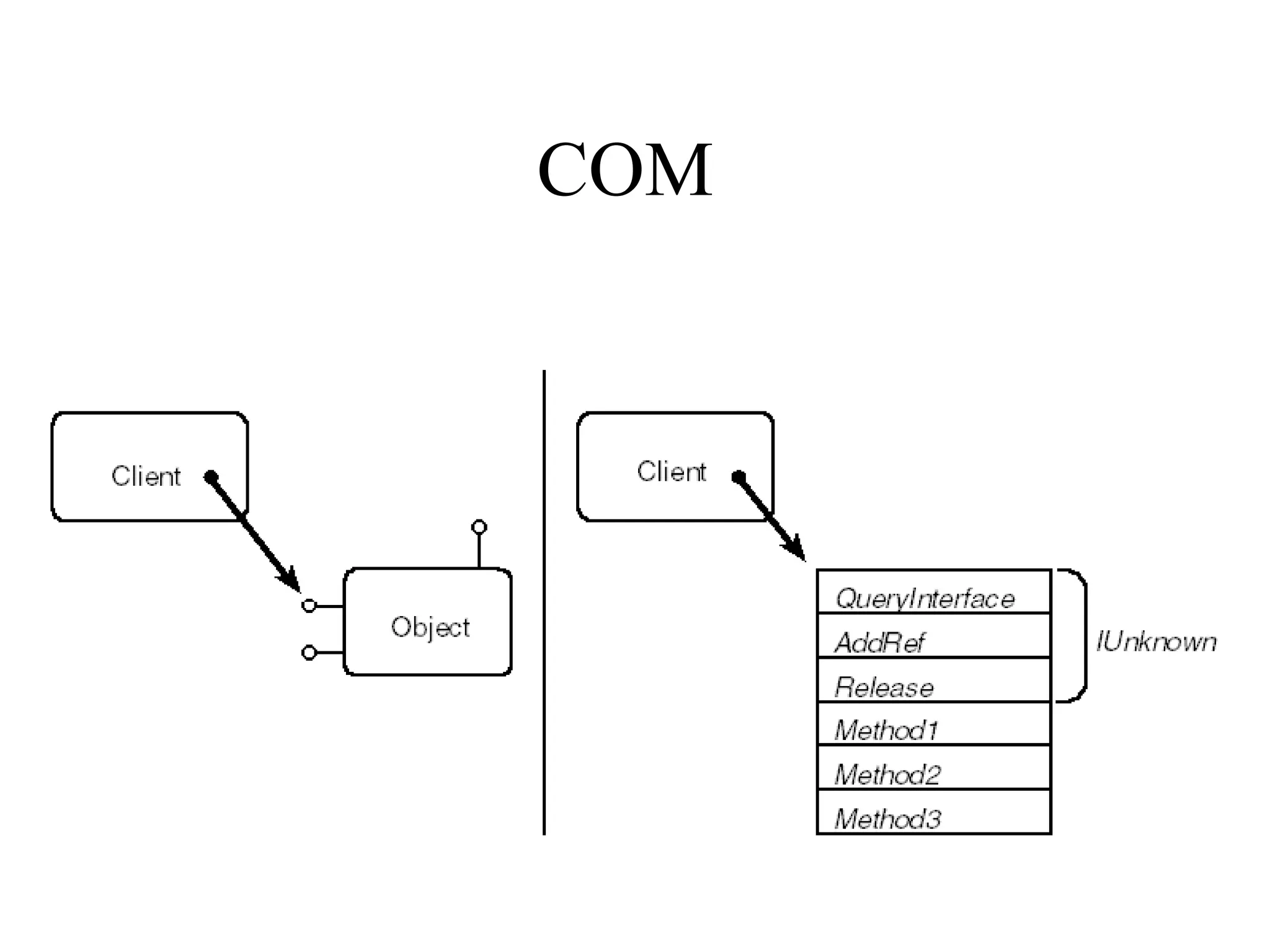
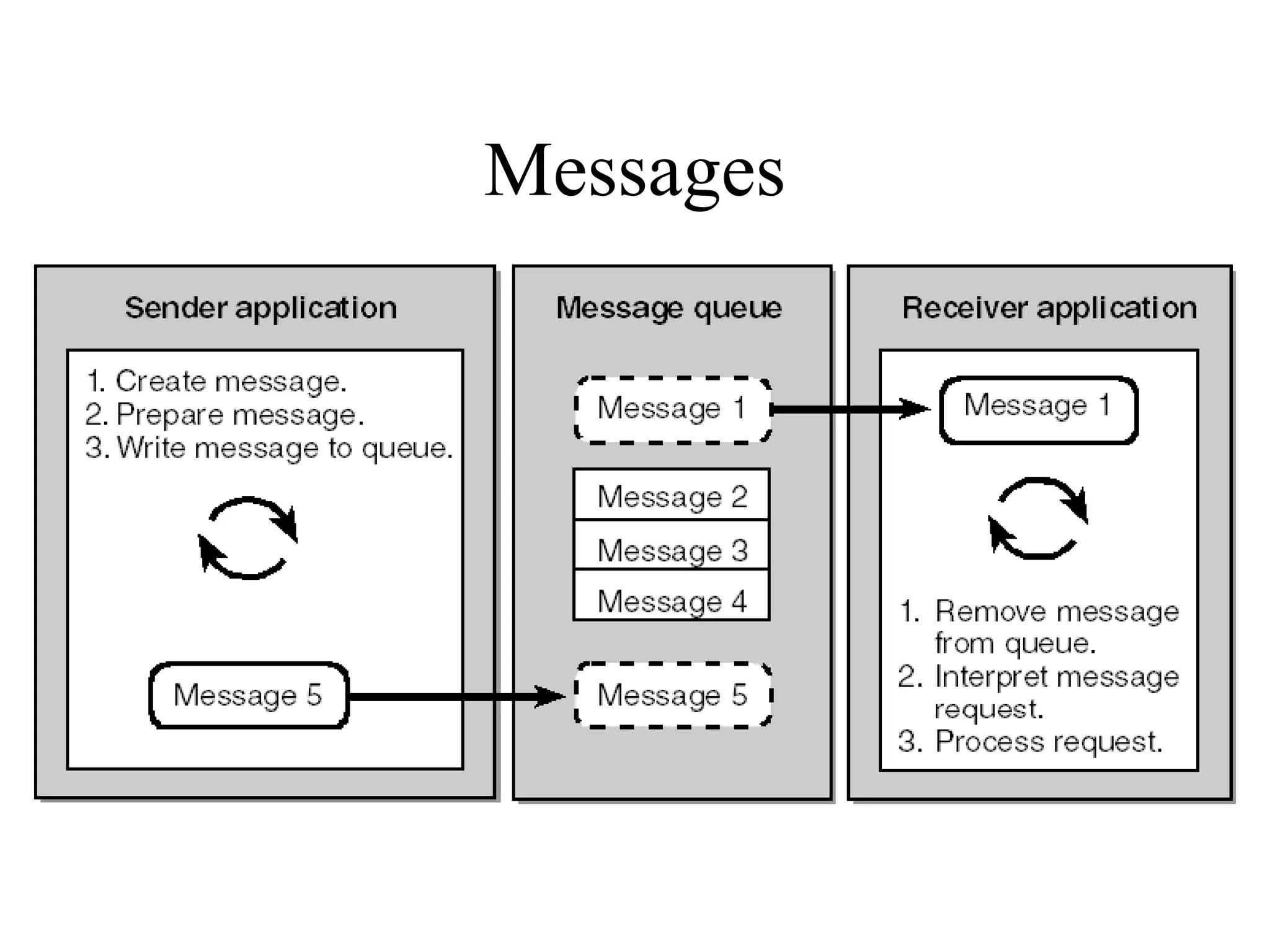
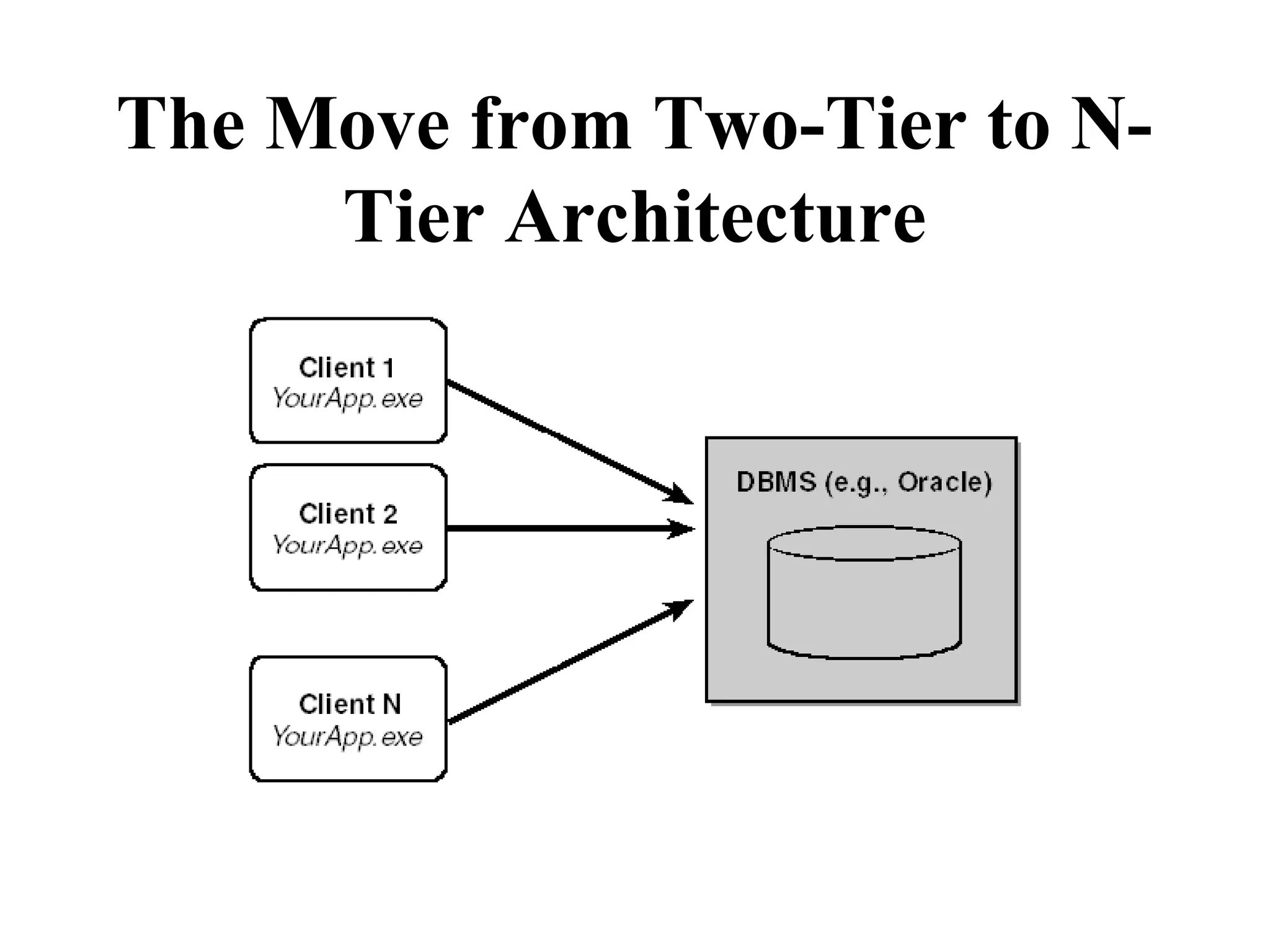
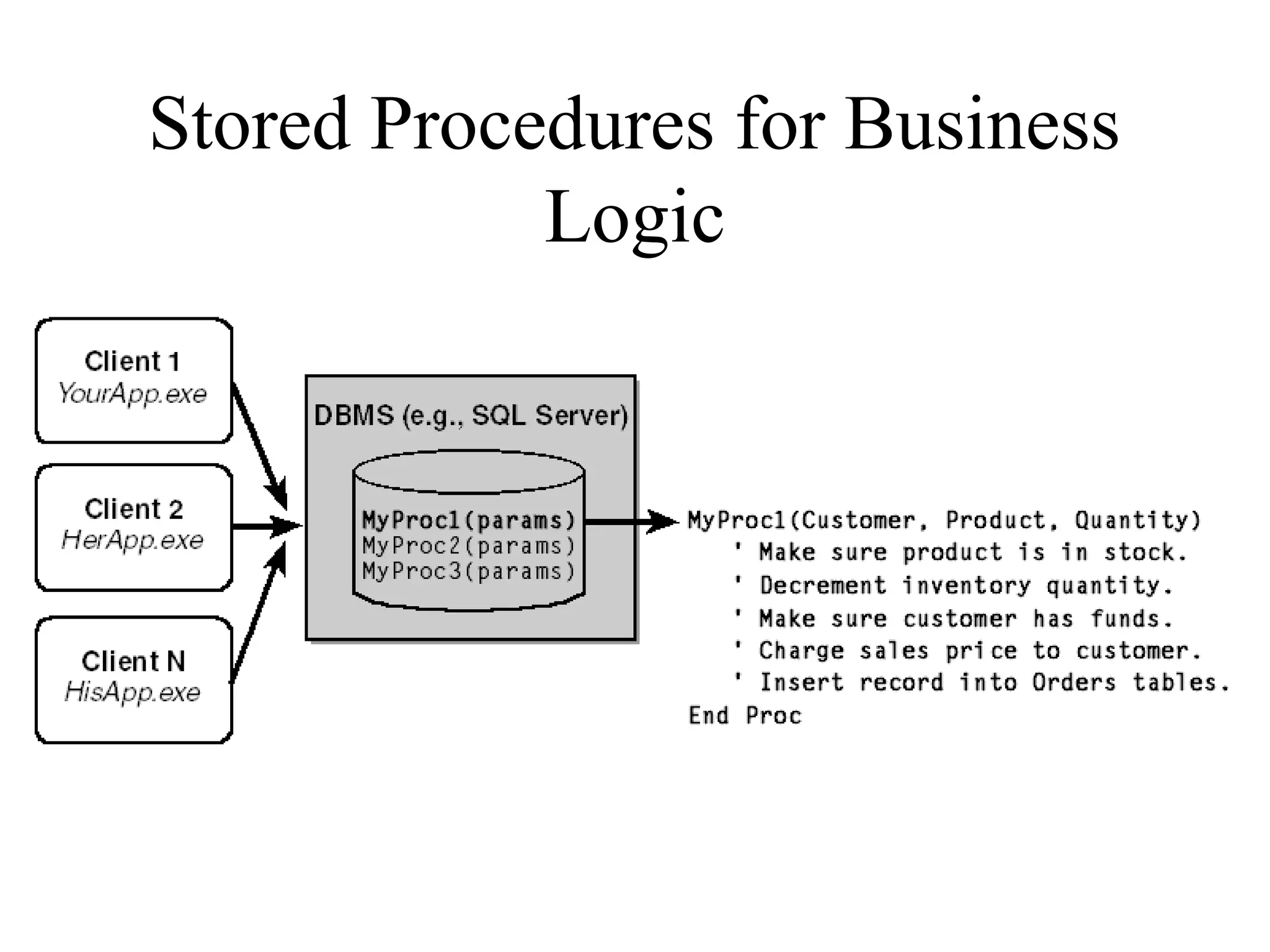
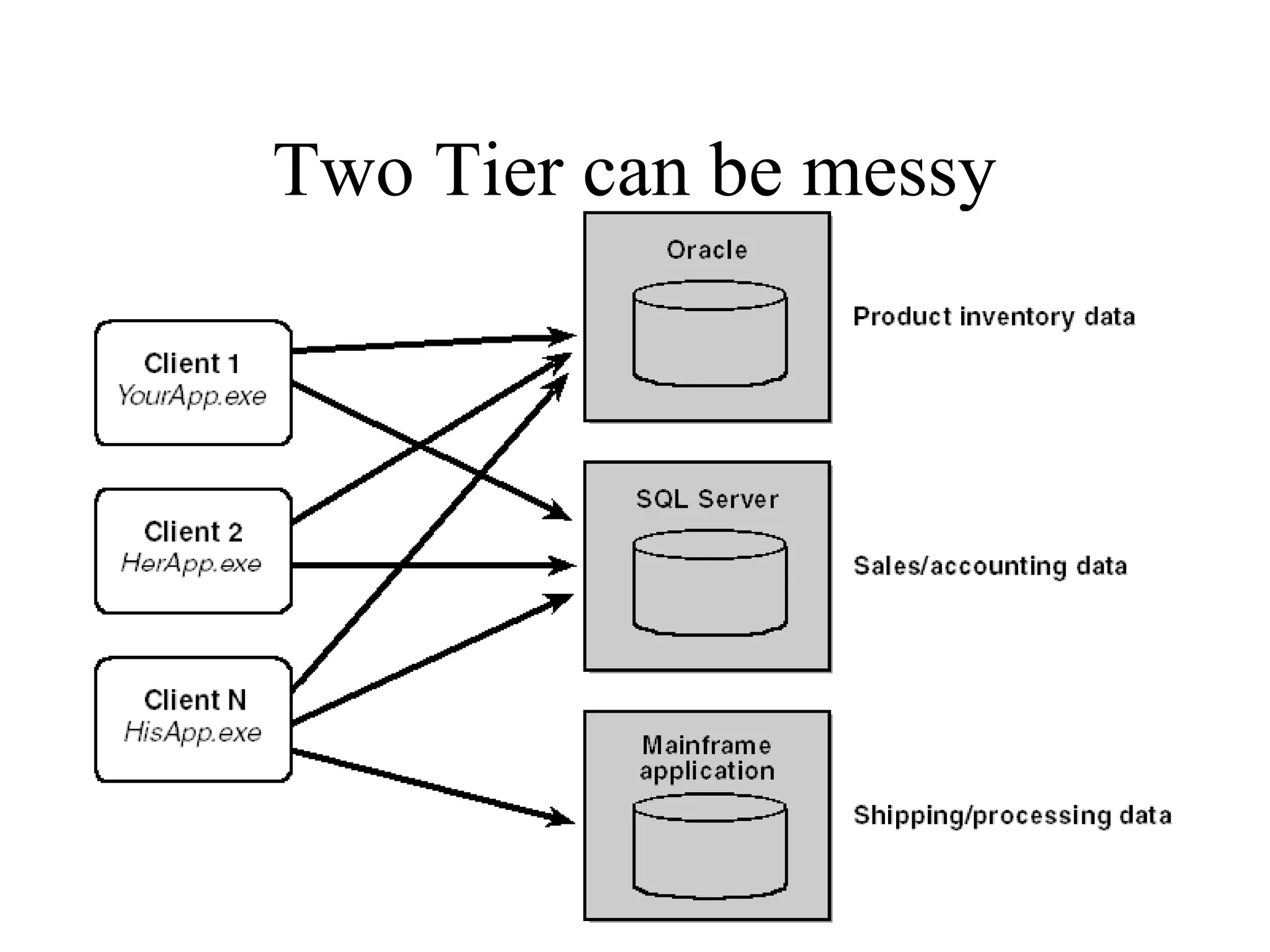
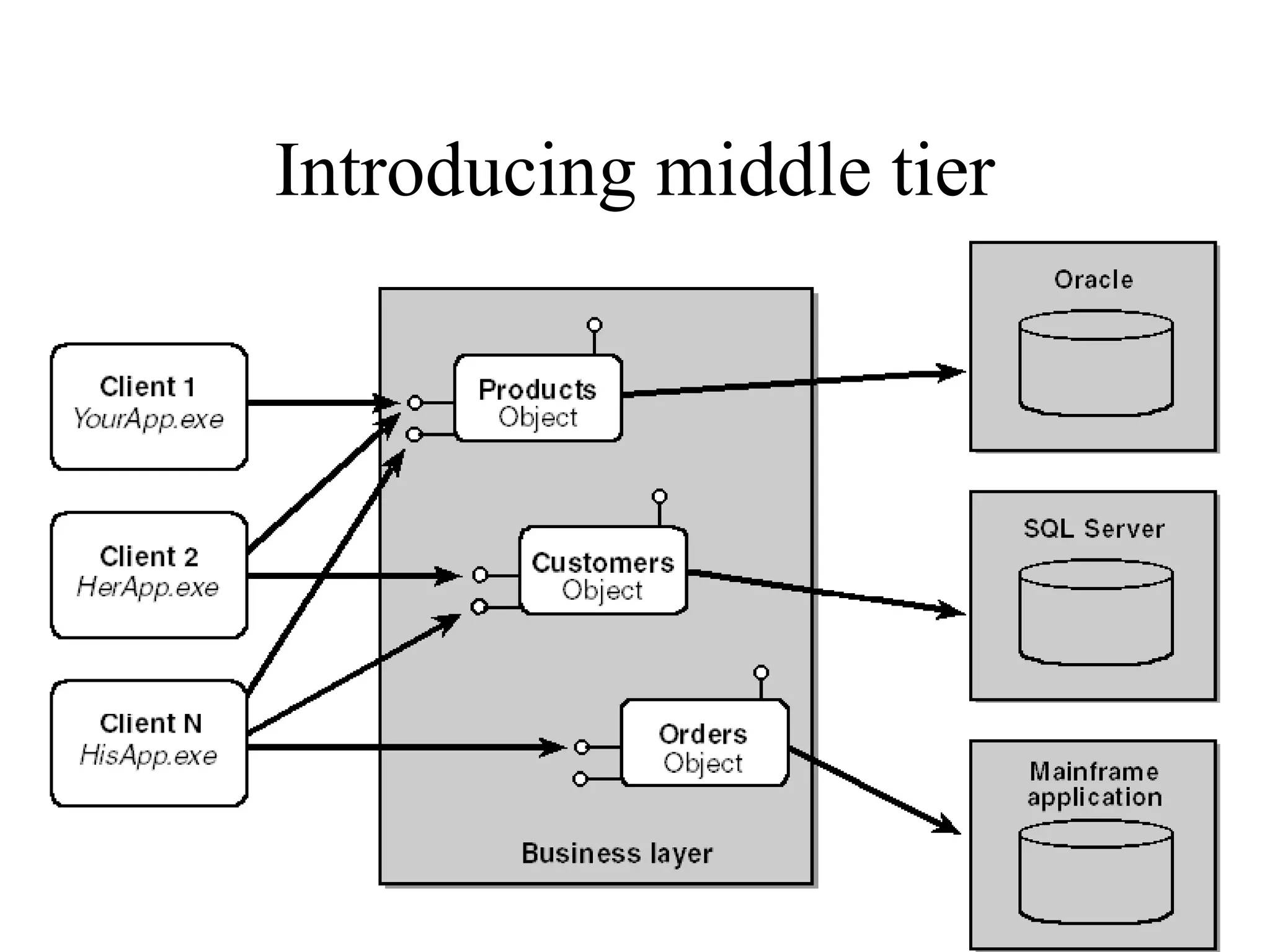
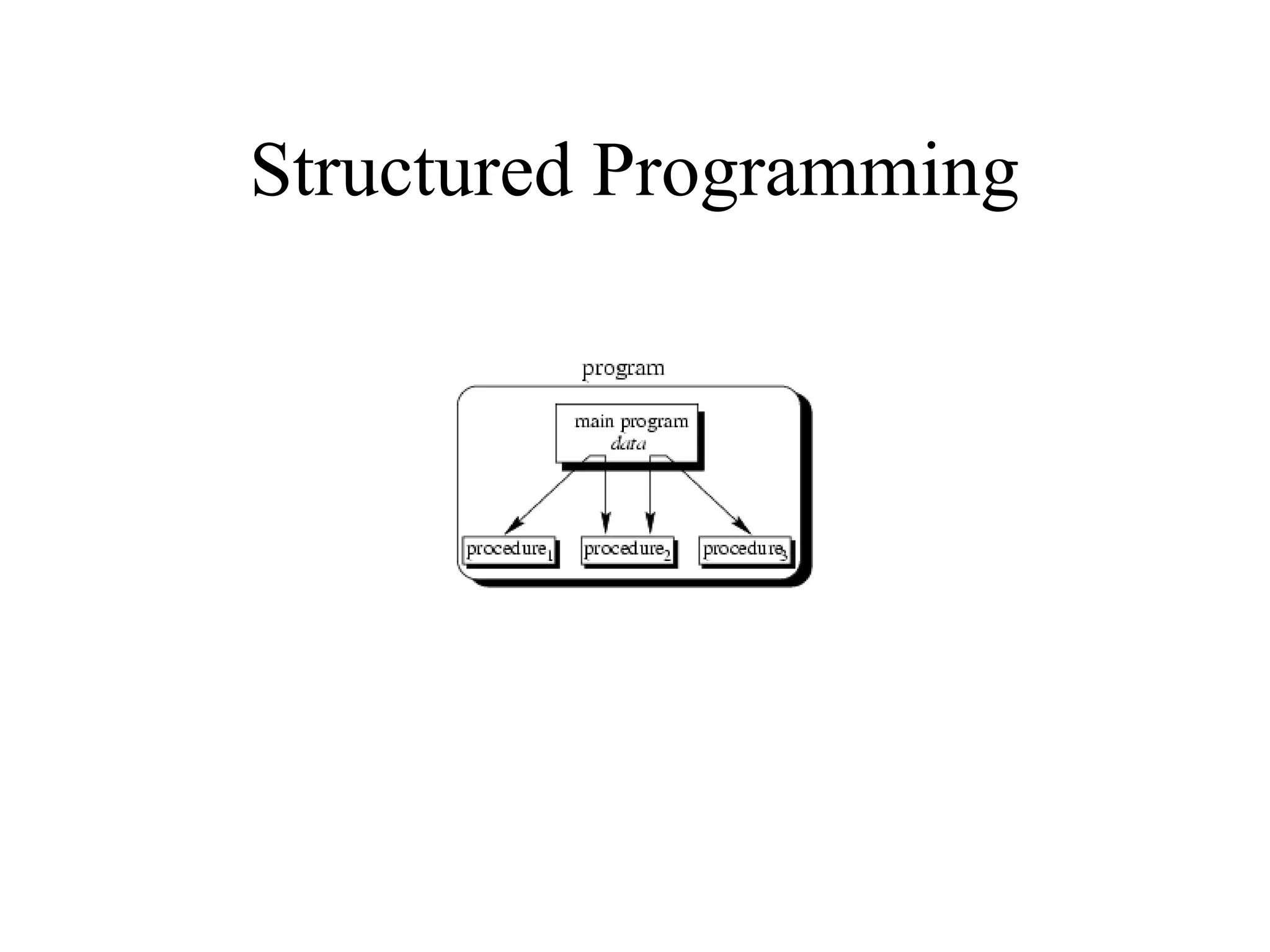
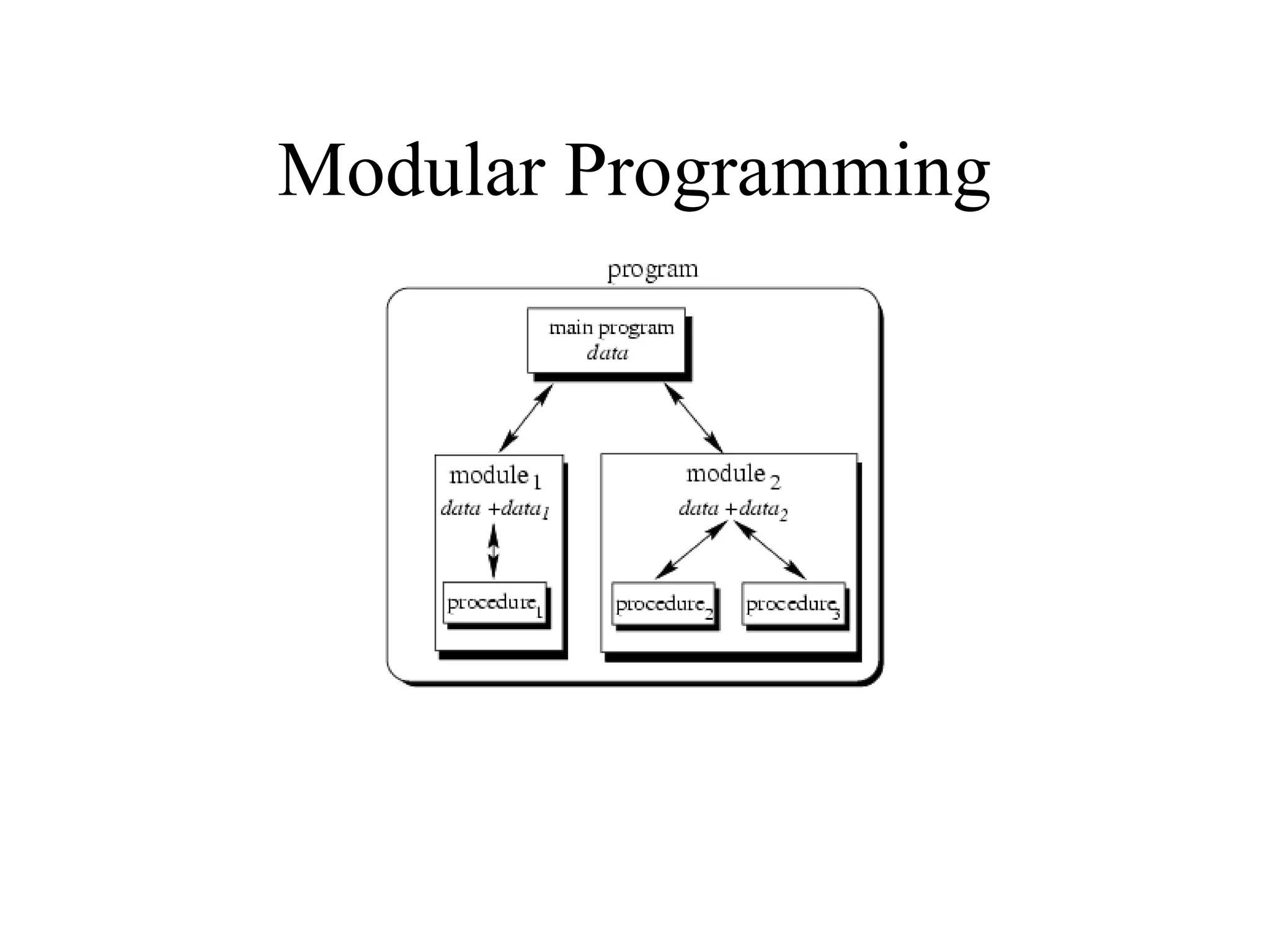
