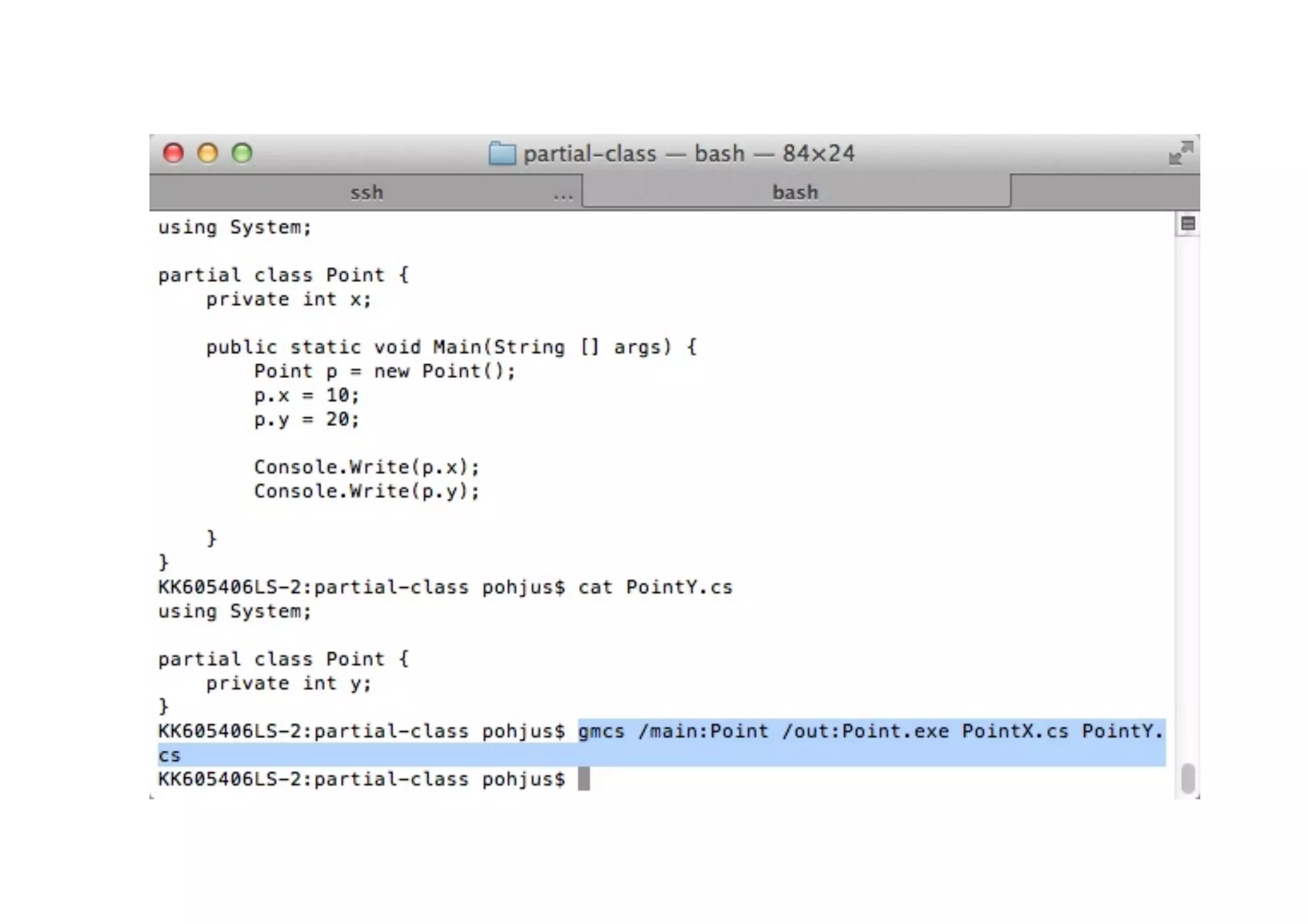
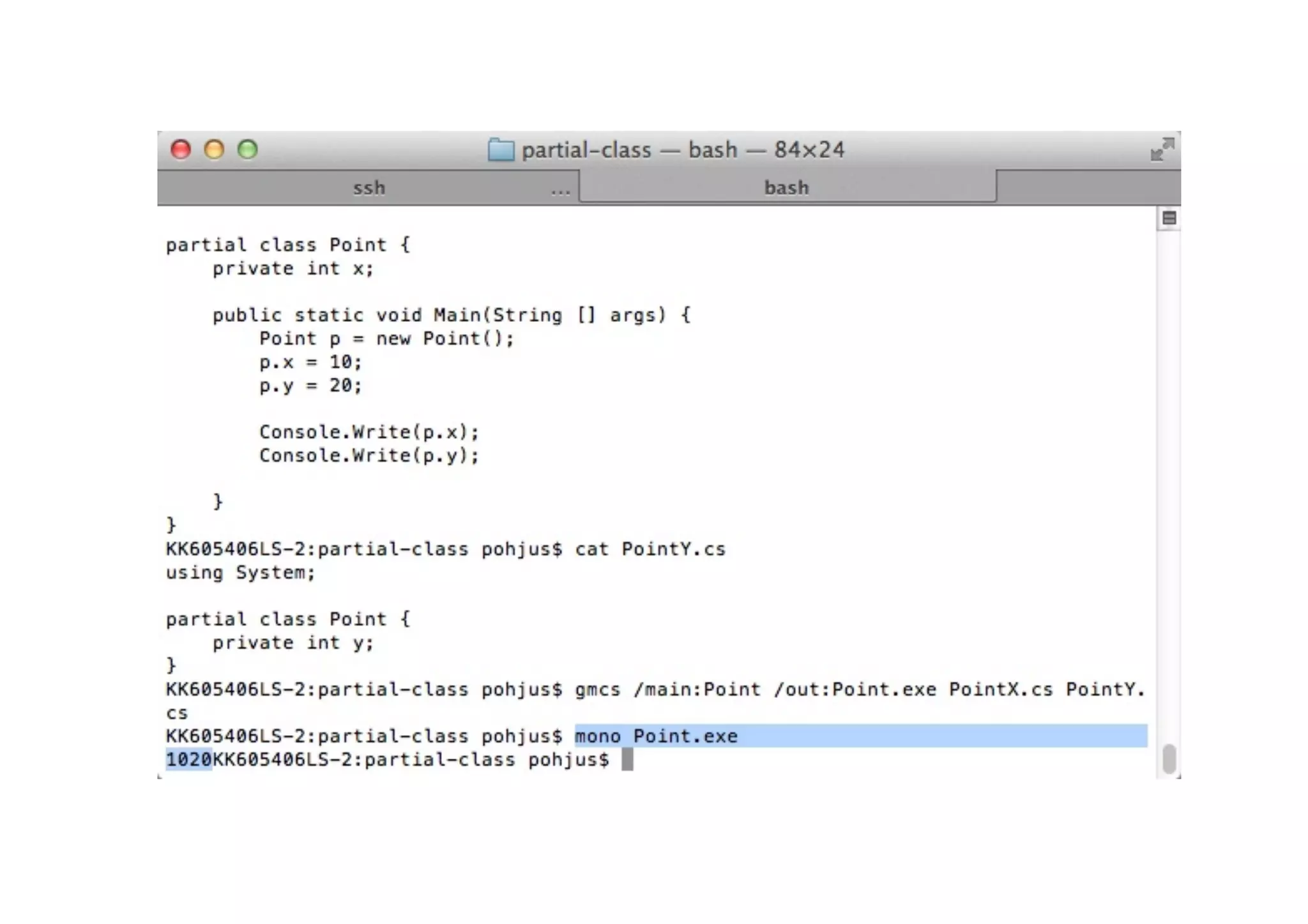
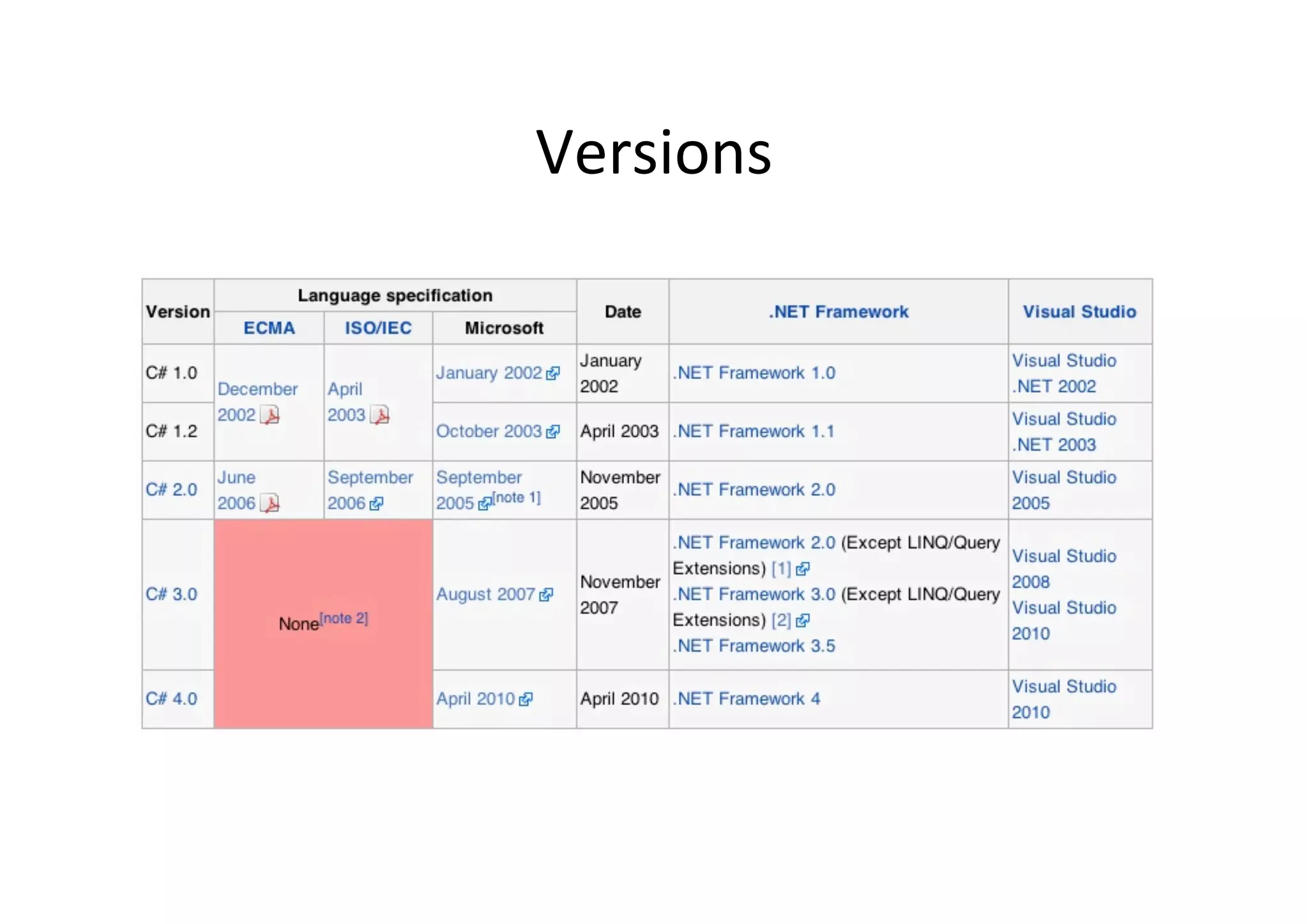
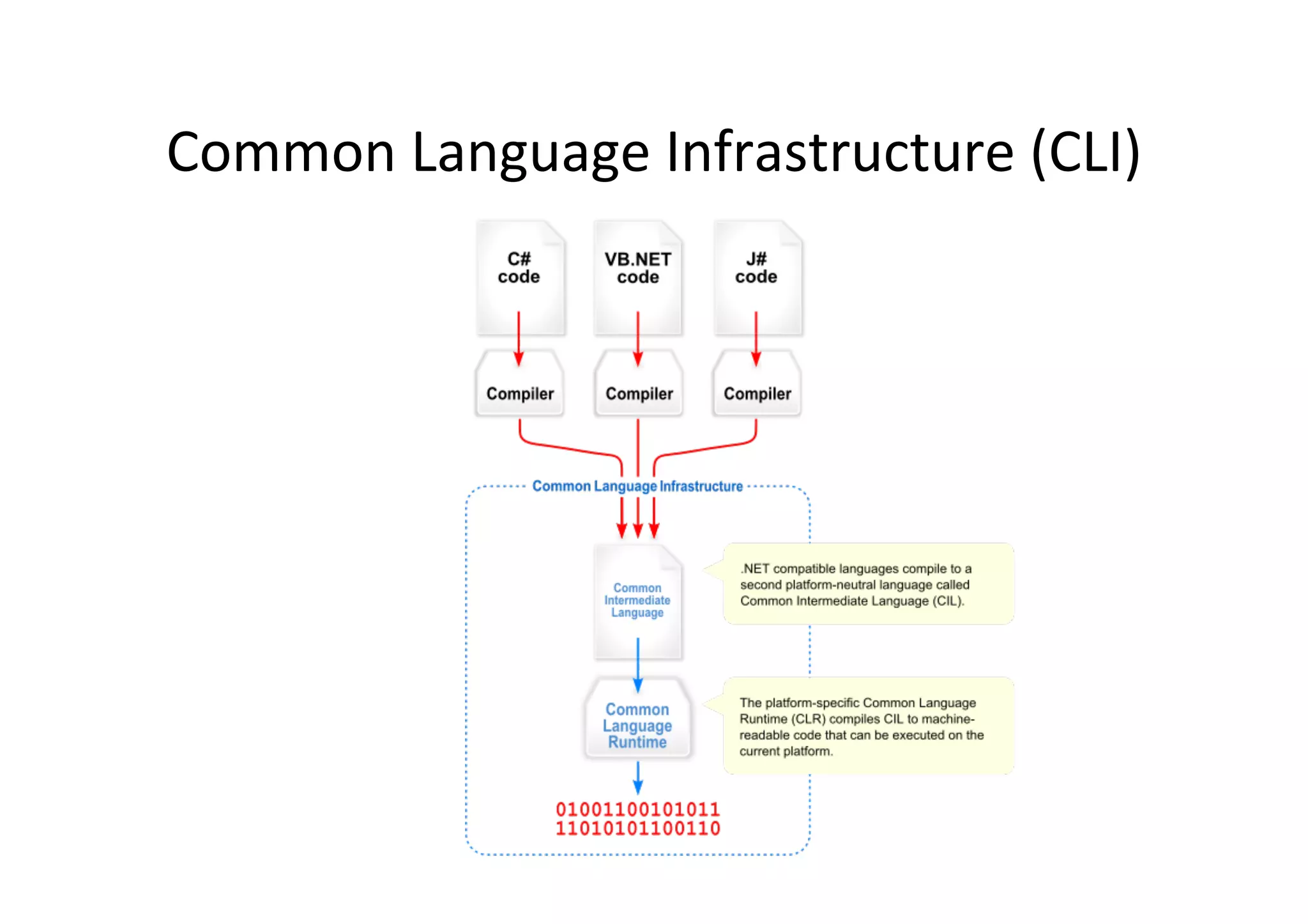
The document provides an overview of C# for Java developers. It discusses that C# is an Ecma and ISO standard developed by Microsoft for use in .NET and Windows Phone 7. It also covers the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) which includes the Common Type System (CTS), Common Language Specification (CLS), Virtual Execution System (VES), and Common Intermediate Language (CIL). The document then compares C# to Java in areas like memory handling, keywords, object-oriented concepts, and more.









