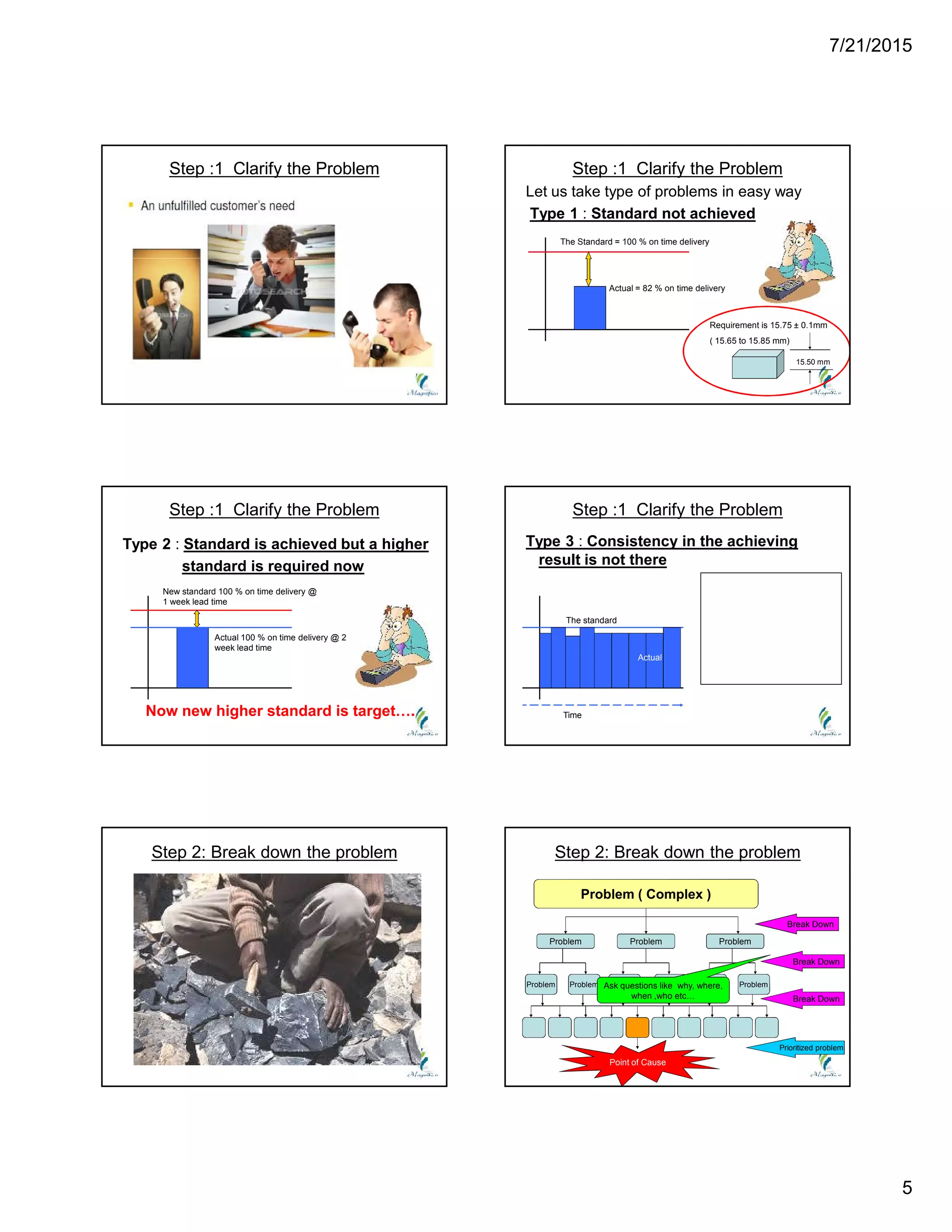
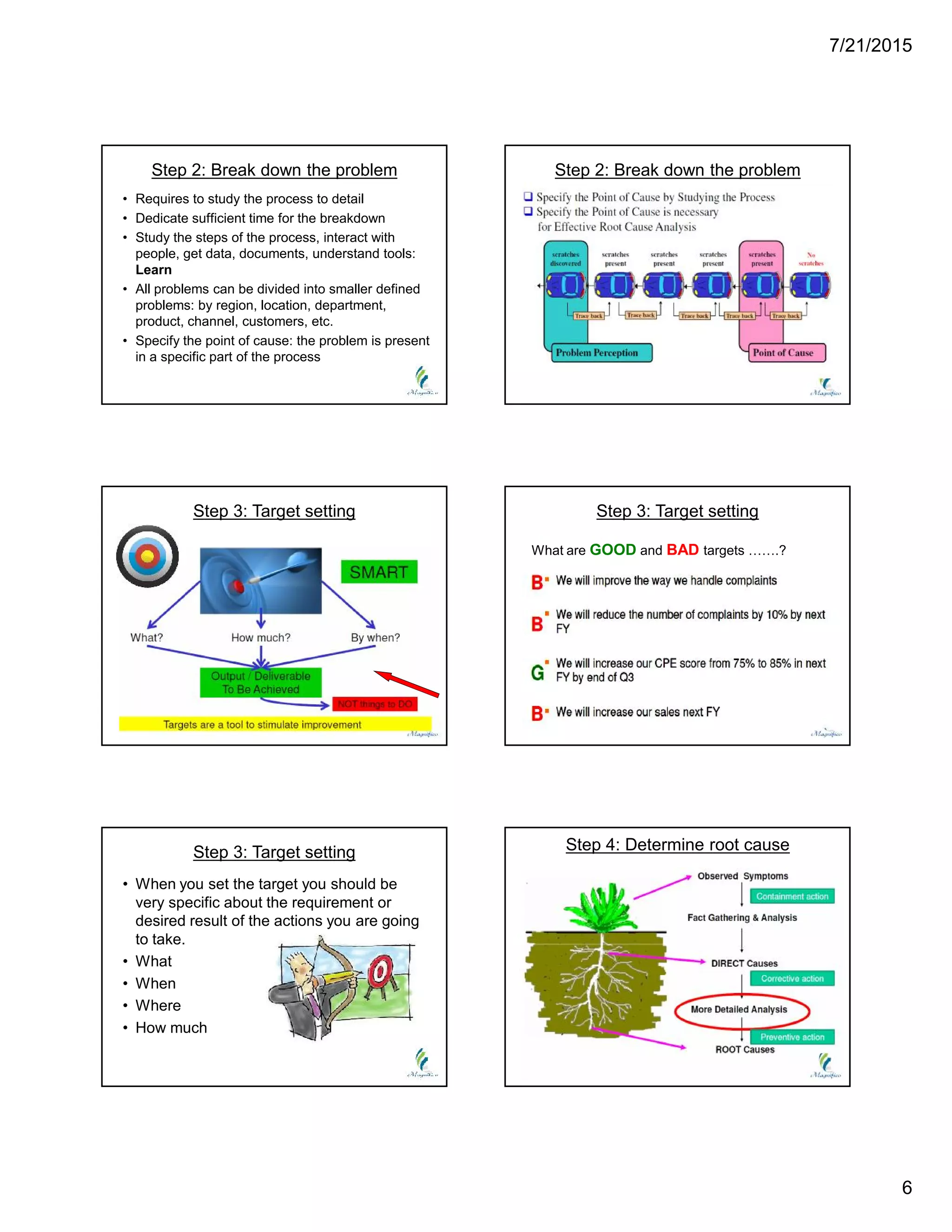
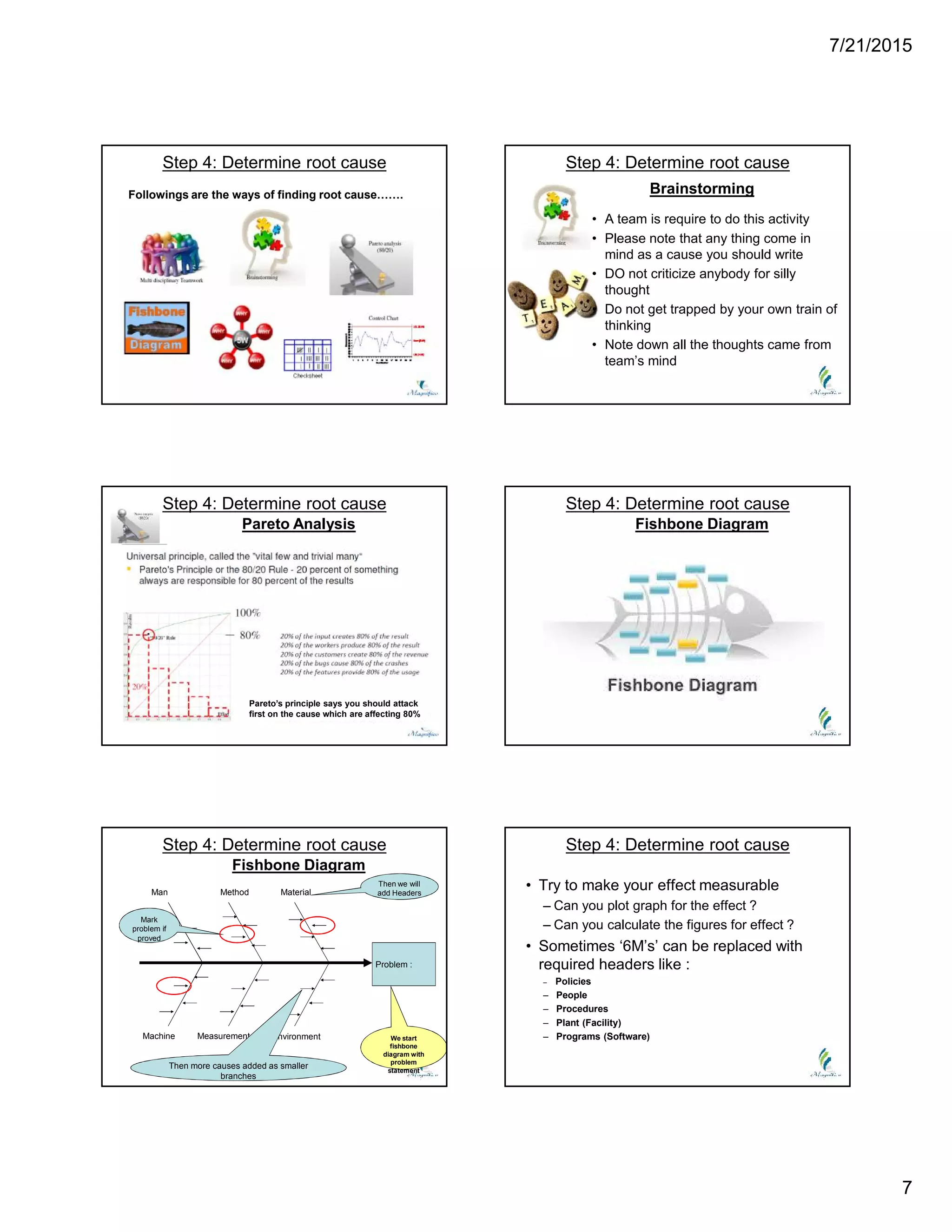
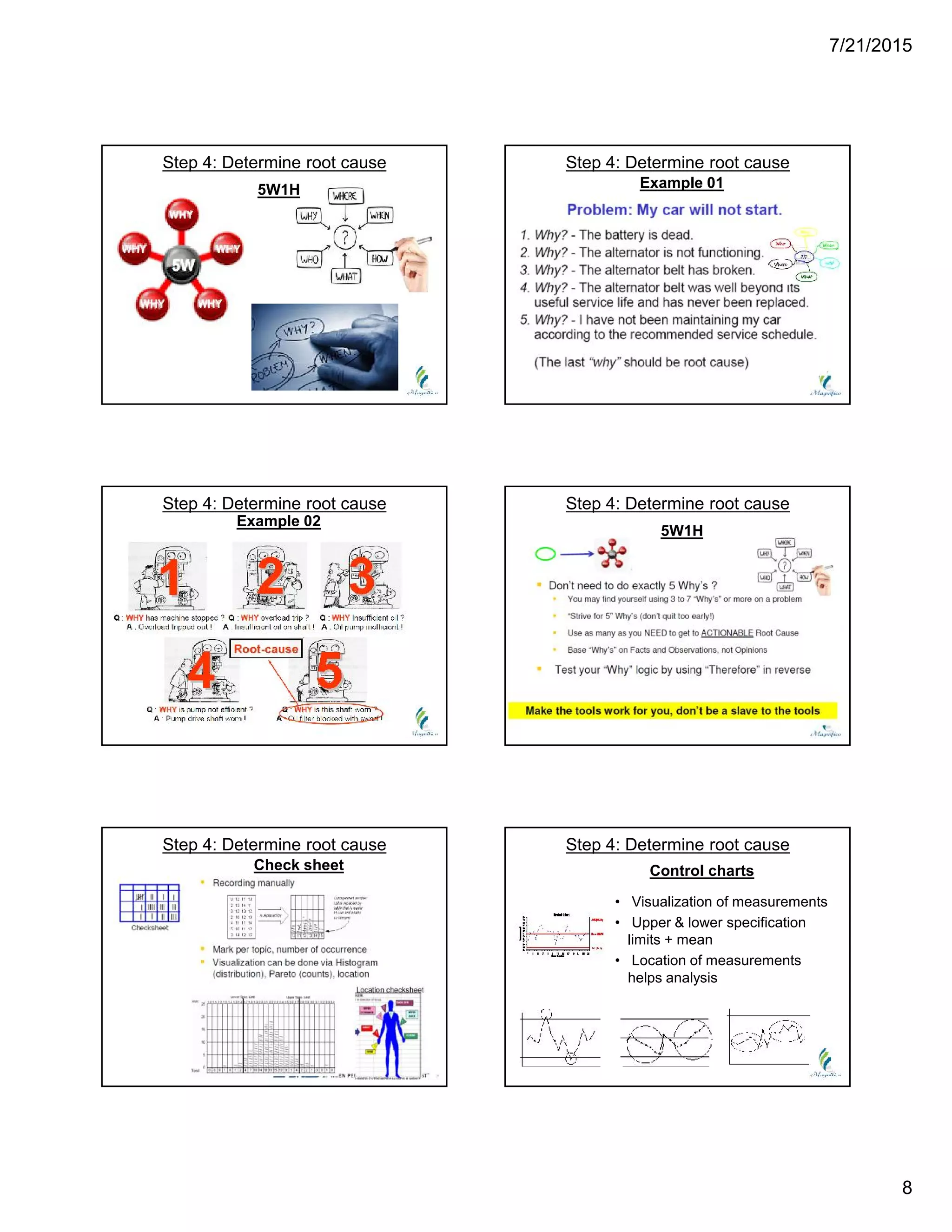
This document discusses problem solving techniques. It begins by defining what a "problem" is, such as when specifications are not met, processes are out of control, rejection rates are high, or delivery performance is below 100%. The document then outlines 8 steps to solve problems: 1) define the problem, 2) build a team, 3) take containment actions, 4) determine the root cause, 5) verify the root cause, 6) take corrective action, 7) implement preventive actions, and 8) congratulate the team. Each step is then explained in more detail with examples provided. Overall, the document provides an overview of a structured 8-step approach to problem solving.