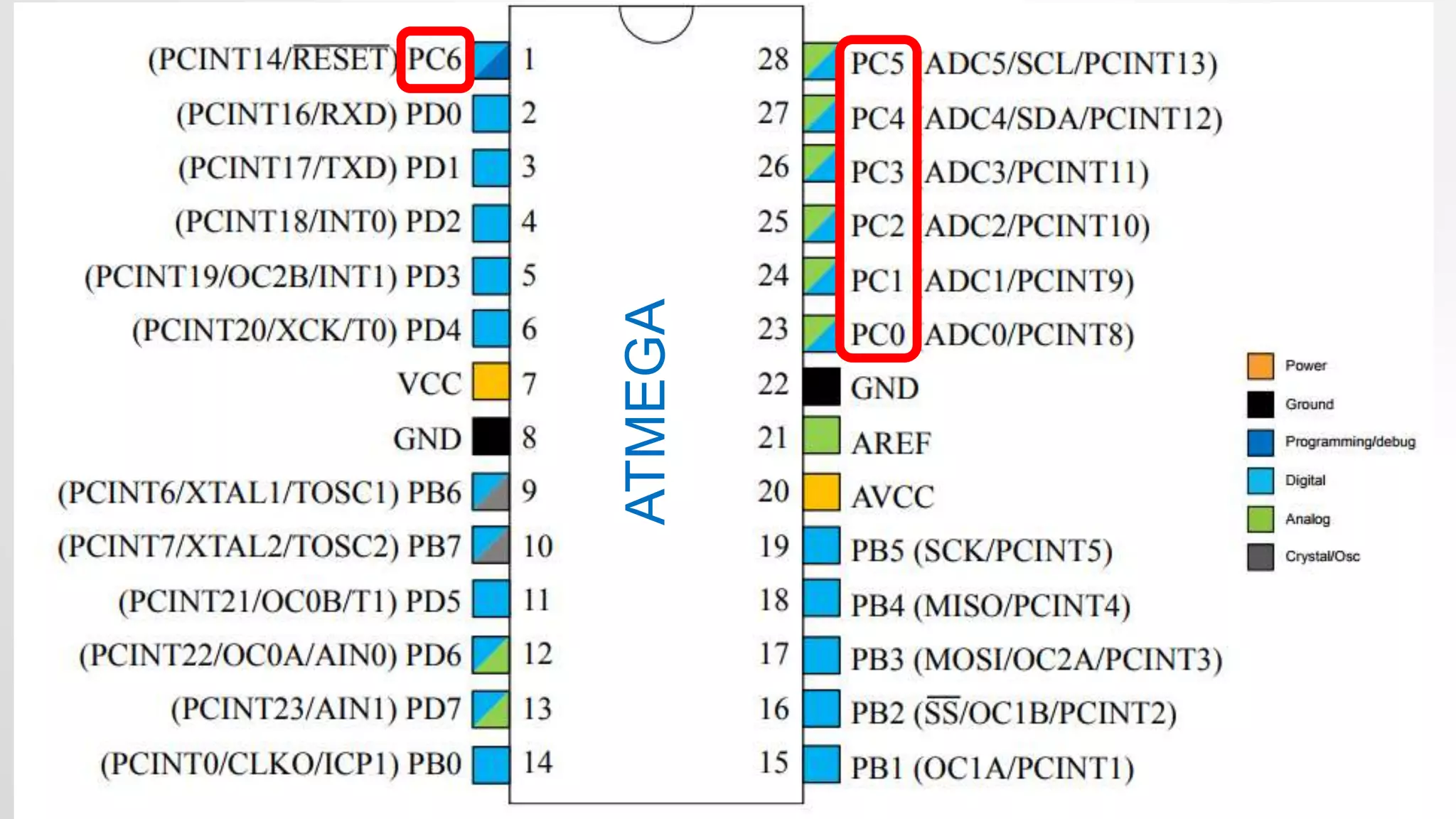
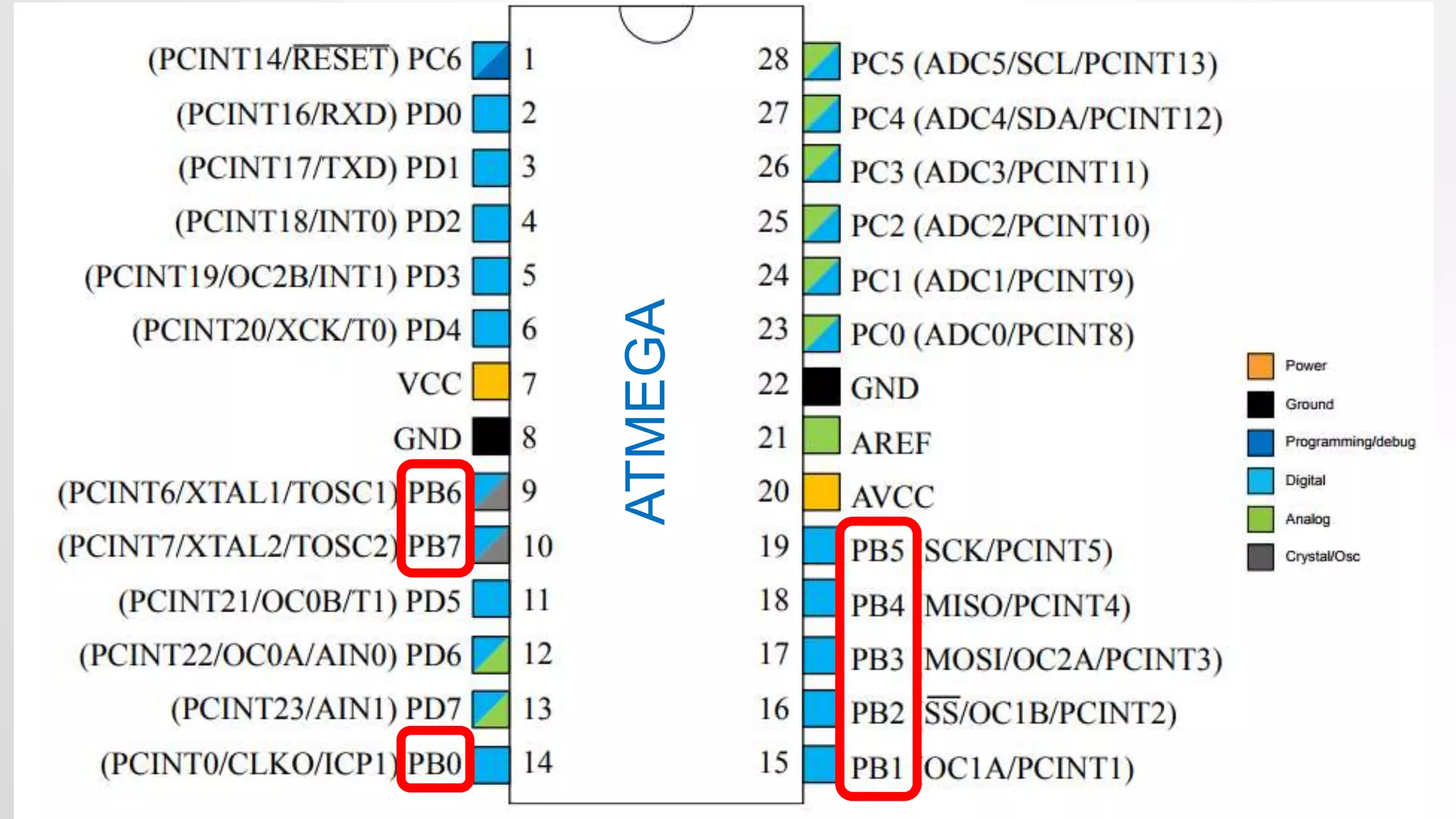
