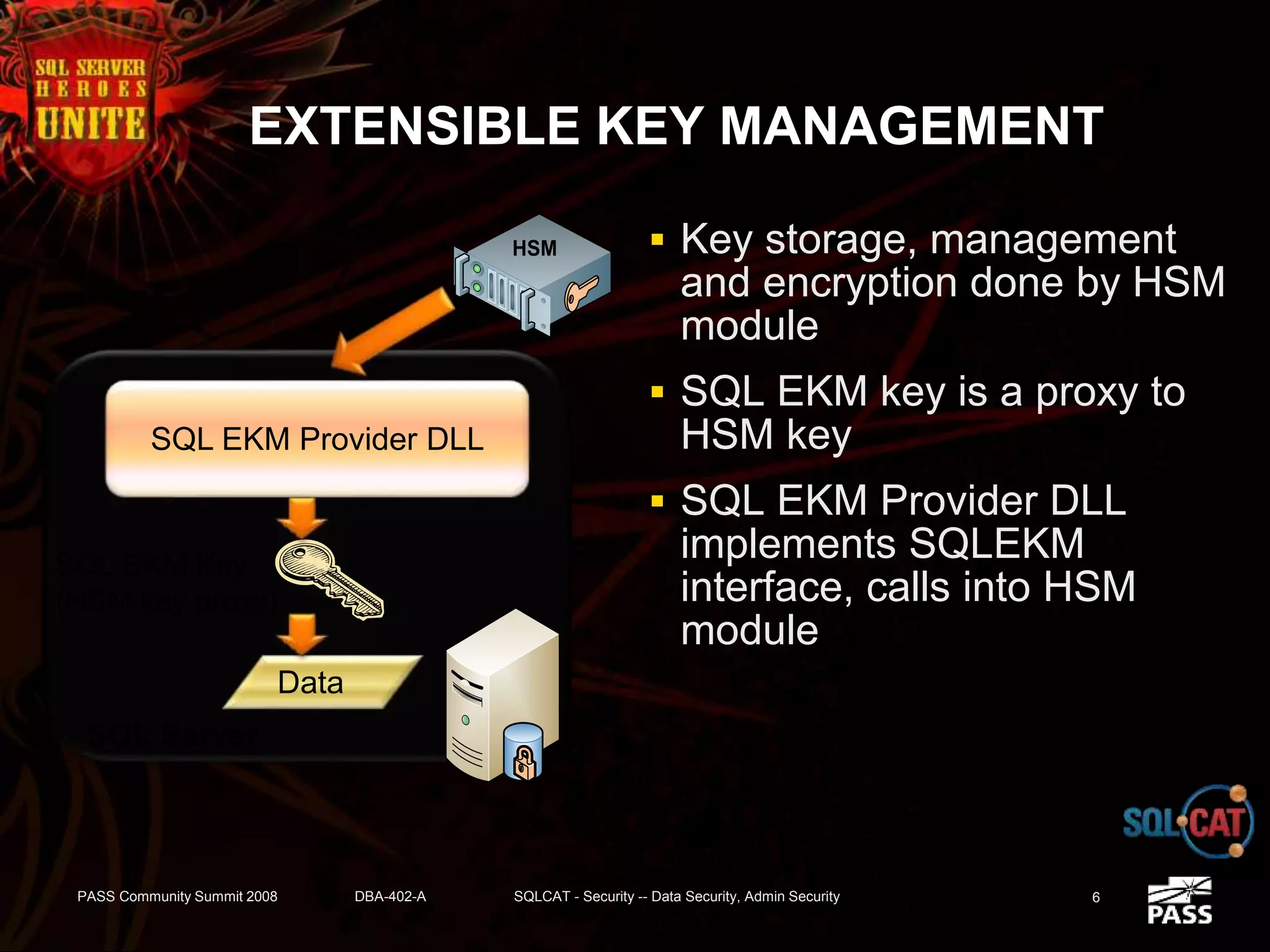
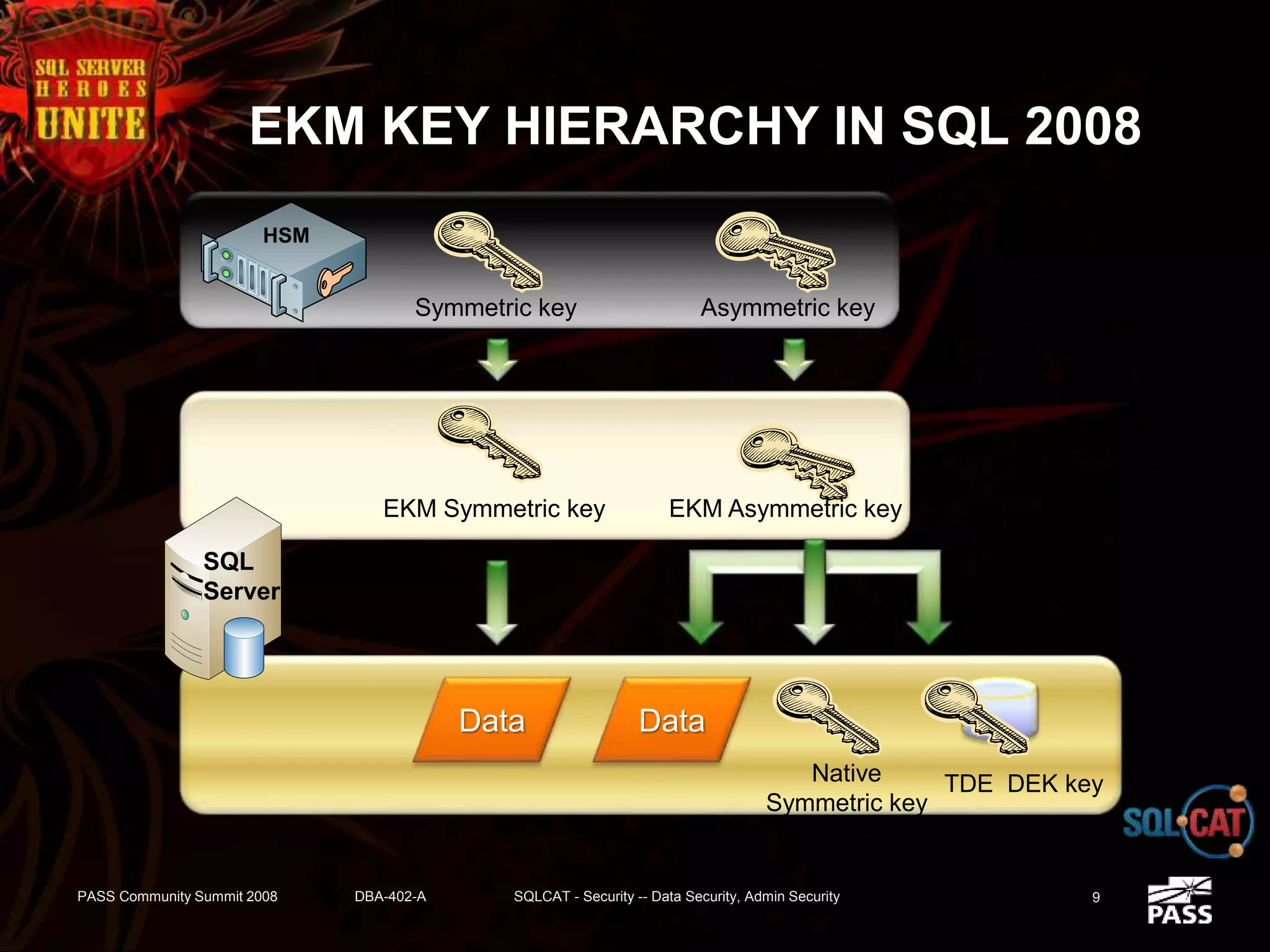
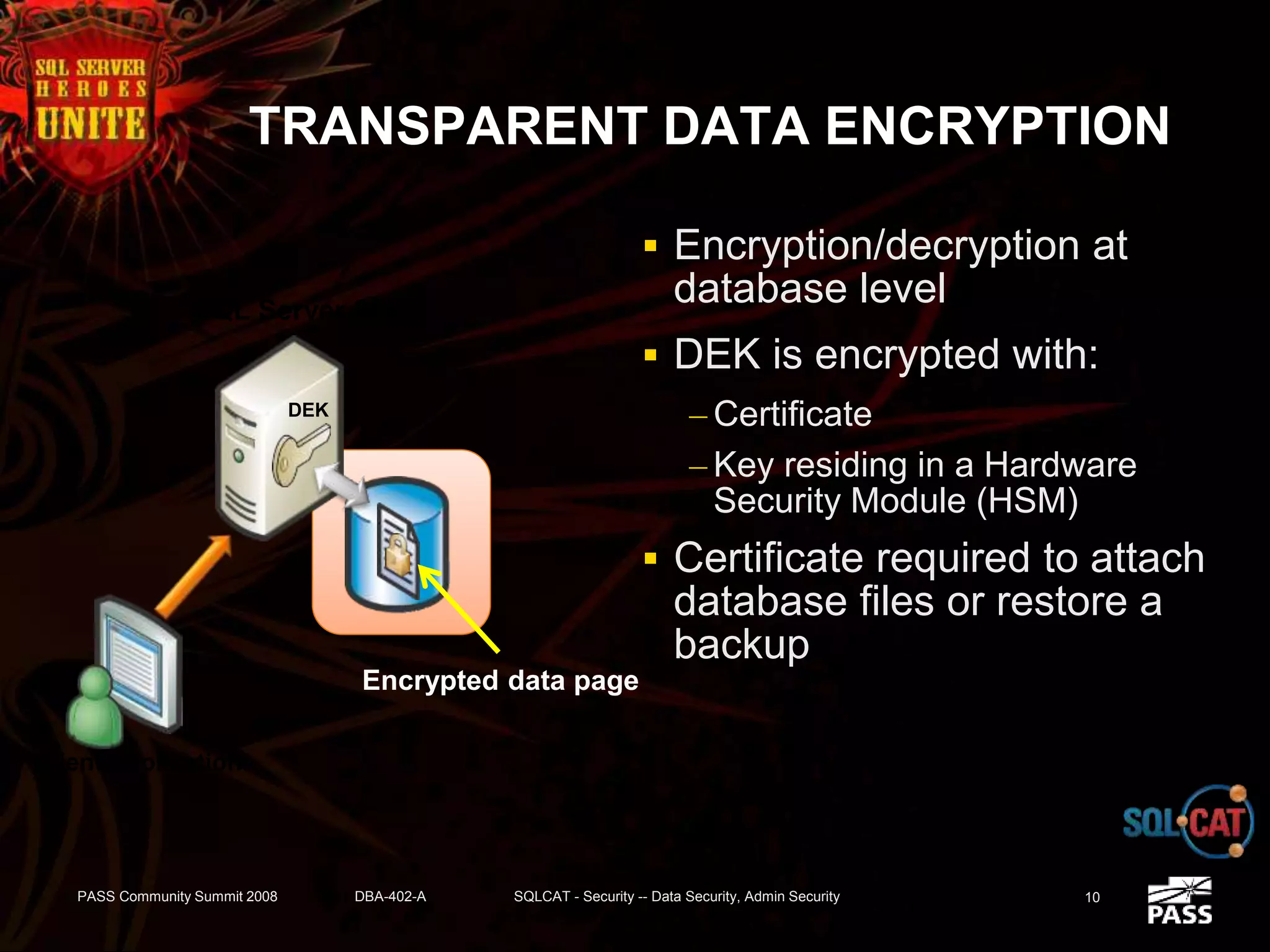
