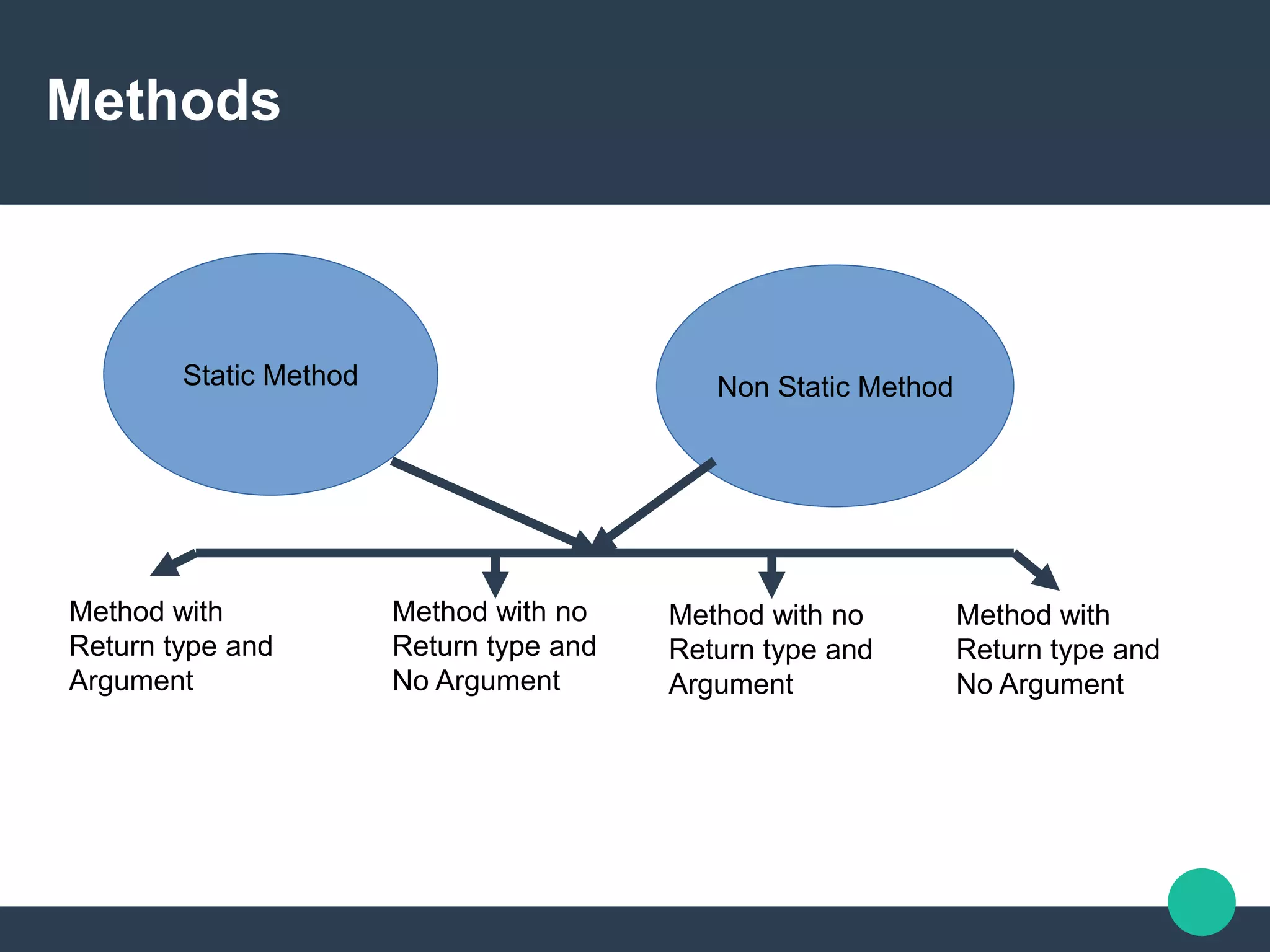
The document discusses tips and tricks for using variables and methods in Java. It defines different types of variables like class variables, static variables, and local variables based on their scope. It also categorizes methods as static or non-static and whether they have a return type and arguments. The document provides examples of declaring and using different variables and calling static and non-static methods correctly.




![Code Example
public class TestOne {
int n2 = 20; //class variable or instance variable
static int n3 = 30; //static variable
static char c1 ;
String str2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = 10; //local variable
System.out.println("the value of a is : "+n1);
//System.out.println(n2);cant be called here because non static field cant be called inside static method
System.out.println(n3);
showValue(); //since this is static method
TestOne tOne = new TestOne();
tOne.display();
c1 = 'J';
System.out.println(c1);
}
public static void showValue(){//static method with no return type and no argument
System.out.println(n3);
//System.out.println(n1);cant be called here because local variable at main method
}
public void display(){//non static method with no return type and no argument
System.out.println(n2);
System.out.println(n3);
String str1 = "hello world";
System.out.println(str1);
str2 = "Hello test";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/variablemethods-200507070147/75/Variable-and-Methods-in-Java-6-2048.jpg)