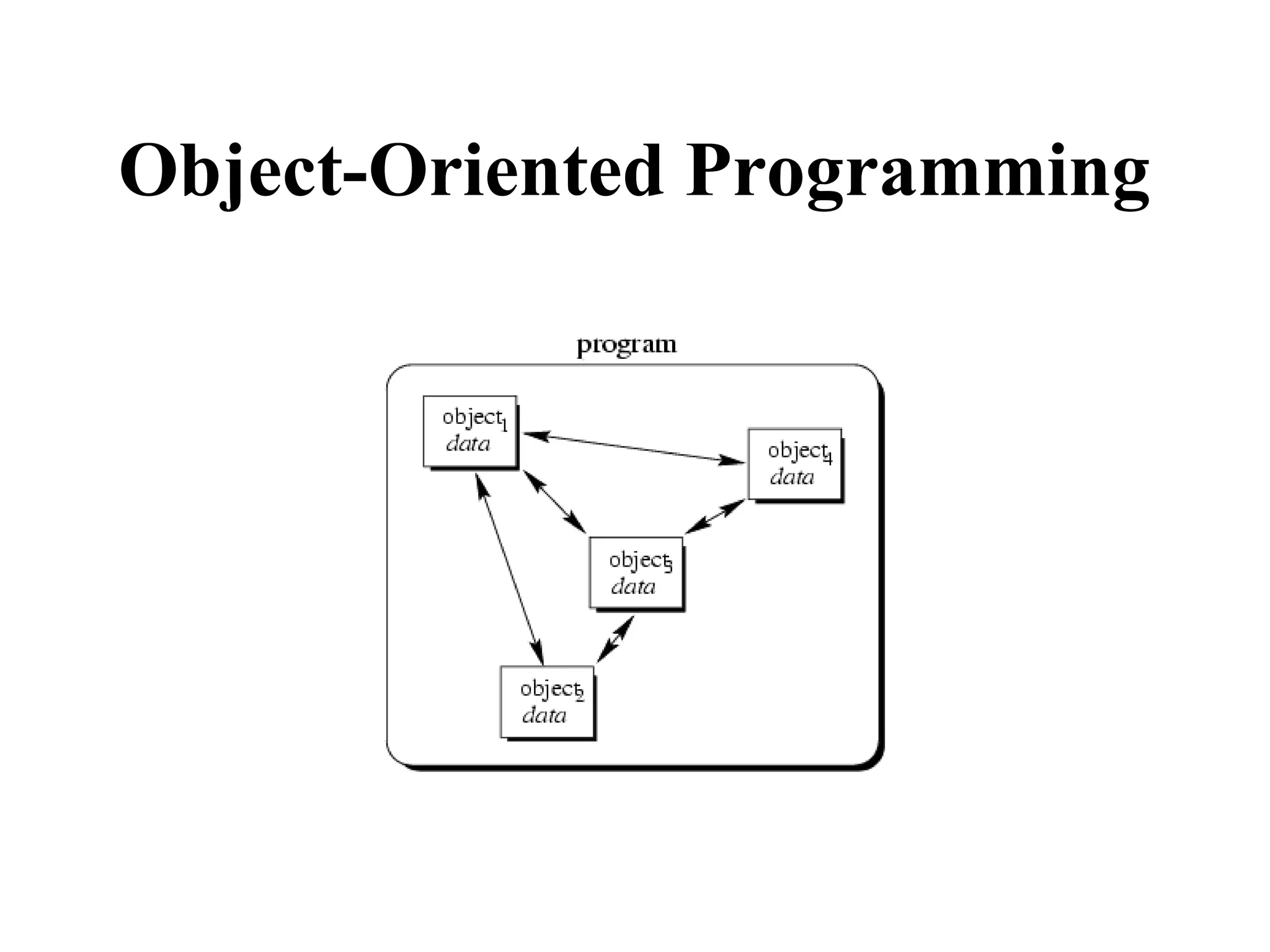
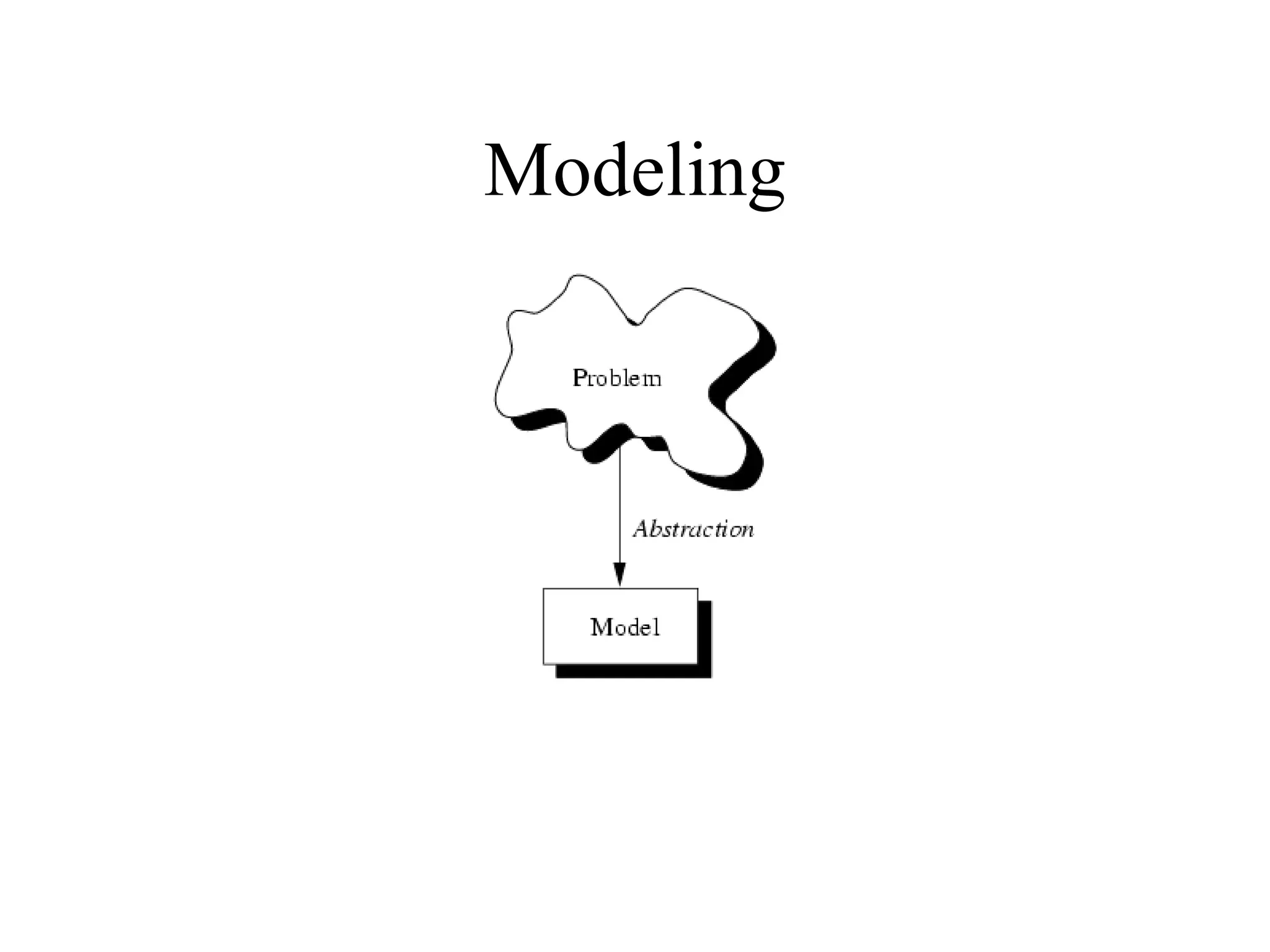
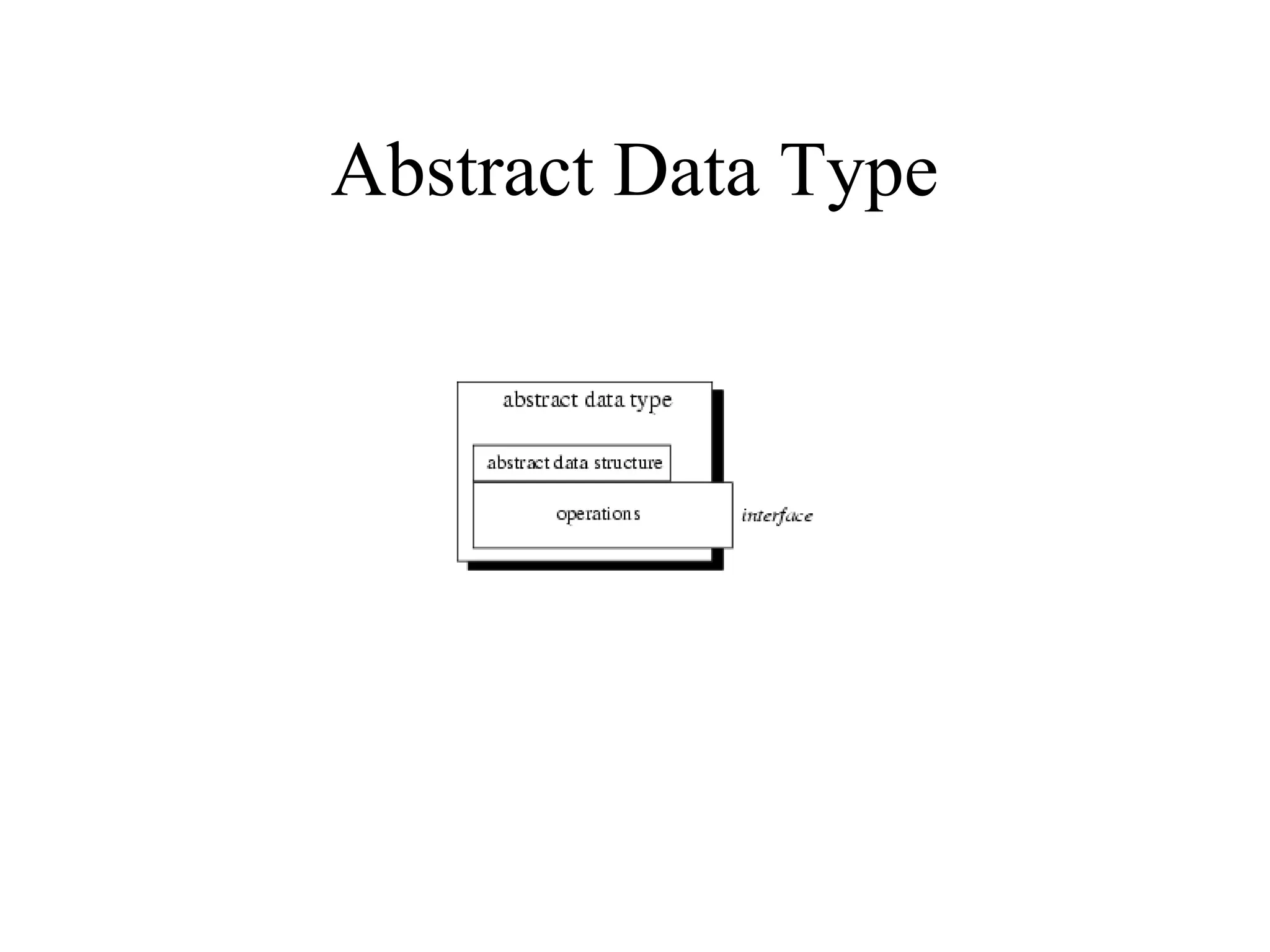
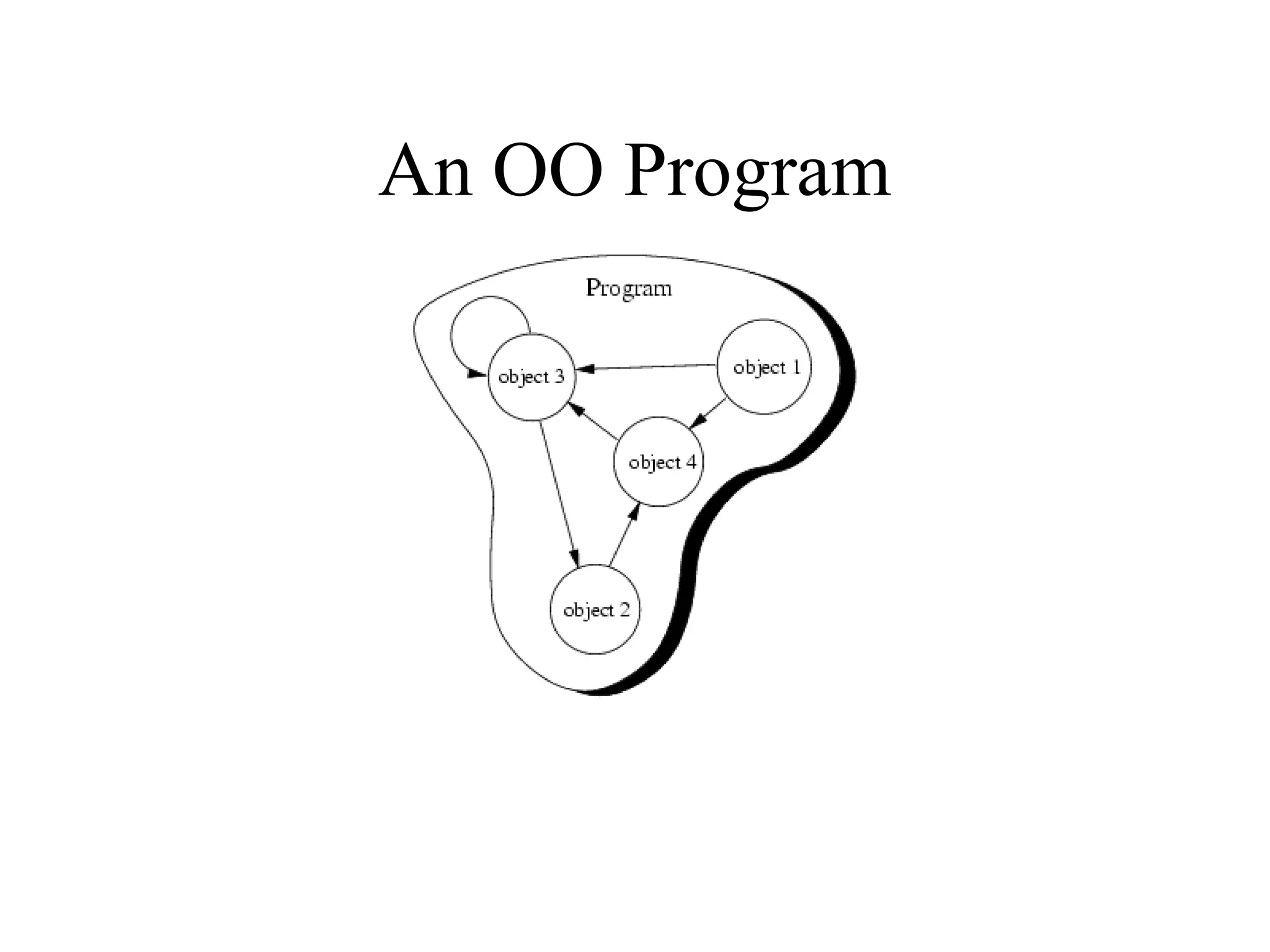
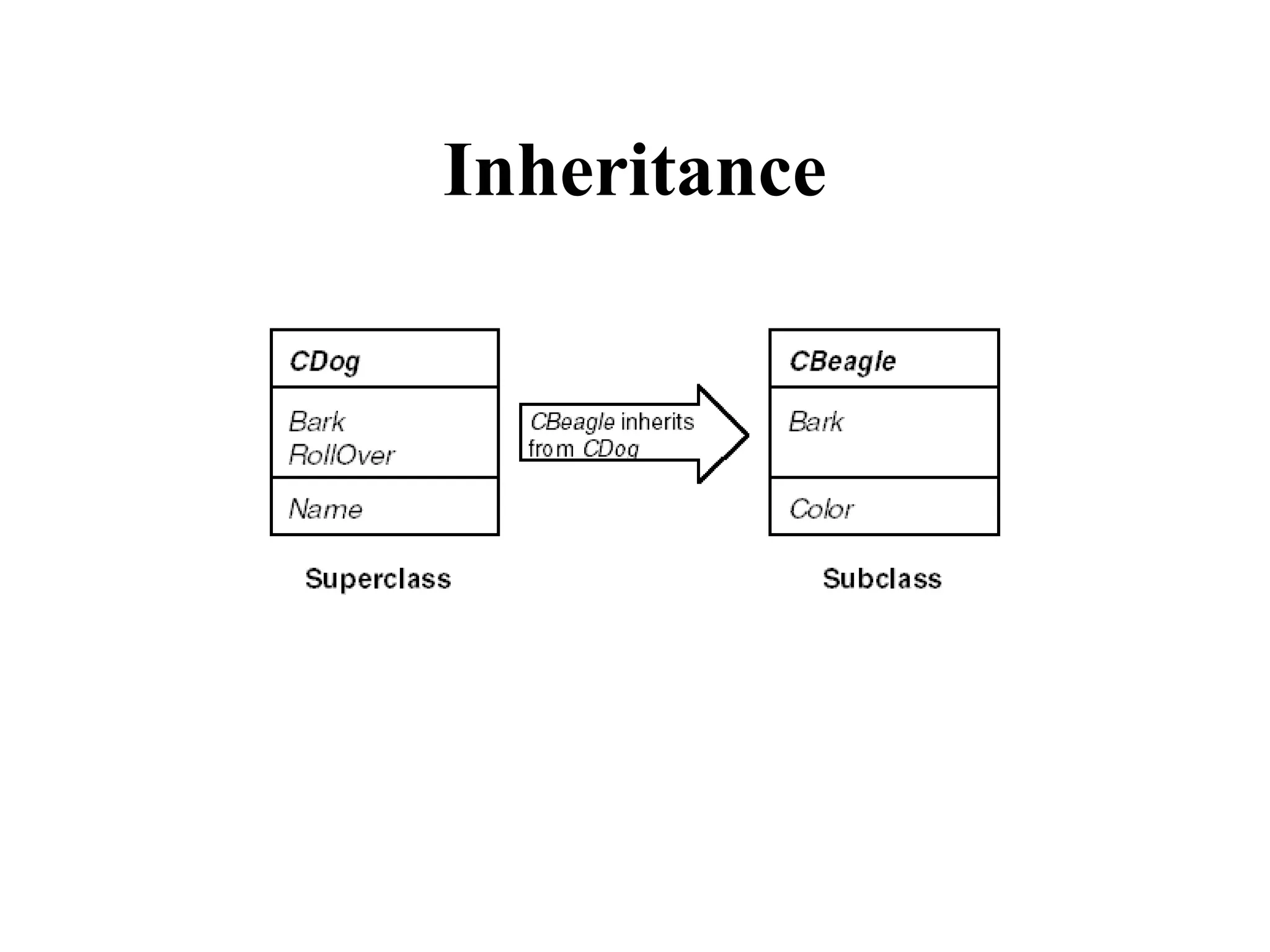
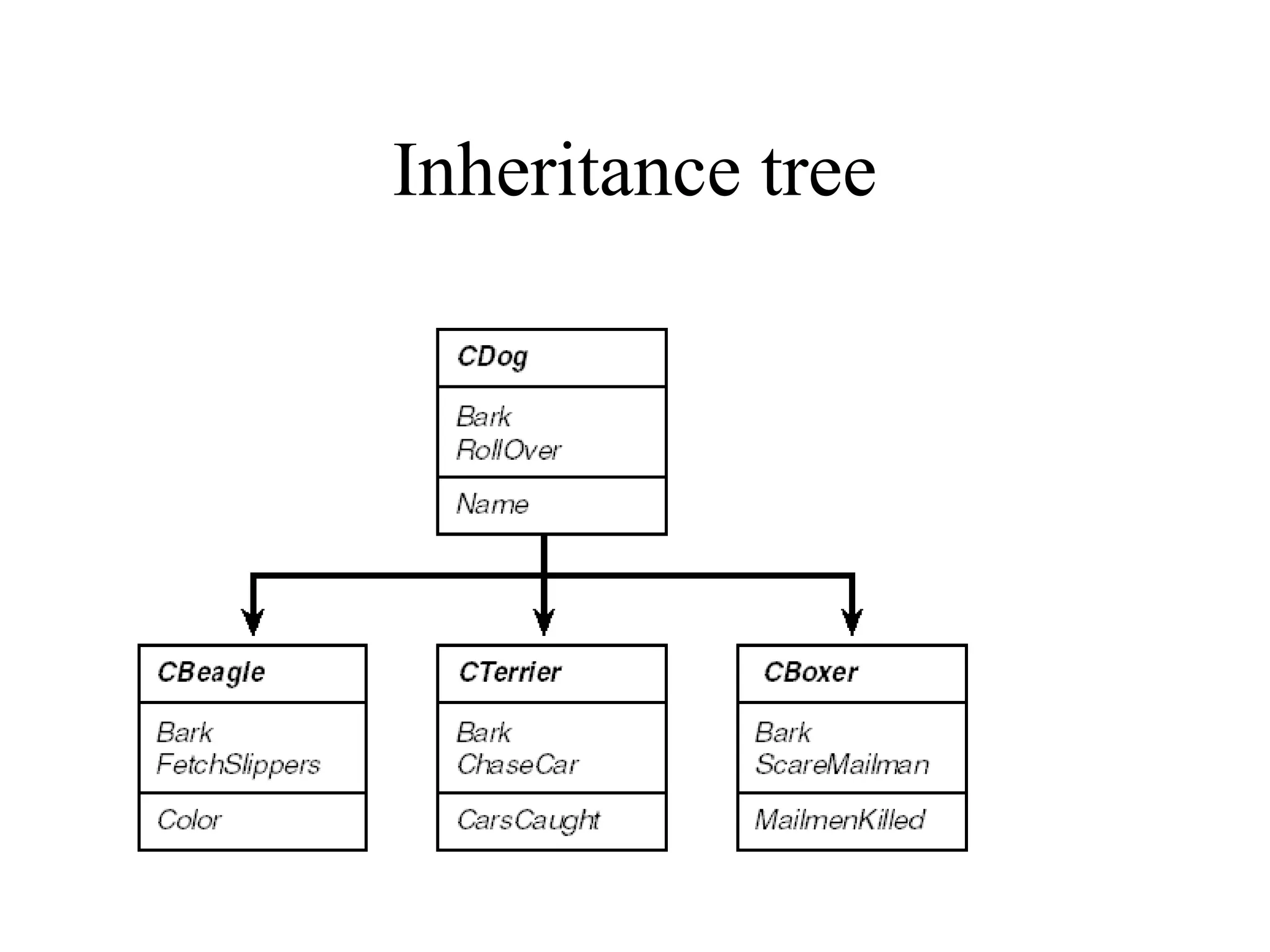
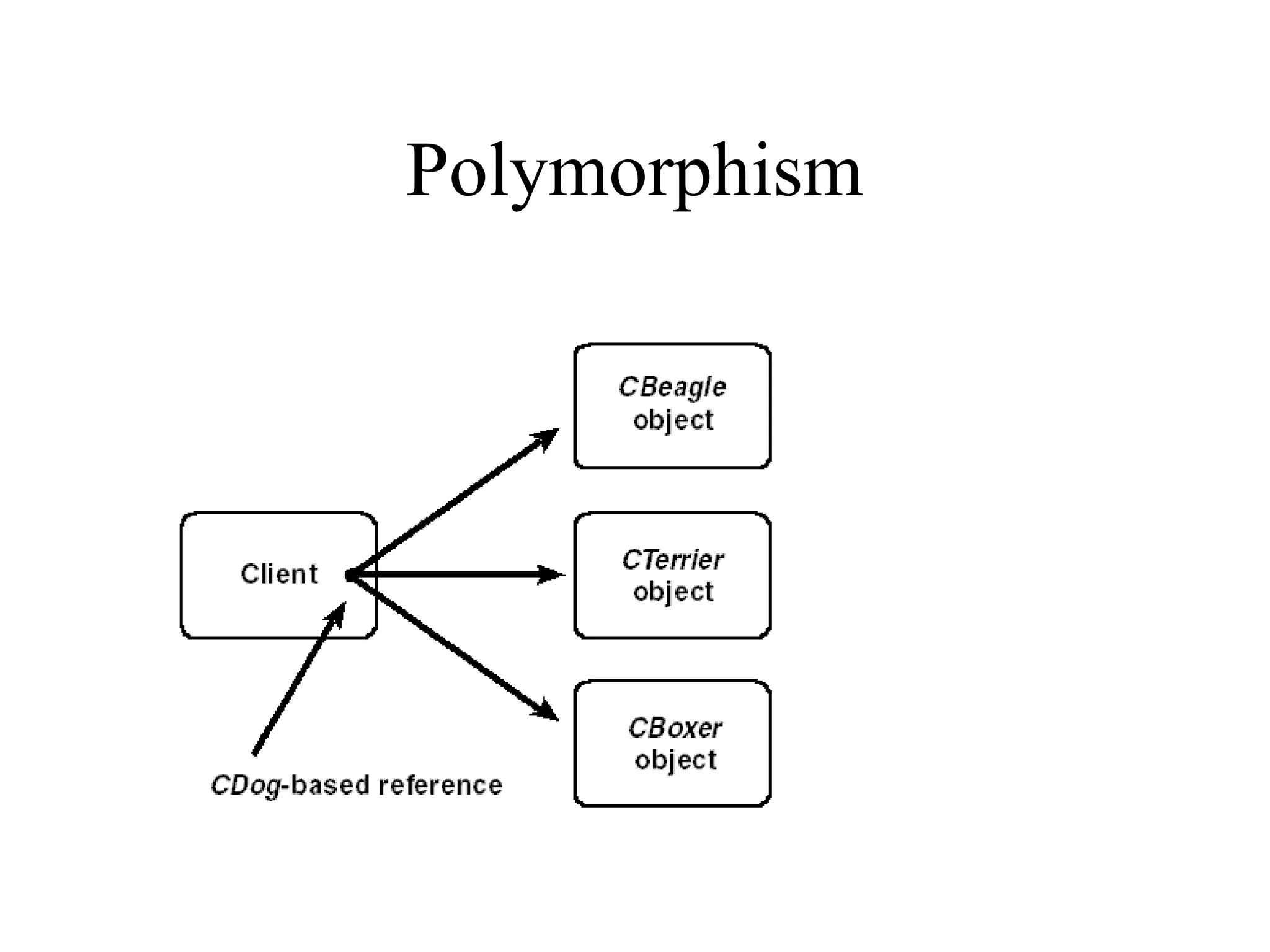
Object Oriented Programming involves analyzing a problem to identify