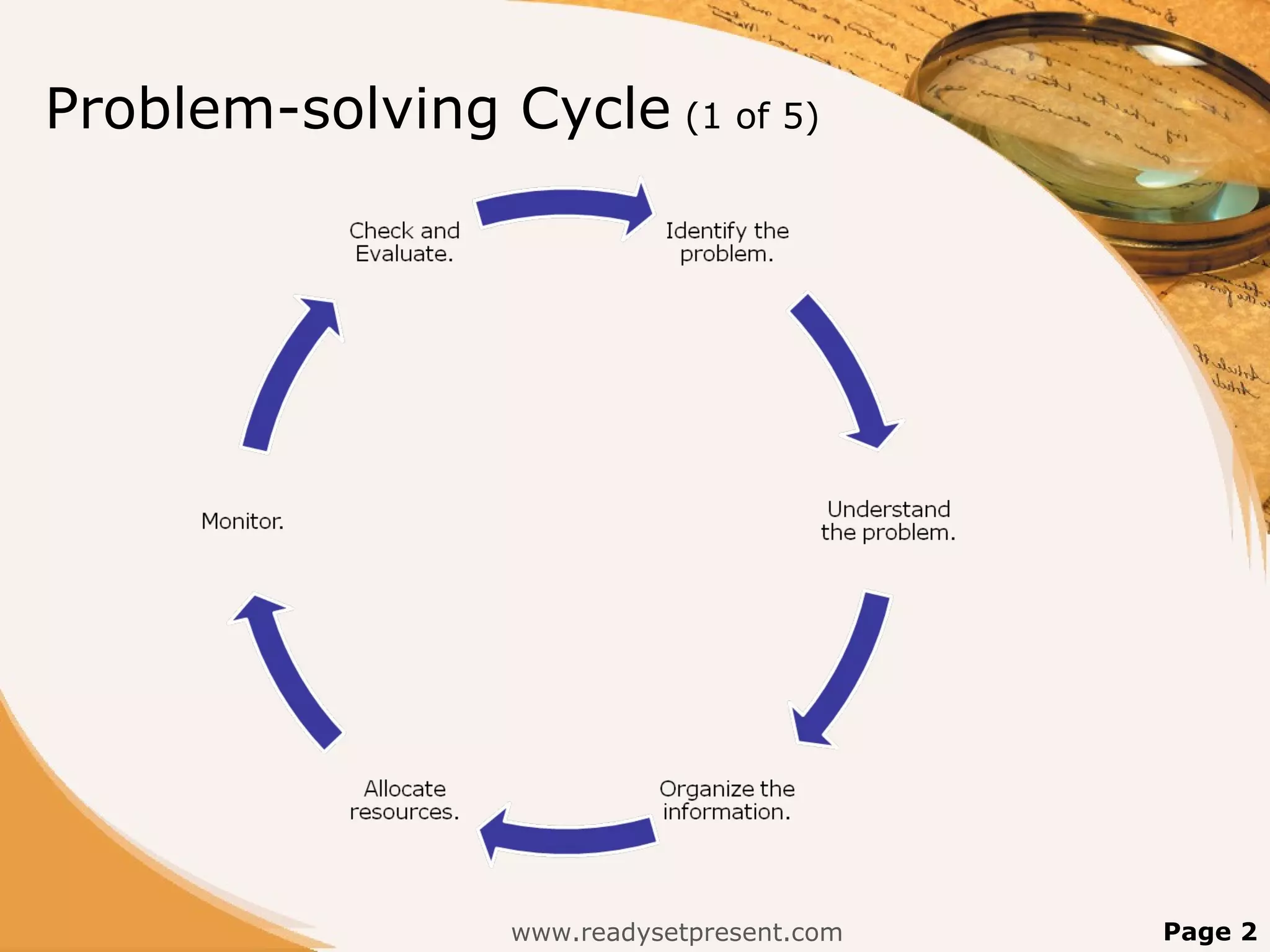
The document discusses problem solving and decision making processes. It defines problem solving as a systematic approach to defining a problem without judging solutions, while decision making is choosing a course of action and considering consequences. The problem solving cycle involves identifying and understanding the problem, developing possible solutions without judgment, and choosing a solution to implement. Additional sections cover understanding the problem, learning problem solving skills, brainstorming individually or in groups, gathering facts when problem solving collaboratively, and using a SWOT analysis to evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.