The document covers programming fundamentals focusing on arrays, including their declaration, initialization, and swapping elements. It explains sorting algorithms such as insertion sort, bubble sort, and selection sort, providing code examples and algorithm descriptions for each. The lecture emphasizes the practical aspects of working with arrays and sorting methods in programming.



![4
Example: Swapping
int num [ ] ={12,4,6,7,78};
for(int i=0; i<=4;i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<"t";
}
cout<<endl;
int x ;
x = num [ 0 ] ;
num [ 0 ] = num [ 3 ] ;
num [ 3 ] = x ;
for(int i=0; i<=4;i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<"t";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingfundamentalslecture-14-241113164655-e7da2e50/75/Programming-Fundamentals-lecture-14-pptx-4-2048.jpg)
![5
Example:function and Array
void functionAndArray(int[], int);
main()
{
int const size=5;
int fArray[]={12,5,14,56,73,34};
functionAndArray(fArray,size);
}
void functionAndArray(int fArray[],int size)
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cout<<fArray[i]<<"t";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingfundamentalslecture-14-241113164655-e7da2e50/75/Programming-Fundamentals-lecture-14-pptx-5-2048.jpg)
![6
Example:function and Array
void functionArray ( int [ ] , int ) ;
main ( )
{
int numbers [ 100 ] ;
functionArray ( numbers , 100) ;
}
void functionArray( int x [ ] , int arraySize )
{
int i ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < arraySize ; i ++)
{
x [ i ] = i ;
cout<<x[i]<<"t";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingfundamentalslecture-14-241113164655-e7da2e50/75/Programming-Fundamentals-lecture-14-pptx-6-2048.jpg)
![7
Sorting
int sort[]={23,4,66,2,44,77,43};
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<7;j++)
{
if(sort[j]<sort[i])
{