classes, their responsibilities, and relationships. It aims to make software more modular, manageable, predictable, reusable, and maintainable. The analysis phase identifies what the software should do, design identifies classes and relationships, and implementation involves programming, testing and deployment. Key concepts include classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism and relationships like dependency, aggregation and inheritance.












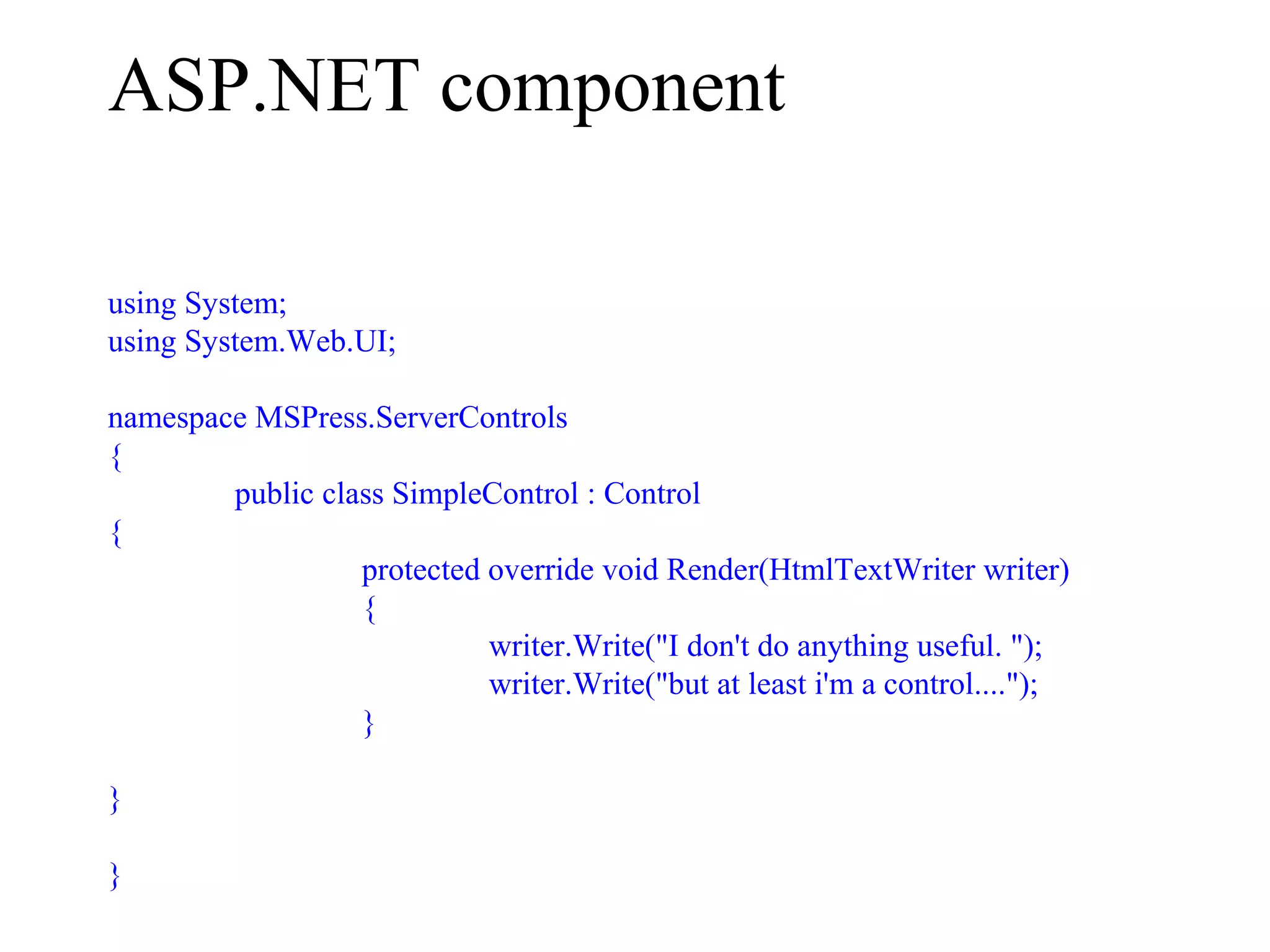




![Sample Program – Part 3
public SSN(string val) : base (val) {}
public bool Validate()
{
Console.WriteLine("[SSN.Validate] : Validating
'{0}'", data);
return (11 == data.Length) && (CorrectFormat());
