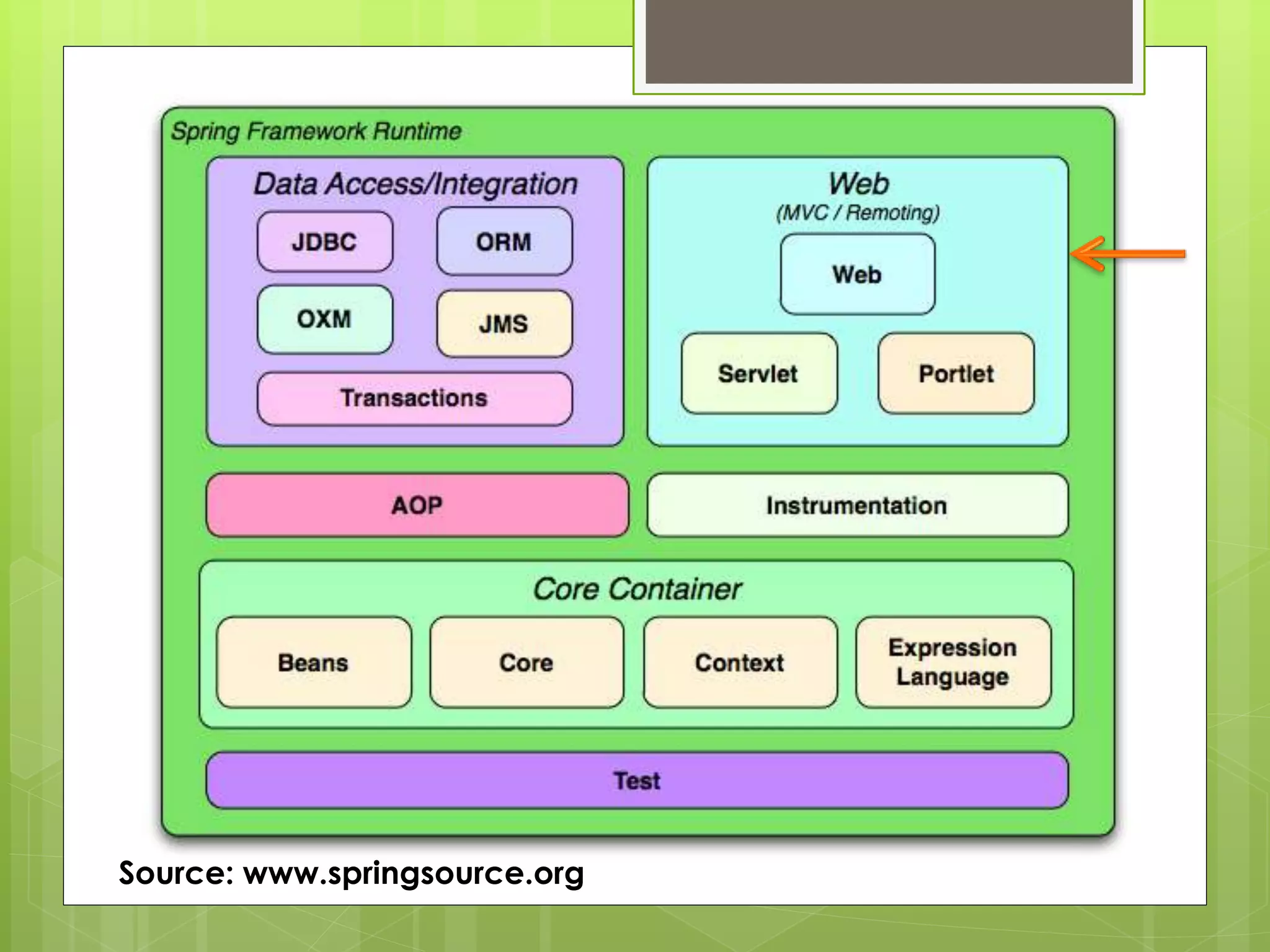
The document provides an overview of the Spring Web MVC framework, highlighting its features, workflow, and essential components such as DispatcherServlet, Controller, HandlerMapping, ModelAndView, and ViewResolver. It explains the framework's flexibility, separation of roles, support for REST-based URLs, and various annotations for simplifying configuration. Additionally, it includes demonstrations on external configuration, form submission, session storage, and AJAX integration within Spring MVC applications.

















