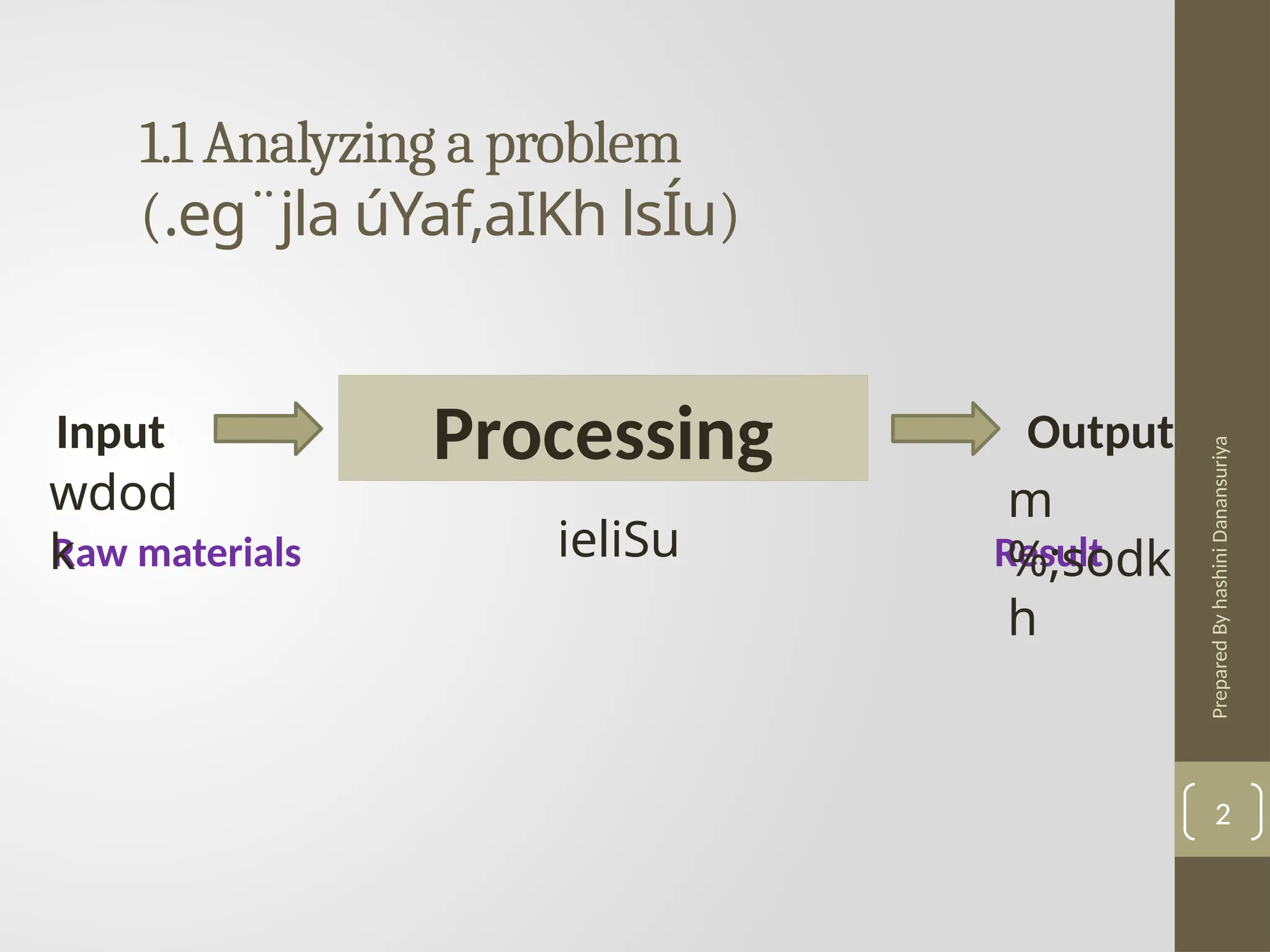
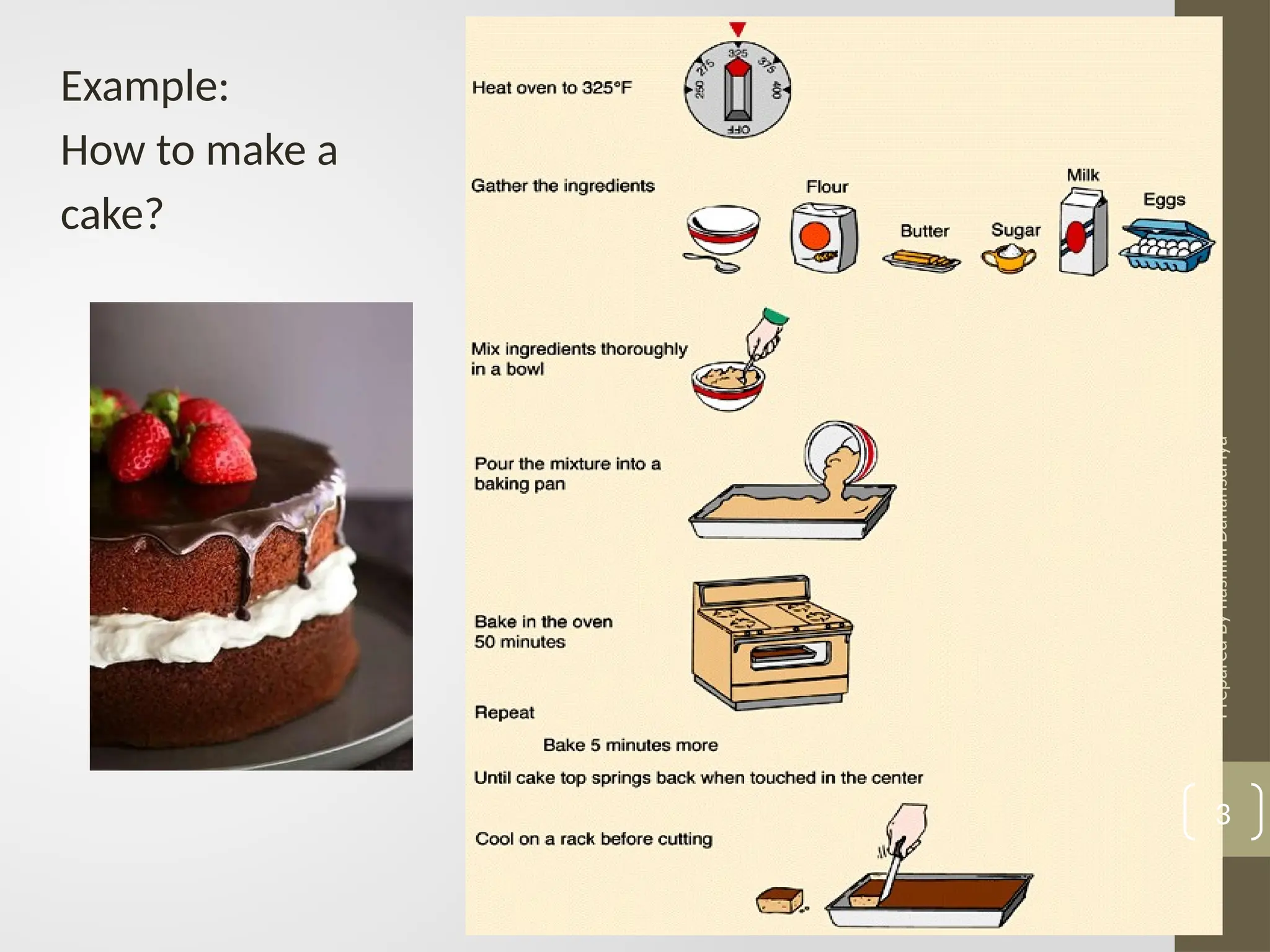
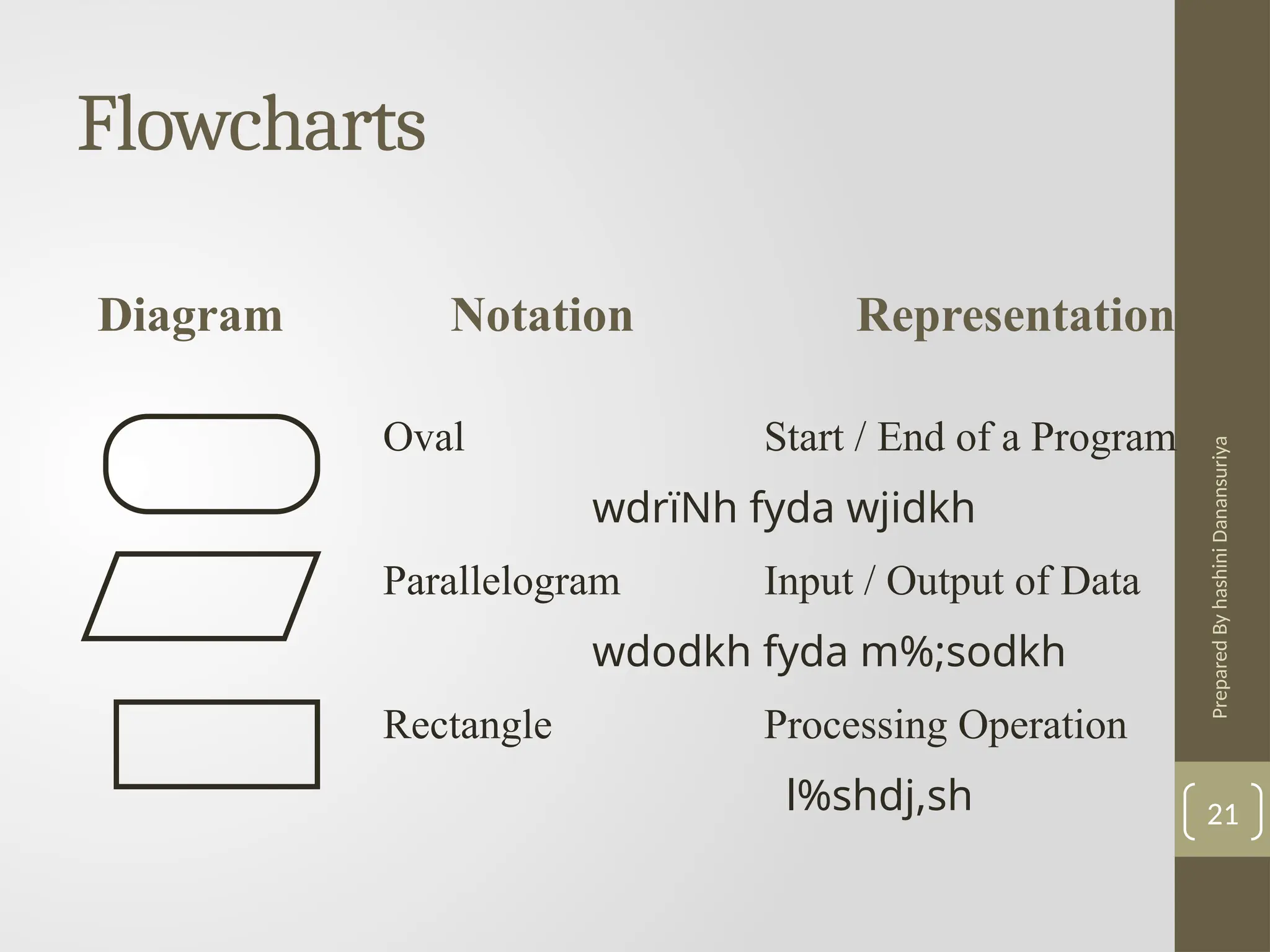