int temp=sort[i];
sort[i]=sort[j];
sort[j]=temp;
}
}
cout<<sort[i]<<"t";
}
}
O
utput](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingfundamentalslecture-14-241113164655-e7da2e50/75/Programming-Fundamentals-lecture-14-pptx-7-2048.jpg)


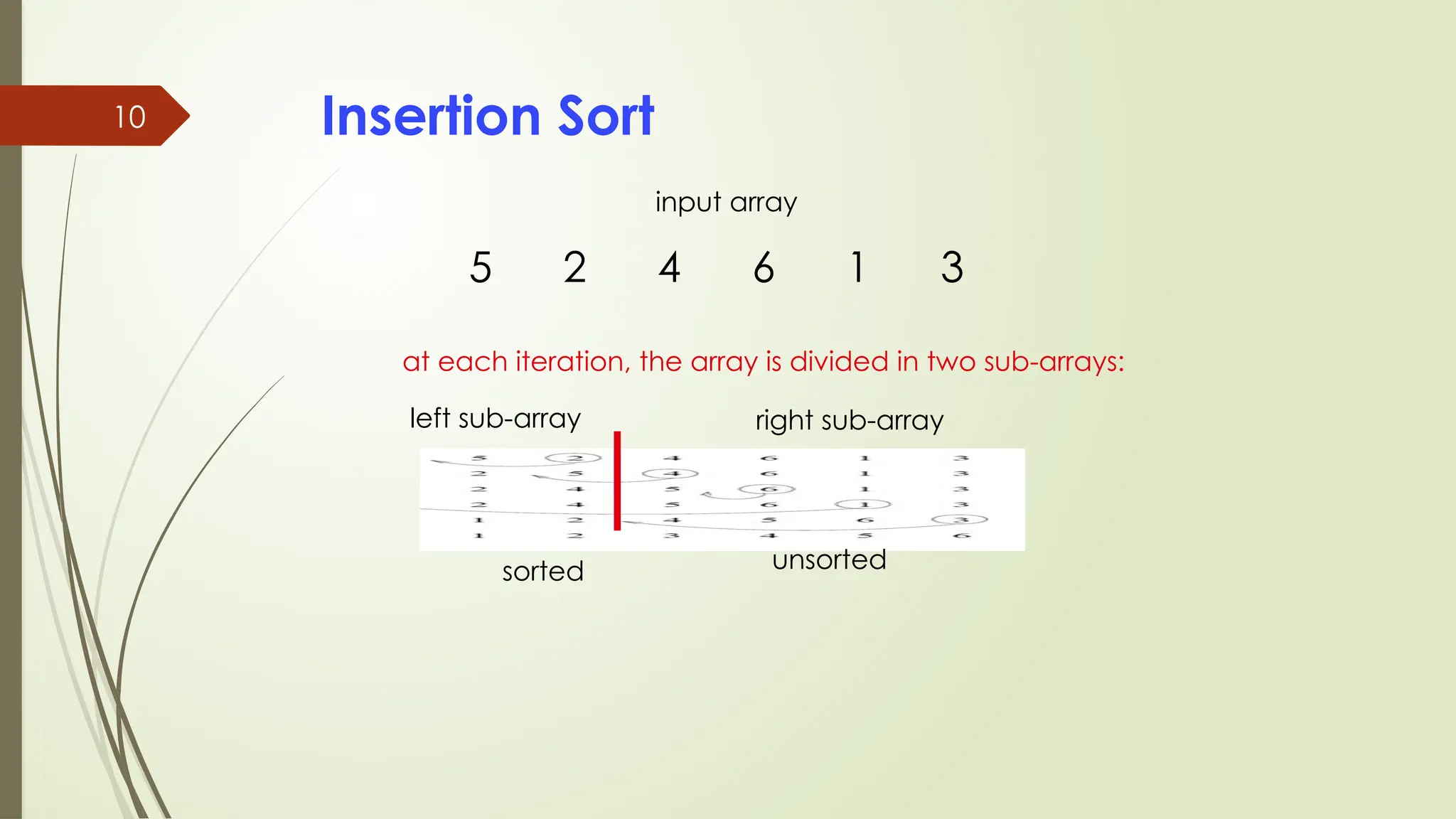
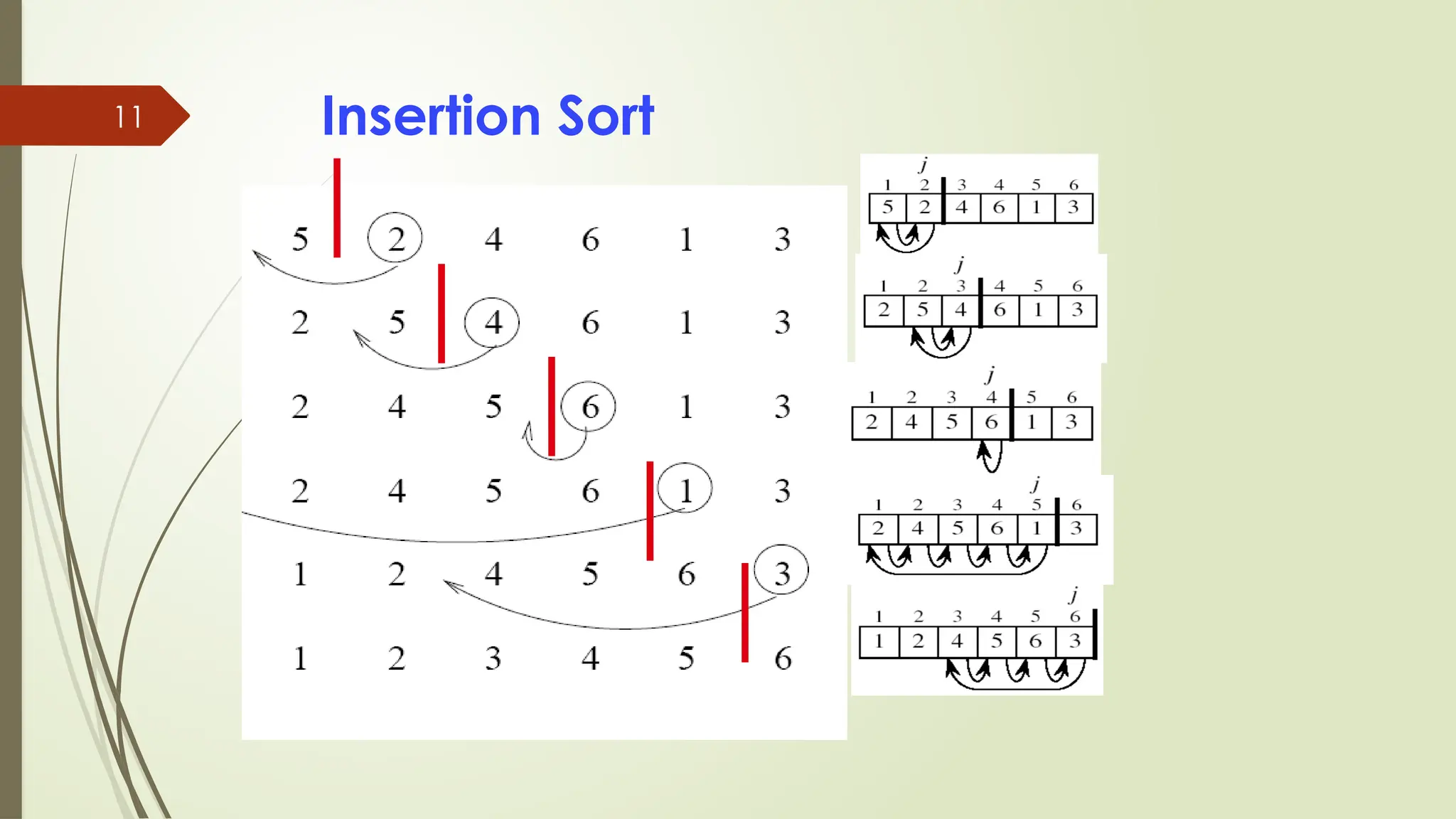
![code
for(i=1;i<count;i++)
{
temp=number[i];
j=i-1;
while((temp<number[j])&&(j>=0))
{
number[j+1]=number[j];
j=j-1;
}
number[j+1]=temp;
}
cout<<“Order of Sorted
elements: “;
for(i=0;i<count;i++)
cout<<number[i];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingfundamentalslecture-14-241113164655-e7da2e50/75/Programming-Fundamentals-lecture-14-pptx-12-2048.jpg)

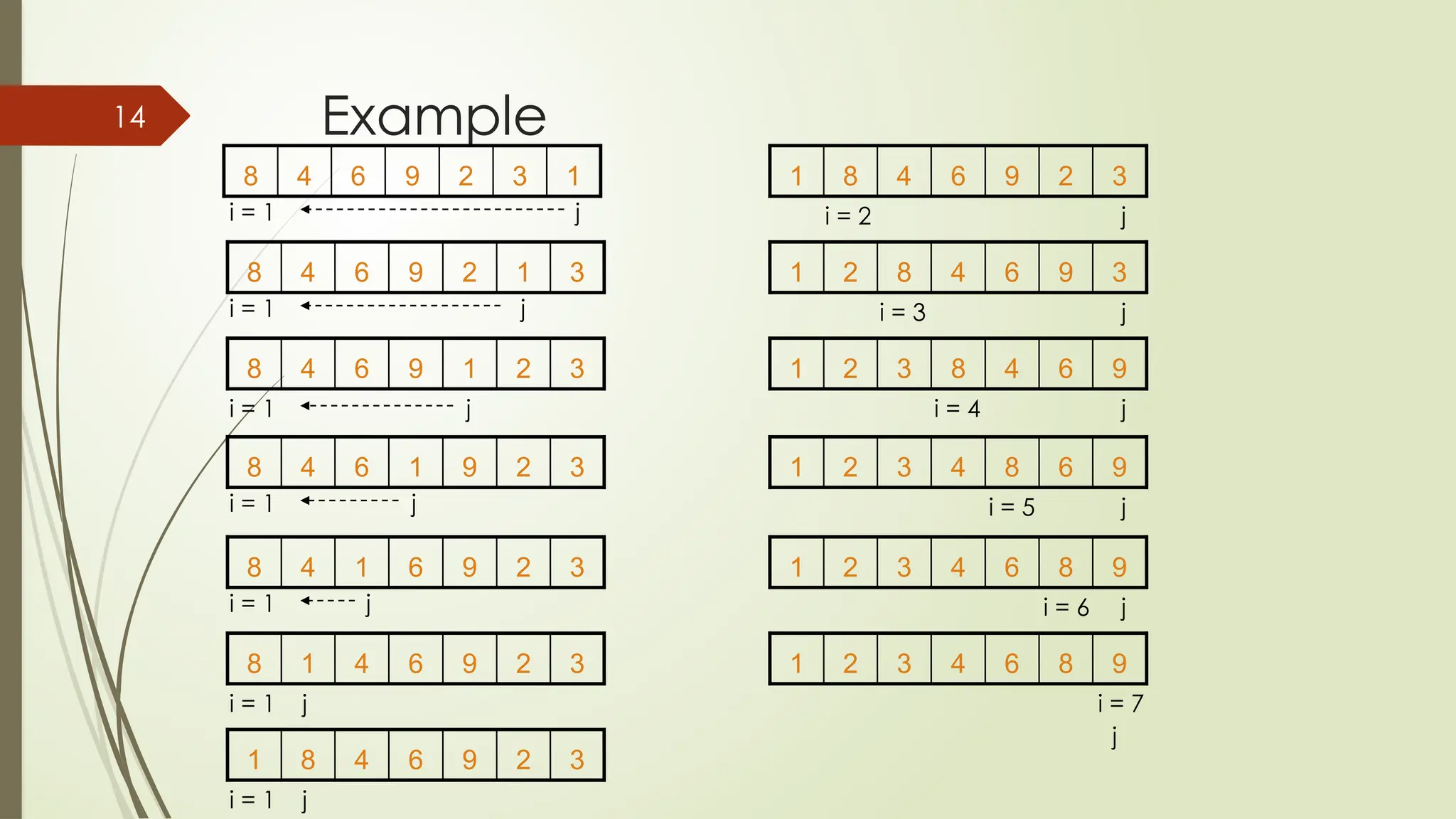
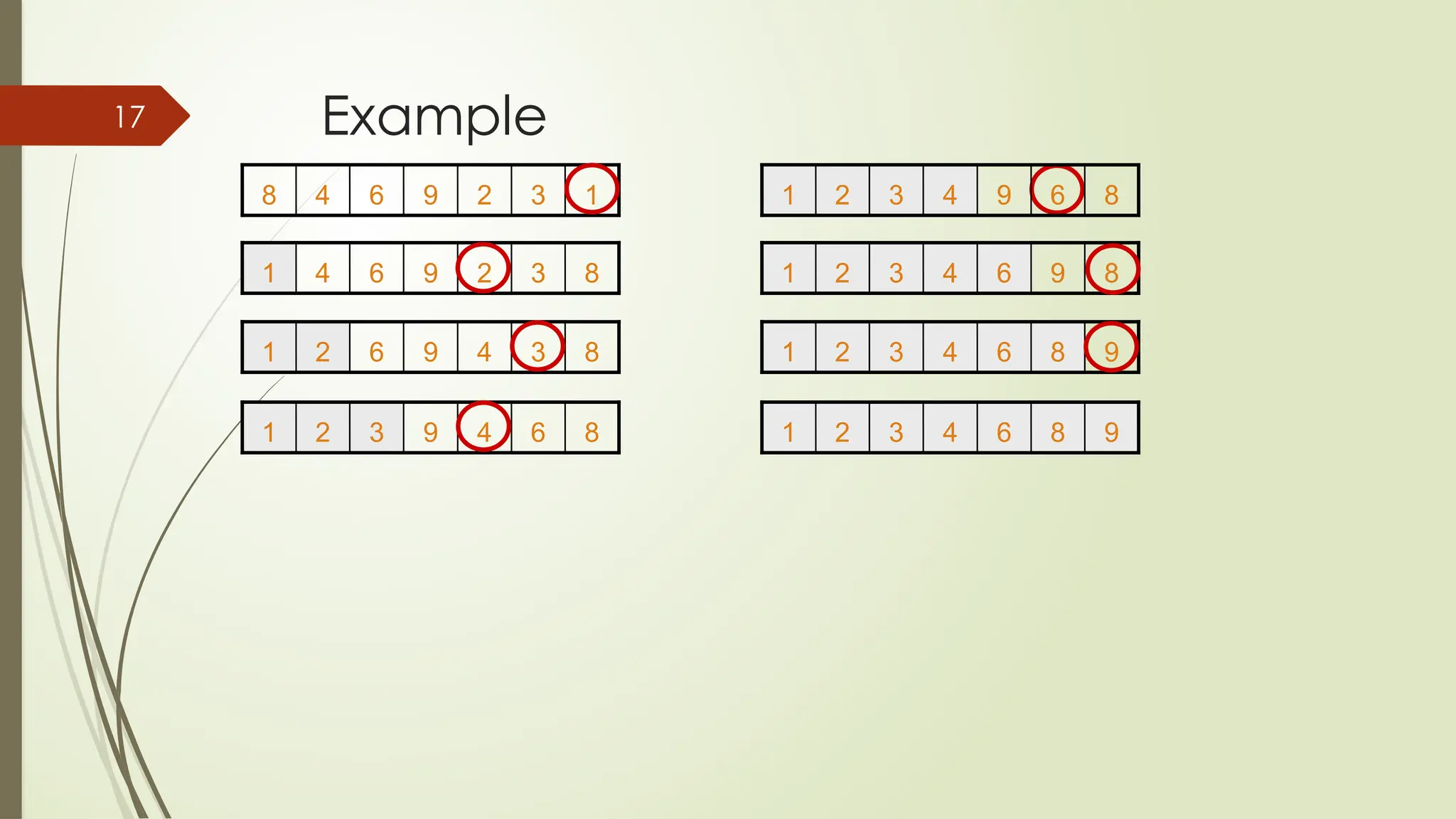
![for(i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
for(j = i+1; j<10; j++)
{
if(a[j] < a[i])
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
pass++;
}
cout <<"Sorted Element List ...n";
for(i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
cout
<<a[i]<<"t";
}
Code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingfundamentalslecture-14-241113164655-e7da2e50/75/Programming-Fundamentals-lecture-14-pptx-15-2048.jpg)

![code
int a[100], n, i, j, swap;
cout<<"Enter number of elementsn";
cin>>n;
cout<<"Enter
Numbers"<<n<<endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin>>a[i];
for(i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for(j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if(a[i] > a[j])
{
swap=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=swap;
}
}
}
cout<<"Sorted Array";
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout<<"t"<<a[i]<<"t";
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingfundamentalslecture-14-241113164655-e7da2e50/75/Programming-Fundamentals-lecture-14-pptx-18-2048.jpg)