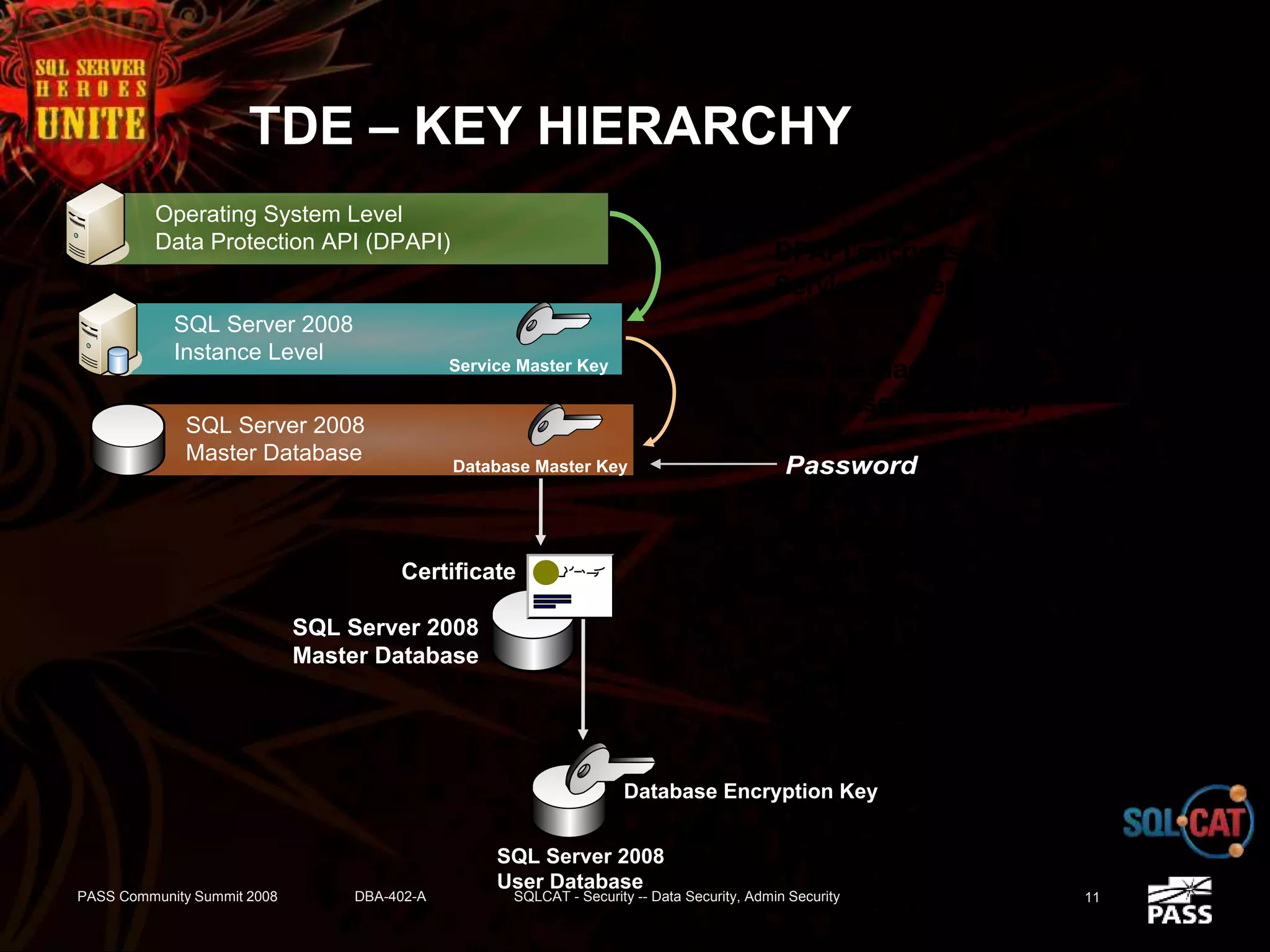
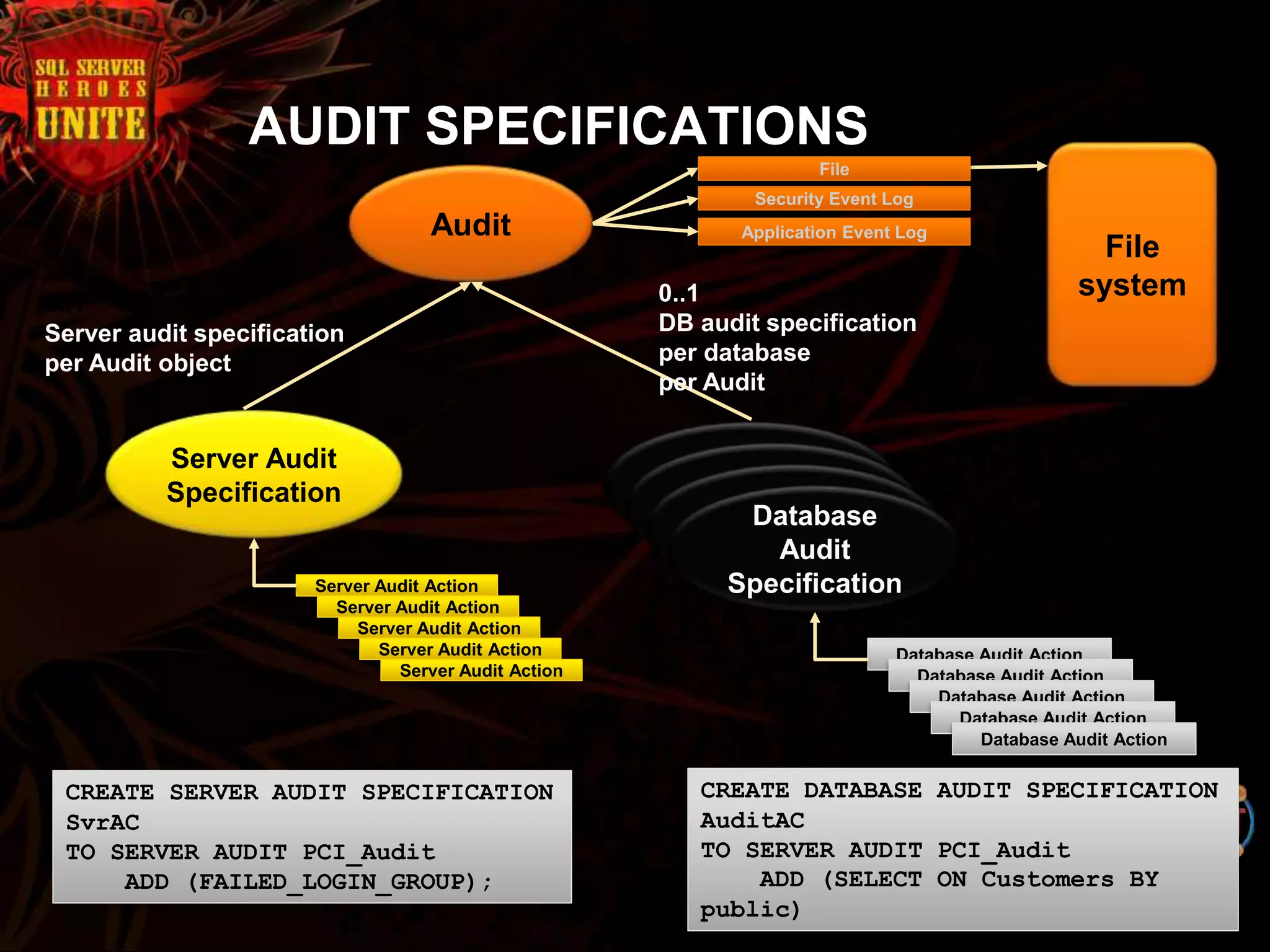
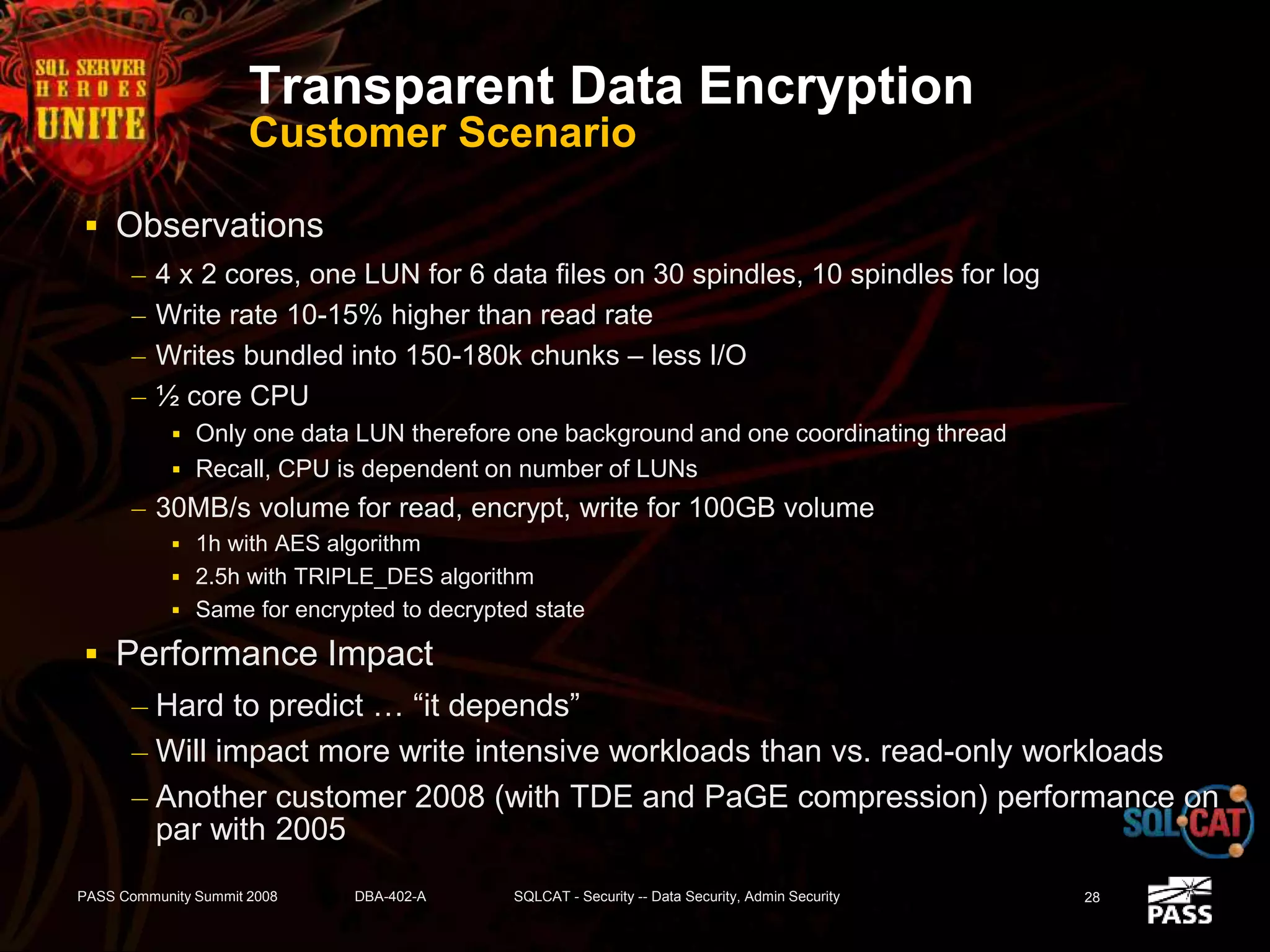