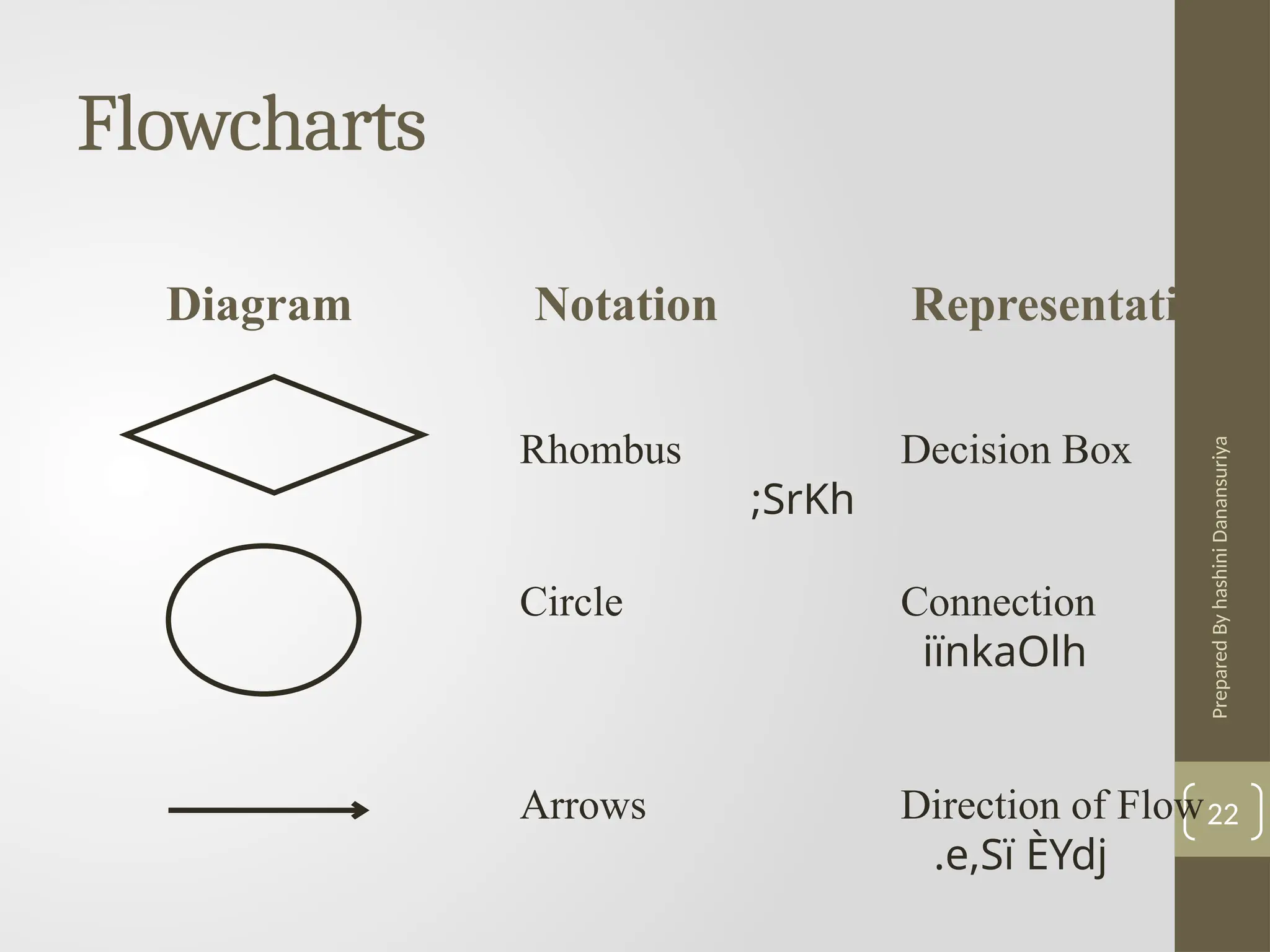
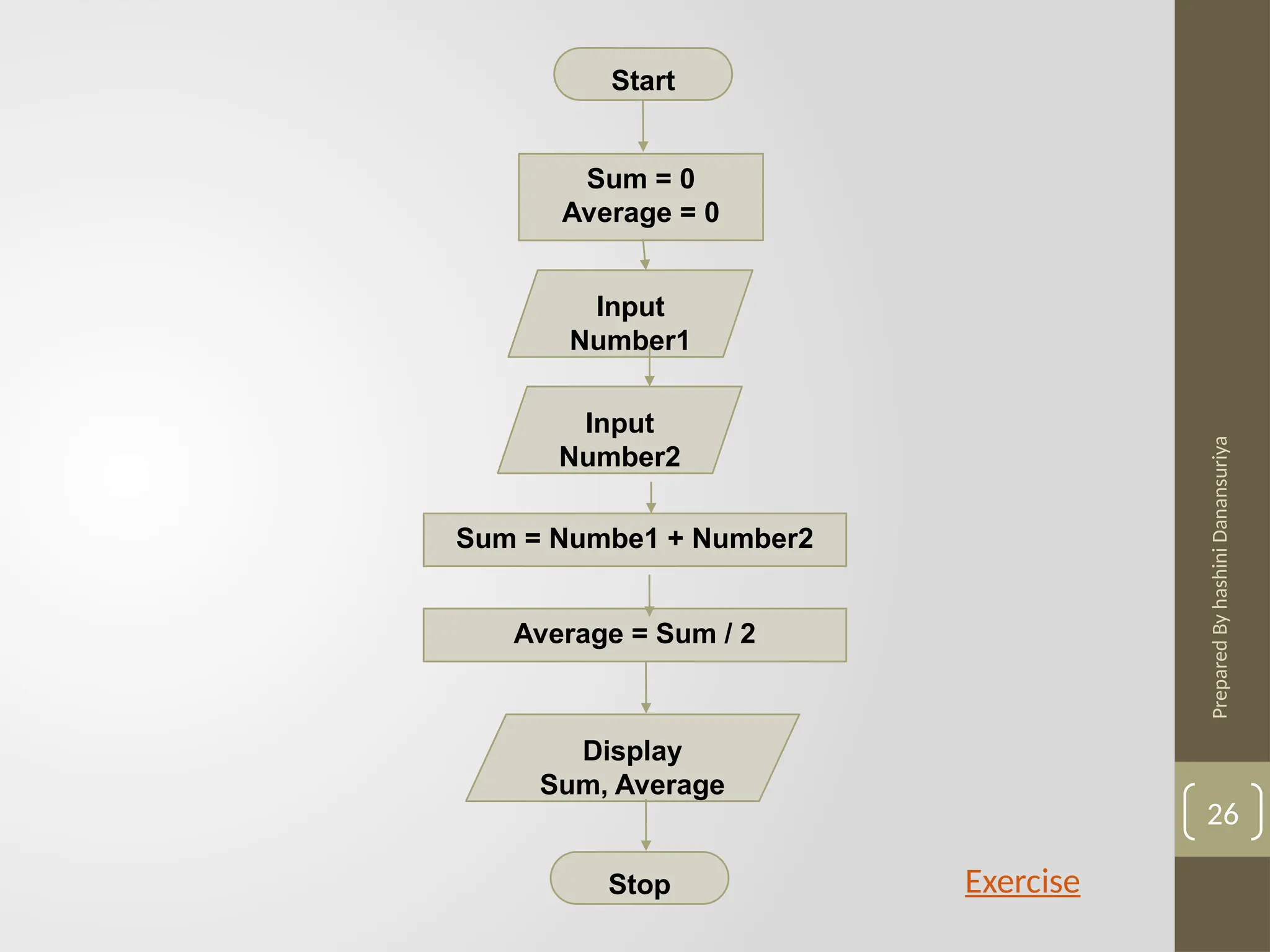
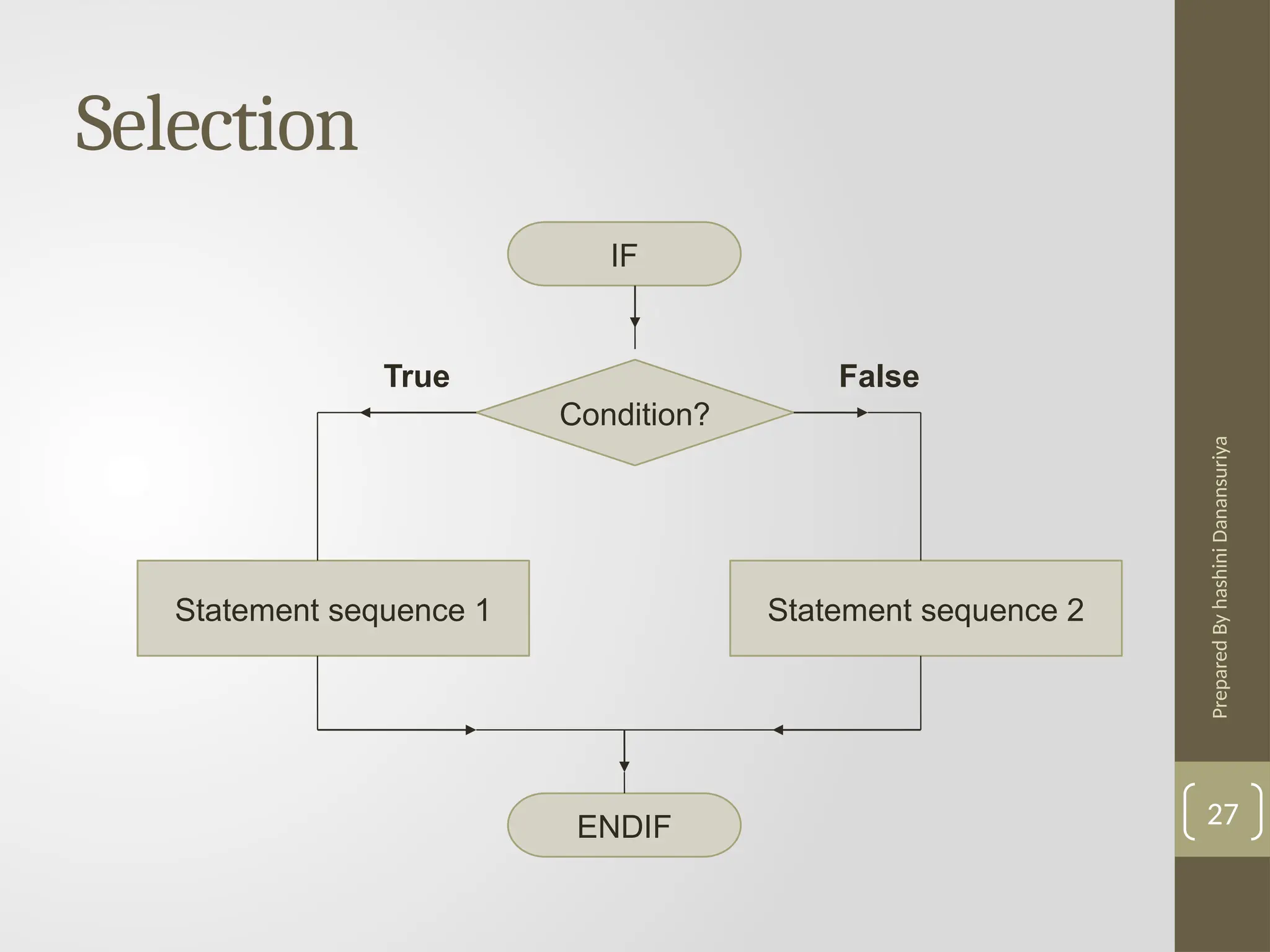
