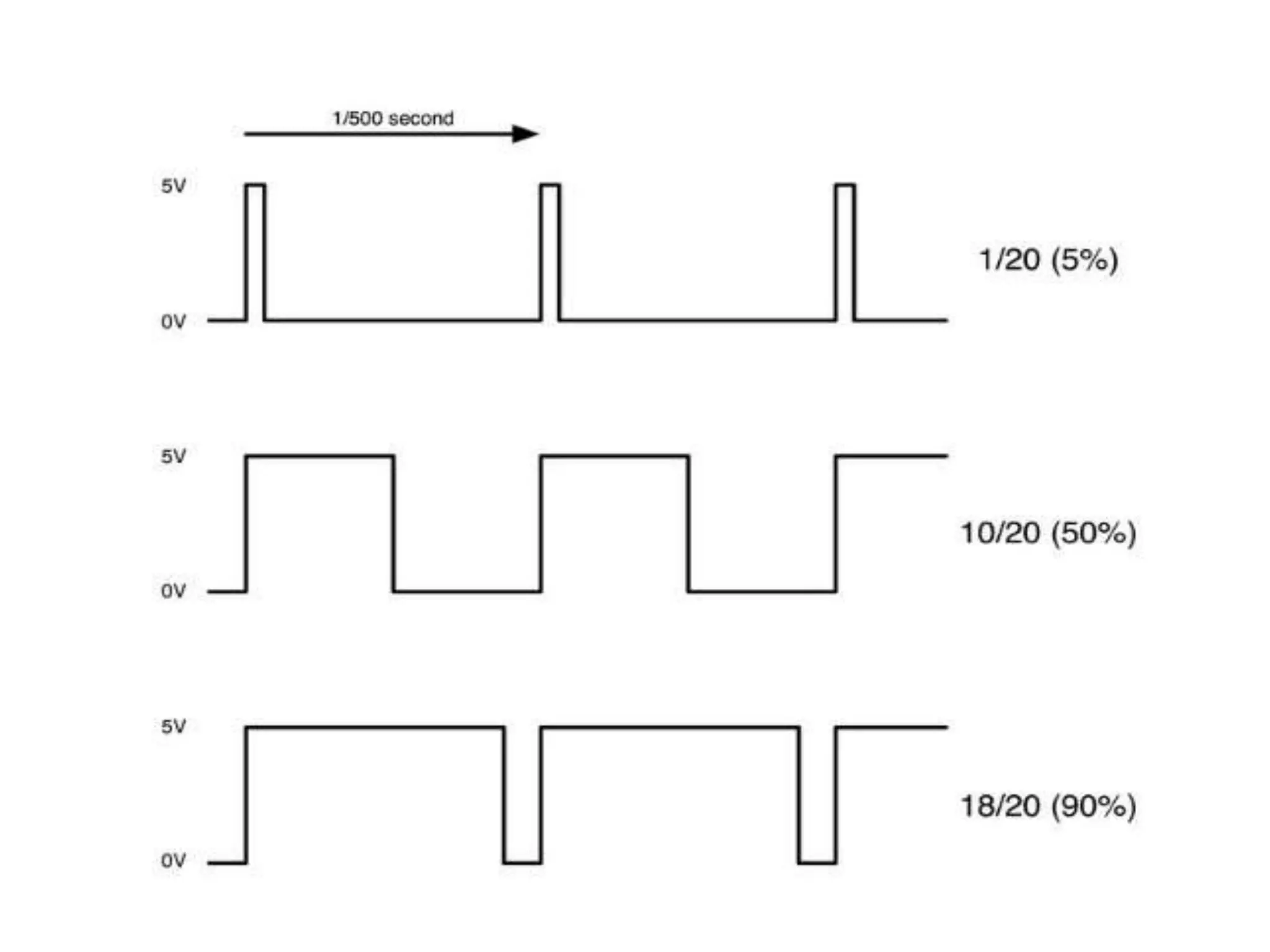
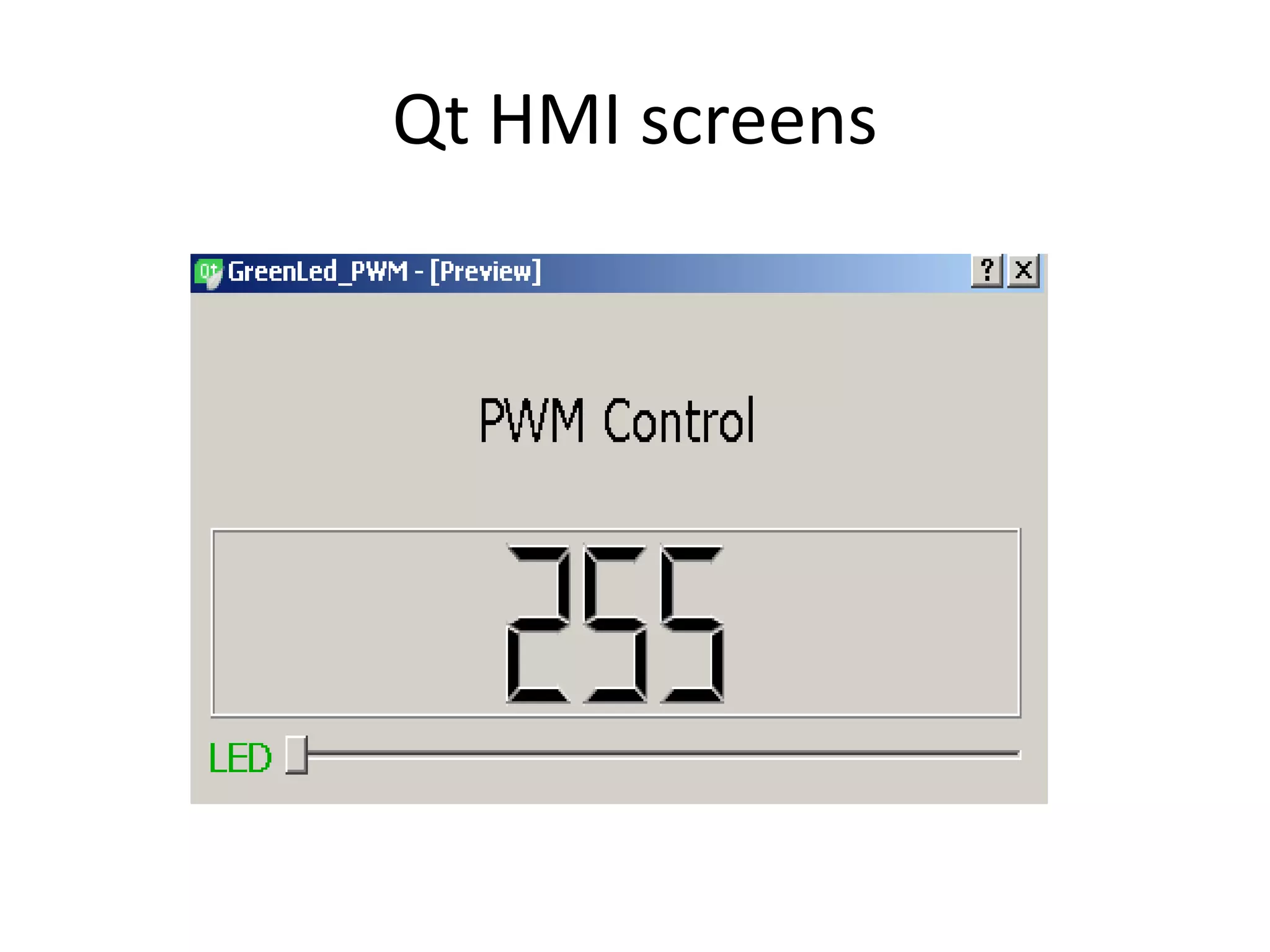
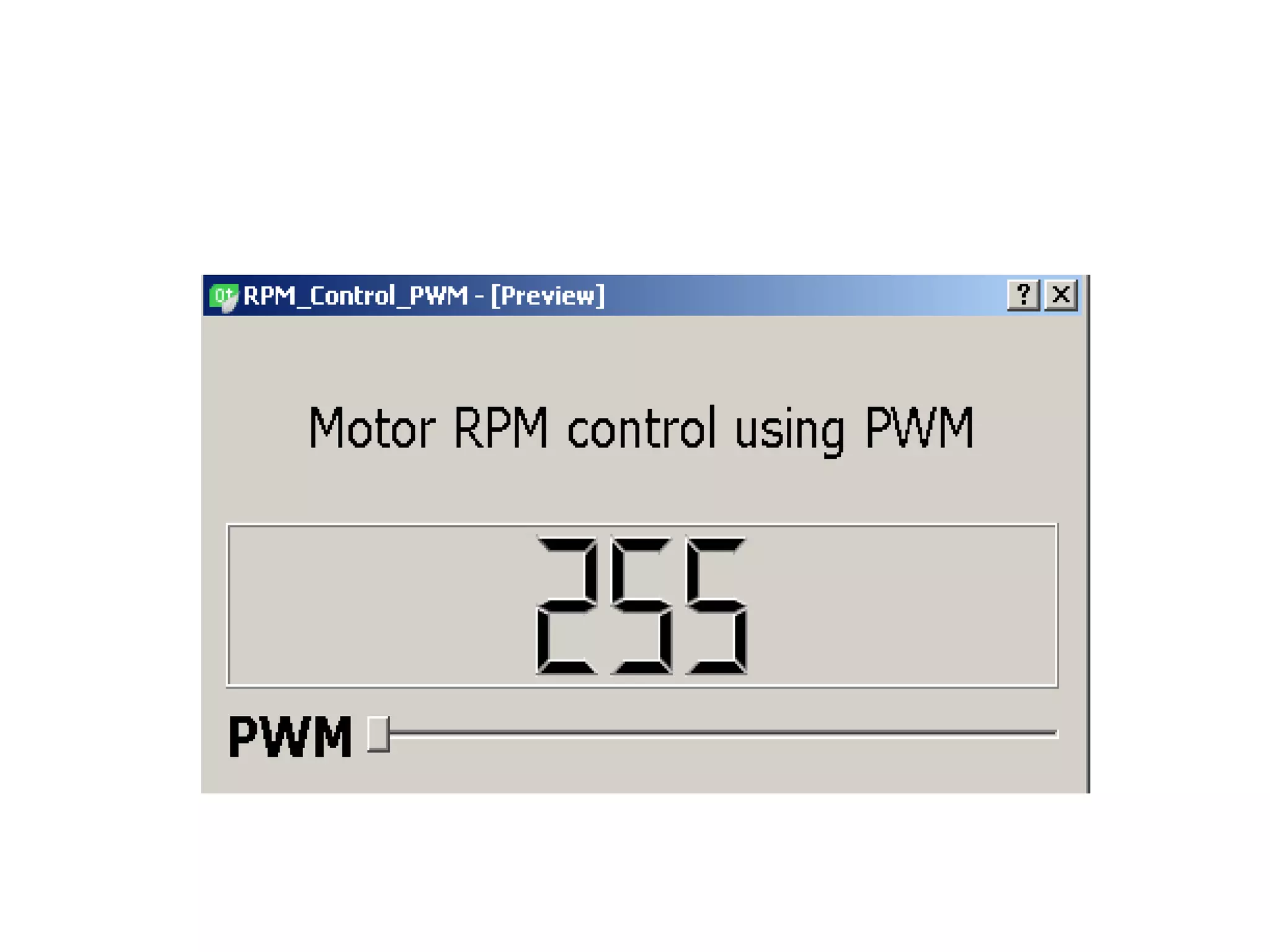
This document is a term paper detailing the development of a customized GUI using Qt to control the brightness of LEDs and the RPM of a DC motor via an Arduino Uno microcontroller. It discusses the required setup, methodology, and theories behind PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), including the use of 'analogWrite()' and 'analogRead()' functions to achieve desired outcomes. References for further reading and related research are also included.