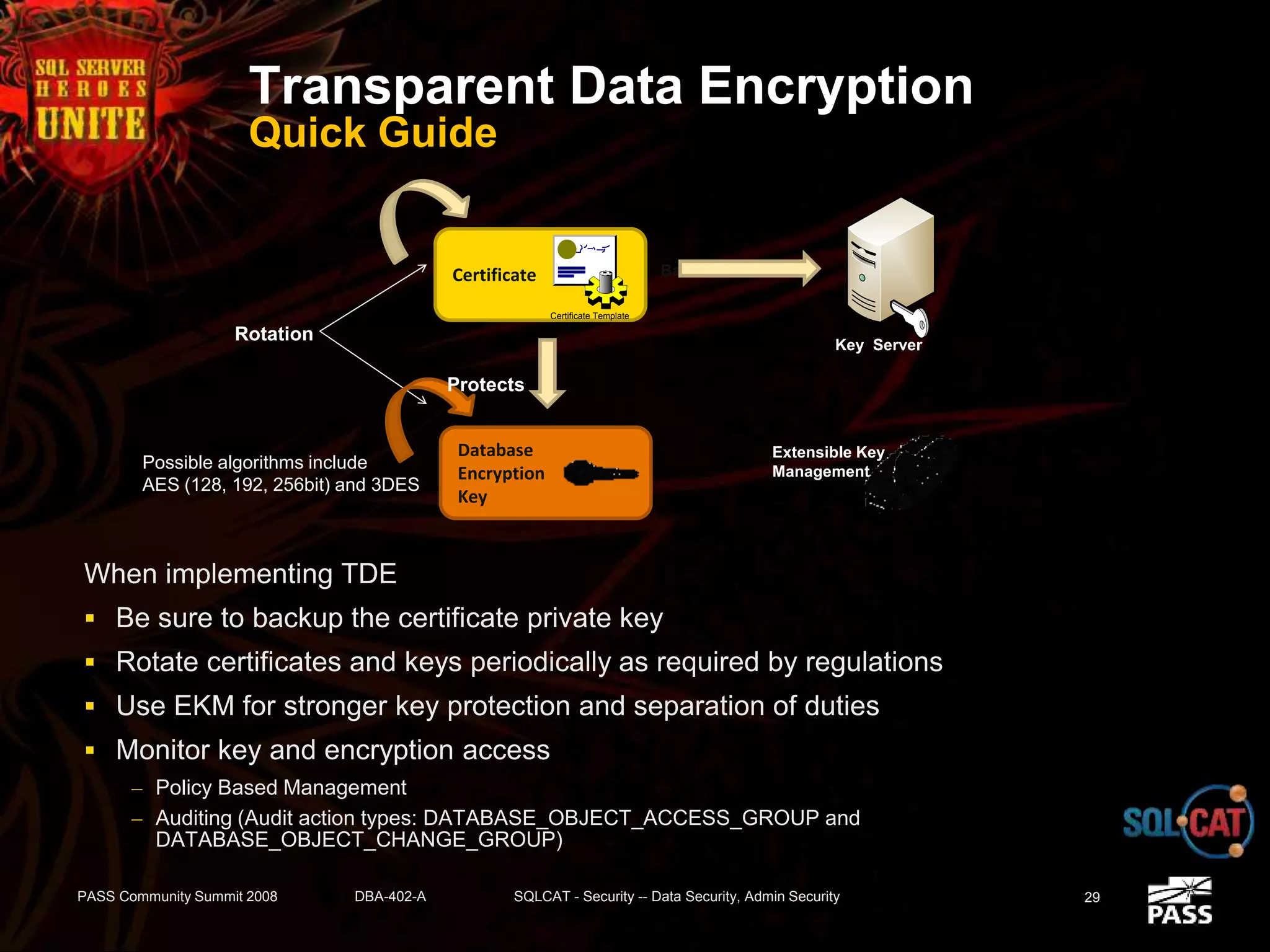
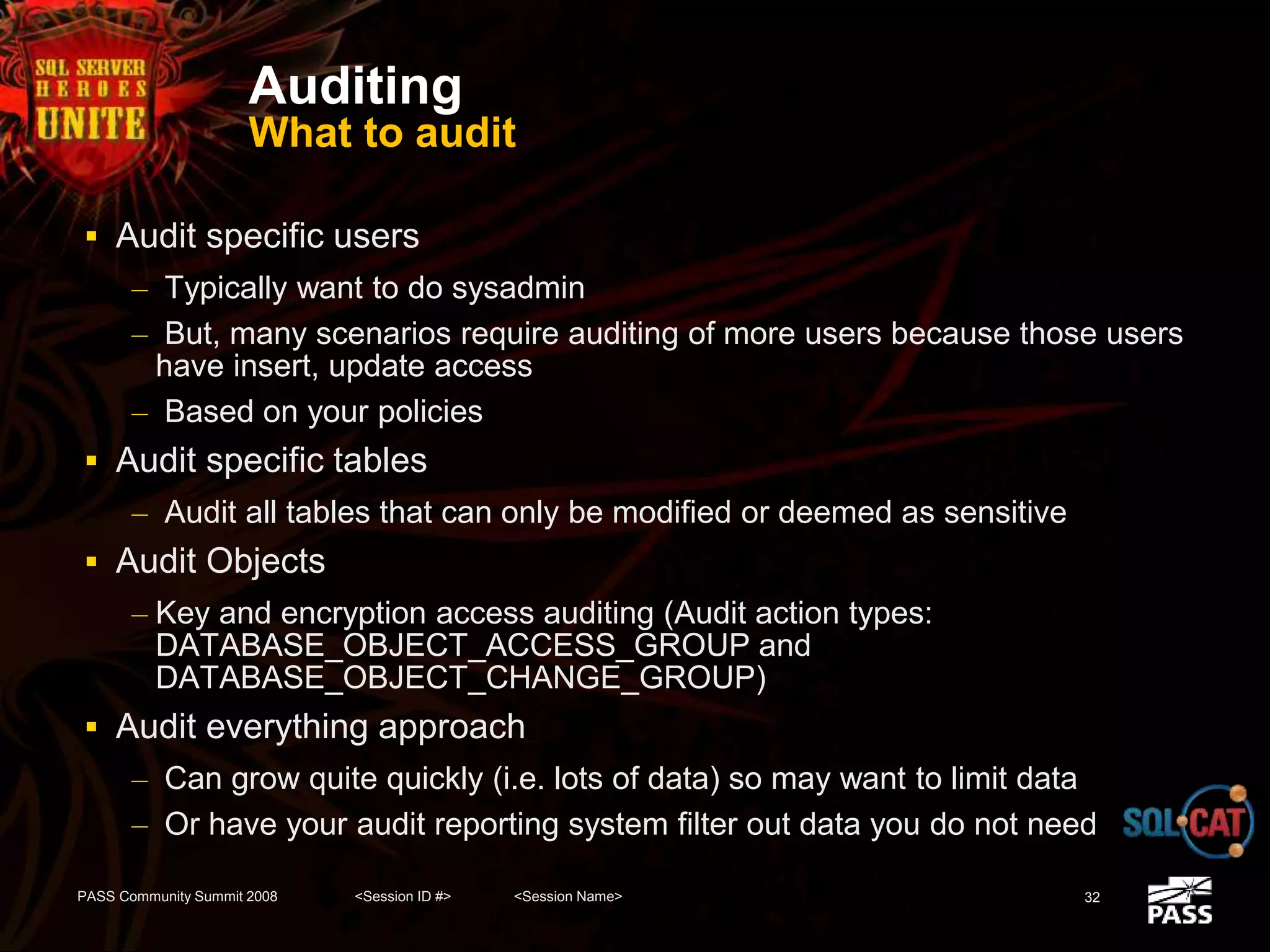