![World without Rules
Return Type?
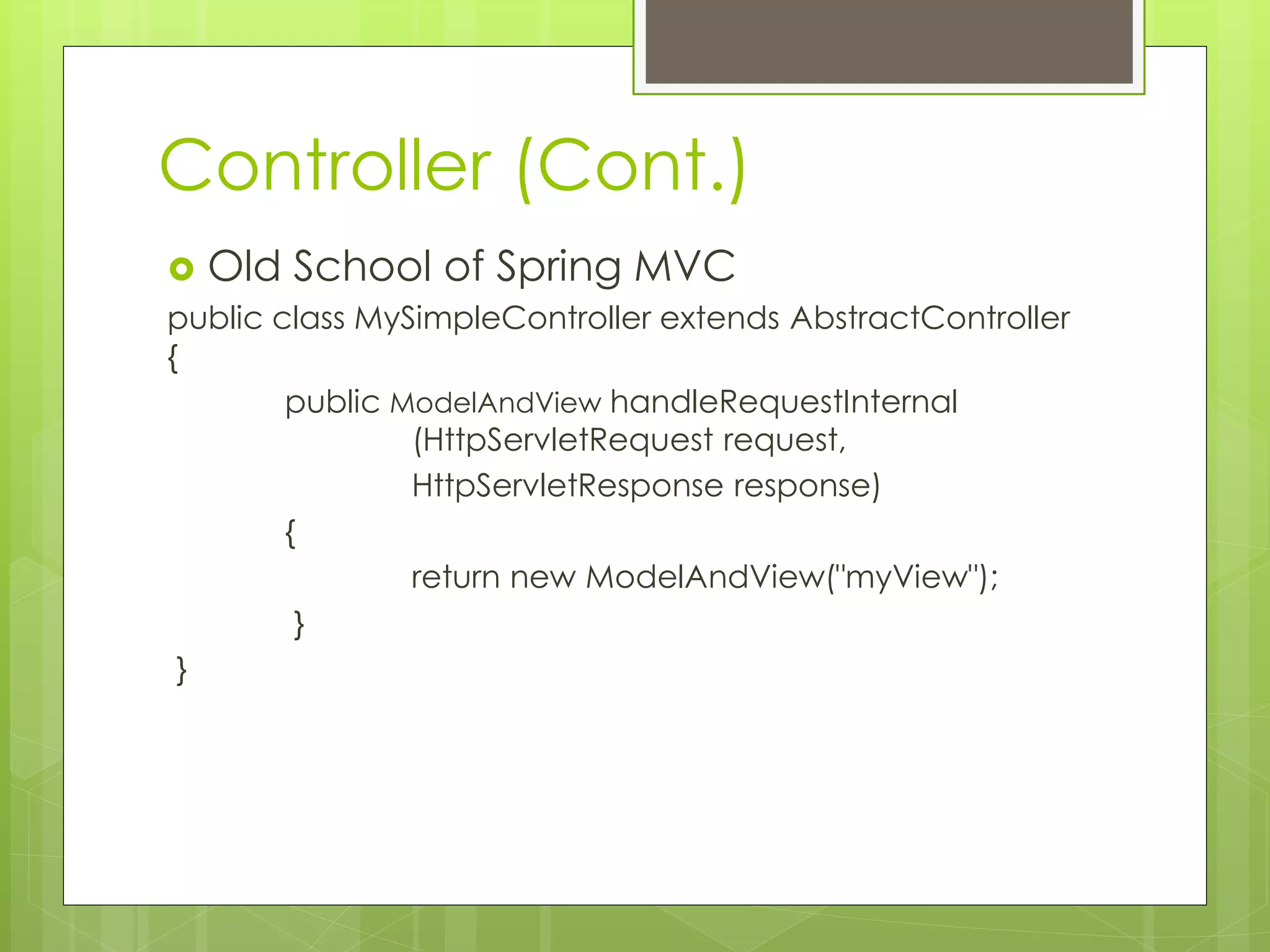
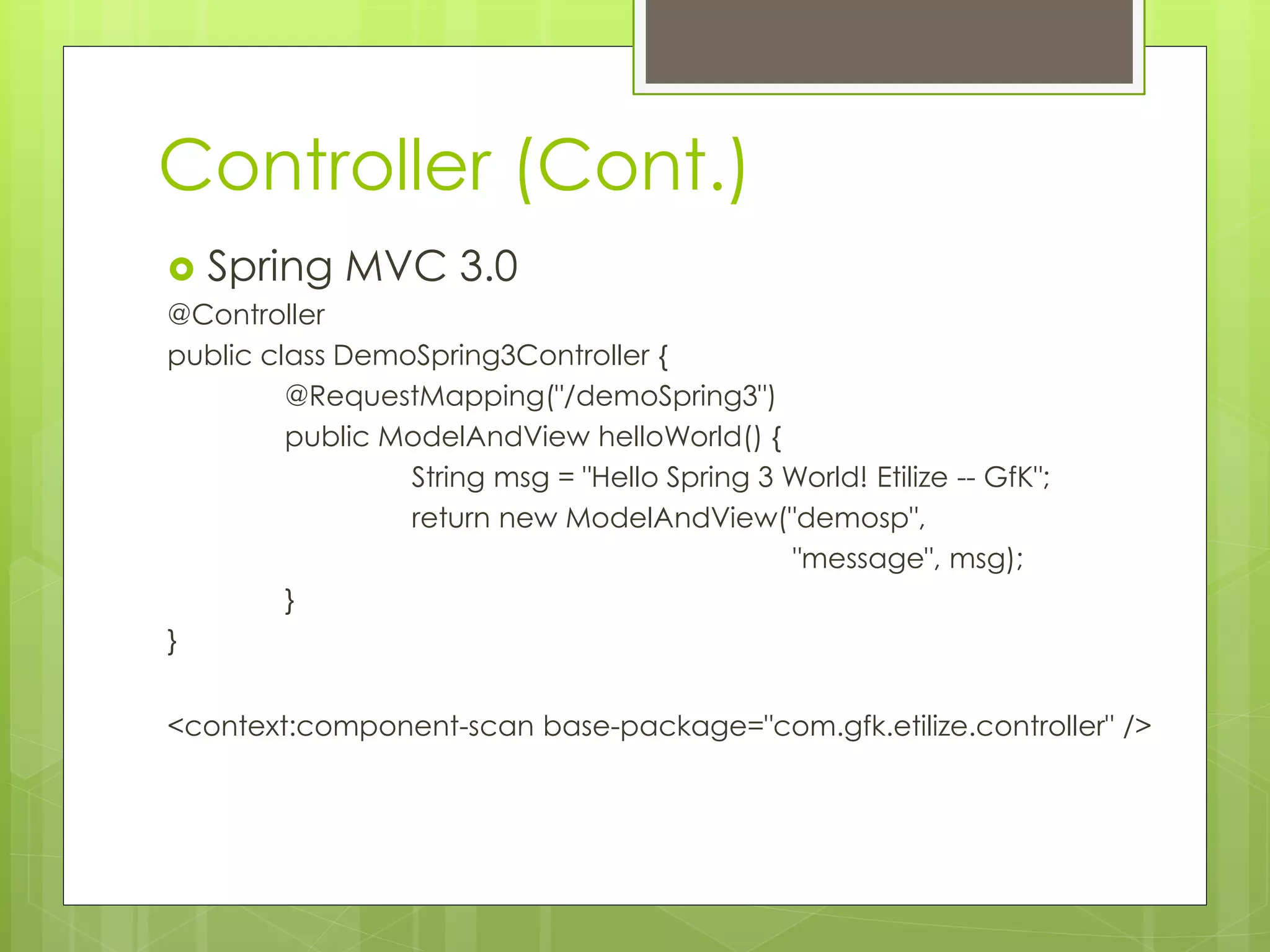
