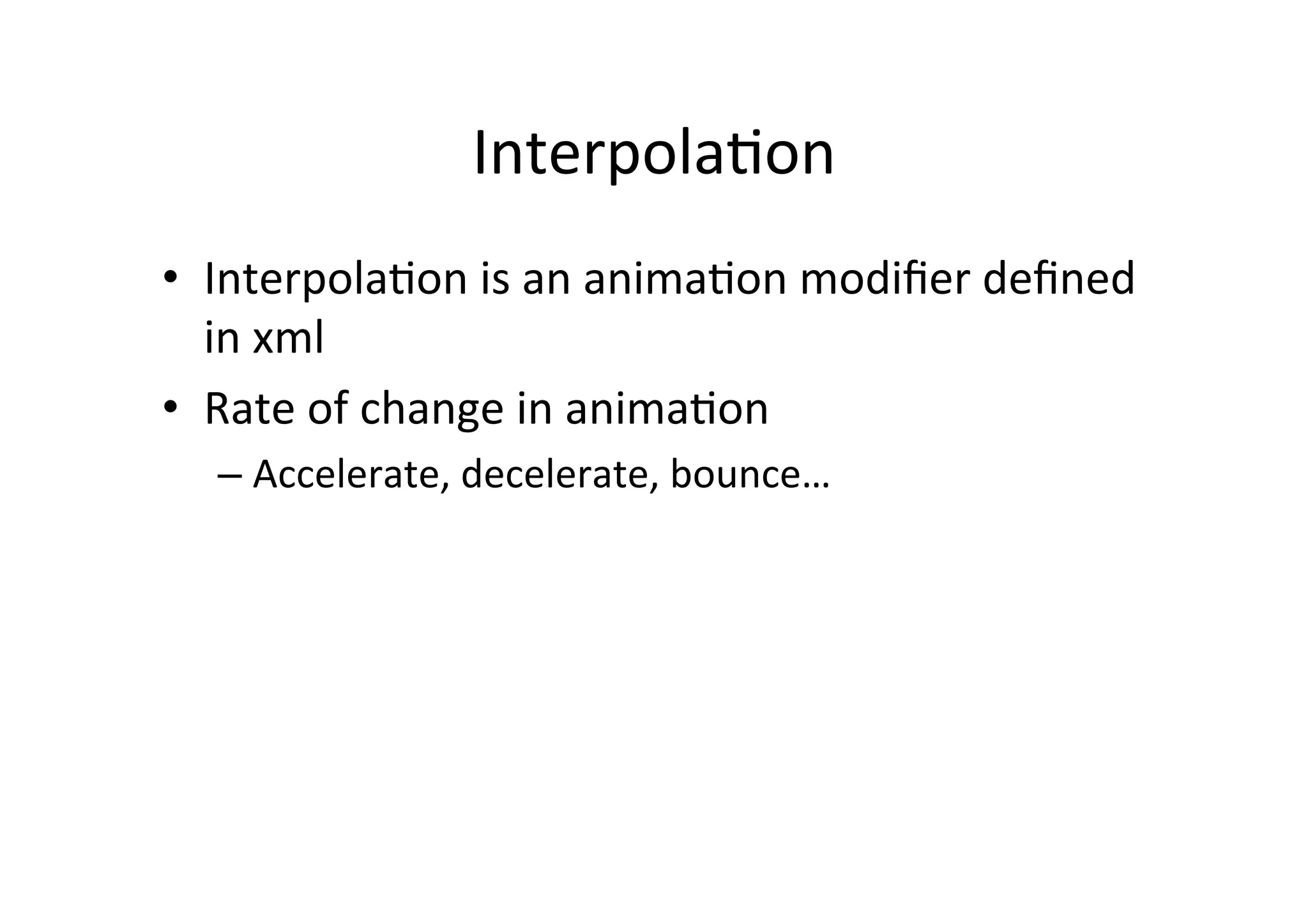
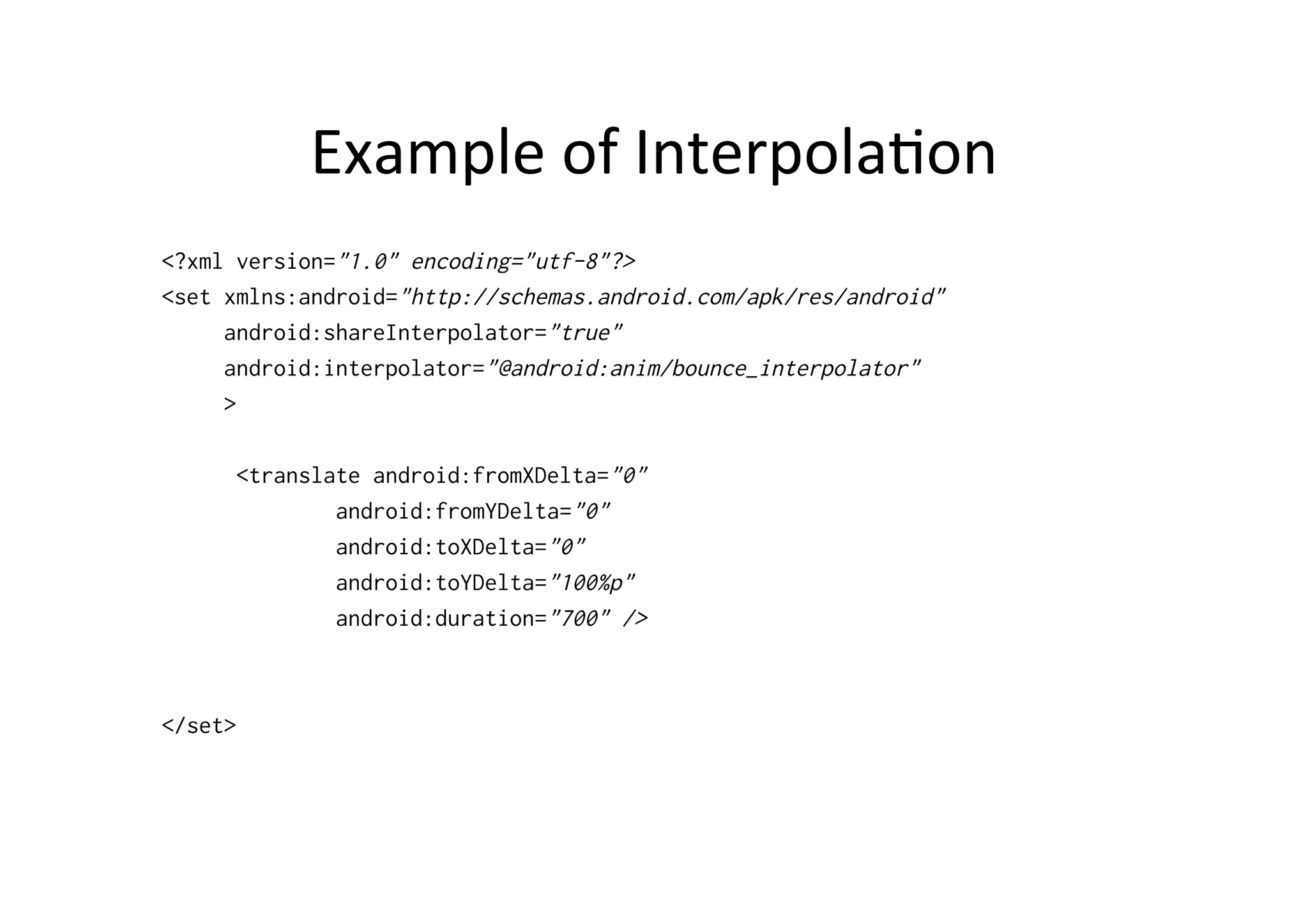
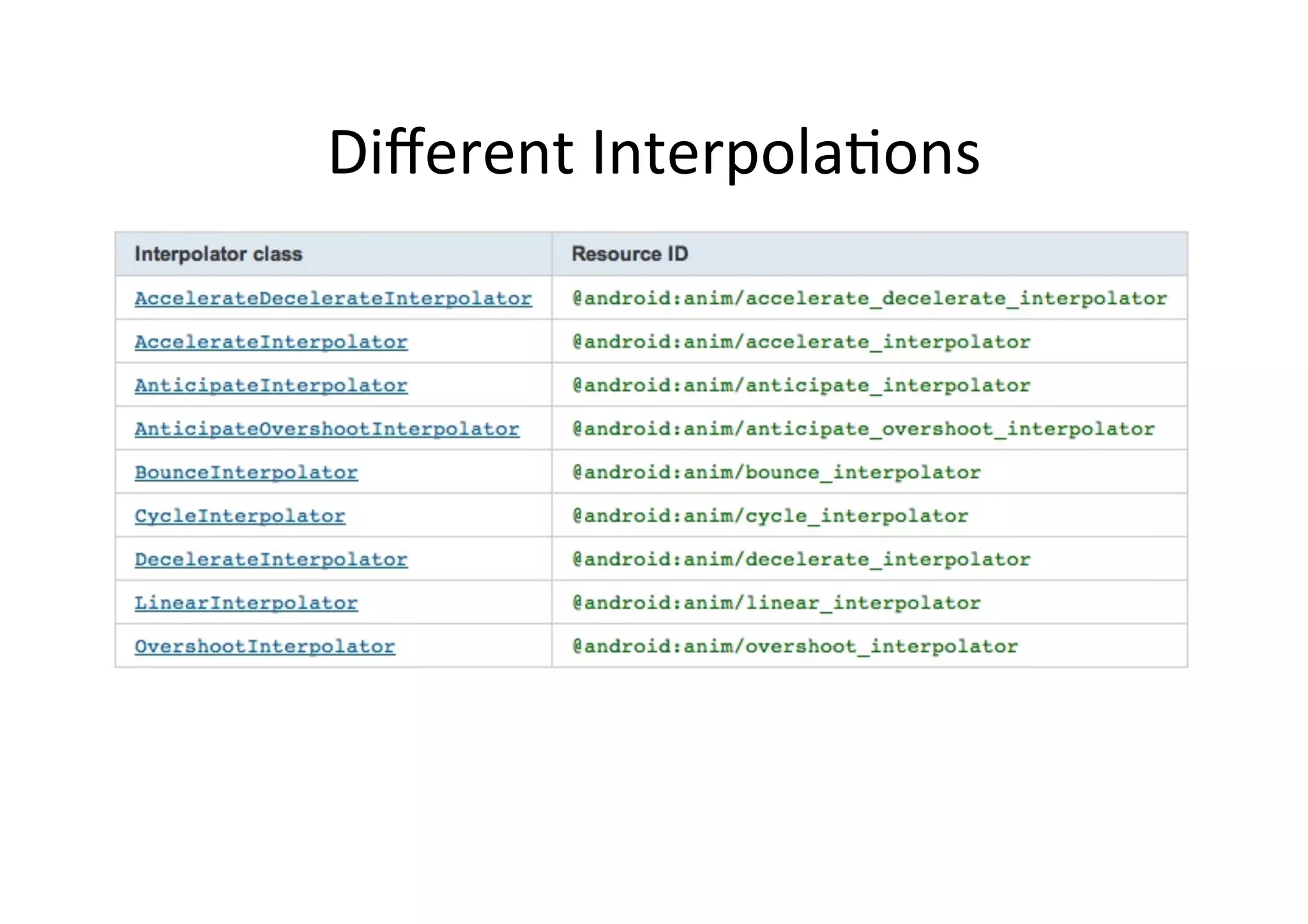
