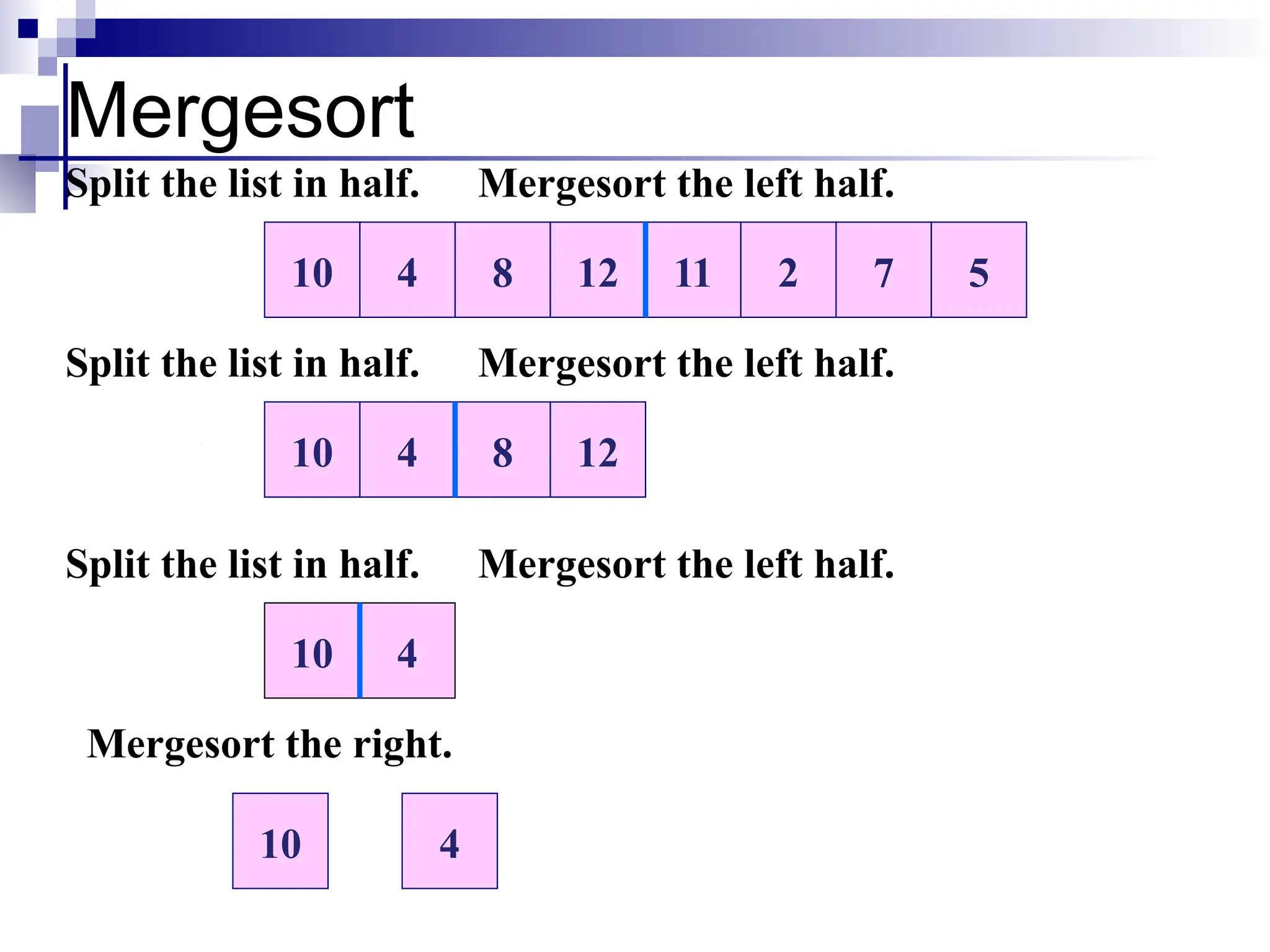