Return Type Can be:
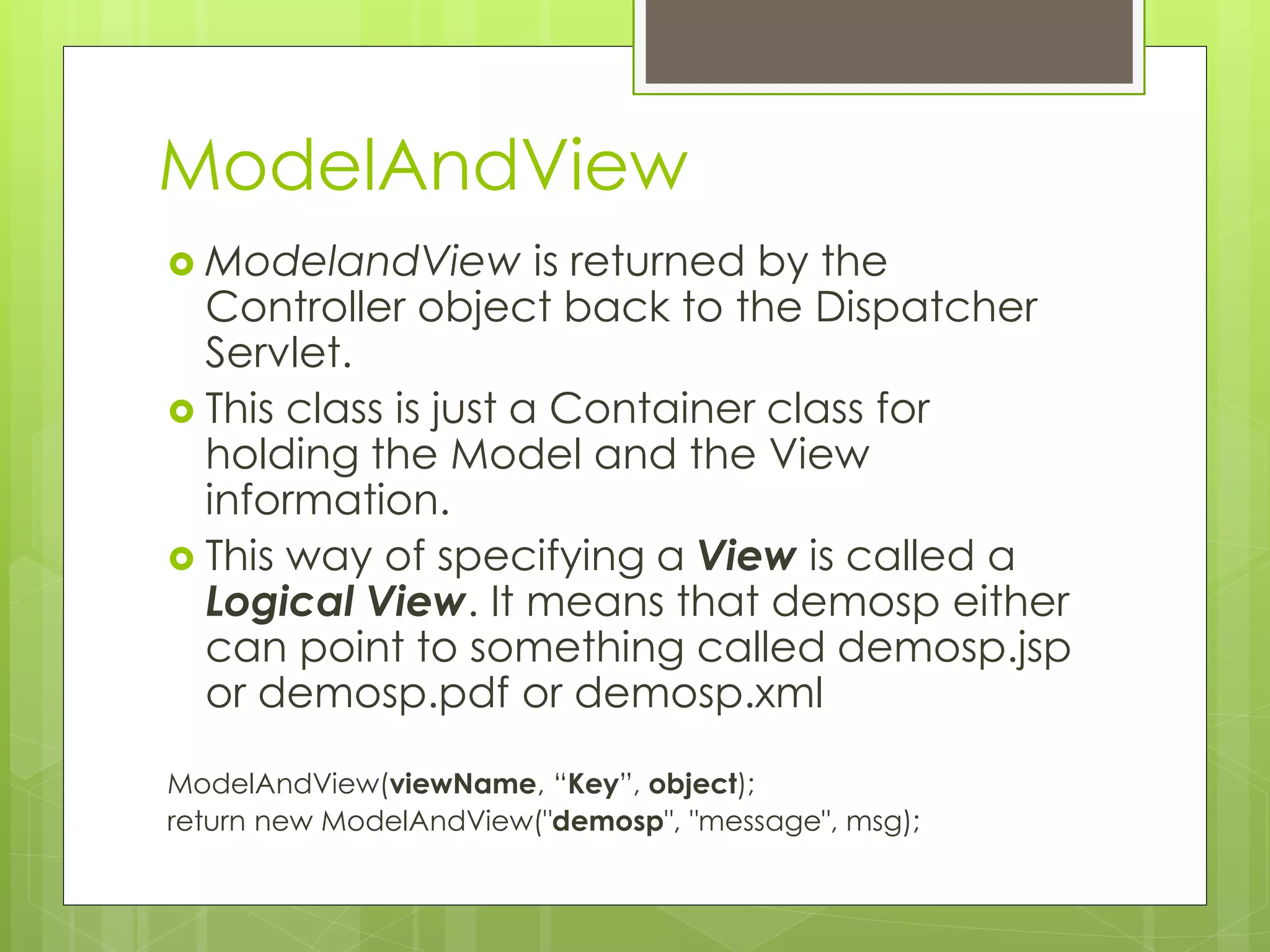
ModelAndViewObject