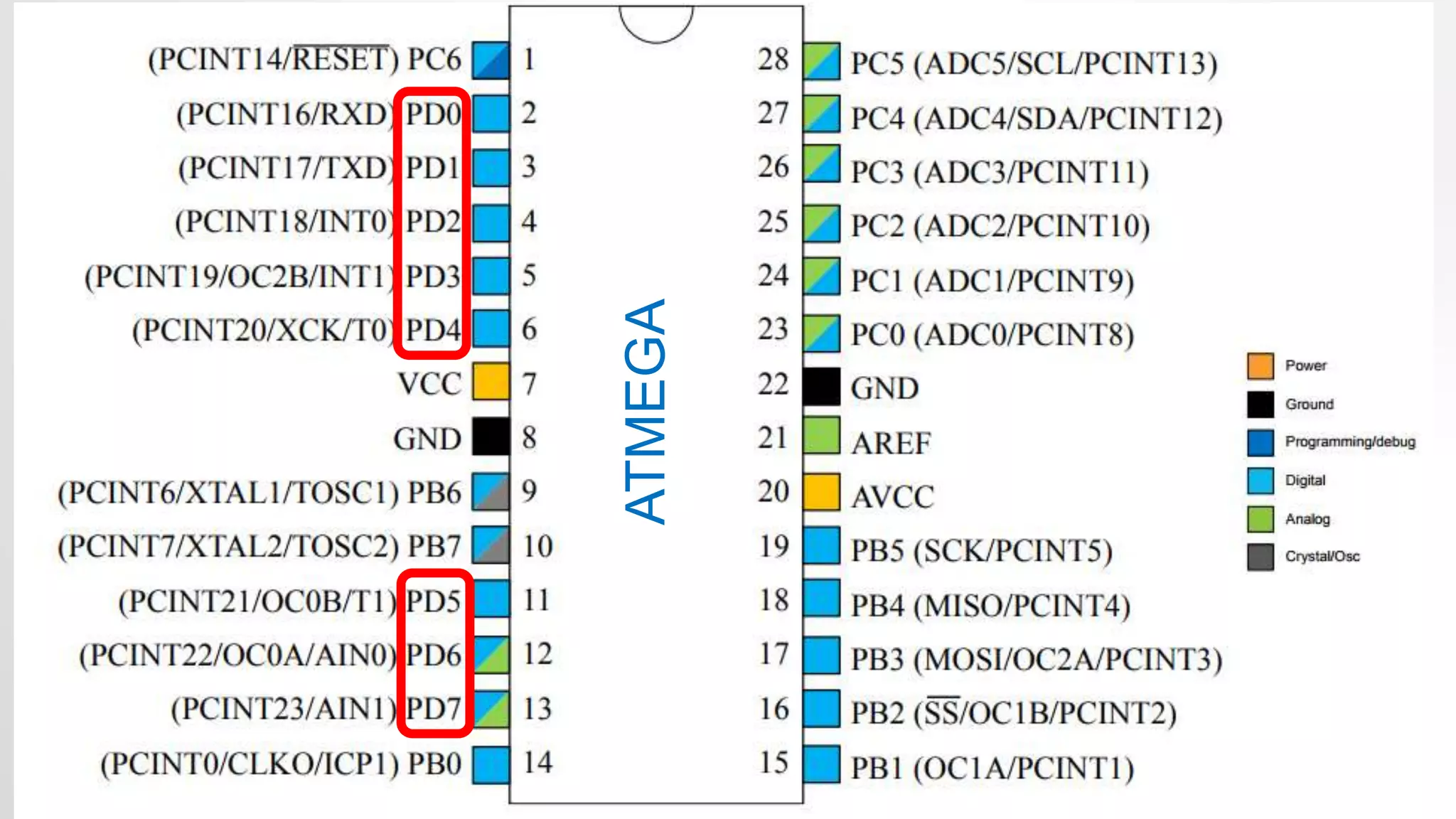
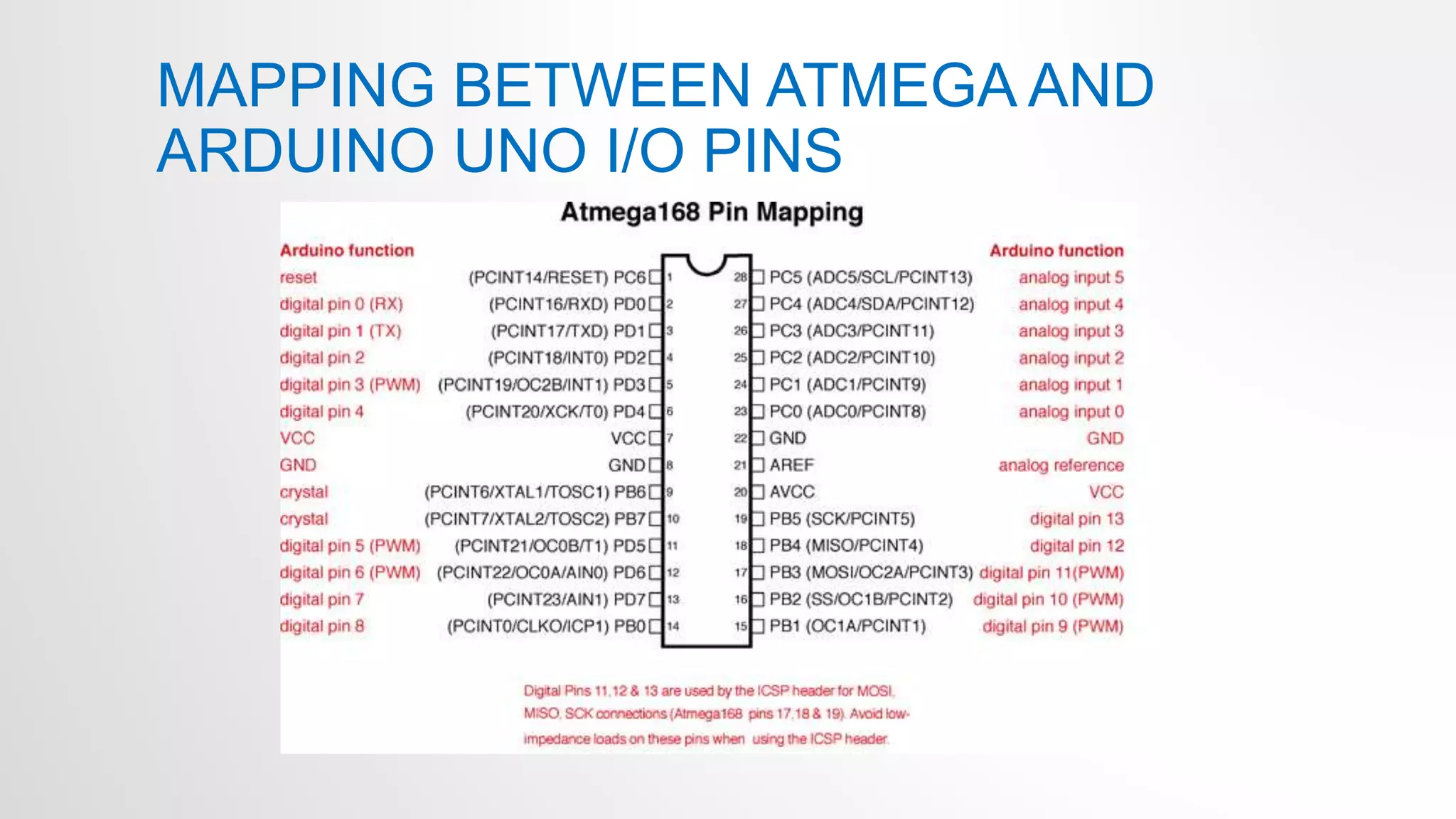
- The Arduino Uno board uses the Atmel ATmega328p microcontroller chip. It has 32KB flash memory, 32 general purpose registers and is programmed using the Arduino IDE.