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogrammingsystems-101109014640-phpapp02/75/Object-oriented-programming-systems-31-2048.jpg)
![Sample Program – Part 4
protected bool CorrectFormat()
{bool correctFormat = true;
for (int i = 0; (correctFormat && i < data.Length);
i++)
{
correctFormat =((IsDelimiterPosition(i) && data[i]
== DELIMITER)|| (IsNumberPosition(i)&&
char.IsNumber(data[i])));
}
return correctFormat; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogrammingsystems-101109014640-phpapp02/75/Object-oriented-programming-systems-32-2048.jpg)
![Sample Program – Part 6
class InterfacesApp
{ //Main class starts here
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string data = "";
if (0 < args.GetLength(0))
data = args[0];
SSN ssn = new SSN(data);
IValidate val = (IValidate)ssn;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogrammingsystems-101109014640-phpapp02/75/Object-oriented-programming-systems-34-2048.jpg)
![Sample Program – Part 7
Console.WriteLine("[Main] Calling SSN.Validate");
bool success = val.Validate();
Console.WriteLine("[Main] The validation of
" +
"SSN '{0}' was {1}successful",
ssn.Data,
(true == success ? "" : "NOT "));
}
} //Main class ends here](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogrammingsystems-101109014640-phpapp02/75/Object-oriented-programming-systems-35-2048.jpg)