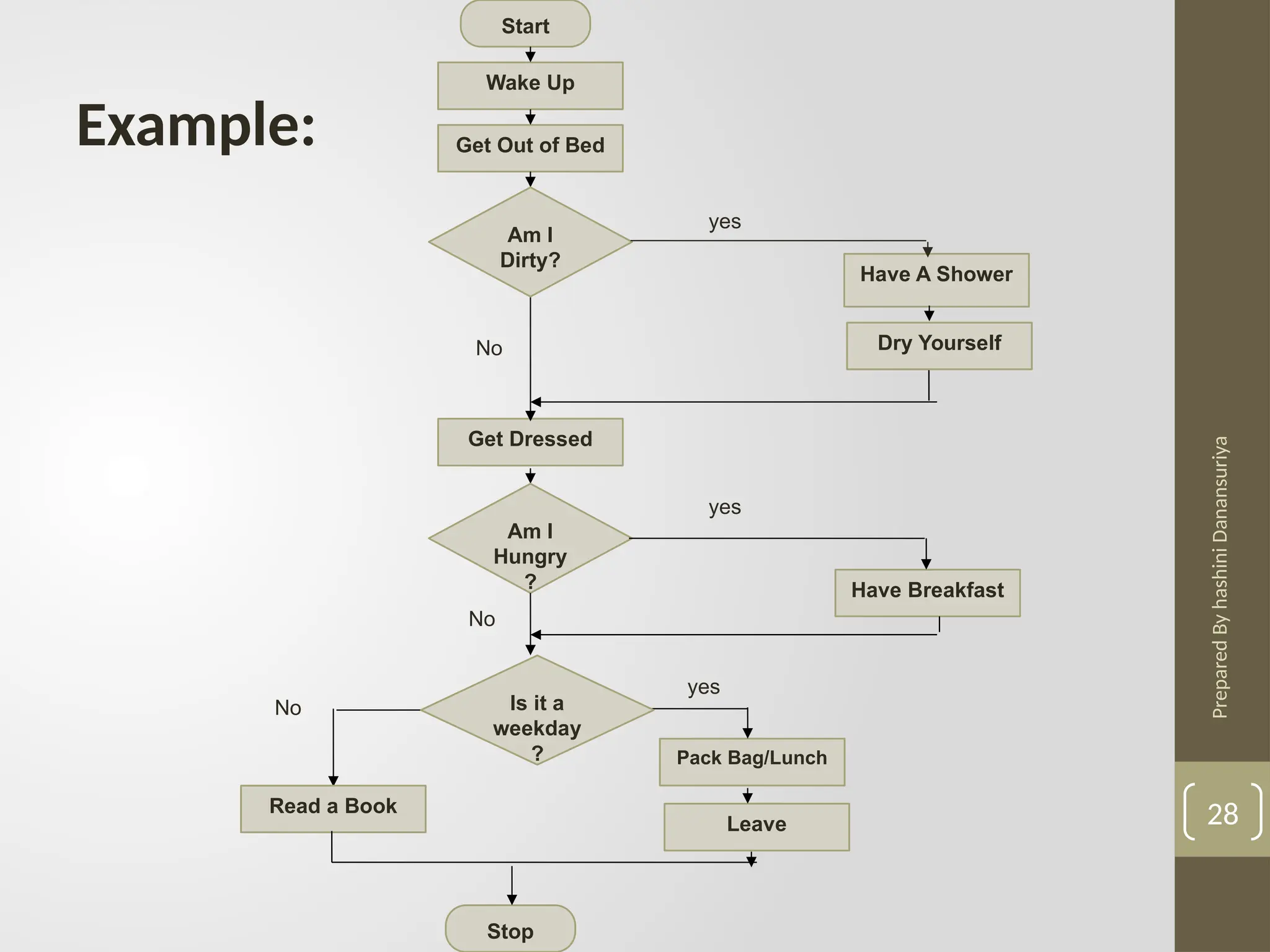
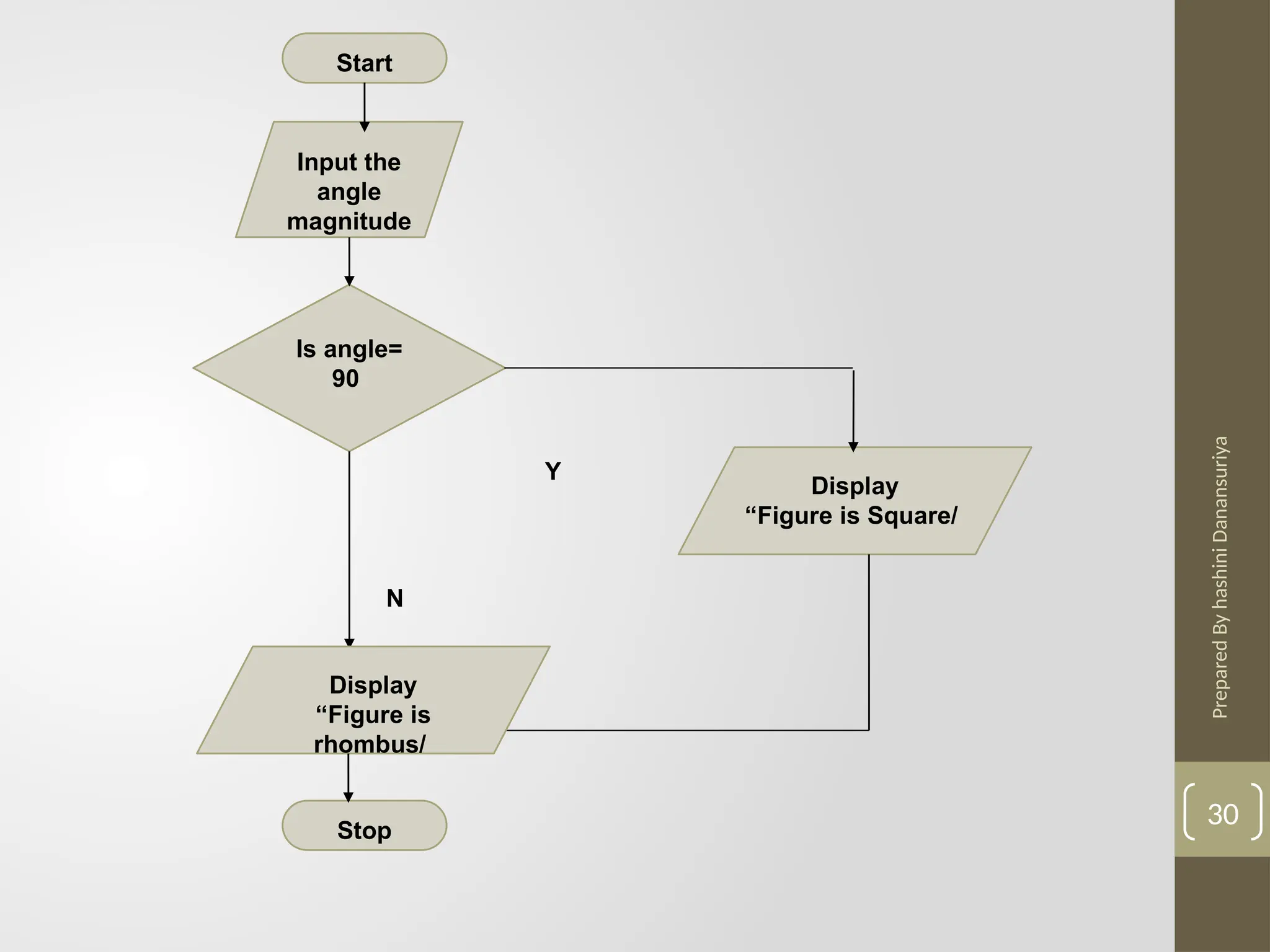
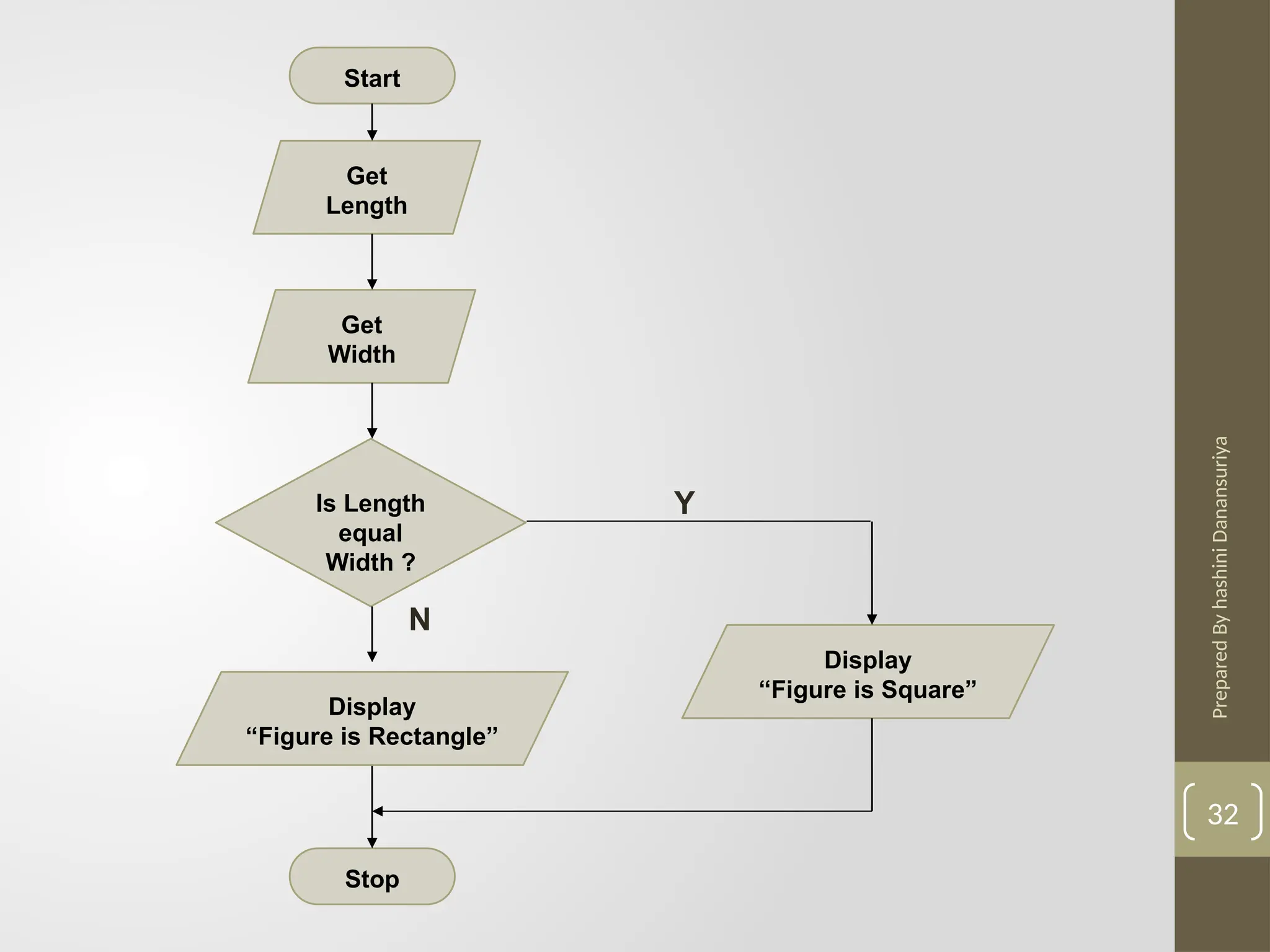
