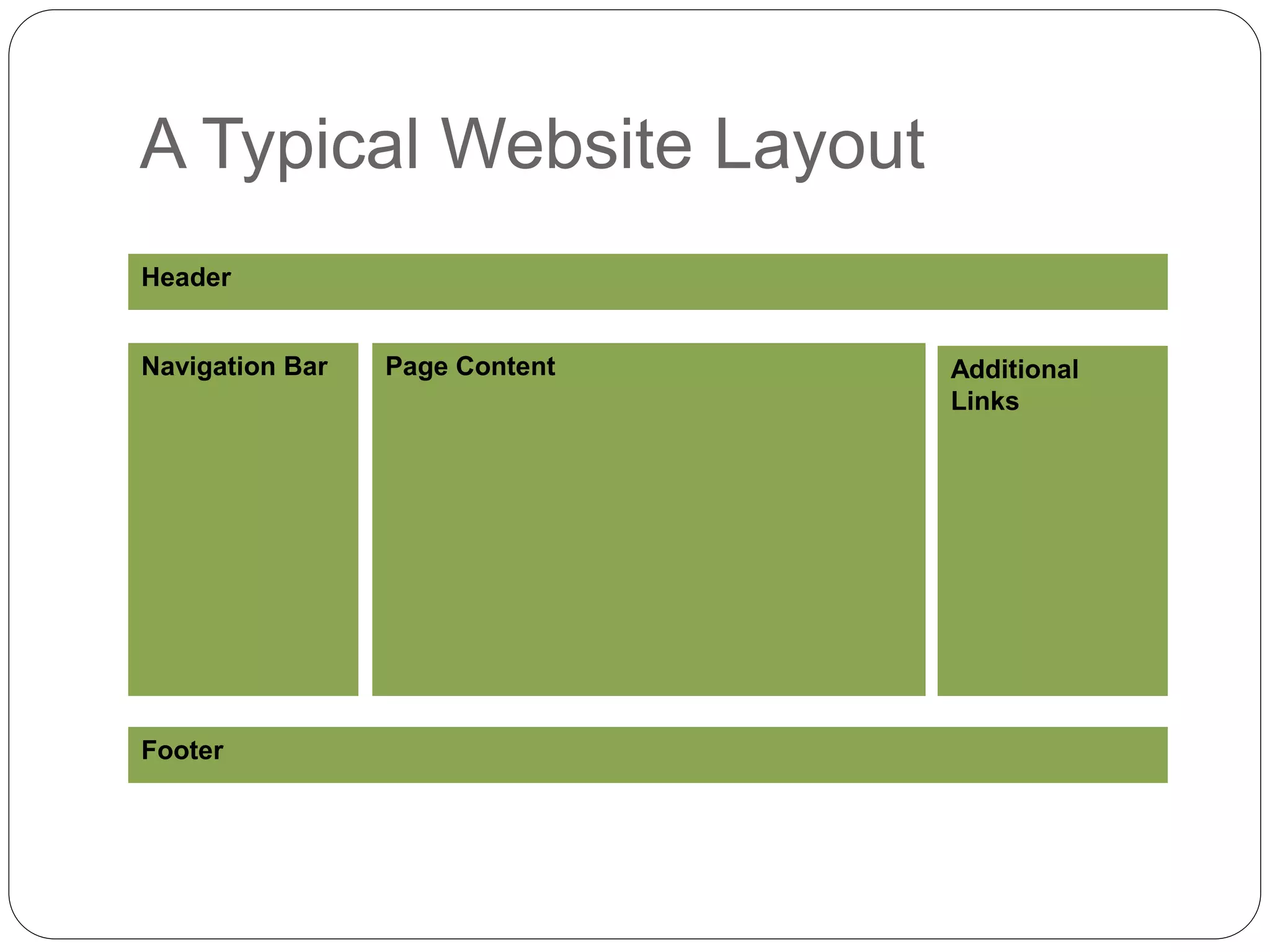
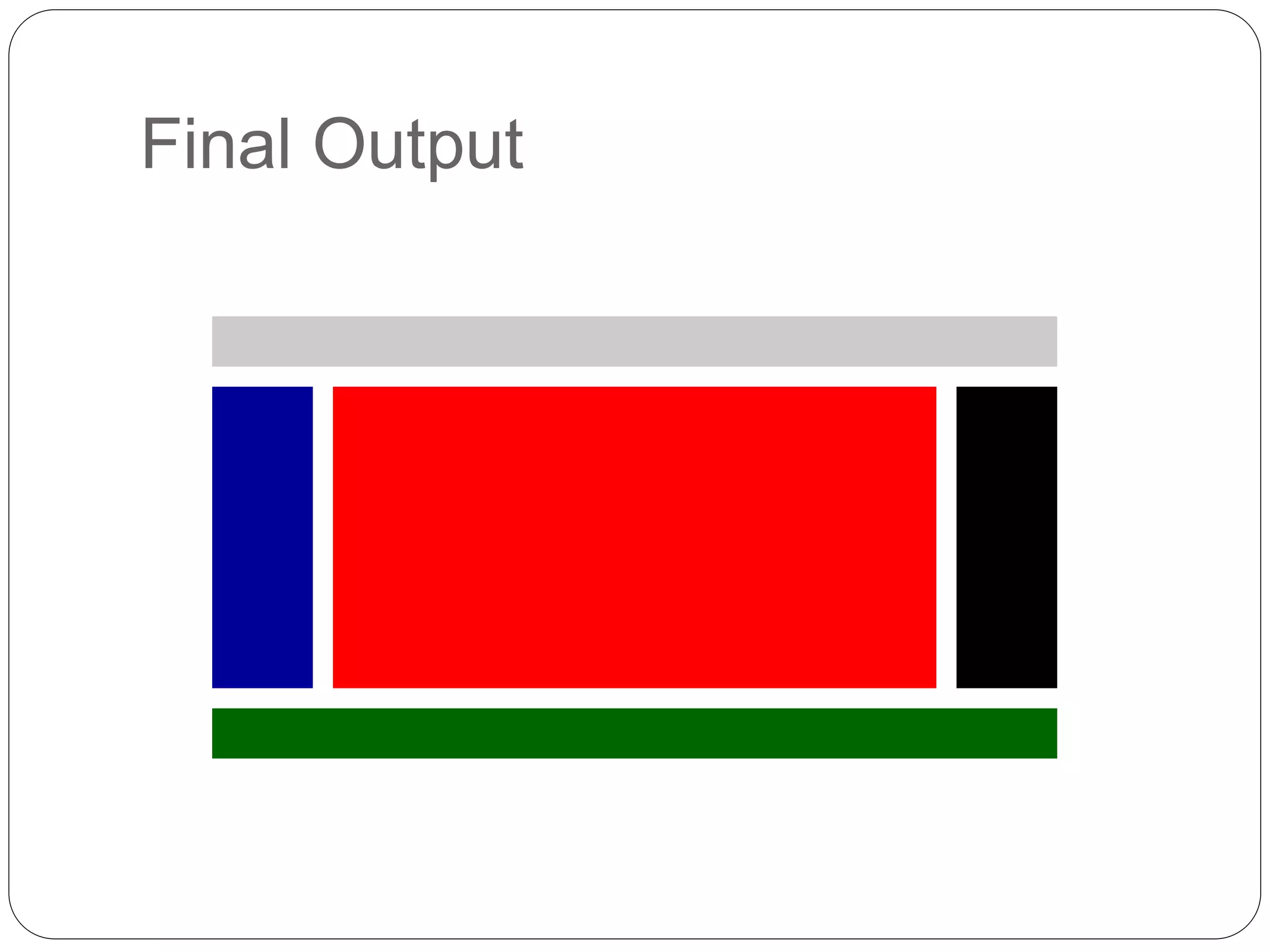
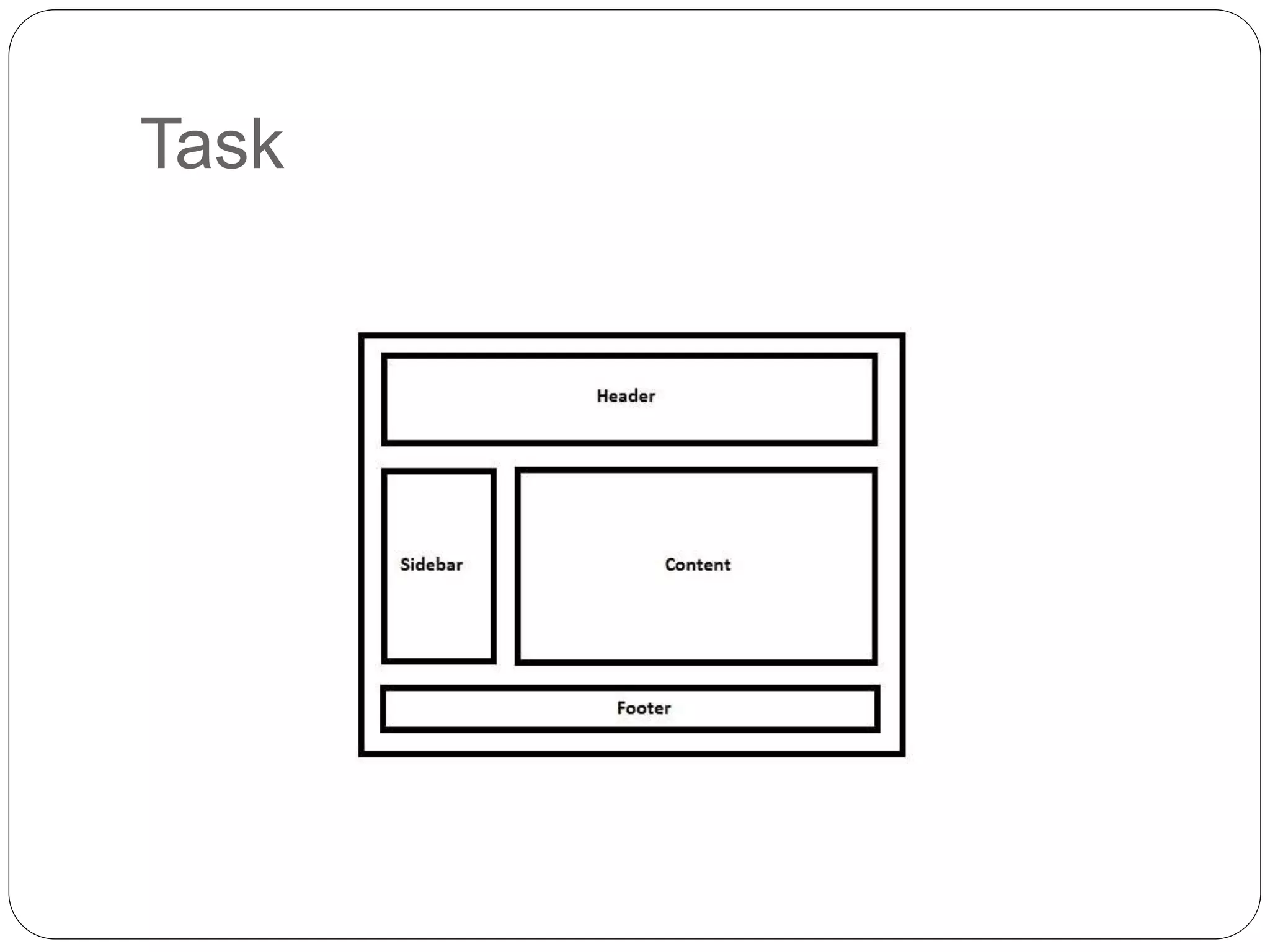
