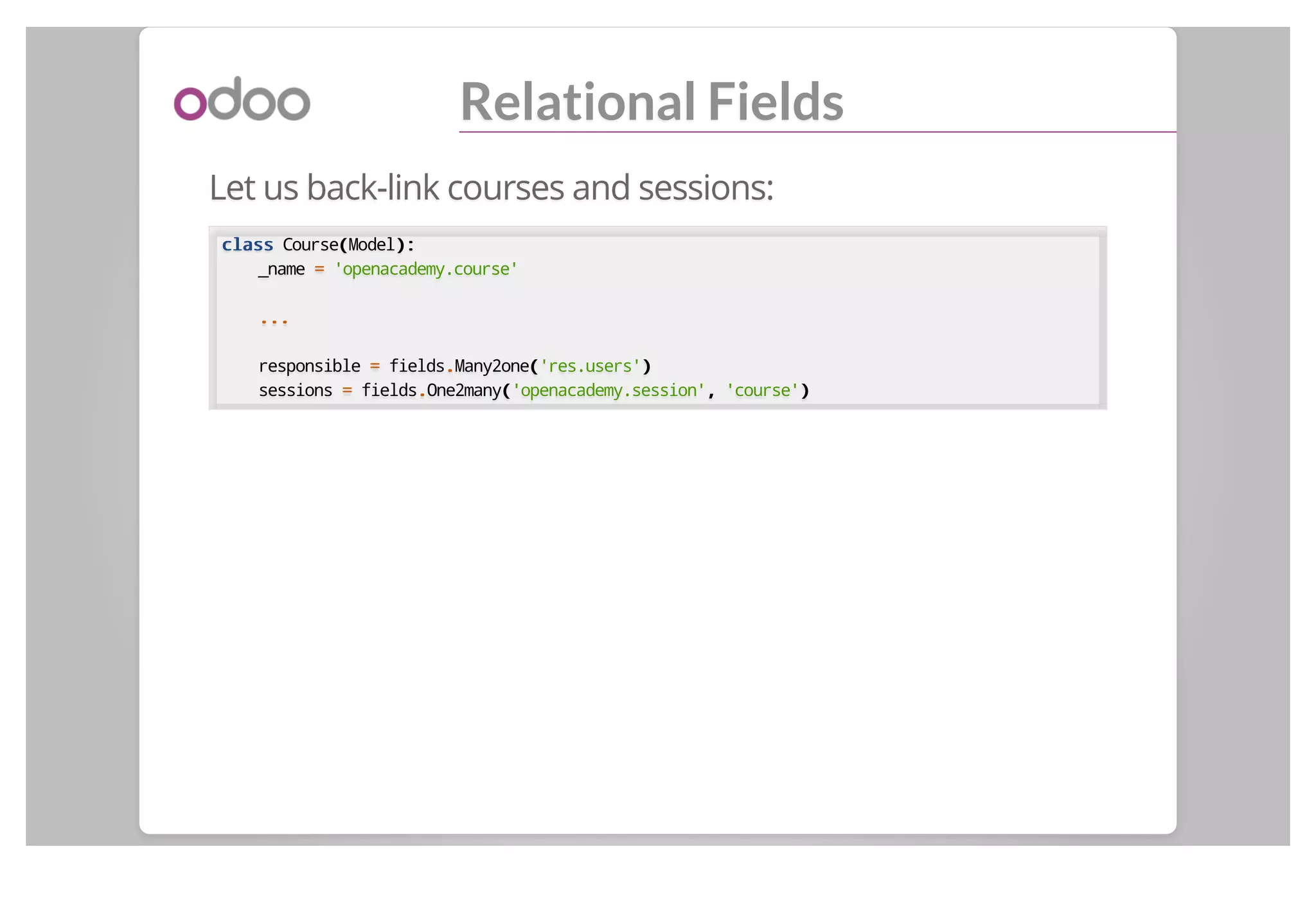
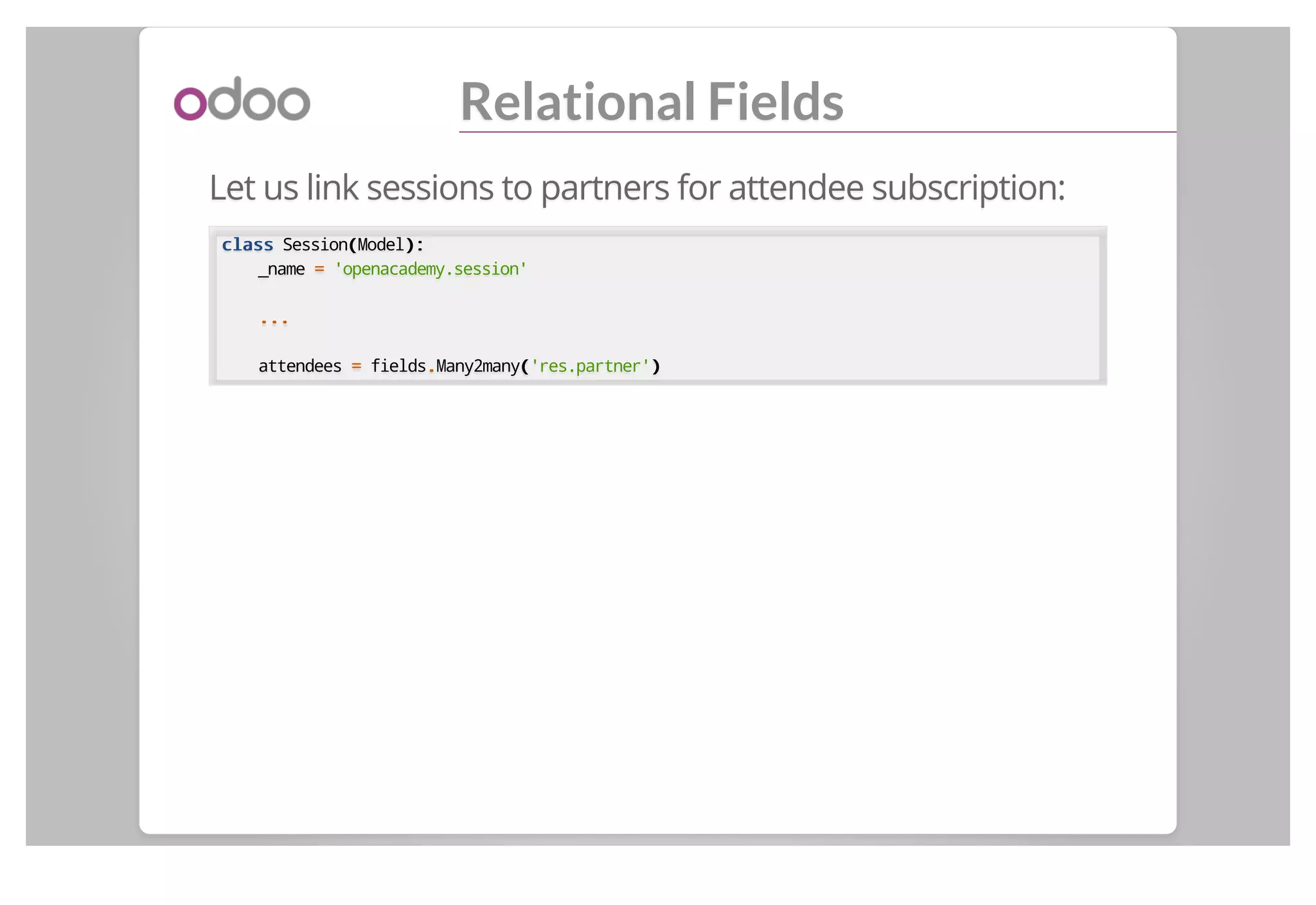
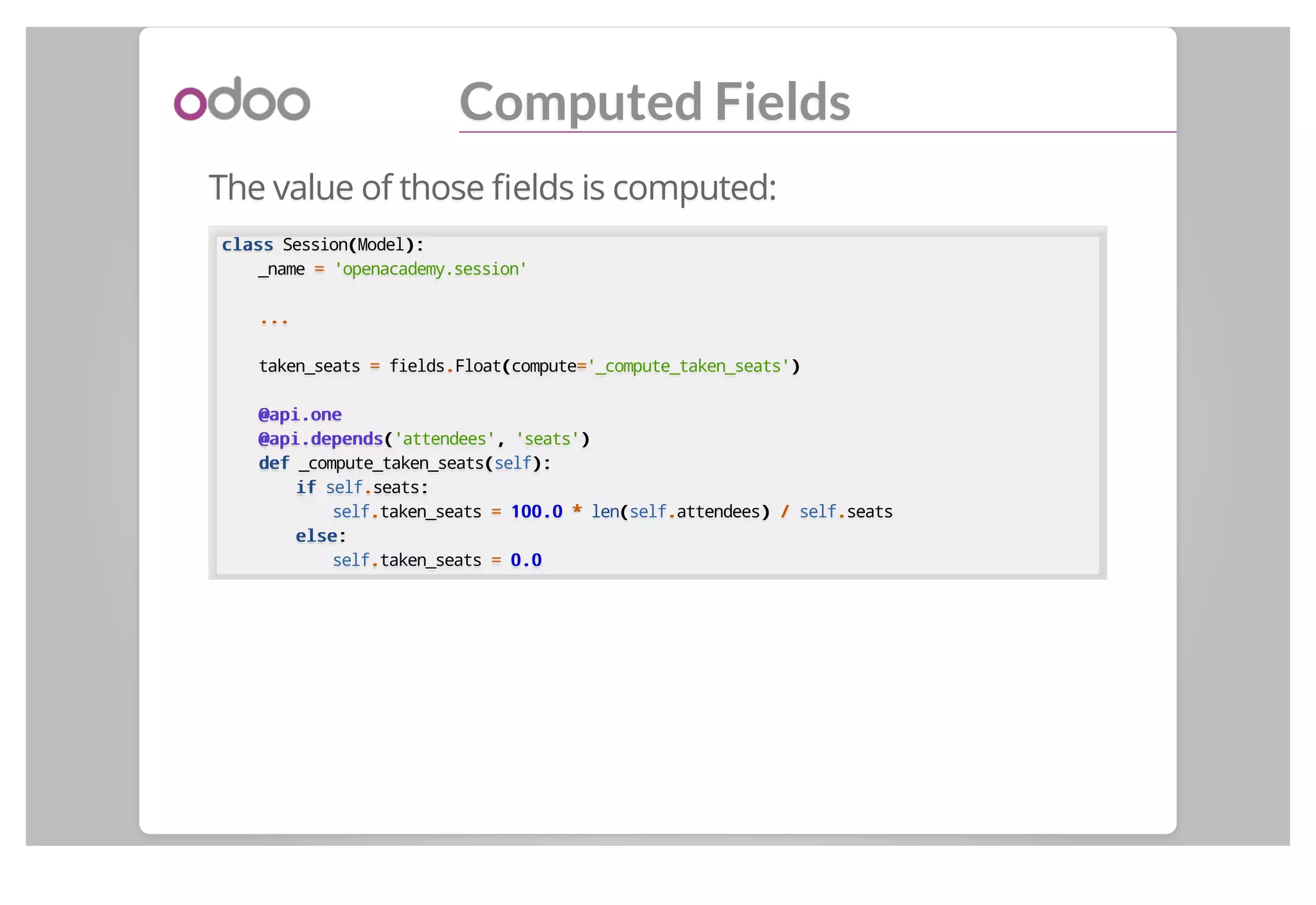
This document discusses backend modules in Odoo. It describes the architecture of Odoo as having a three-tier client/server/database structure. It then discusses the structure of an Odoo module, including its manifest file, data files defining views and menus, and Python code defining models. As an example, it walks through the implementation of an "Open Academy" module to manage courses, sessions, and subscriptions.