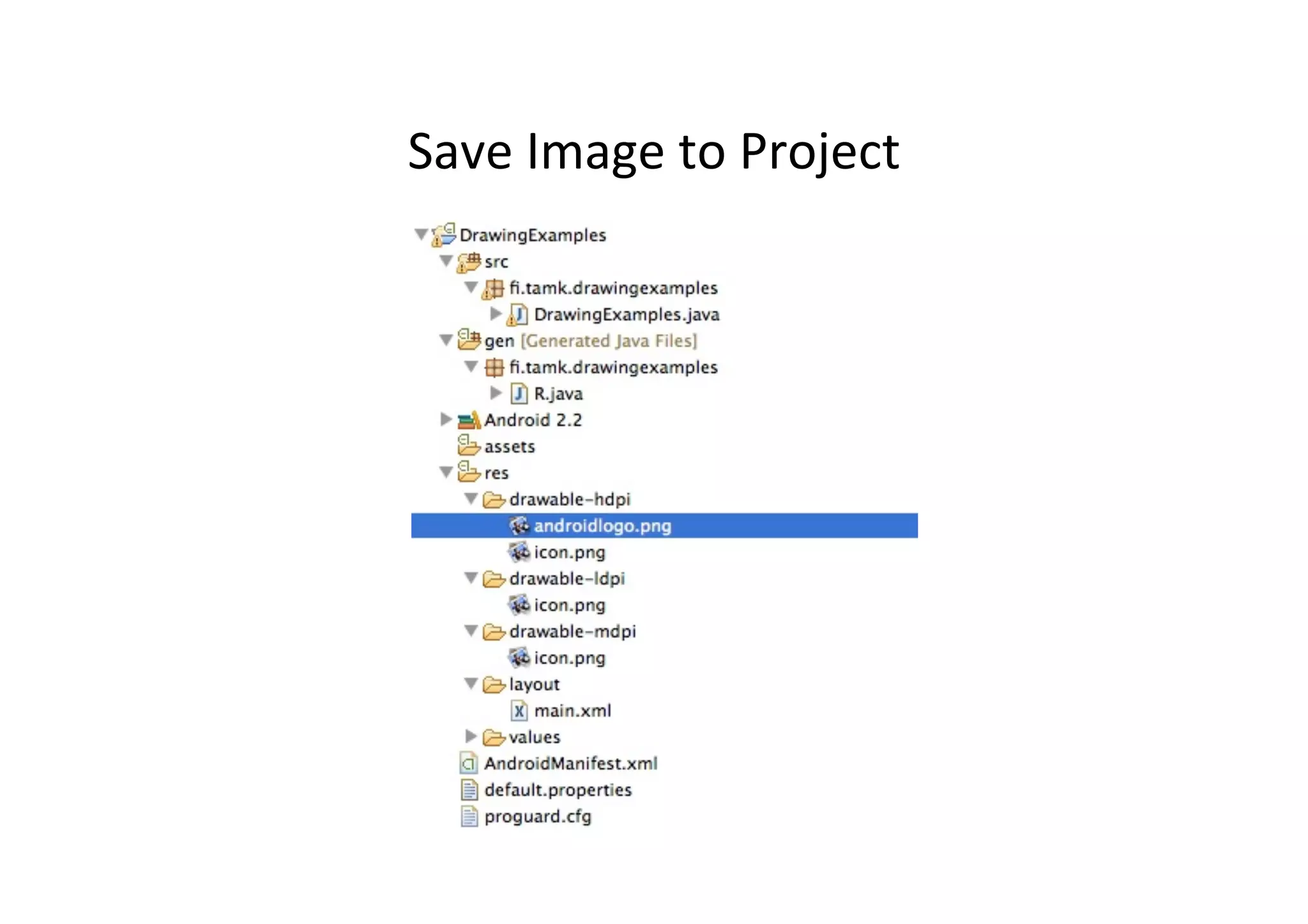
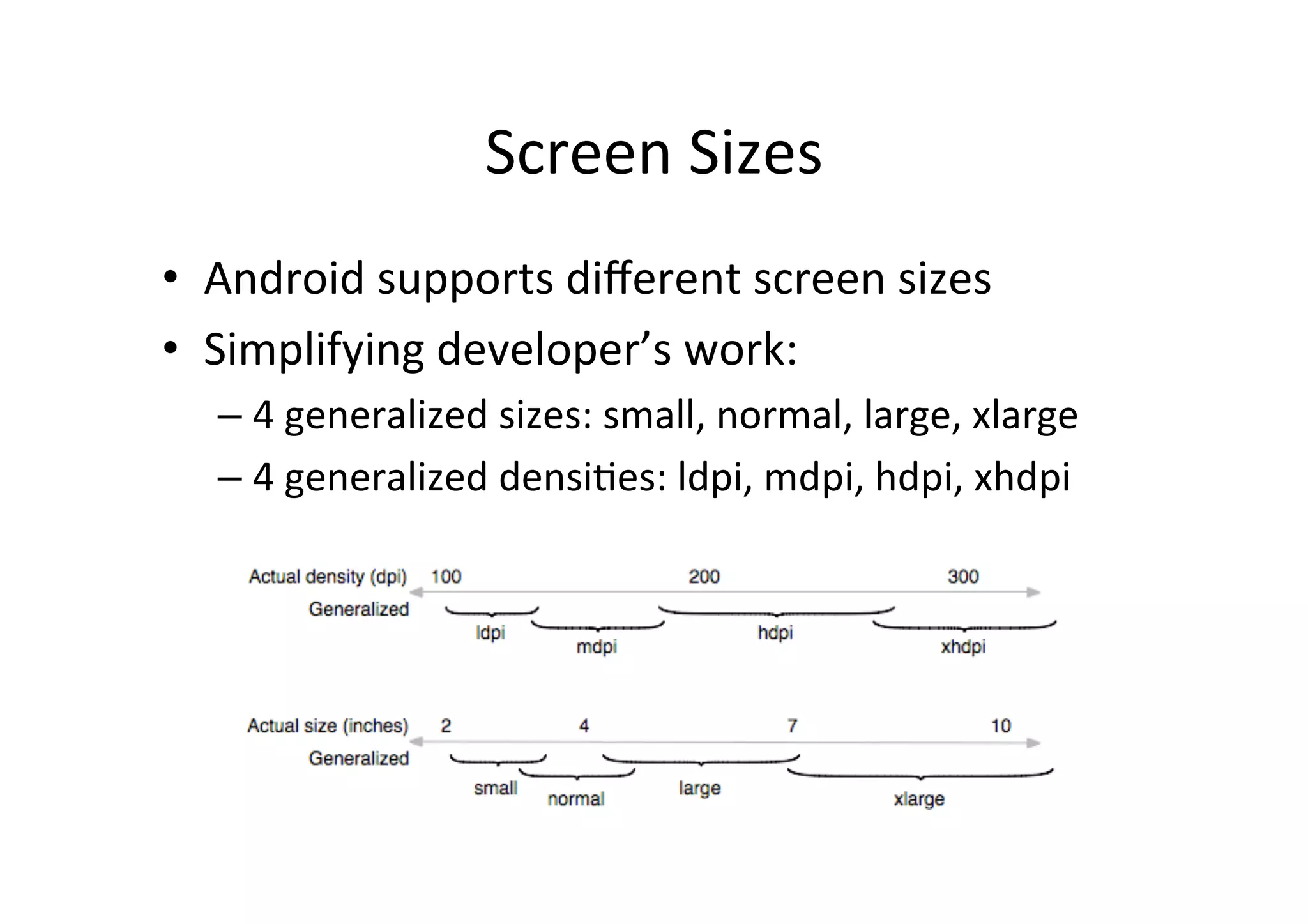
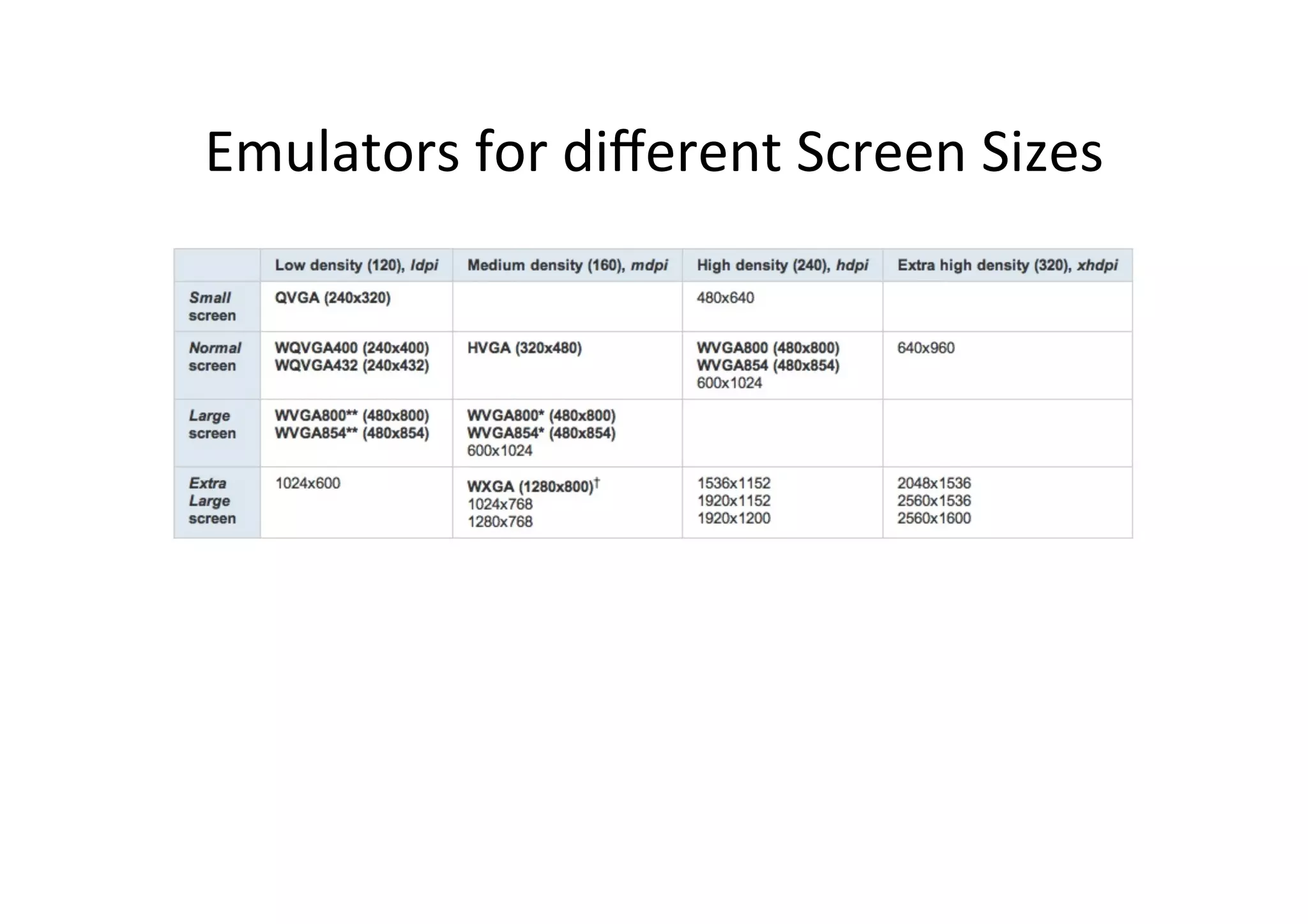