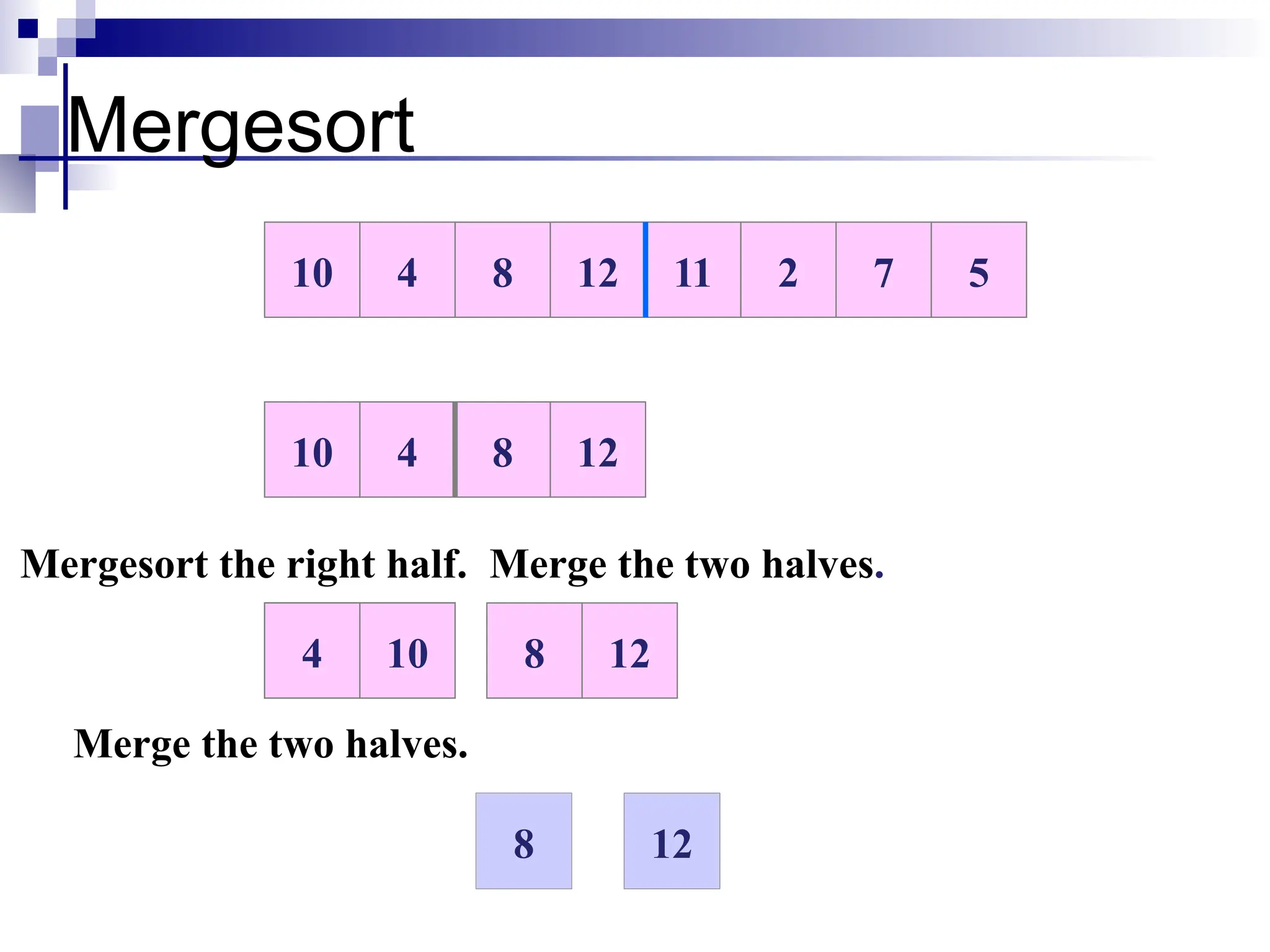