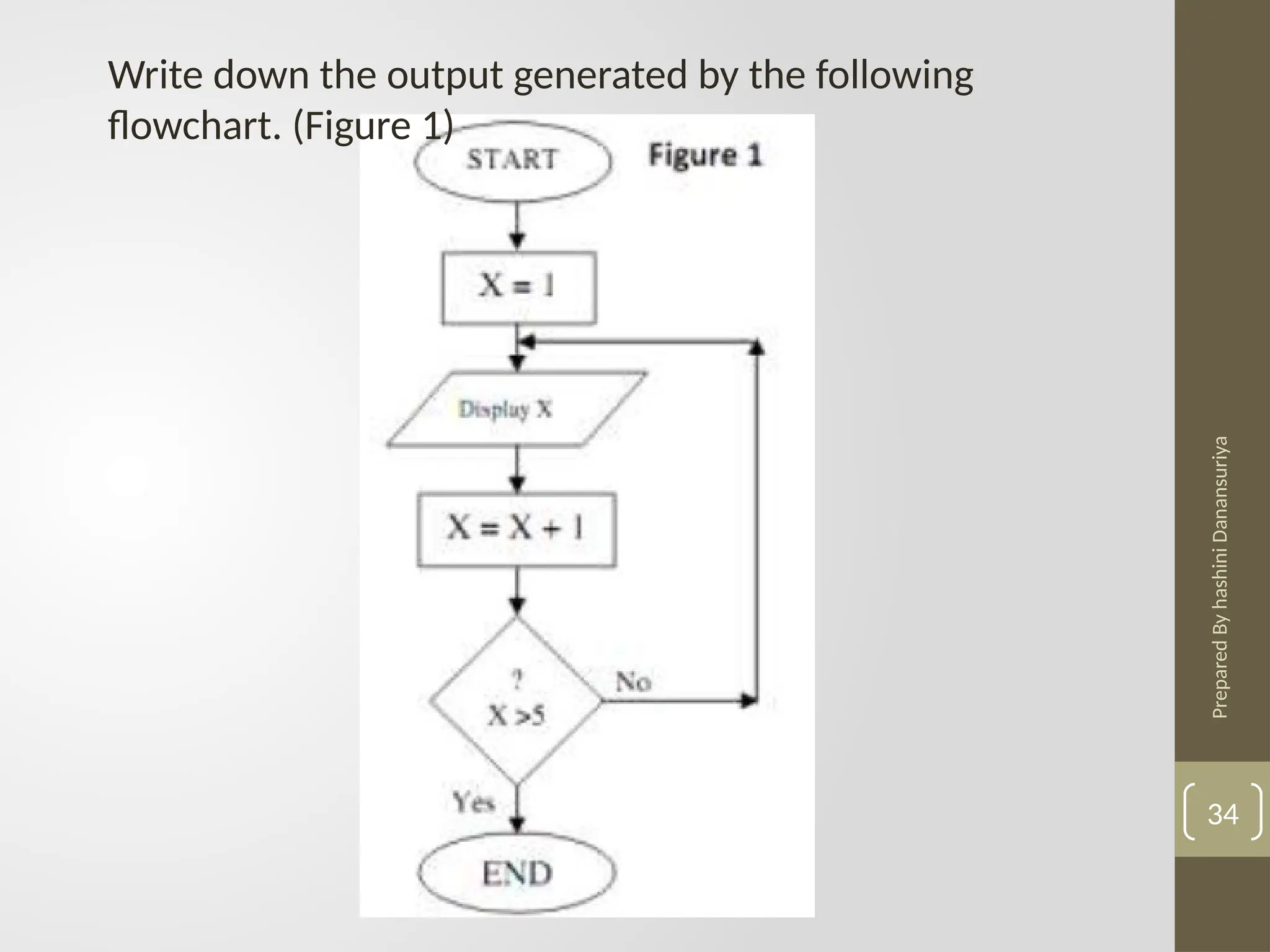
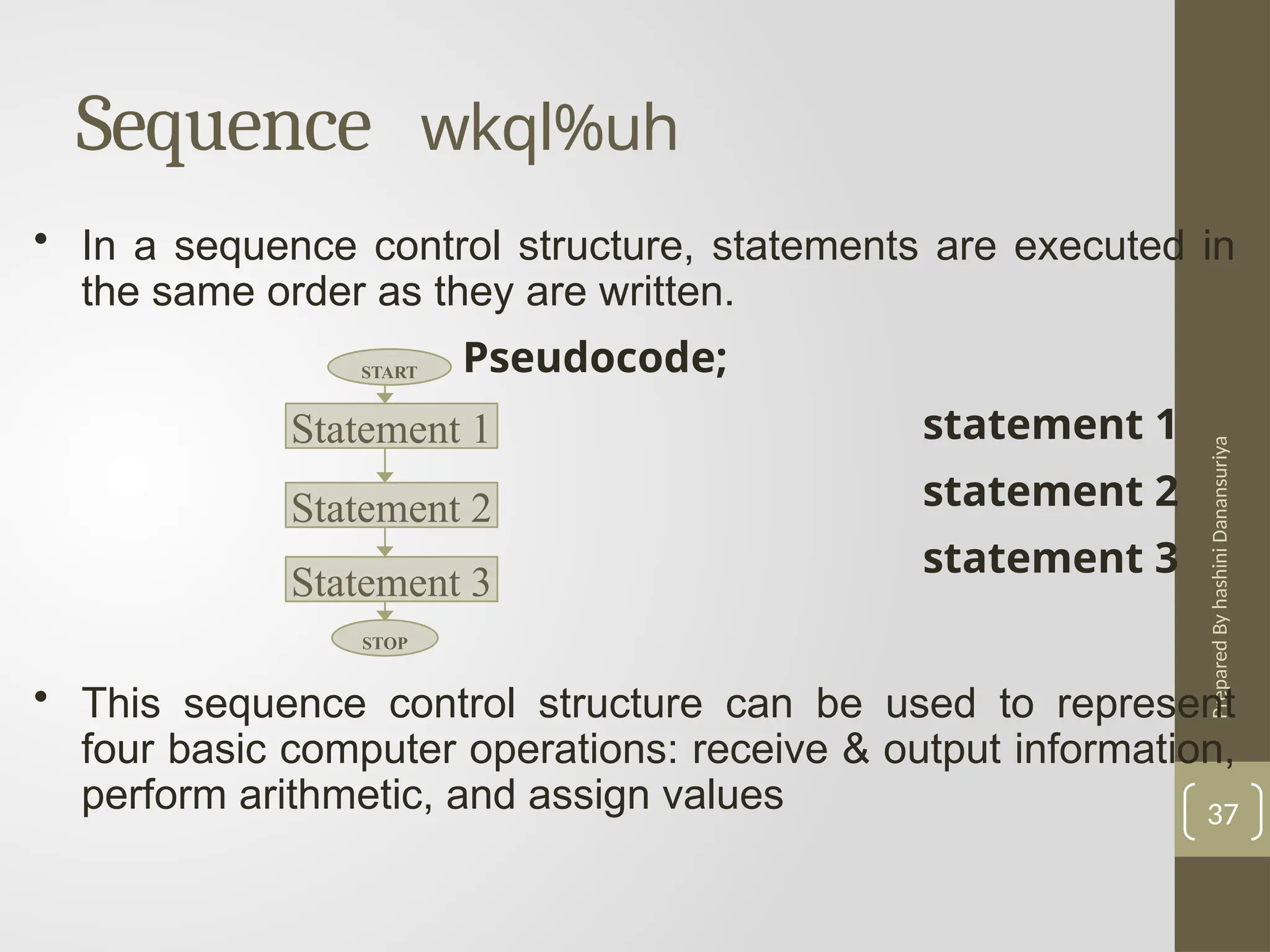
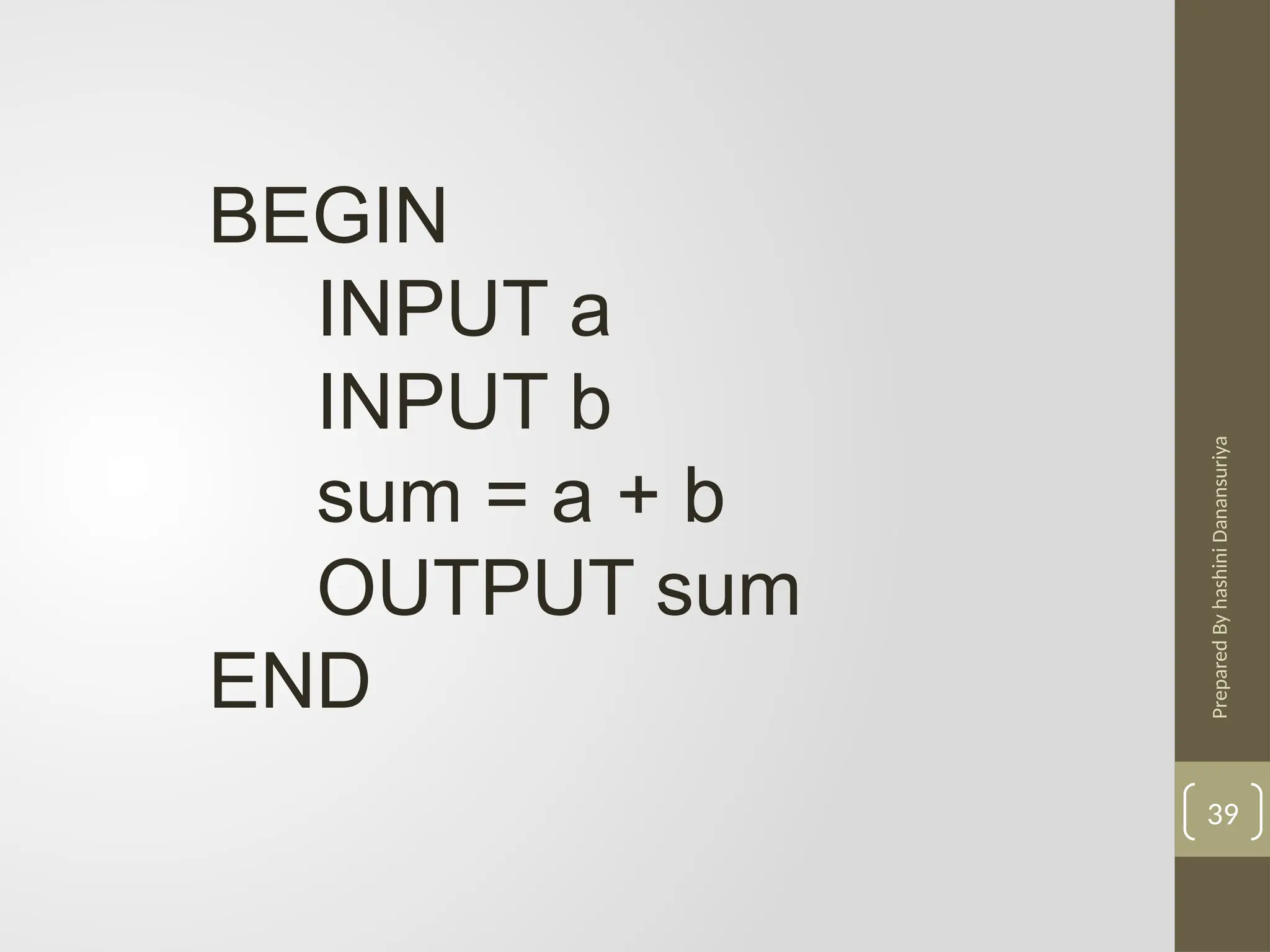