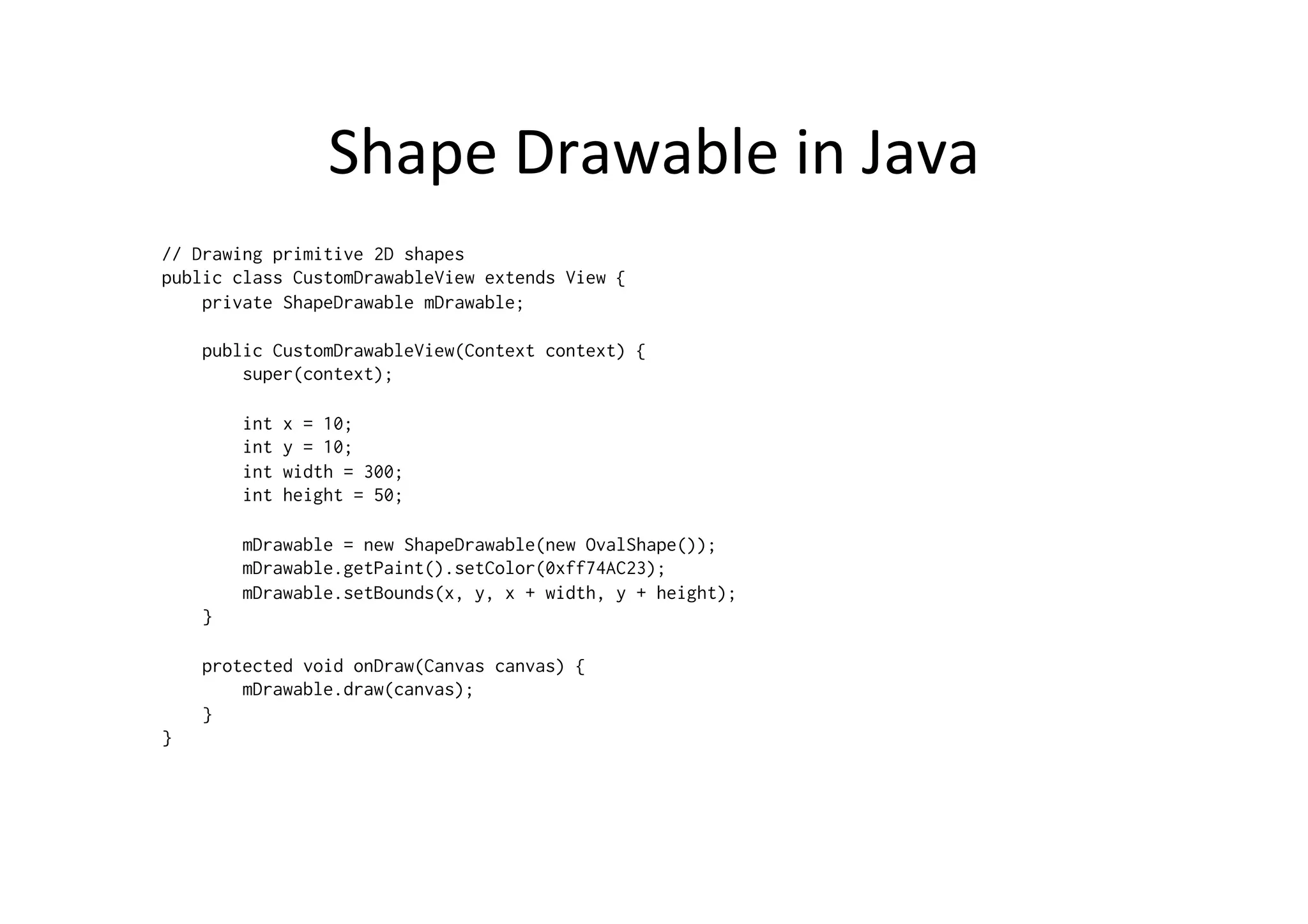
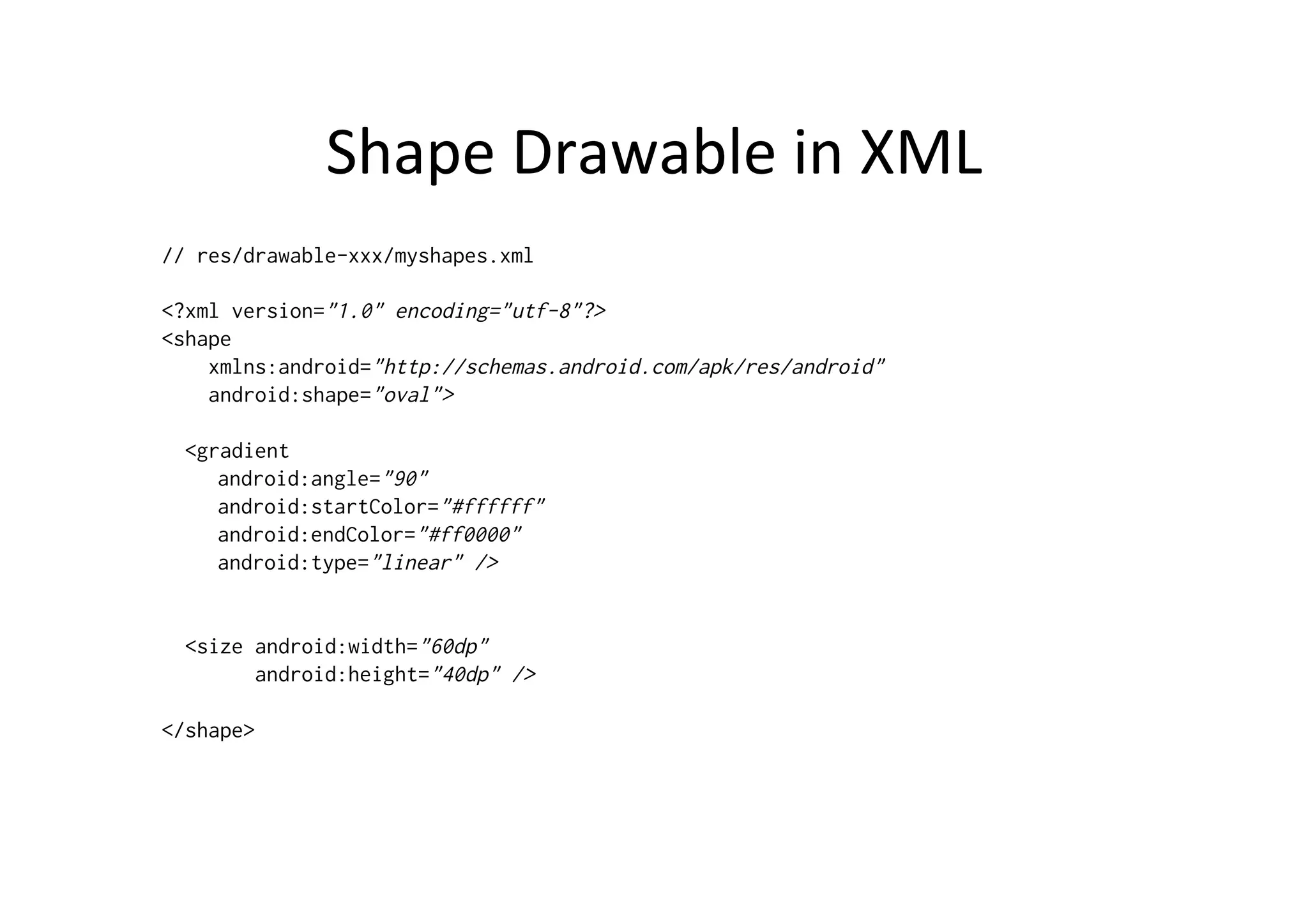
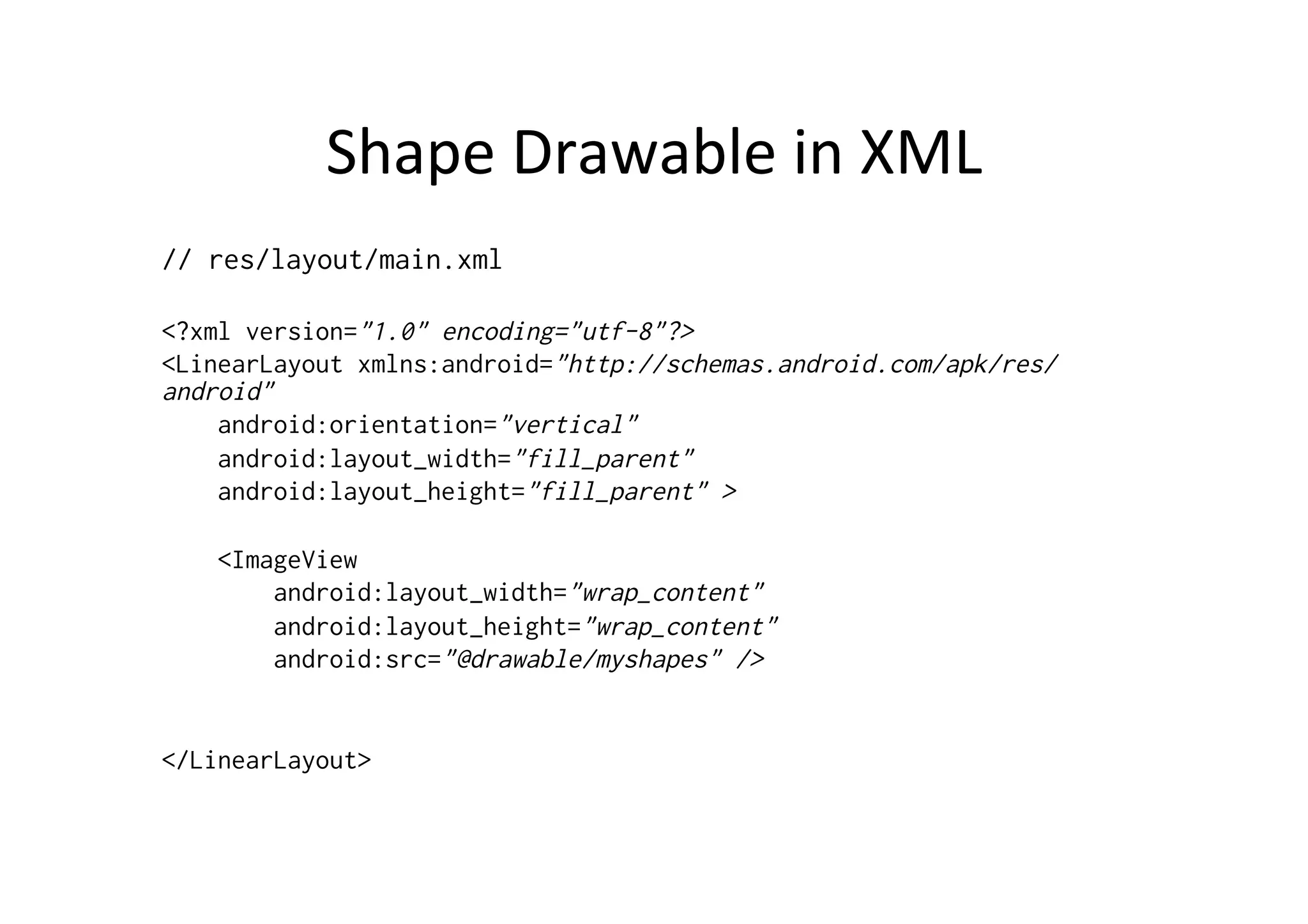