![The Open Academy Module
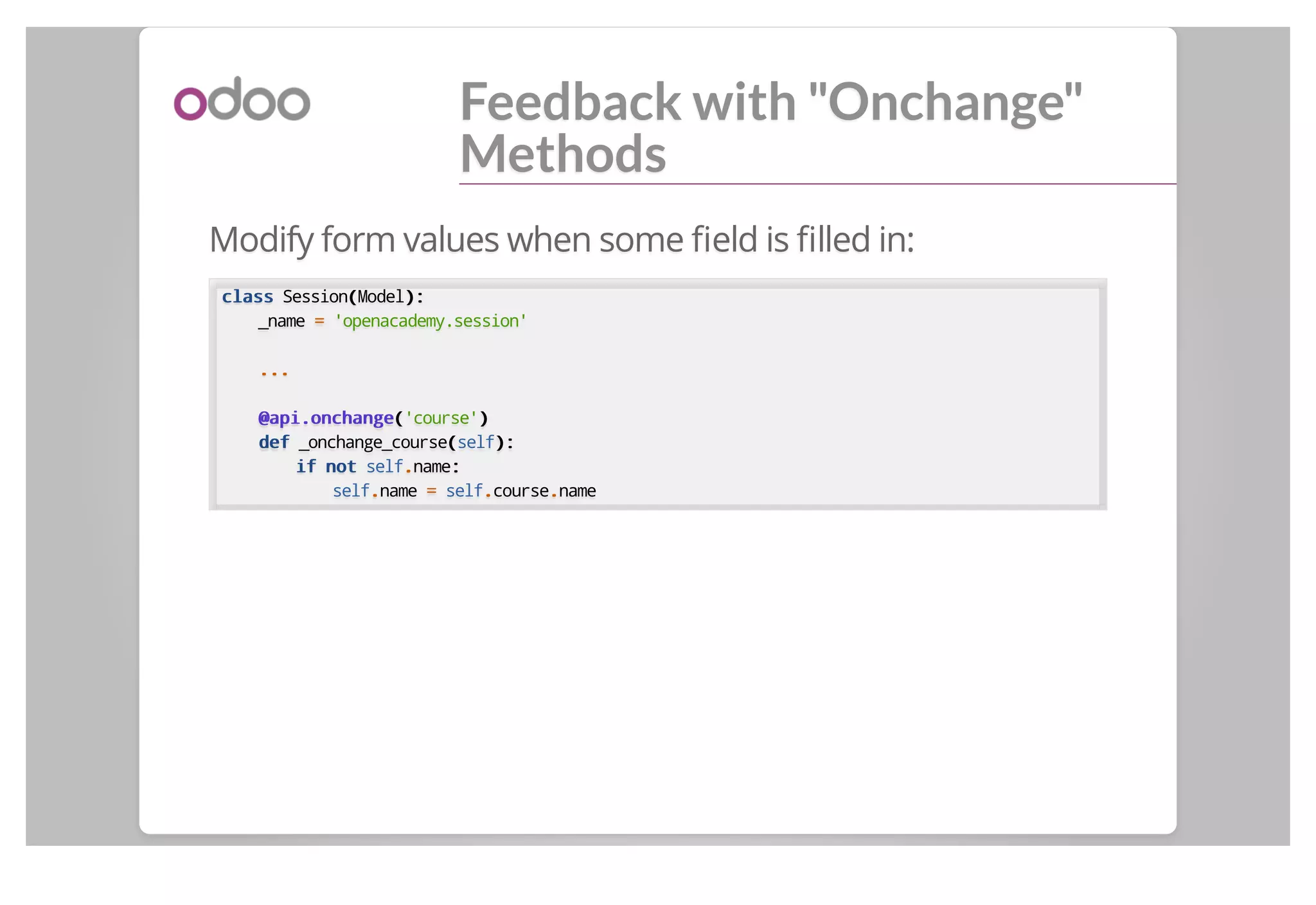
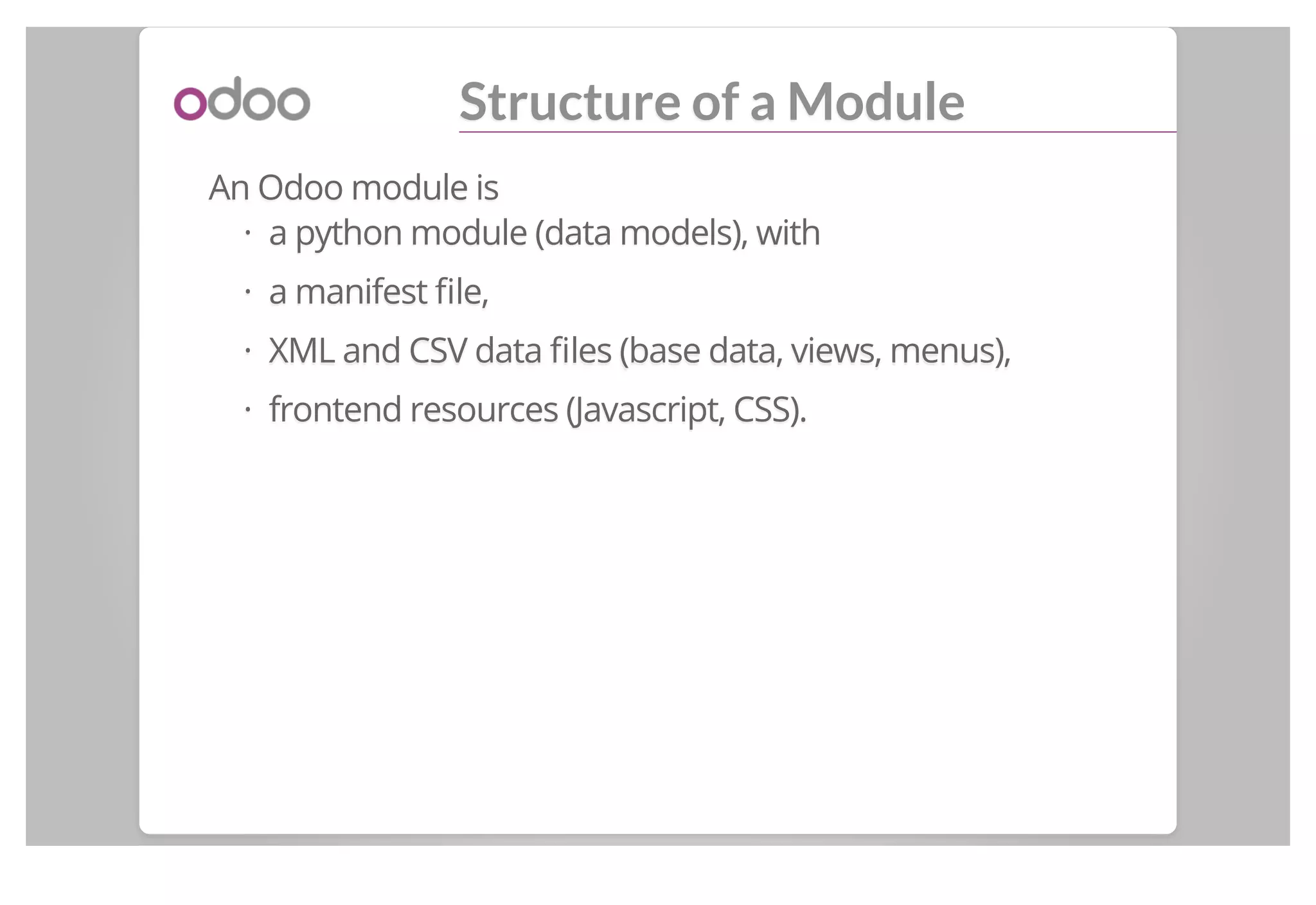
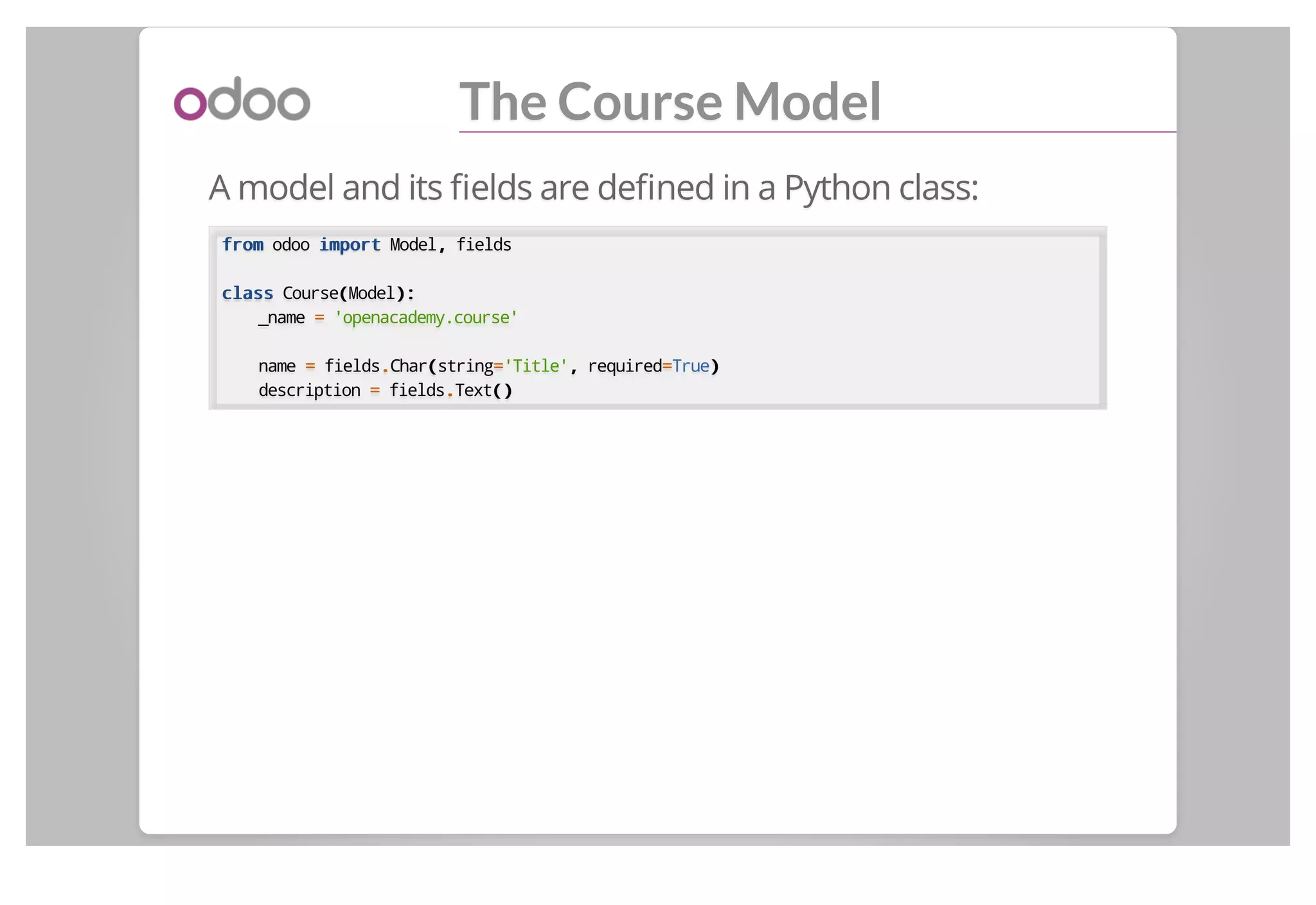
The manifest file __odoo__.py:
{{
'name':: 'Open Academy',,
'version':: '1.0',,
'category':: 'Tools',,
'summary':: 'Courses, Sessions, Subscriptions',,
'description':: "...",,
'depends' :: [['base'],],
'data' :: [['view/menu.xml'],],
'images':: [],[],
'demo':: [],[],
'application':: True,,
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/backendmodulesinv8-140611045714-phpapp01/75/Odoo-Backend-modules-in-v8-8-2048.jpg)

![About self
Model instances are recordsetsrecordsets.
A recordset is an hybrid concept:
collection of records
record
forfor session inin self::
printprint session..name
printprint session..course..name
assertassert self..name ==== self[[00]]..name
·
·](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/backendmodulesinv8-140611045714-phpapp01/75/Odoo-Backend-modules-in-v8-17-2048.jpg)