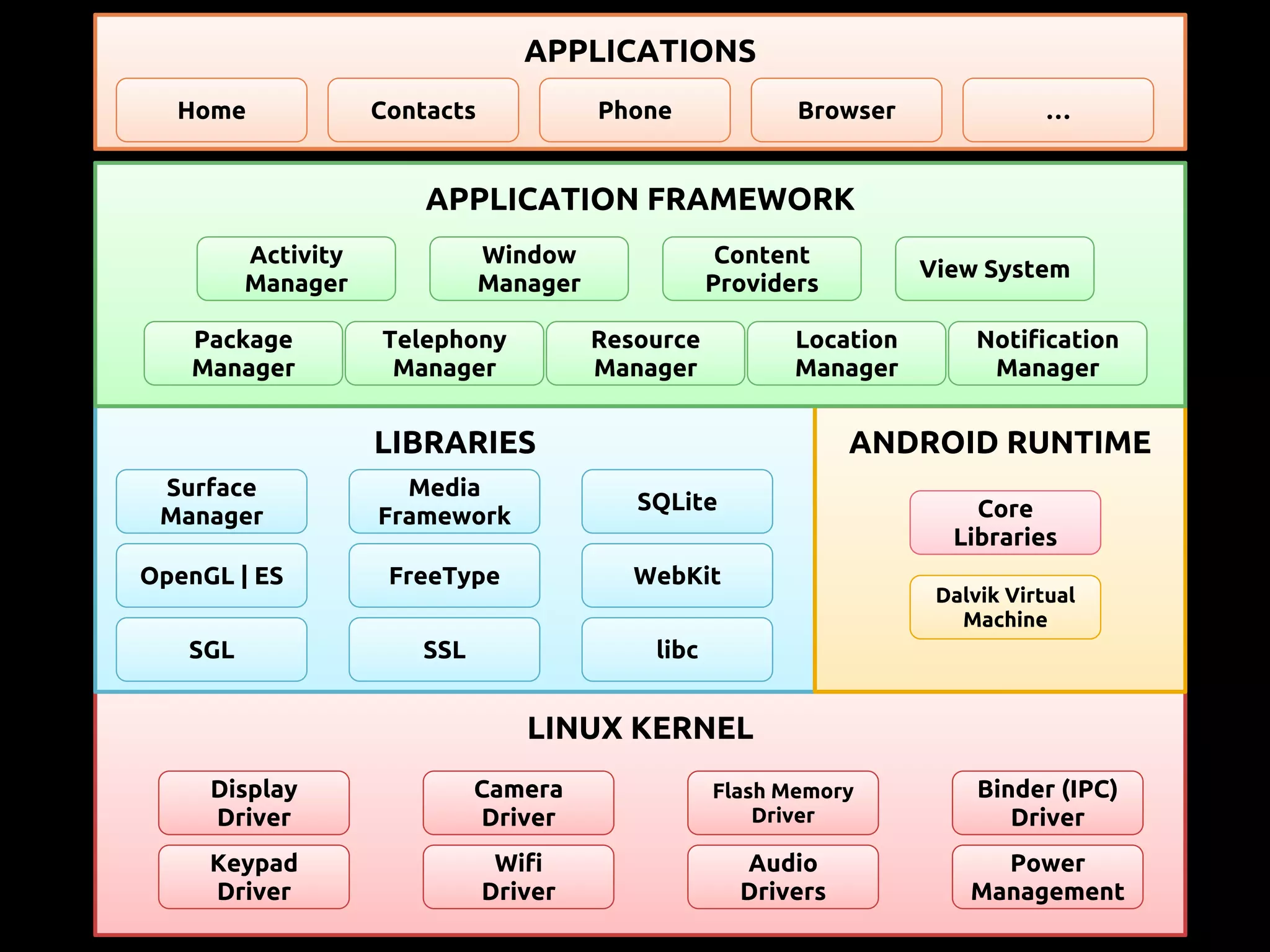
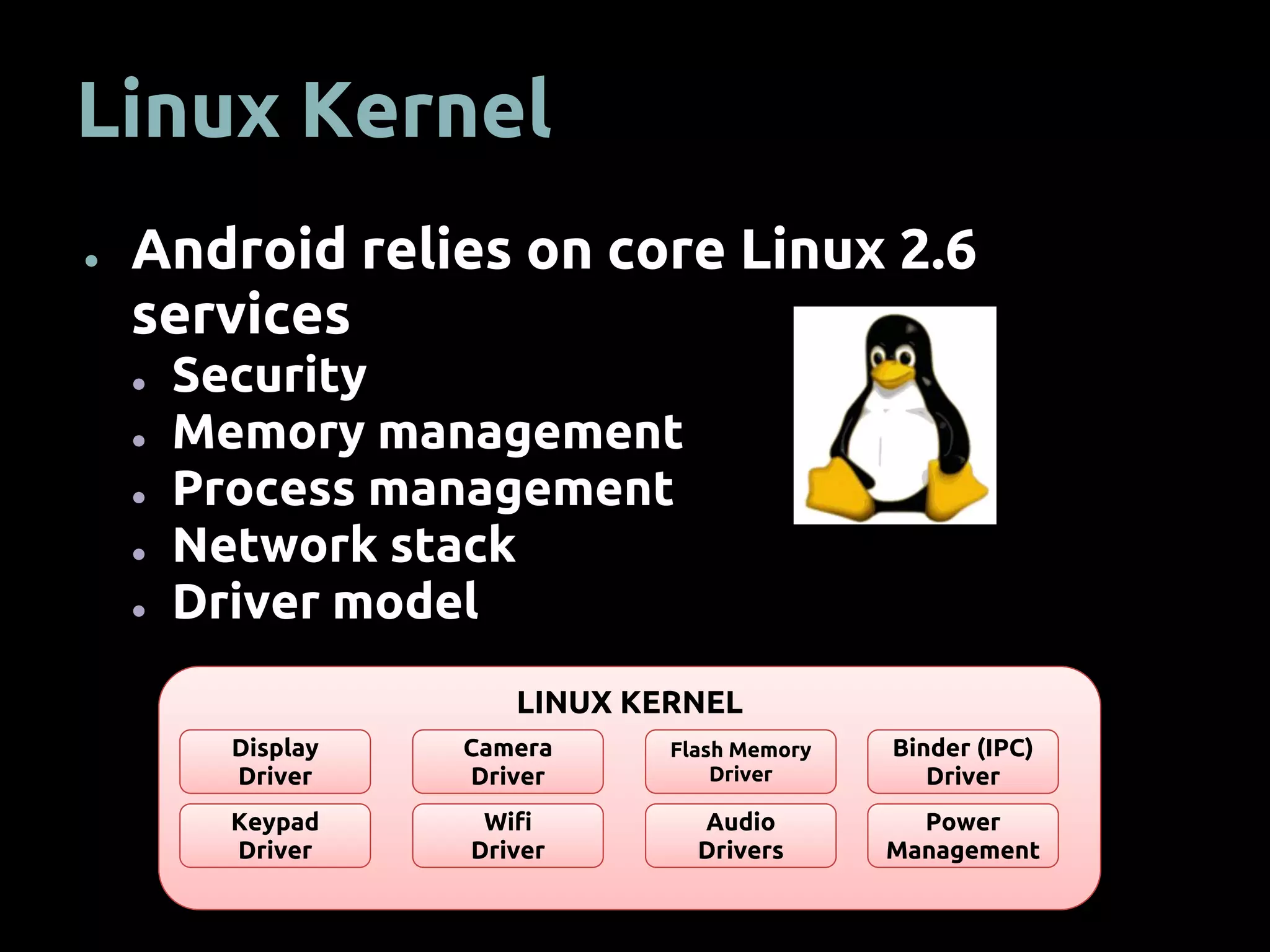
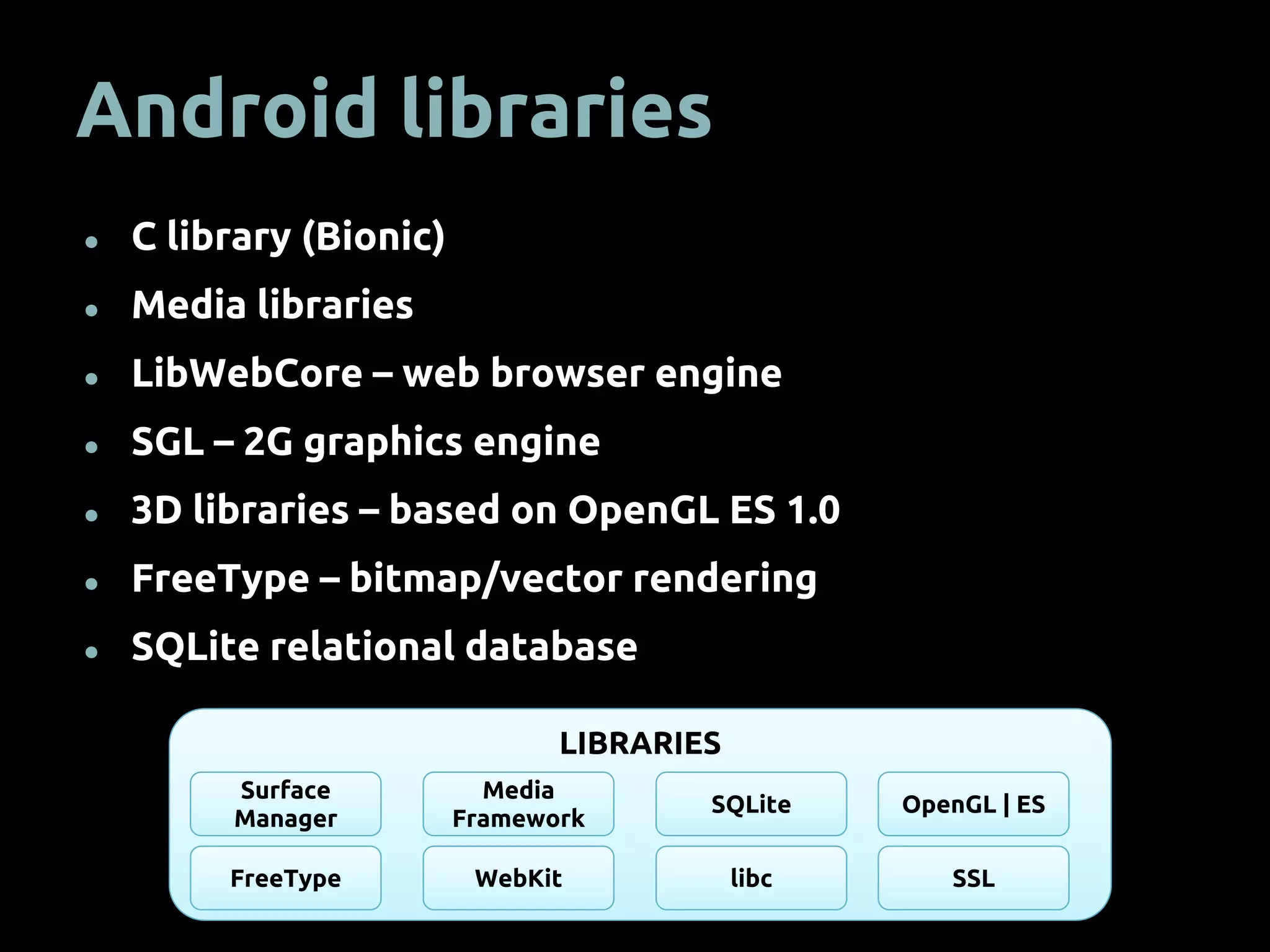