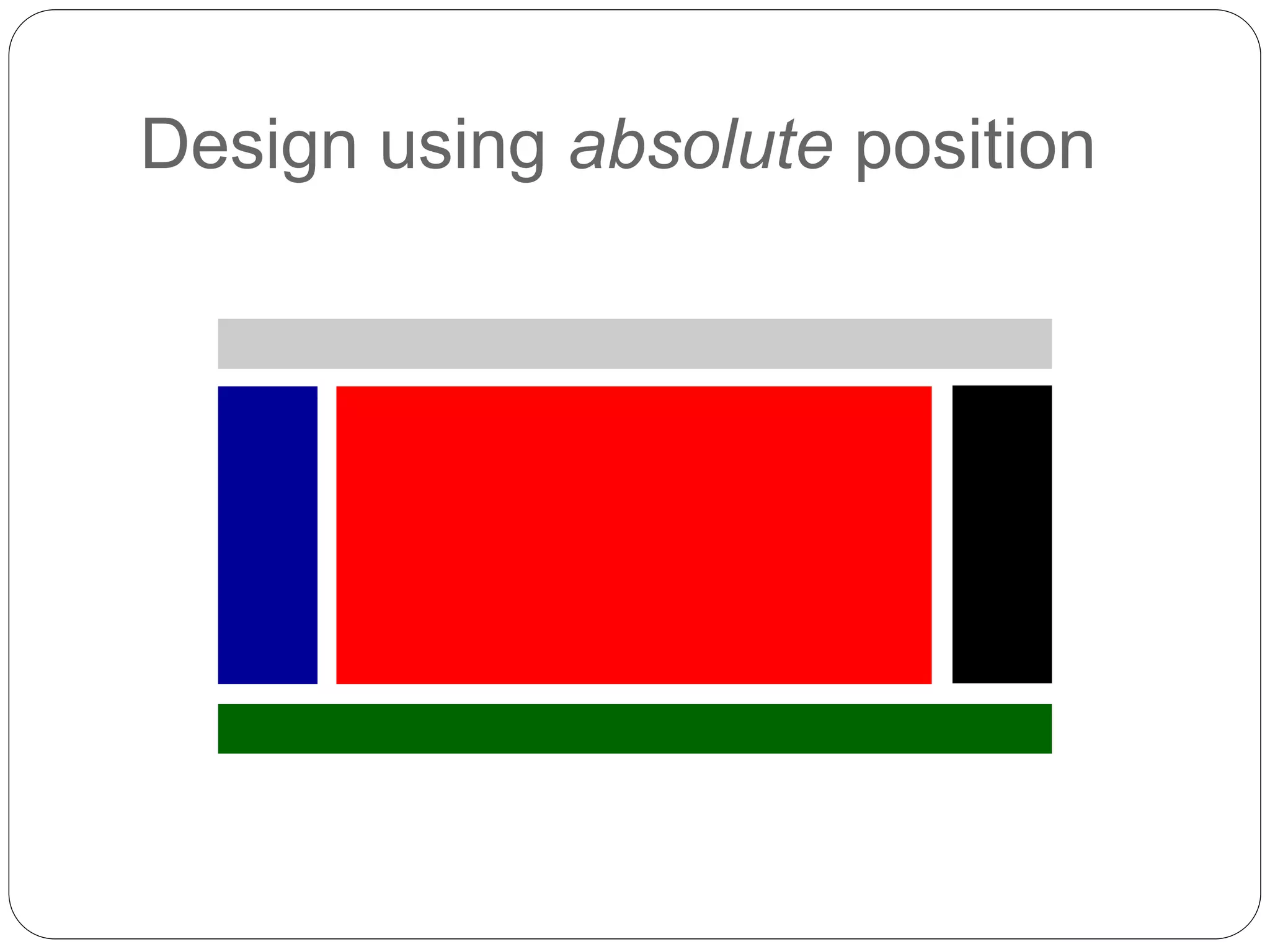
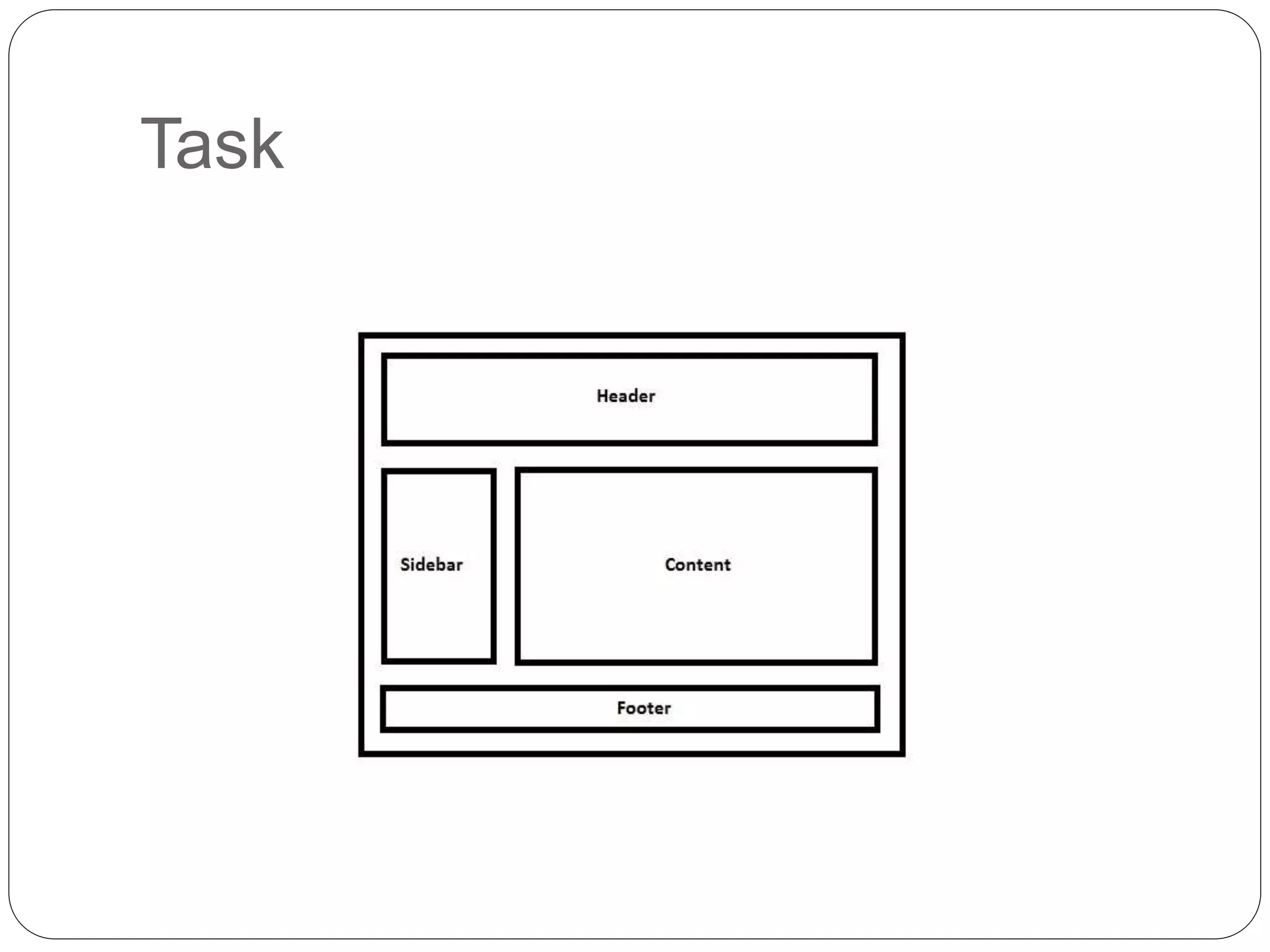
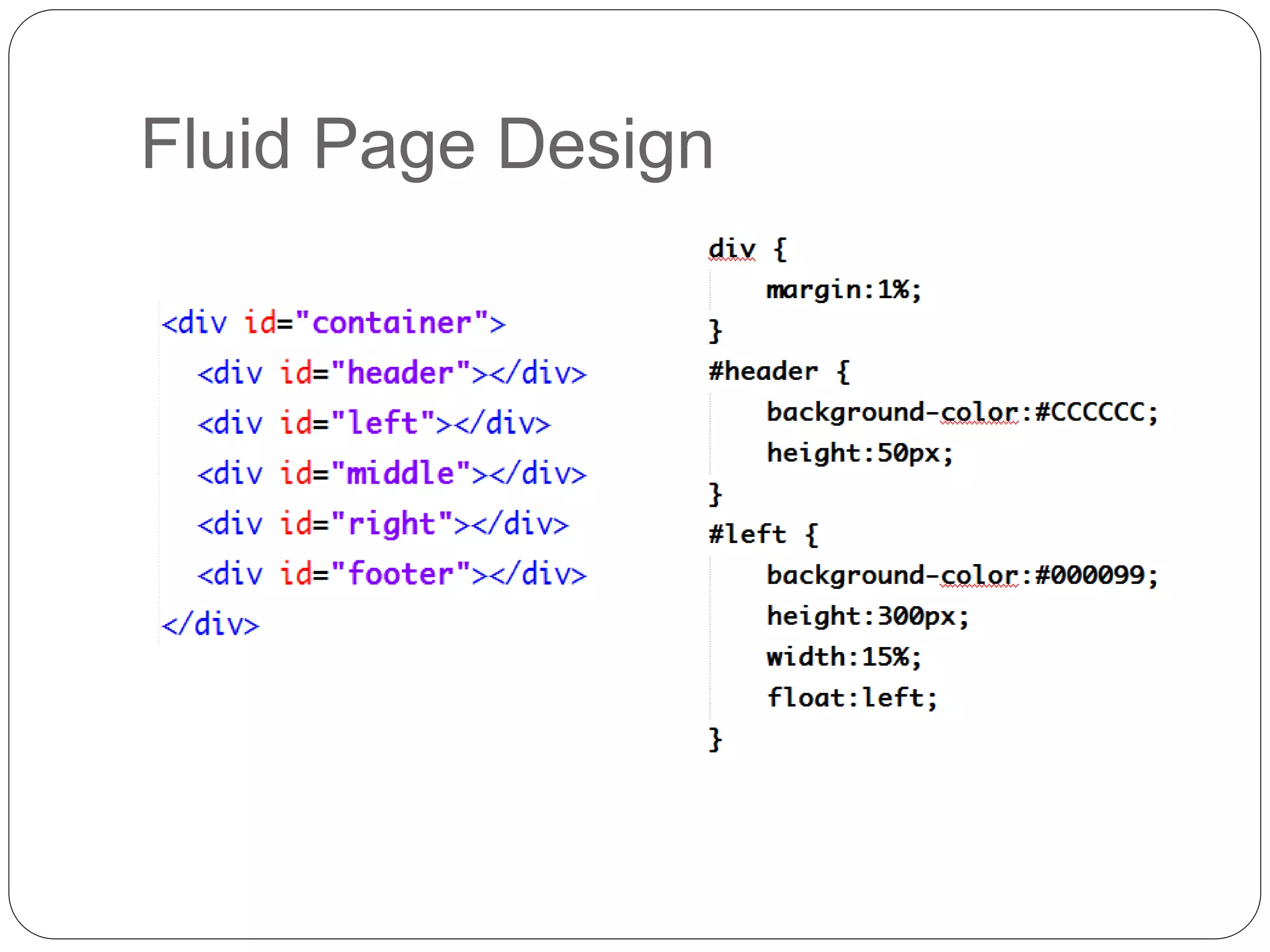
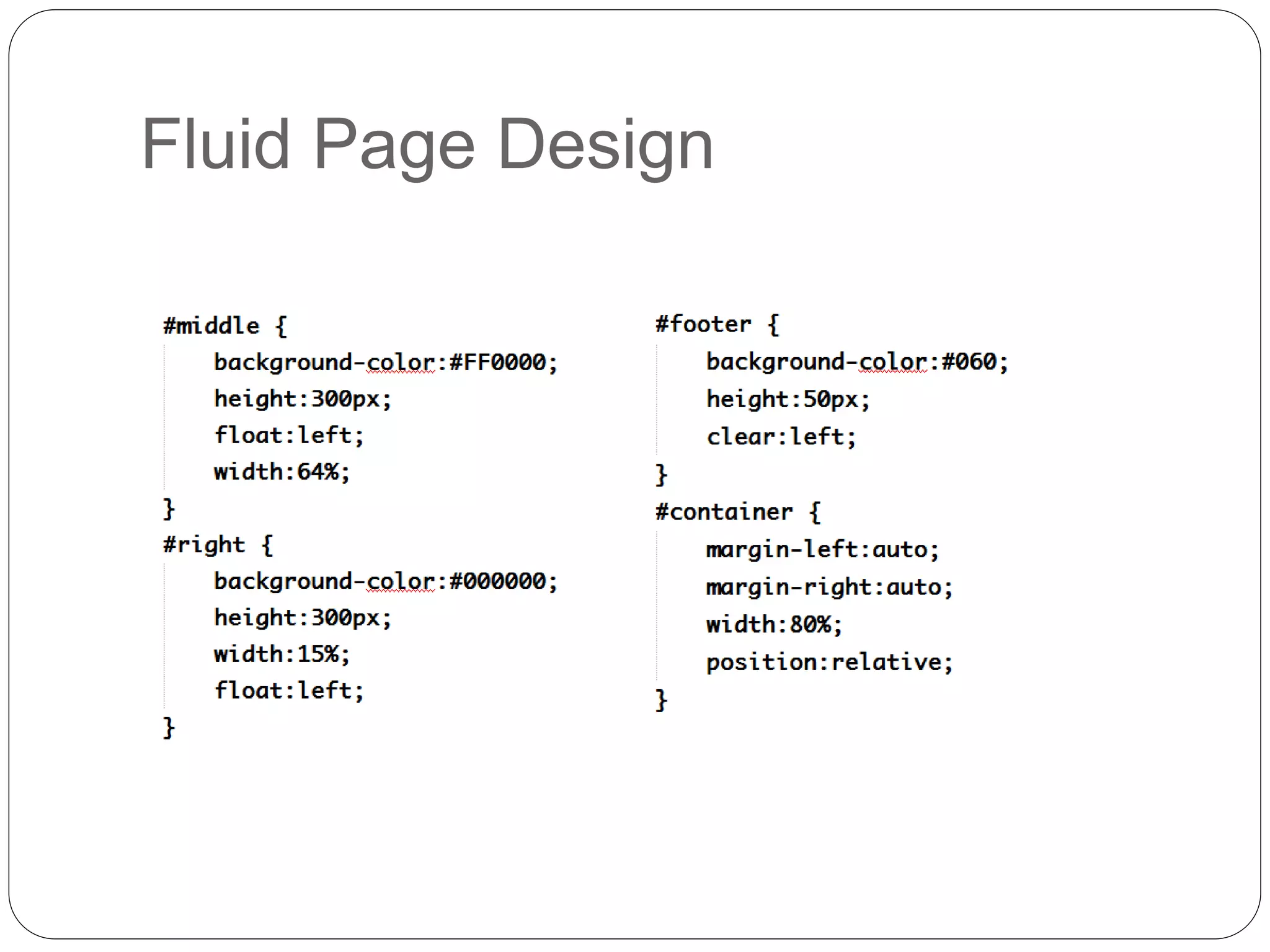