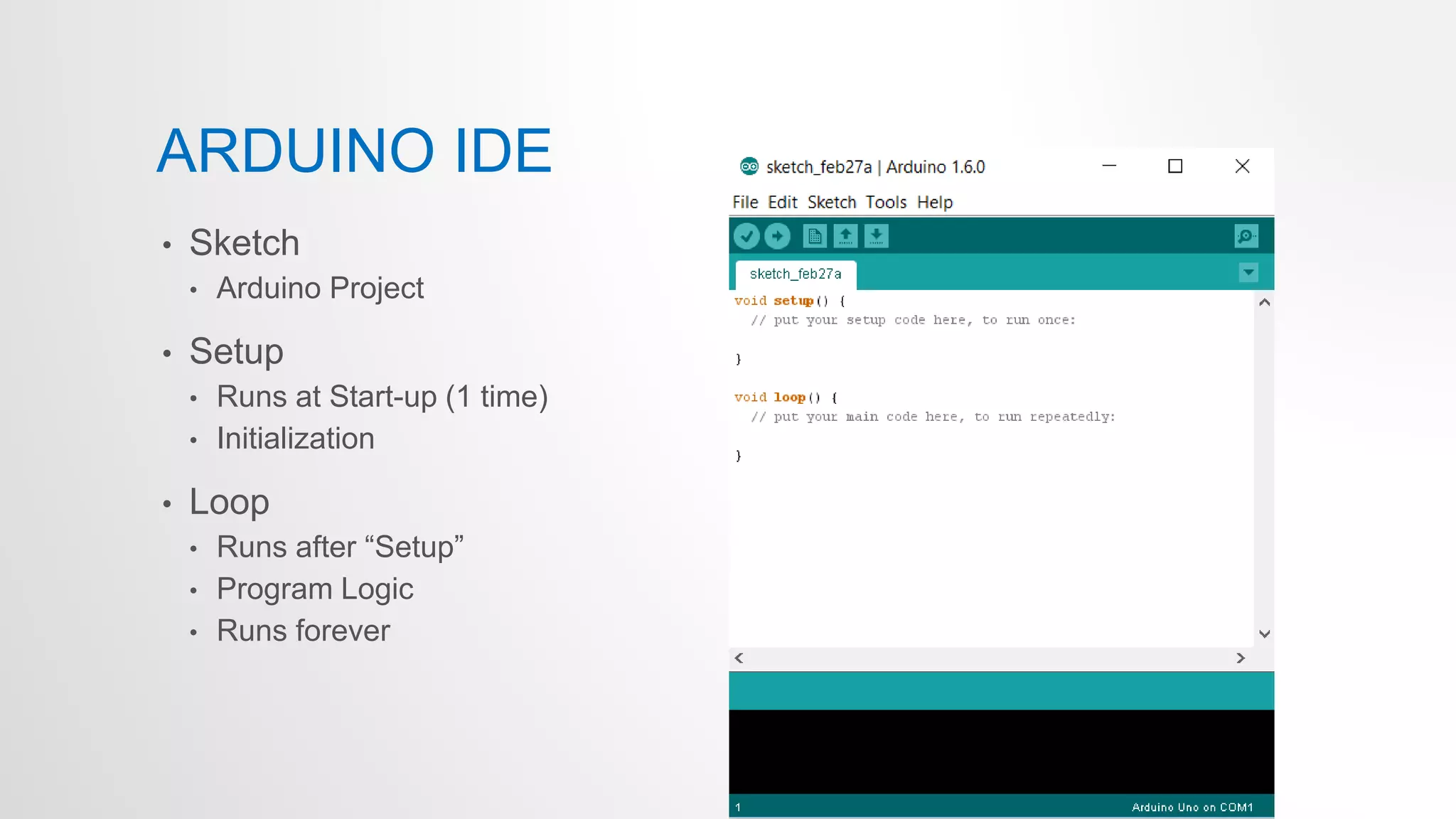
- The Arduino language is based on C/C++ and is used to write codes that can control digital input/output pins, analog pins, serial communication and more on the Arduino board.