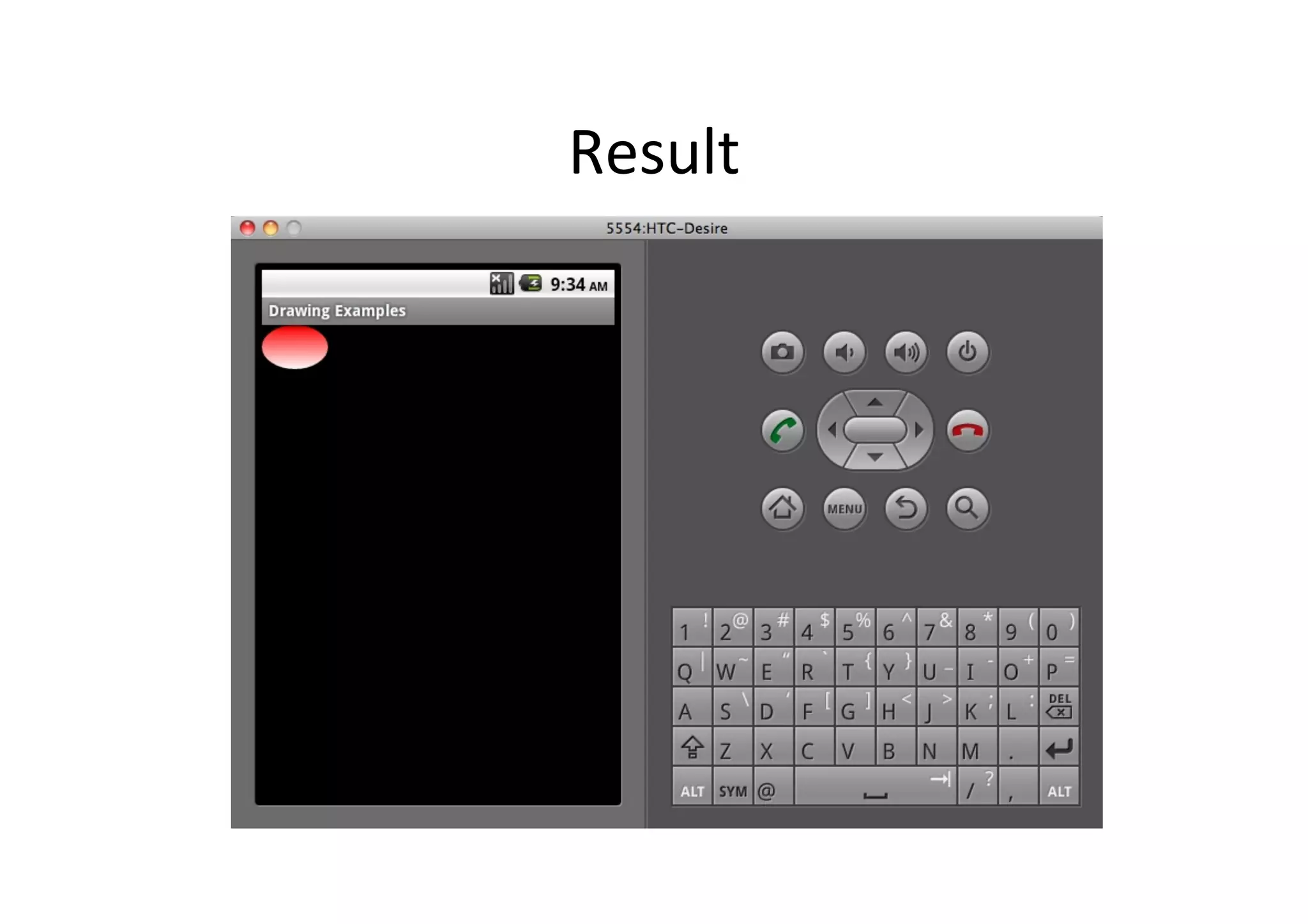
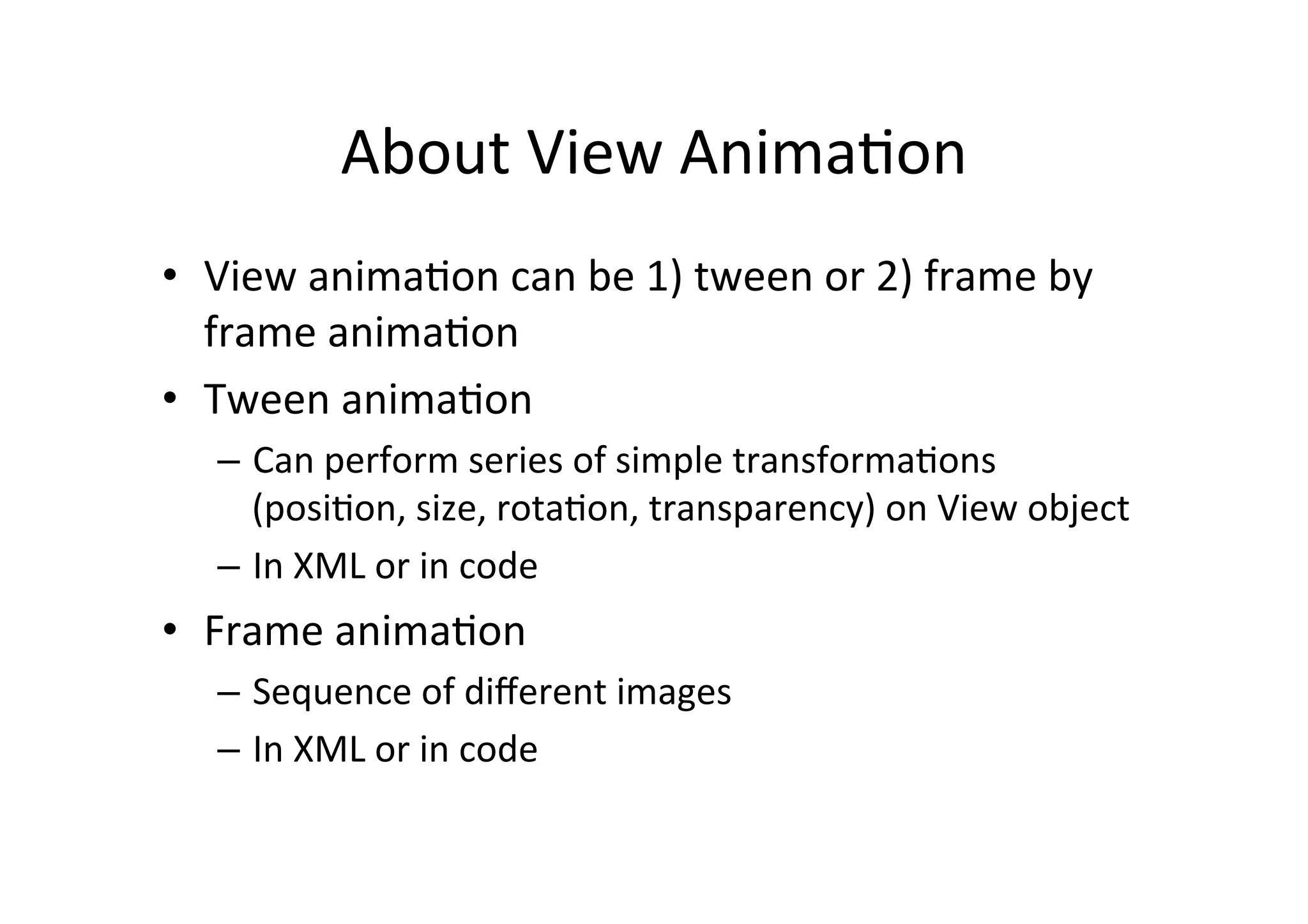
The document discusses Android drawing and animation. It covers drawing using drawables, shapes, and custom views. It also covers view animation, which includes tween animation defined in XML files to transition views between states, and frame animation to transition between drawables. The document also introduces the Android property animation system for animating any object properties.



