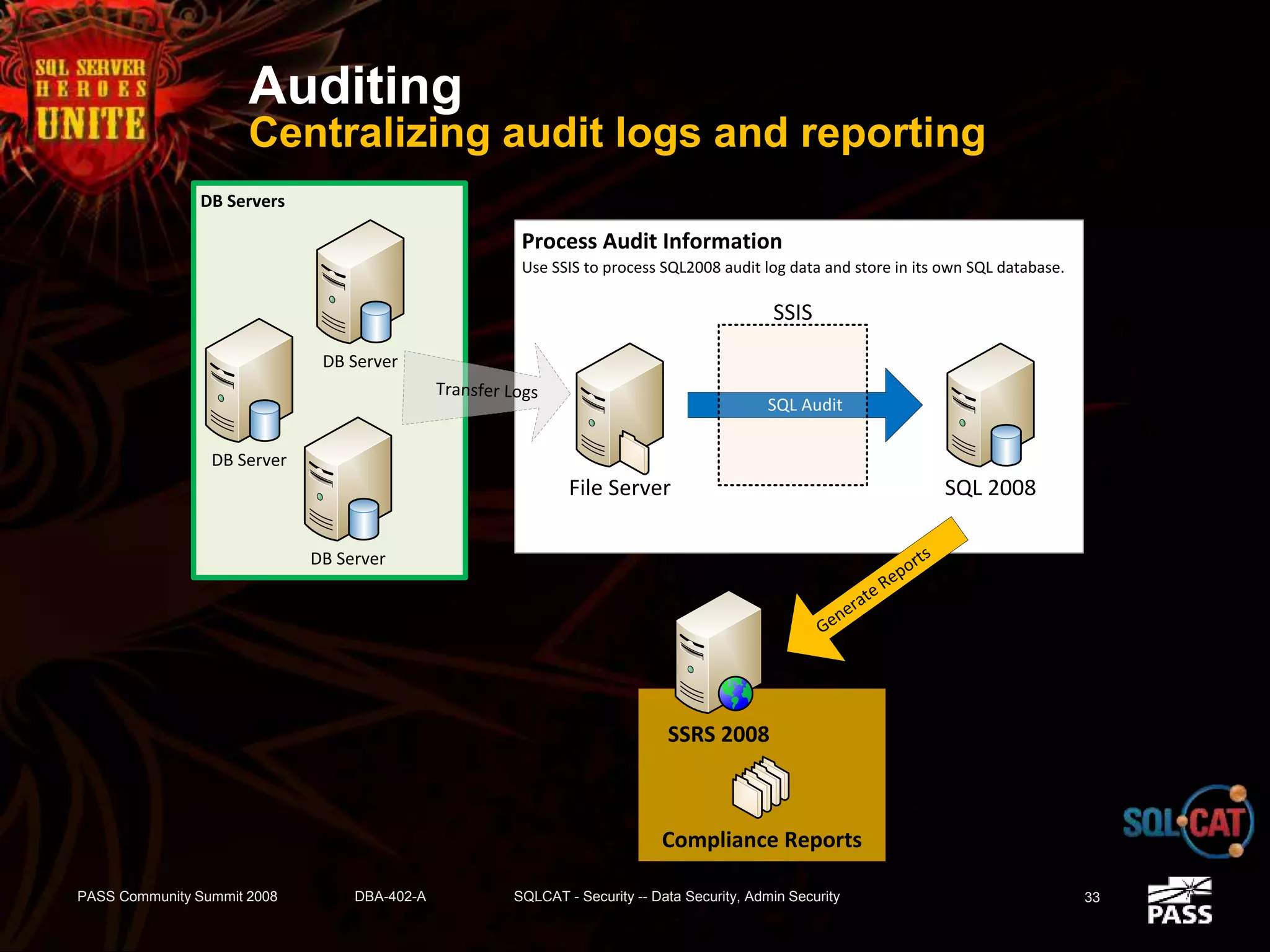
The document discusses SQL Server's security features, particularly focusing on extensible key management, transparent data encryption, and auditing capabilities presented at the PASS Community Summit 2008. It outlines the benefits of these security features for handling sensitive data, improving compliance with regulations like HIPAA and PCI, and optimizing key management processes. Moreover, the document highlights real-world applications and customer scenarios that illustrate the importance and practical uses of these security enhancements.