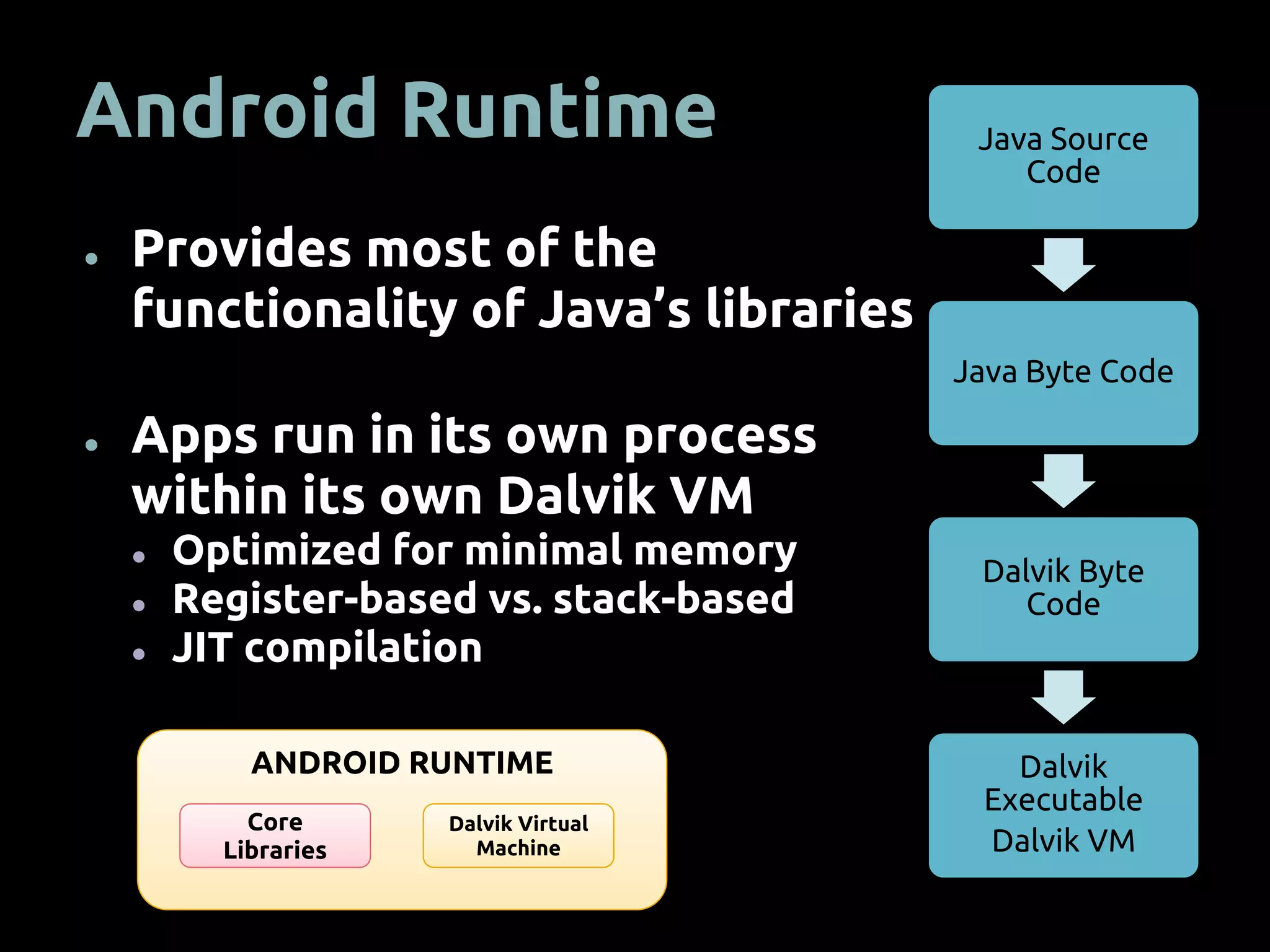
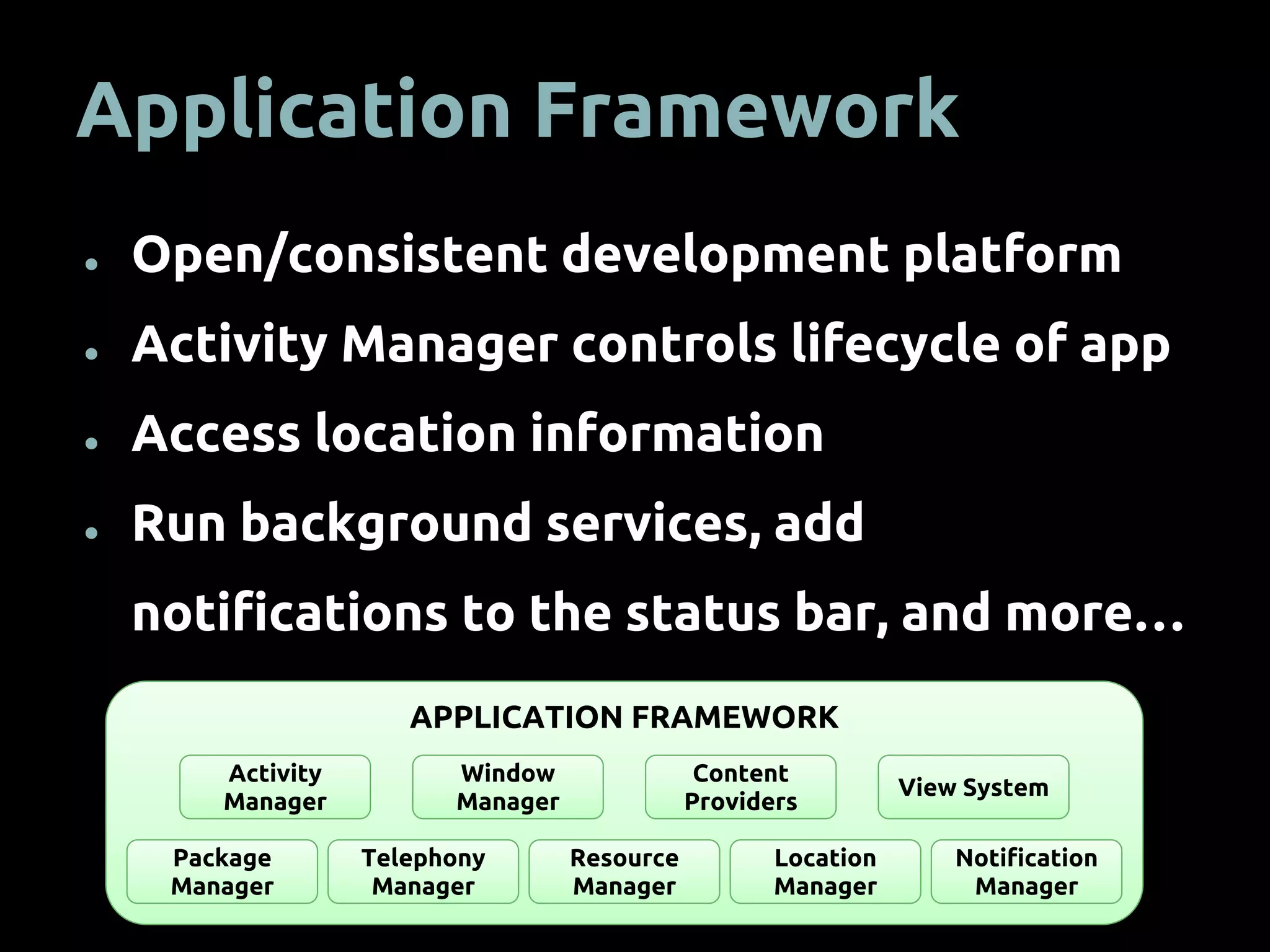