![Main
using System;
class A {
public static void Main(String[] args){
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-17-2048.jpg)



![Inheritance
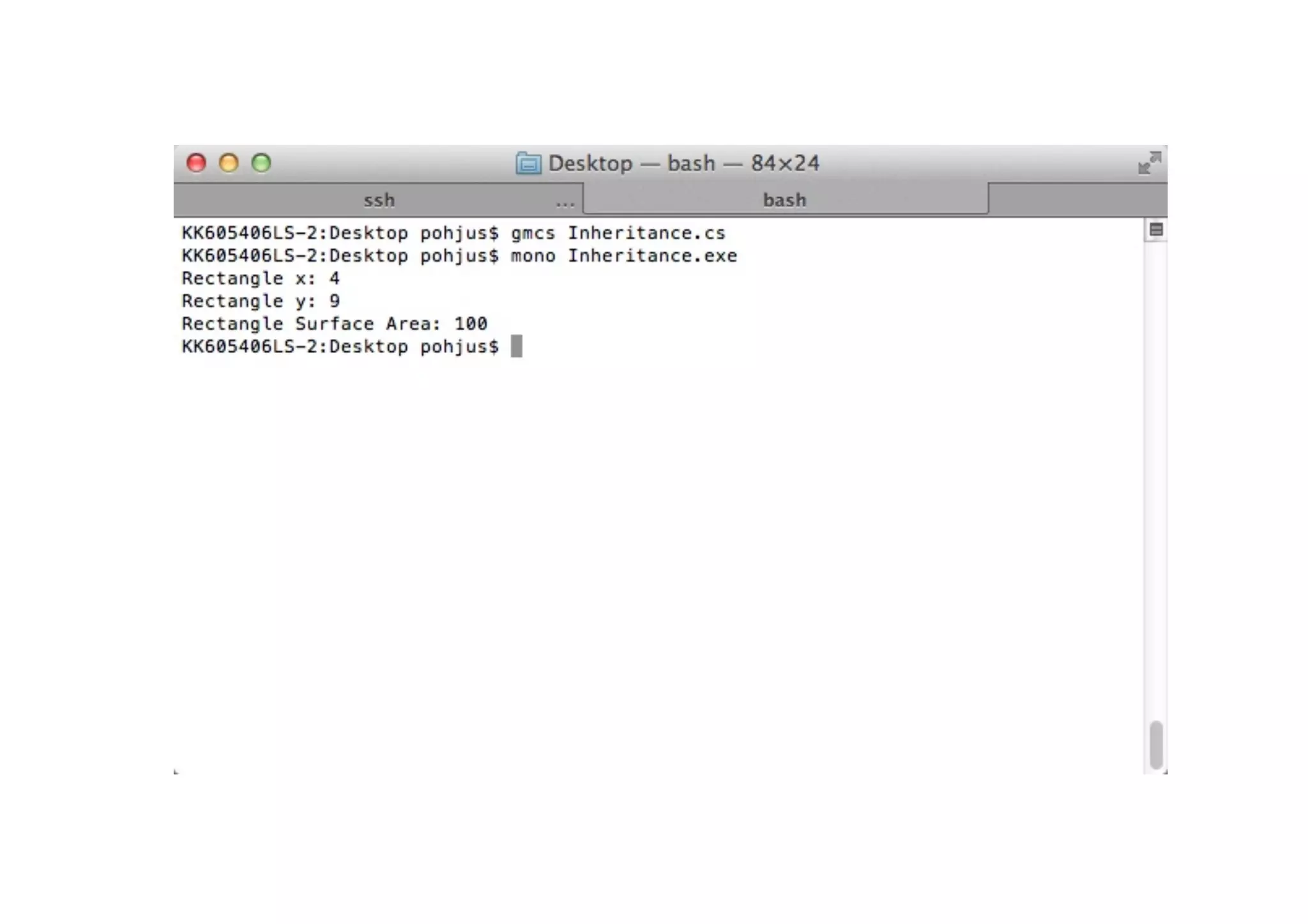
public class Rectangle : Figure, IMove {
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height) : base(x,y) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public void MoveTo(int x, int y) {
SetX( GetX() + x );
SetY( GetY() + y );
}
public override double CalculateSurfaceArea() {
return width * height;
}
public static void Main(String [] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(4, 5, 10, 10);
Console.Write( "Rectangle x: " );
Console.Write( r.GetX() );
r.MoveTo(5, 0);
Console.Write( "nRectangle y: " );
Console.Write( r.GetX() );
Console.Write( "nRectangle Surface Area: " );
Console.Write( r.CalculateSurfaceArea() );
Console.Write( "n" );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-21-2048.jpg)
![Run
Time
Type
IdenRficaRon
public static void Main(String [] args) {
Object rectangleObject = new Rectangle(4, 5, 10, 10);
// Type cast from Object to Rectangle
Rectangle temp1 = rectangleObject as Rectangle;
// Check if cast was successfull
if(temp1 != null) {
Console.Write("Success: Object was casted to Rectangle!");
temp1.SetX(0);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-23-2048.jpg)
![ProperRes
public class Rectangle : Figure, IMove {
private int height;
private int width;
public int Width {
get {
return width;
}
set {
if(value > 0) {
width = value;
} else {
Console.WriteLine("Value was not set.");
}
}
}
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height) : base(x,y) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
…
public static void Main(String [] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(5,5,10,10);
r.Width = 10;