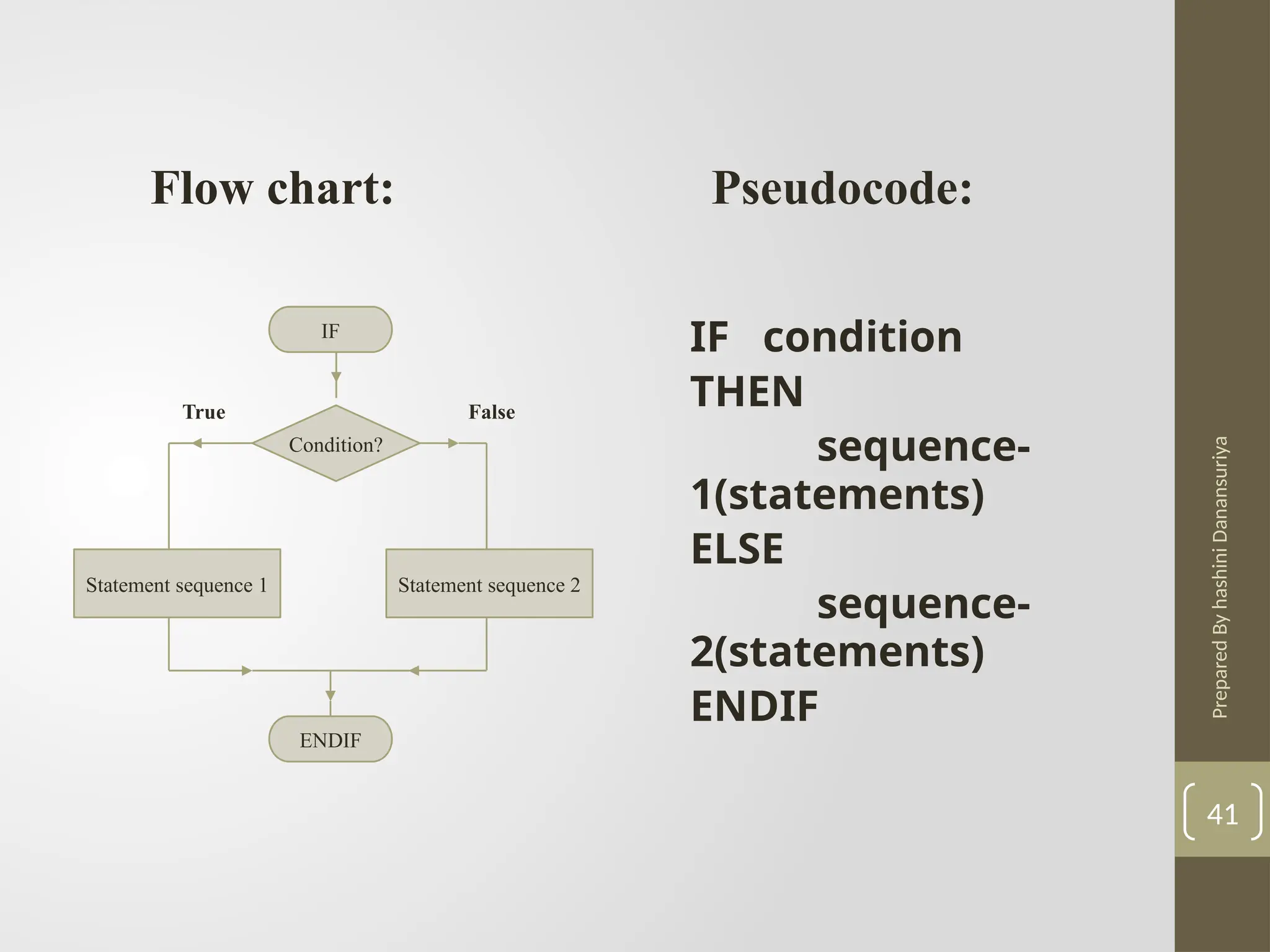
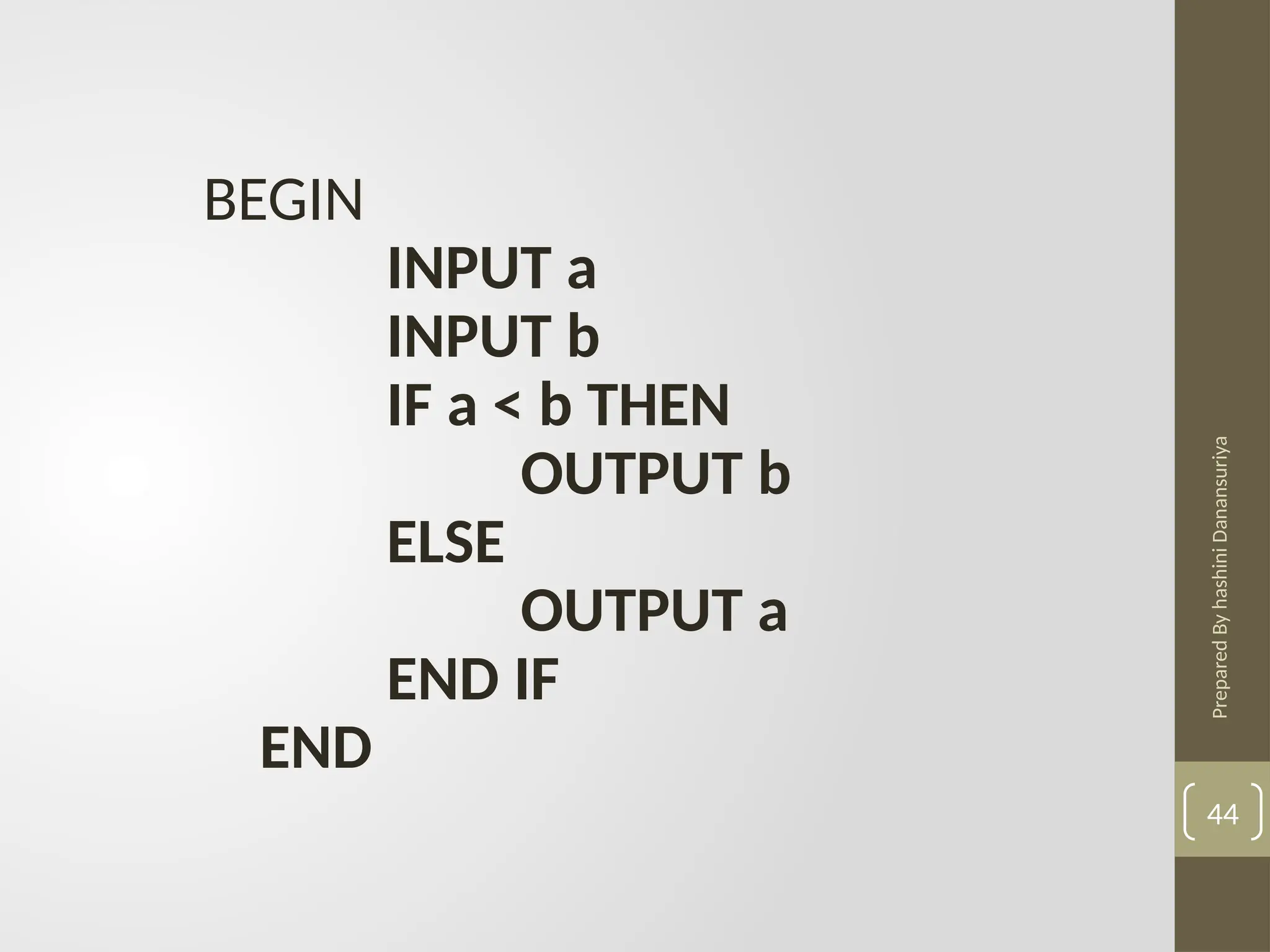
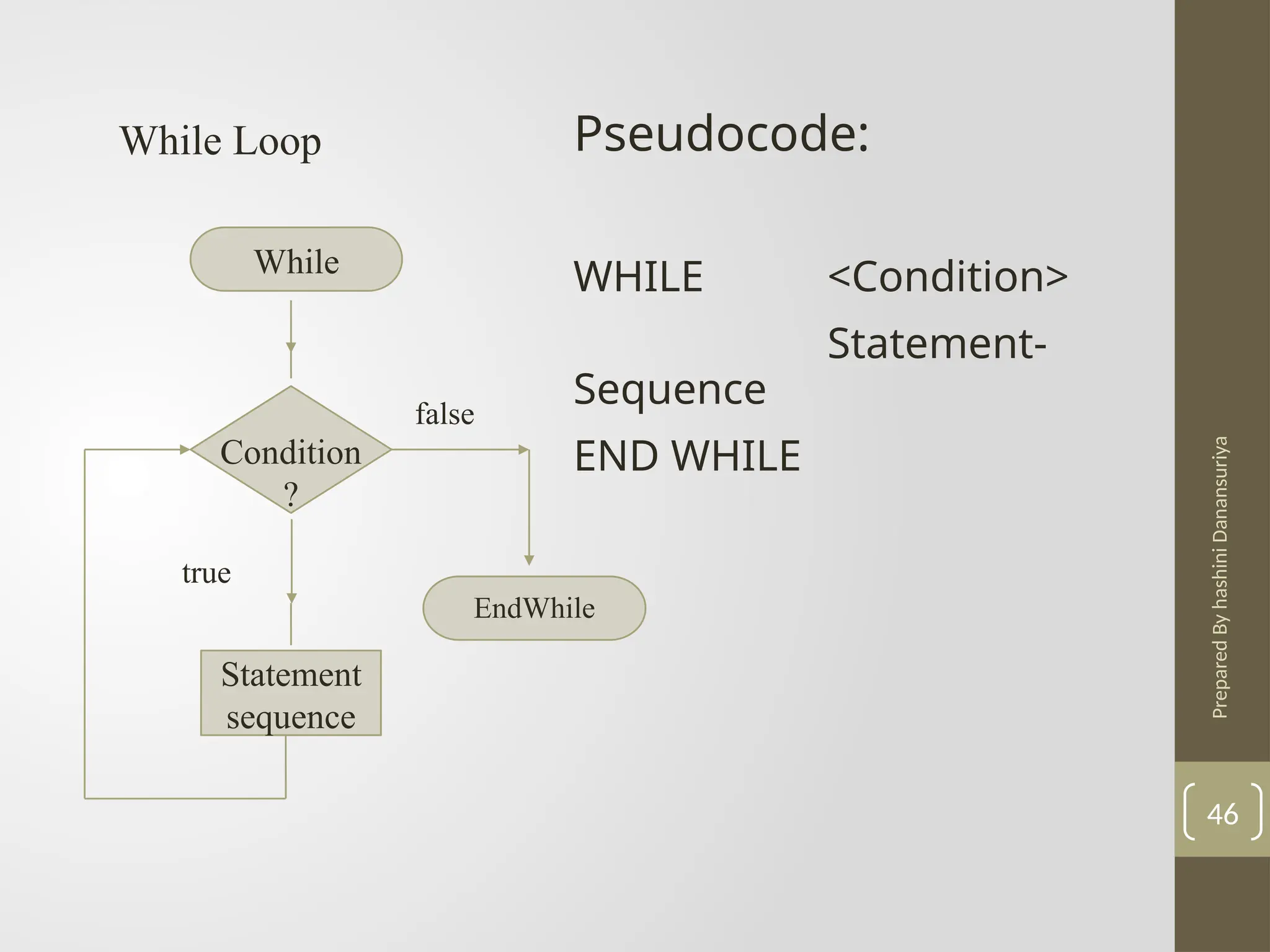
The document outlines the basics of problem-solving using algorithms, focusing on their definition, characteristics, and control structures (sequence, selection, and repetition). It provides examples and exercises related to algorithm development, flowcharts, and pseudocode. The importance of clear and logical steps in programming and problem-solving is emphasized throughout.