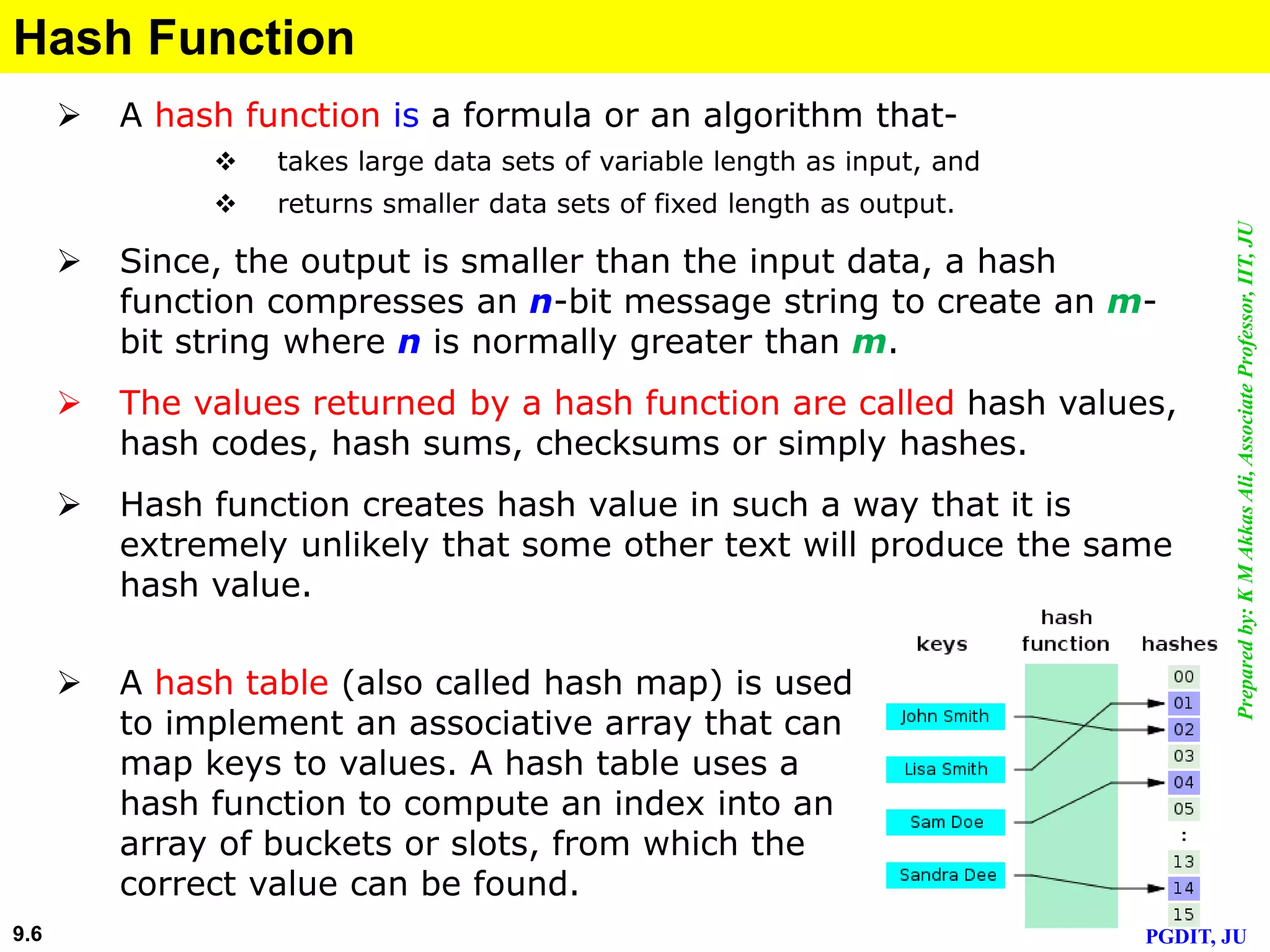
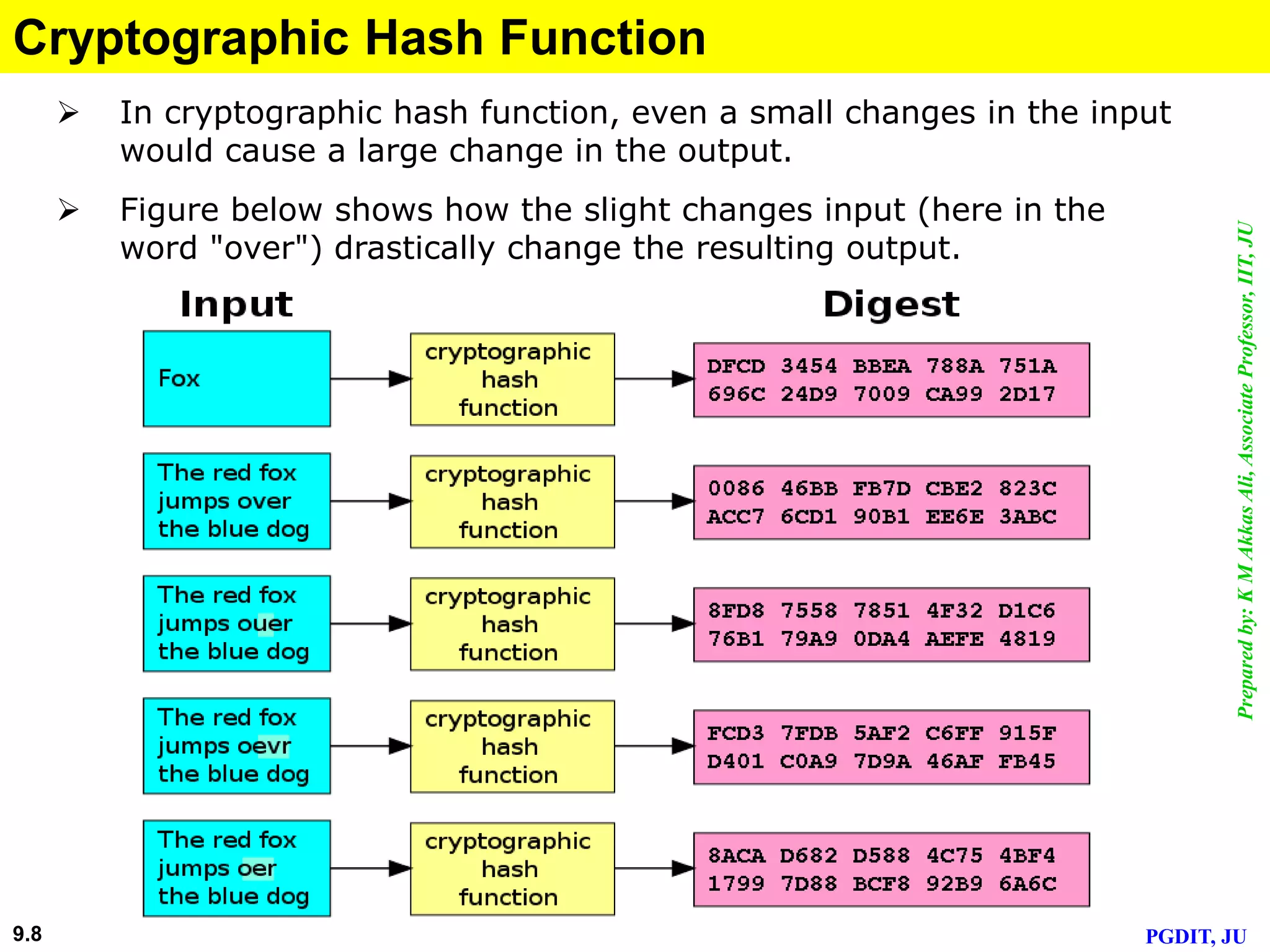
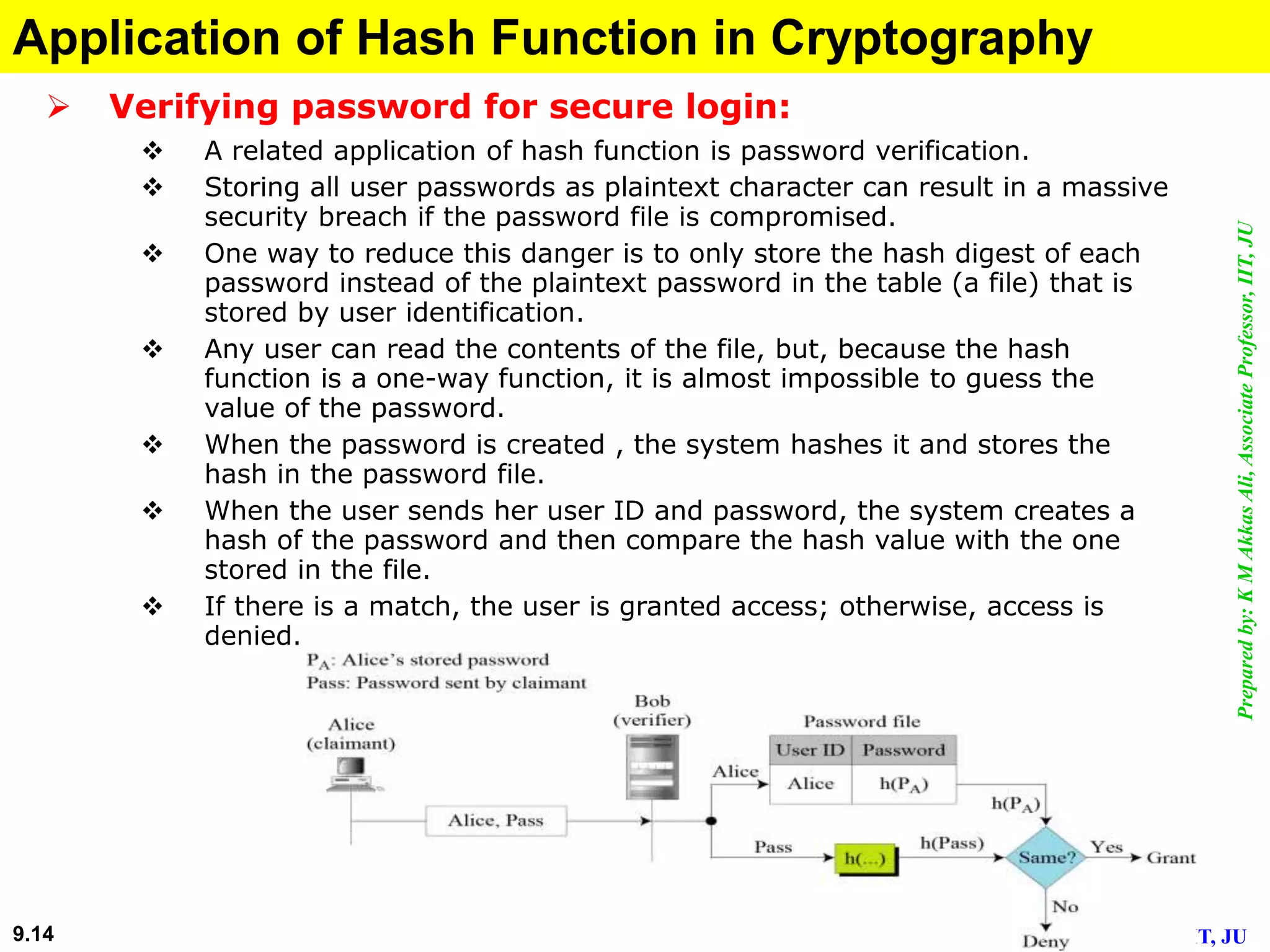
This document discusses cryptographic hash functions. It defines hashing as transforming a variable length string into a shorter, fixed length value. Cryptographic hash functions are designed to be one-way and resistant to tampering. They are important for security applications like digital signatures, message authentication and password verification. Commonly used hash functions include MD5 and SHA-1 which take arbitrary inputs and produce fixed-length outputs.