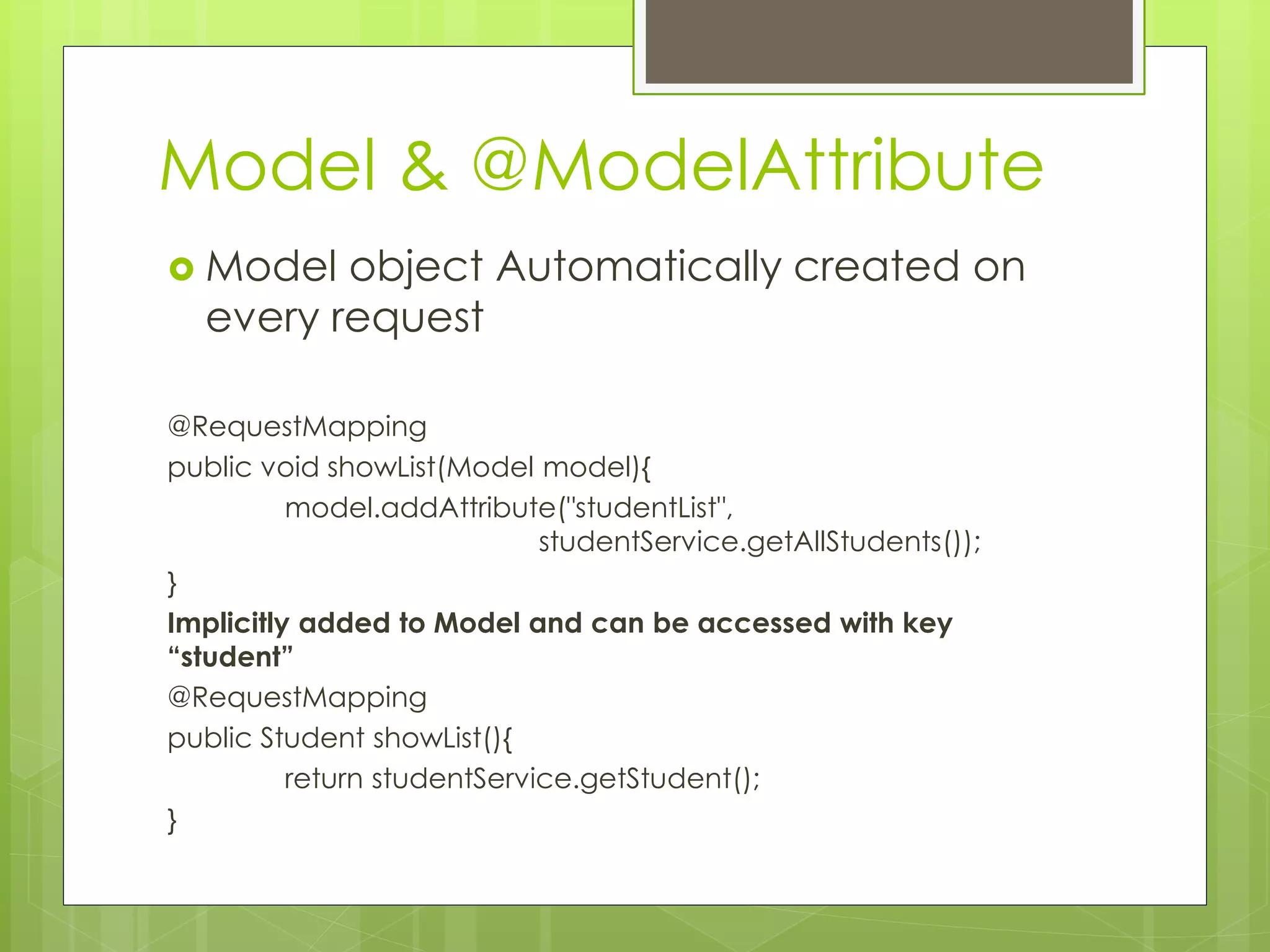
Model
Map
View
String
Void
Any Custom or built-in datatype
e.g. Student, Student[],ArrayList etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springwebmvc-111226164628-phpapp02/75/Spring-Web-MVC-32-2048.jpg)