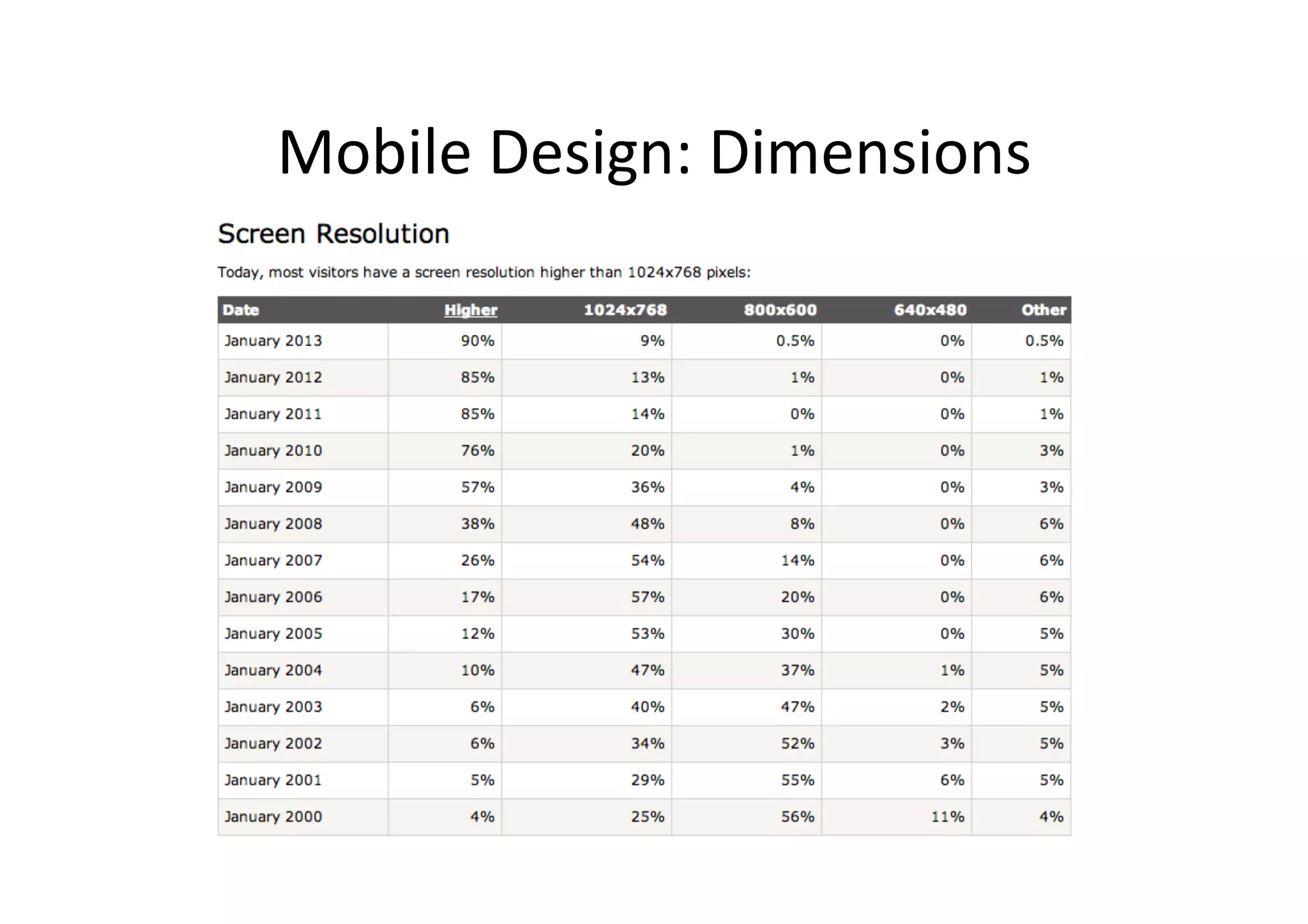
This document discusses responsive web design (RWD), an approach that makes web content accessible and usable across various devices and screen sizes. It recommends designing first for mobile screens and using fluid grids, flexible images and CSS3 media queries to dynamically adapt layouts. Key aspects of RWD covered include viewing on different devices, orientations and resolutions using media features and queries to apply distinct styling rules. Examples are provided for implementing breakpoints and adapting designs for large, medium and small screens.