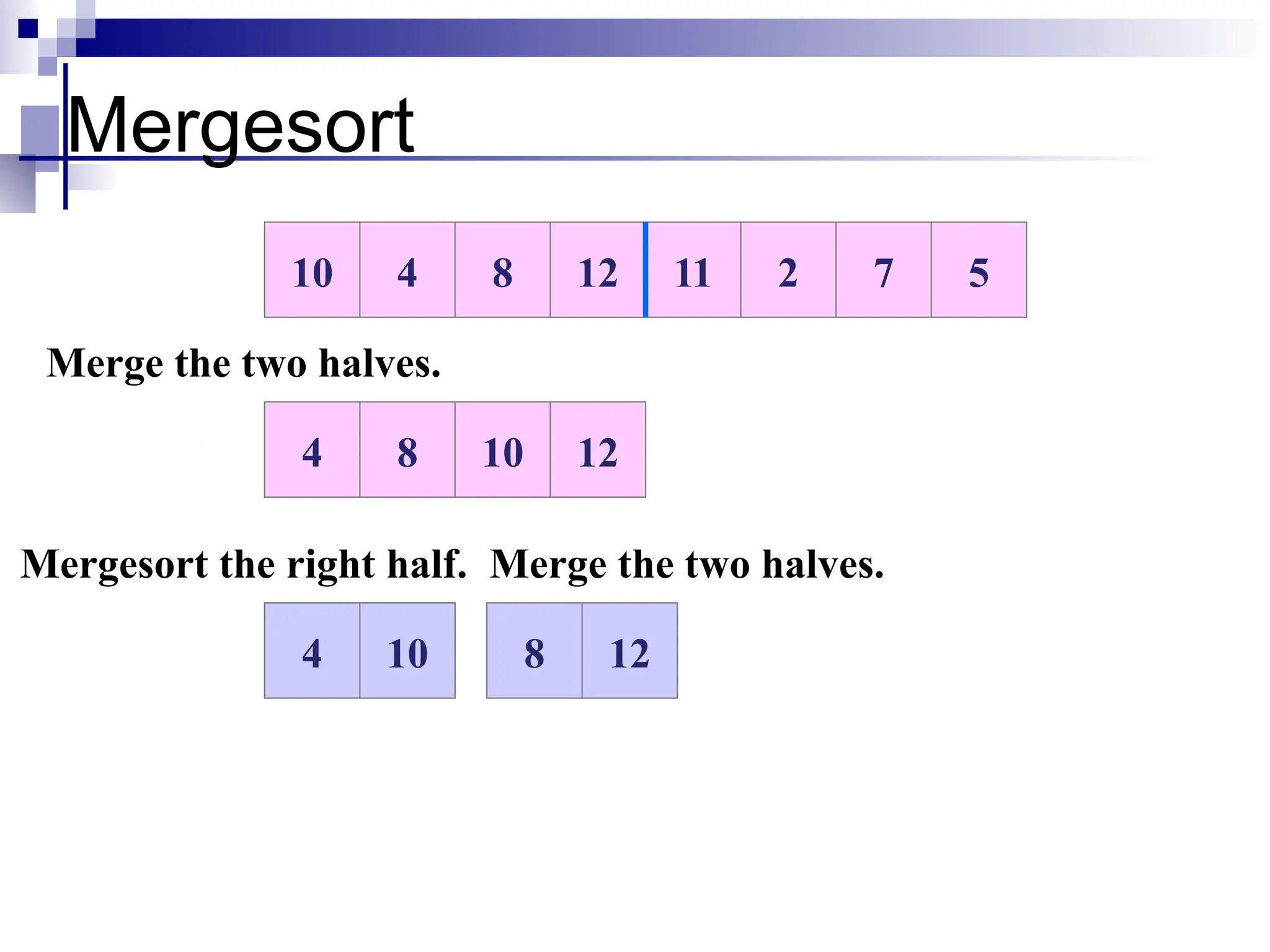