![Tween
Anima-on:
XML
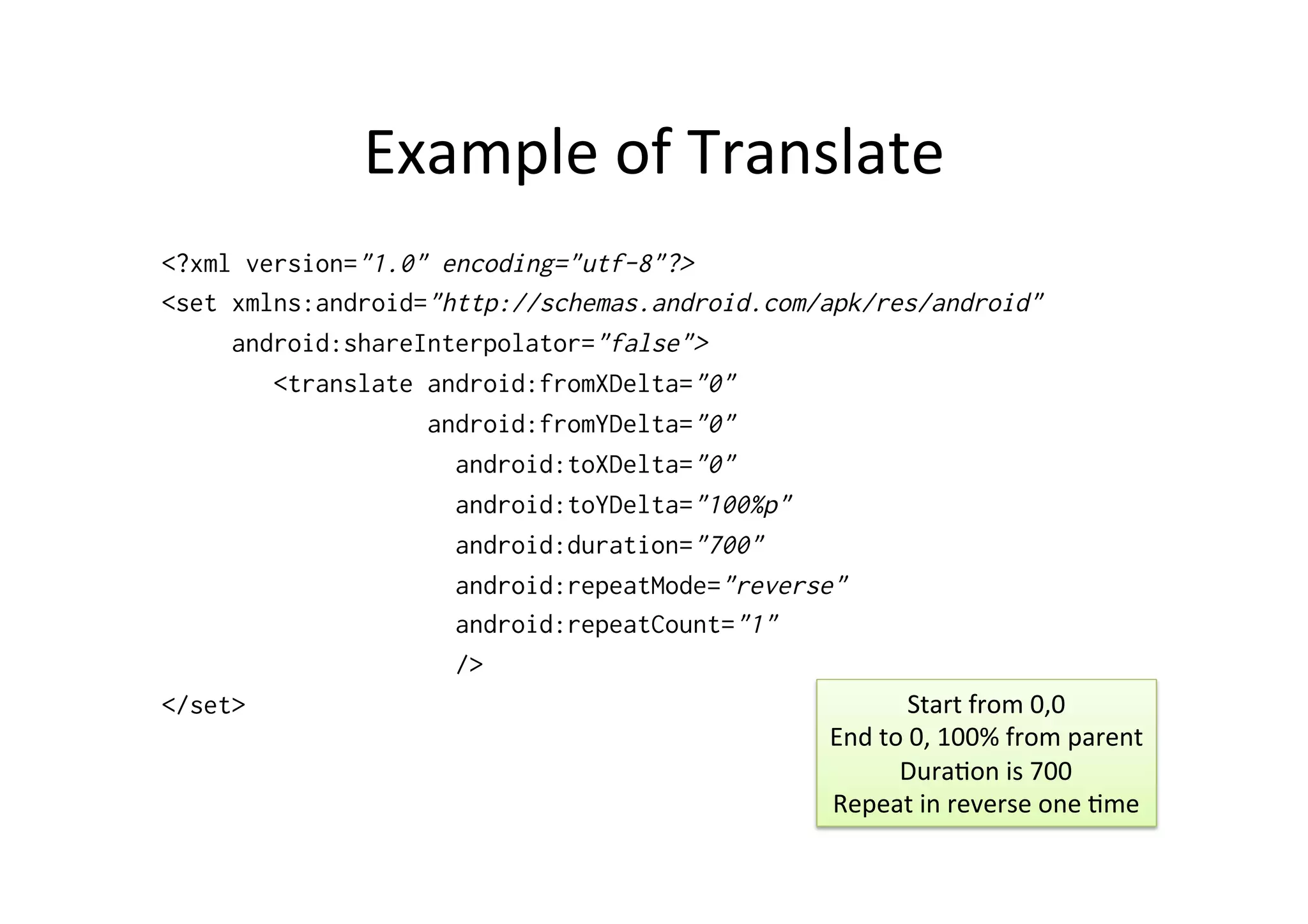
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:interpolator="@[package:]anim/interpolator_resource"
android:shareInterpolator=["true" | "false"] >
<alpha
android:fromAlpha="float"
android:toAlpha="float" />
<scale
android:fromXScale="float"
android:toXScale="float"
android:fromYScale="float"
android:toYScale="float"
android:pivotX="float"
android:pivotY="float" />
<translate
android:fromXDelta="float"
android:toXDelta="float"
android:fromYDelta="float"
android:toYDelta="float" />
<rotate
android:fromDegrees="float"
android:toDegrees="float"
android:pivotX="float"
android:pivotY="float" />
<set>
...
</set>
</set>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06-android-drawing-and-animation-110810020455-phpapp01/75/Android-2D-Drawing-and-Animation-Framework-28-2048.jpg)