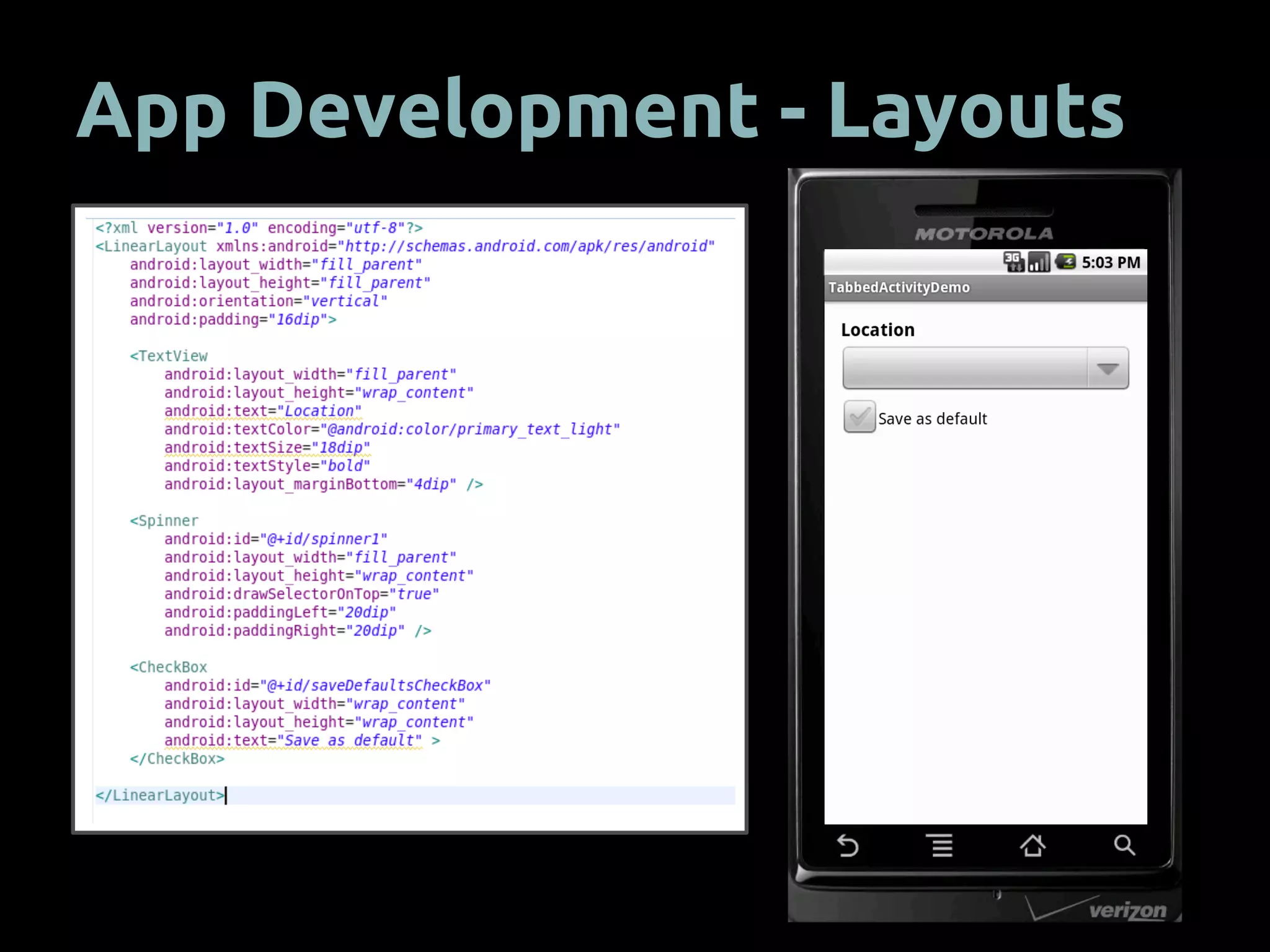
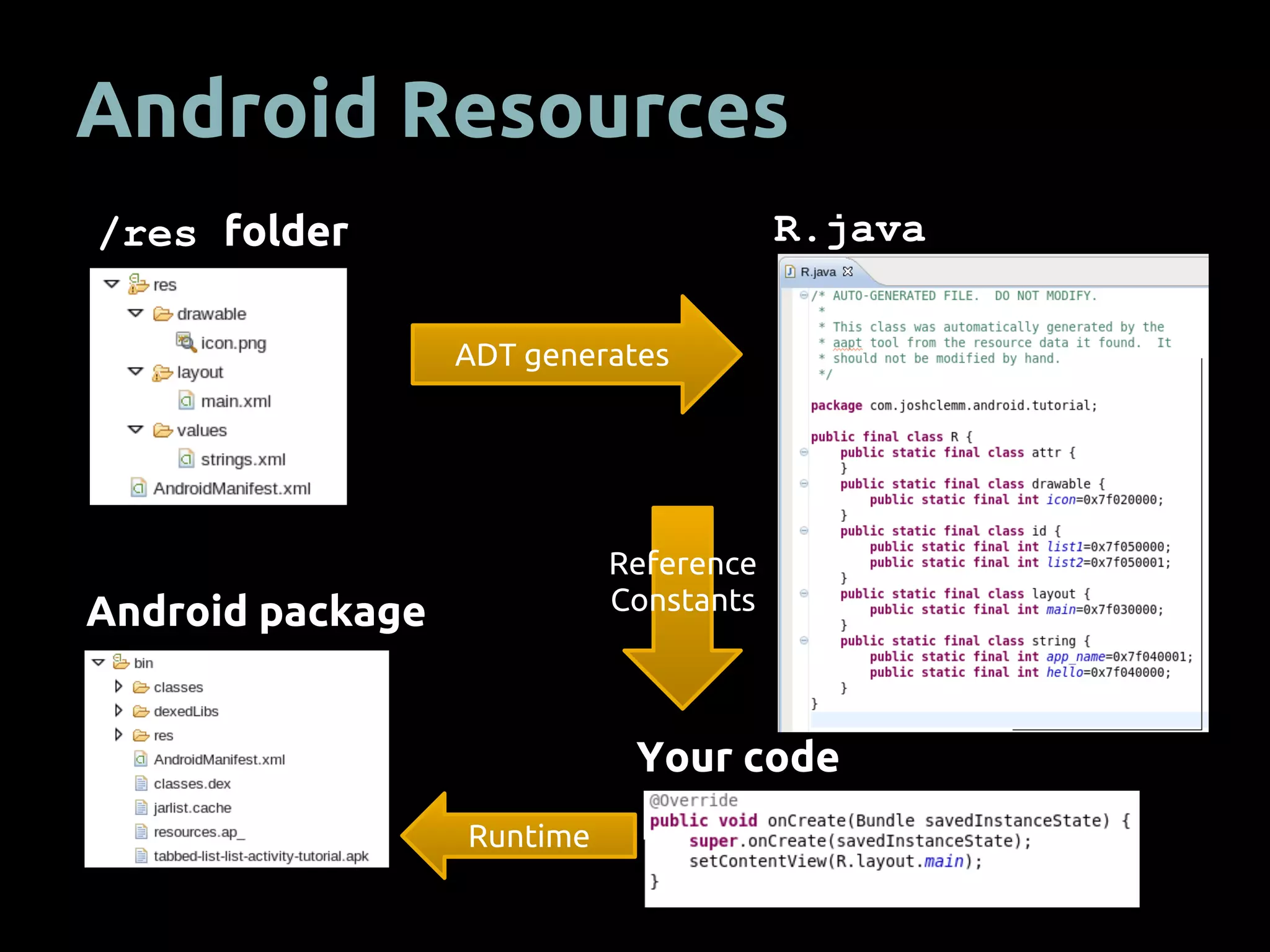
The document provides an overview of mobile app development using the Android SDK, highlighting its software stack and key components like the Linux kernel and Android runtime. It outlines steps for app development, including the required tools, coding logic, testing, publishing, and security measures involved. The document also covers resource management in Android and advice for developers on creating and publishing their applications.