Console.Write(r.Width);
// Value was not set
r.Width = -5;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-24-2048.jpg)
![Alias
using Terminal = System.Console;
class Test {
public static void Main(string[] args){
Terminal.WriteLine("Please don’t use this");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-25-2048.jpg)
![Namespaces
using System;
namespace fi.tamk.tiko.ohjelmistotuotanto {
public class Test {
public static void method() {
Console.Write("ohjelmistotuotanton");
}
}
}
namespace fi.tamk.tiko.pelituotanto {
public class Test {
public static void method() {
Console.Write("pelituotanton");
}
}
}
class App {
public static void Main(String [] args) {
fi.tamk.tiko.ohjelmistotuotanto.Test.method();
fi.tamk.tiko.pelituotanto.Test.method();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-26-2048.jpg)

![Variable
Length
Parameters
and
foreach
using System;
public class Params {
public static void Method(params int[] array) {
foreach(int num in array) {
Console.Write(num);
Console.Write("n");
}
}
public static void Main(String [] args) {
Method(1,2,3,4,5);
Method(1,2);
int [] myArray = {1,2,3,4};
Method(myArray);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-28-2048.jpg)
![OperaRon
Overloading
using System;
public class MyNumber {
private int value;
public MyNumber(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public static MyNumber operator+(MyNumber number1, MyNumber number2) {
int sum = number1.value + number2.value;
MyNumber temp = new MyNumber(sum);
return temp;
}
public static void Main(String [] args) {
MyNumber number1 = new MyNumber(5);
MyNumber number2 = new MyNumber(5);
MyNumber sum = number1 + number2;
Console.Write(sum.value);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-for-java-developers-111212062137-phpapp02/75/C-for-Java-Developers-29-2048.jpg)