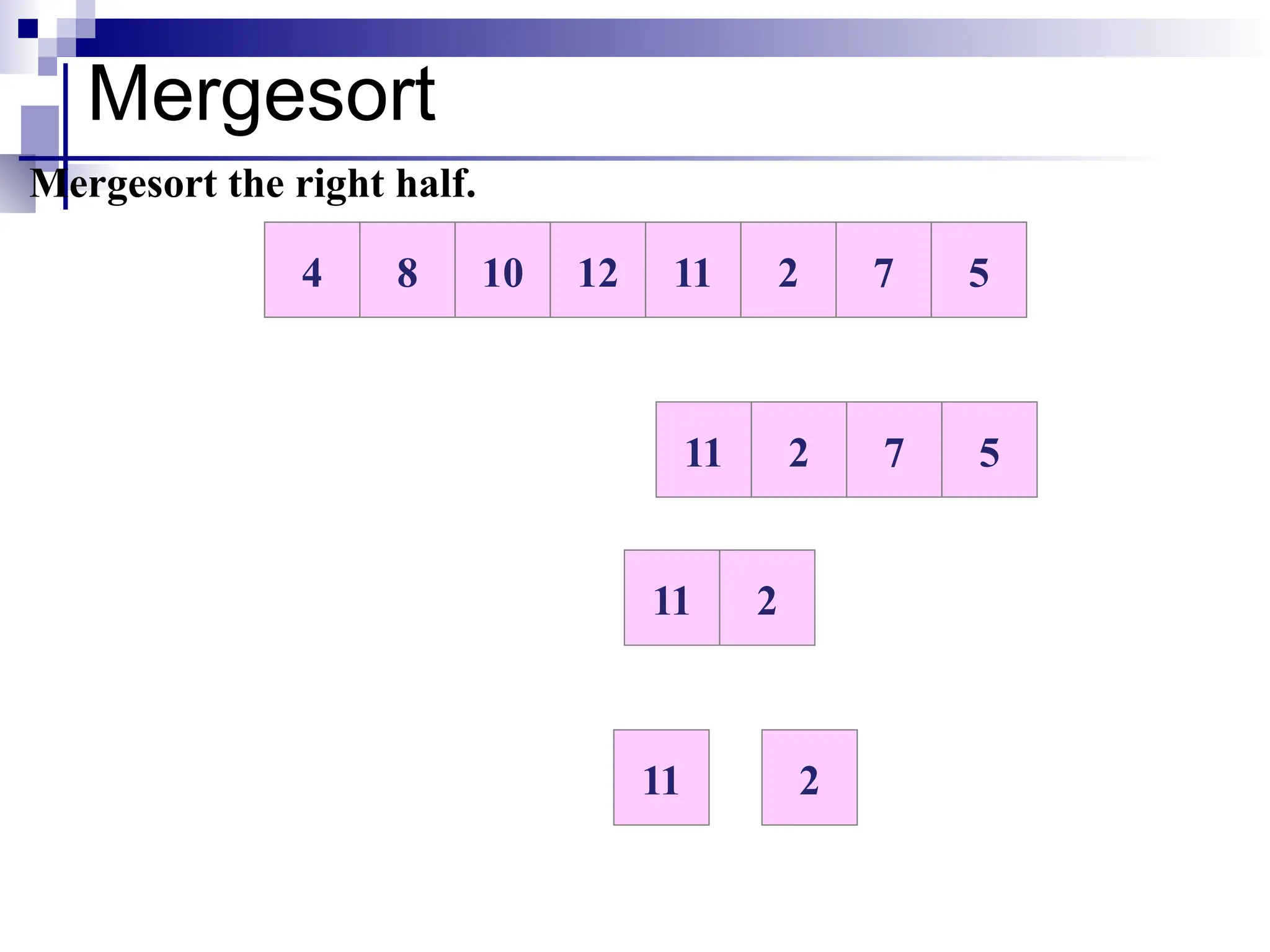