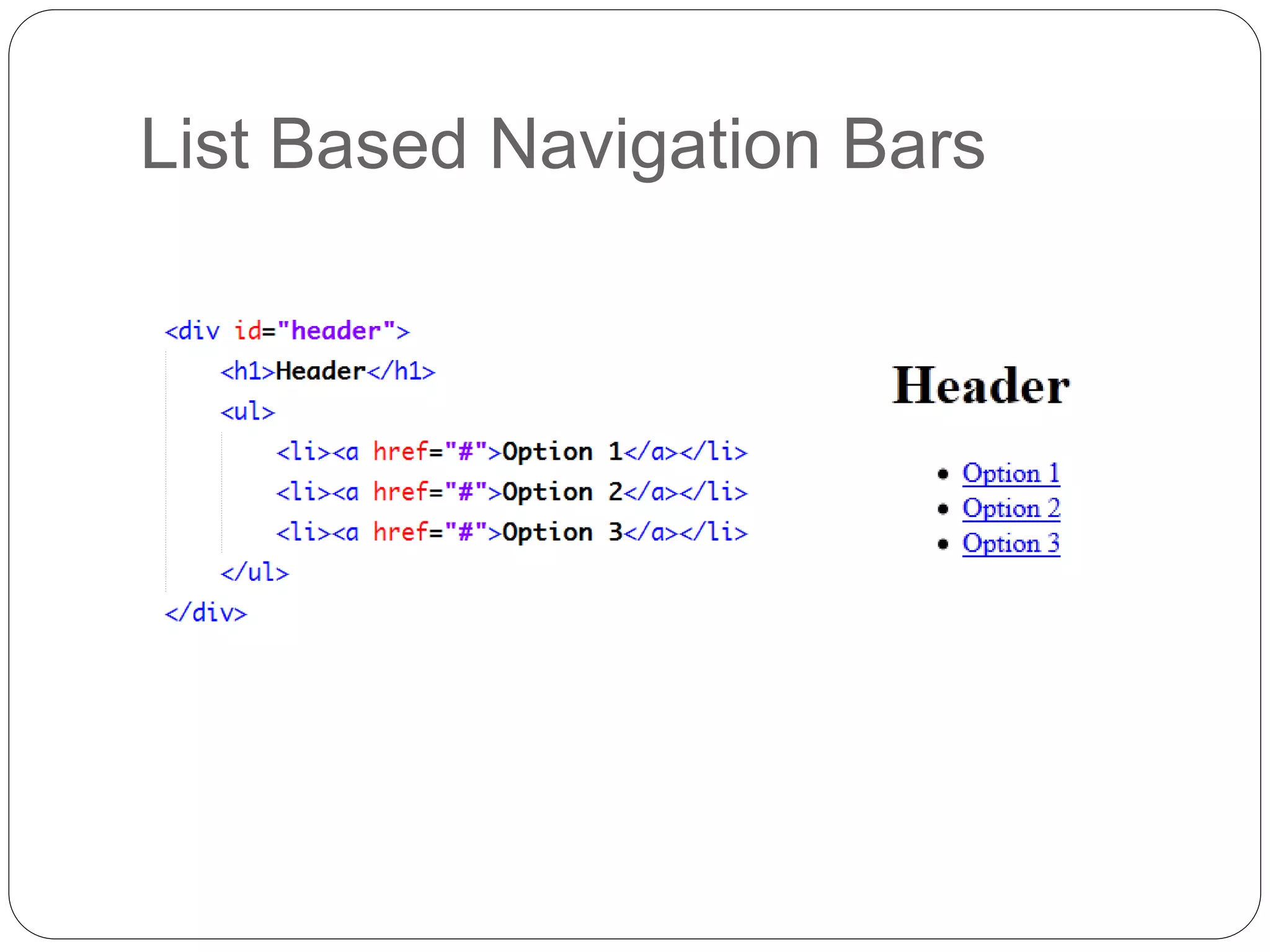
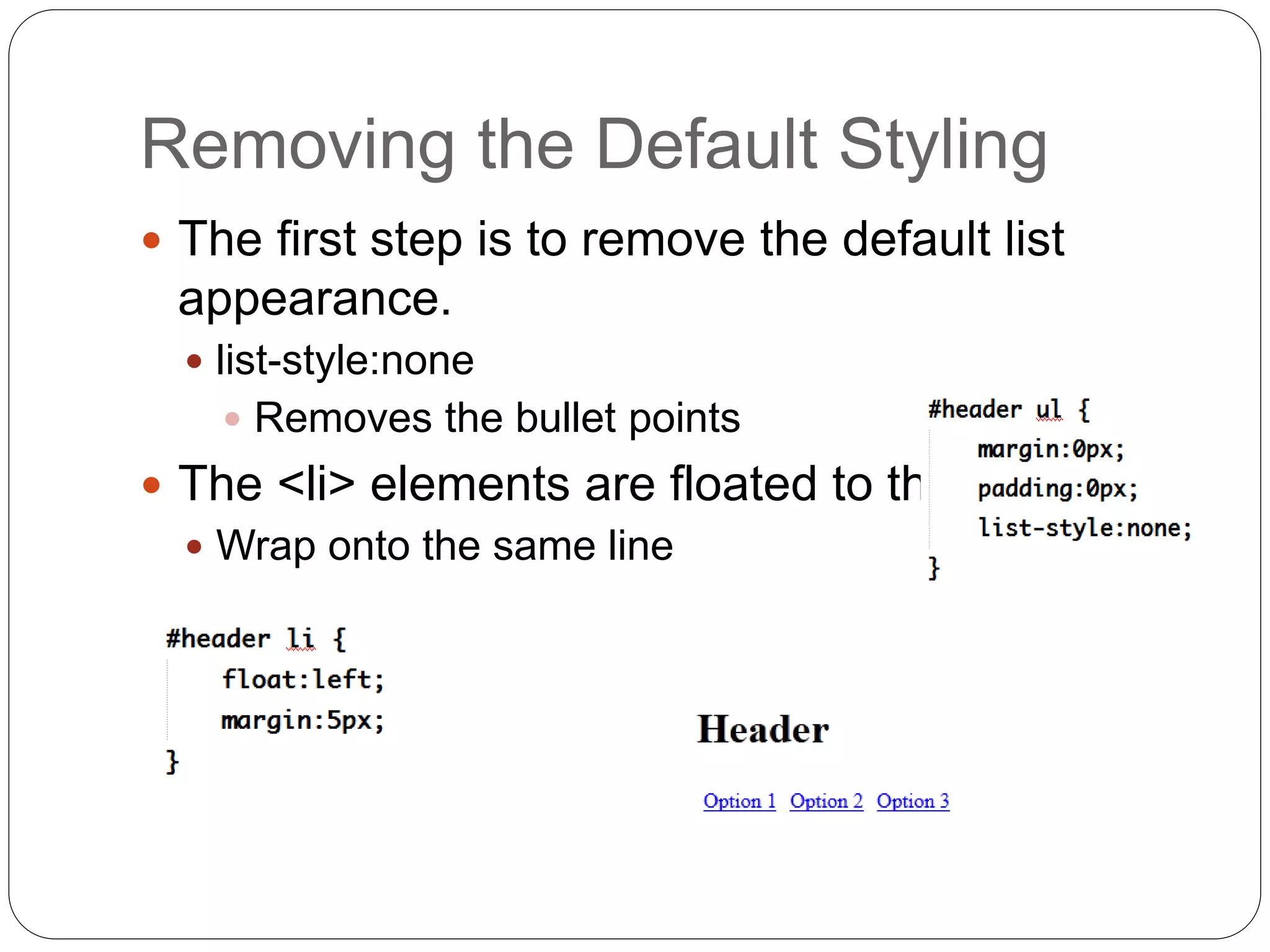
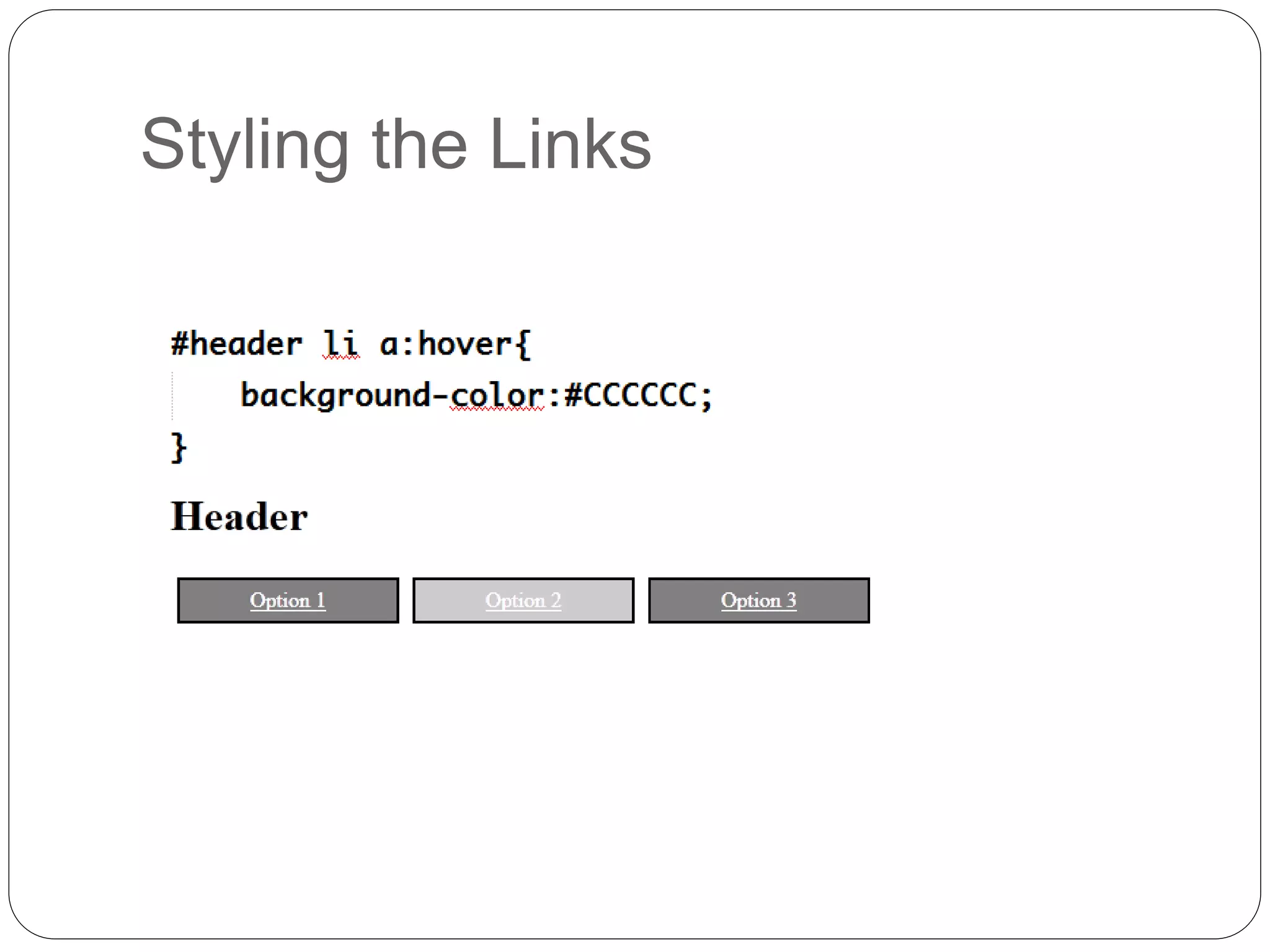
This document discusses various page layout techniques using CSS, including floats, positioning, and responsive design. It begins by outlining a typical website layout with common elements like headers, navigation bars, page content, and footers. It then covers using CSS properties like float and clear to create basic page layouts with columns. The document also discusses centering pages, different positioning techniques, and creating fluid and responsive designs that adapt to different screen sizes using media queries. Specific techniques covered include removing default styling from lists to create navigation bars, and styling list items as navigation buttons.