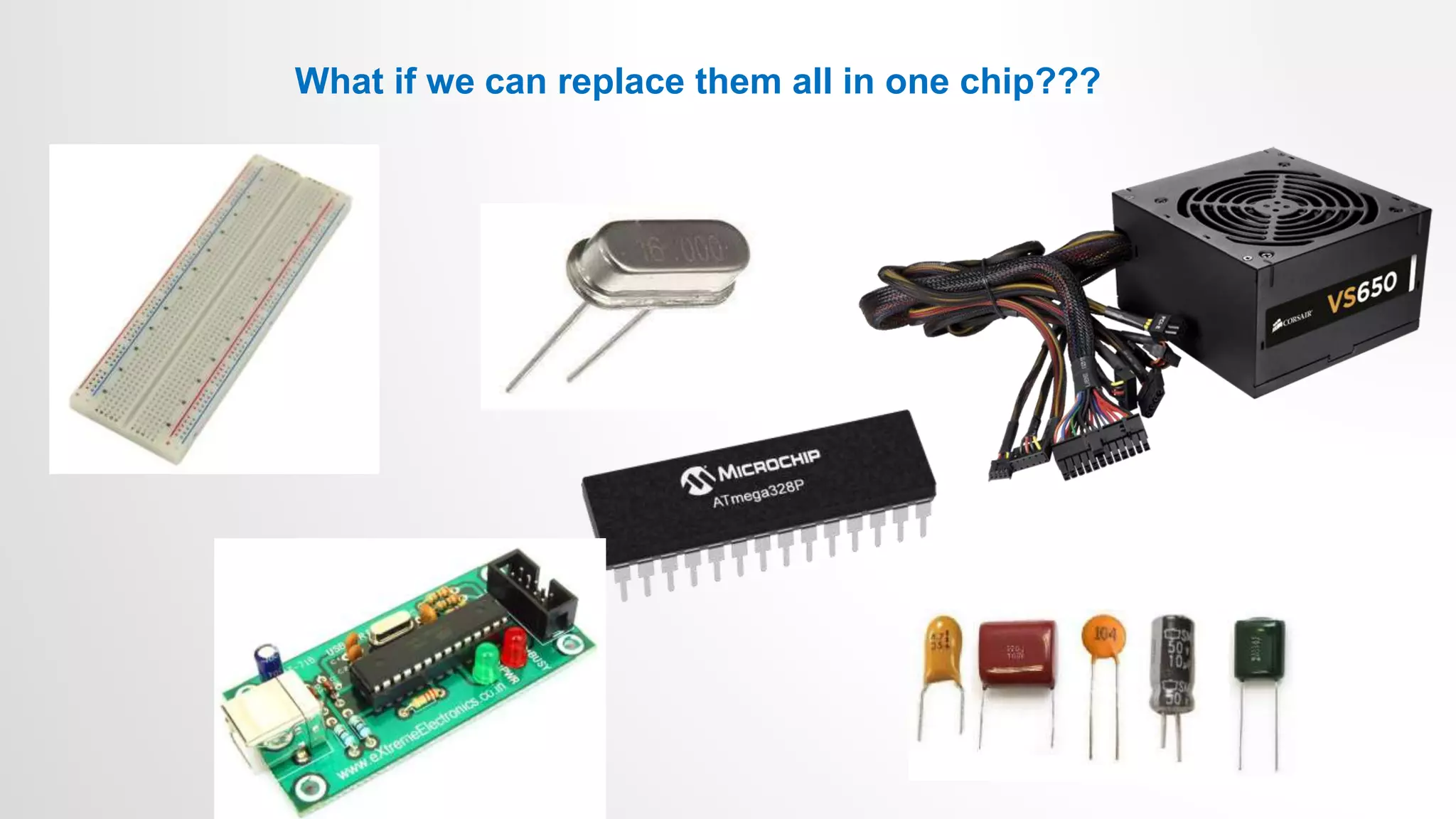
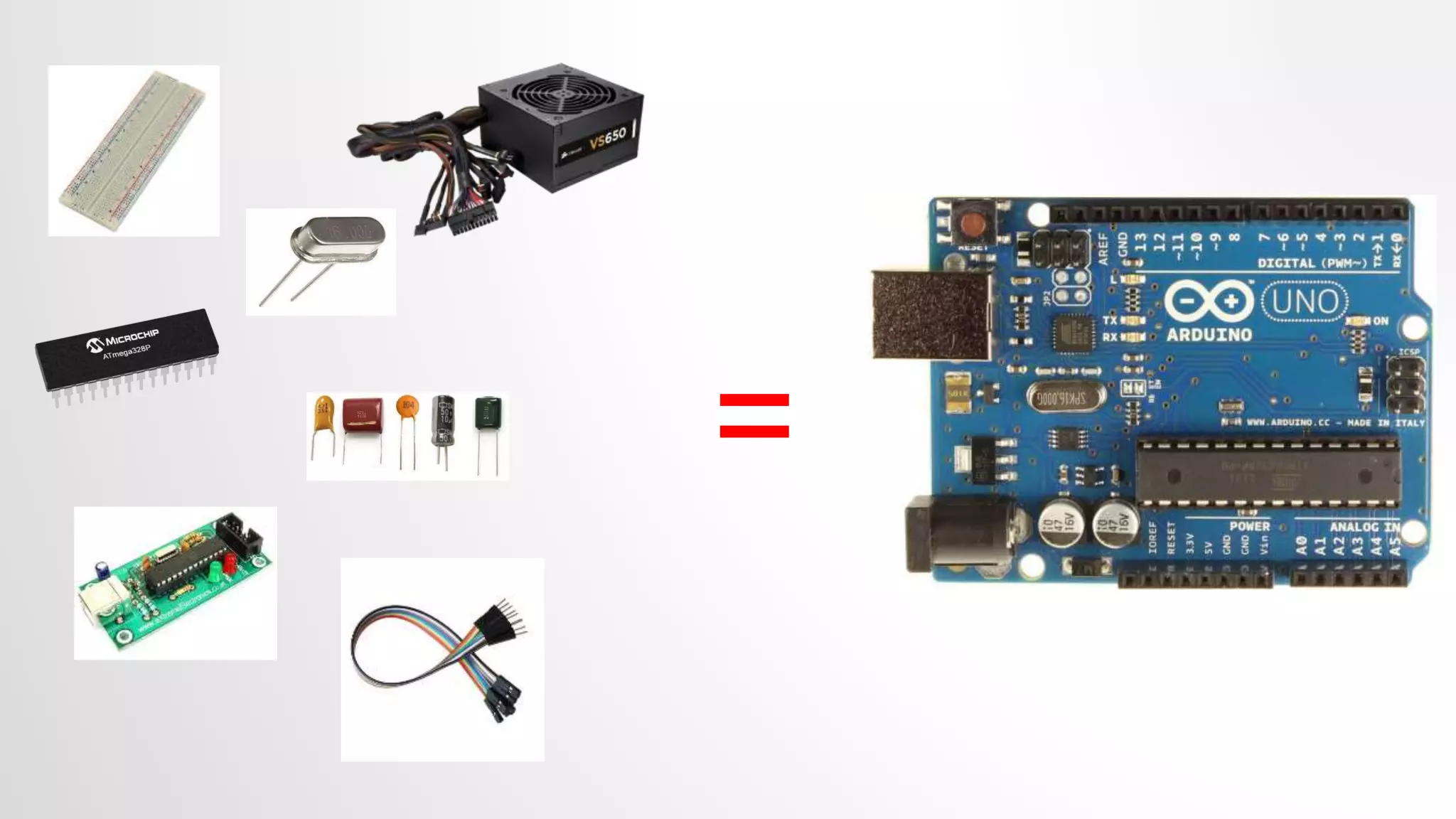
![ARDUINO BOARD
• Ready to use Board
• Atmega µC
• Plug-n-Play
• Open Source
• Arduino language is based on c and c++ [reference provided]
• Large Community](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/75/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-11-2048.jpg)



![ARDUINO LANGUAGE
• Data types ( char arrays)
• char like[] = "I like coffee and cake"; // create a string
• like[12] = 't’;
• char str[40];
• num = strlen(str); // get the length of the string (excludes null terminator)
• All the string c library applies here.
• We can define arrays with other datatypes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/75/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-24-2048.jpg)


![ARDUINO LANGUAGE
• Debugging:
• Open the serial monitor
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// send data only when you receive data:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// read the incoming byte:
incomingByte = Serial.read();
char str[] = "This is my string"; // create a string
Serial.print("String length is: ");
Serial.println(str);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/75/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-28-2048.jpg)

![• Write Arduino code that sums the elements in array of
10 integers defined as a global variable integer array
[87, 68, 94, 100, 83, 78, 85, 91, 76, 87 ]
• Make each loop print to the serial one integer only
• Make a delay of 0.5 second between each print
• Print every integer in a new line
Ex1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microcontrollerslab1introtoarduino-230302071057-e91de9aa/75/Micro_Controllers_lab1_Intro_to_Arduino-pptx-30-2048.jpg)