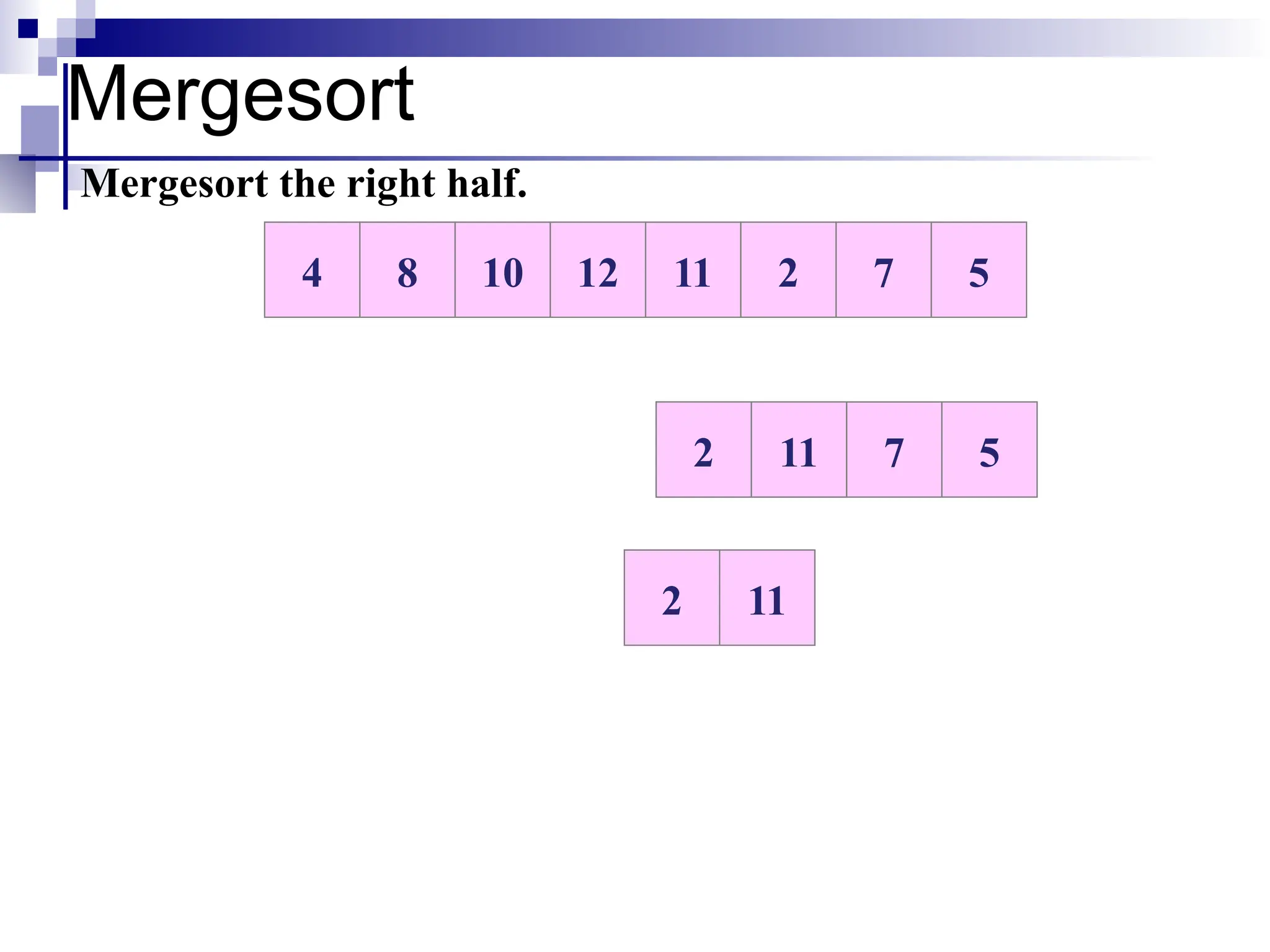
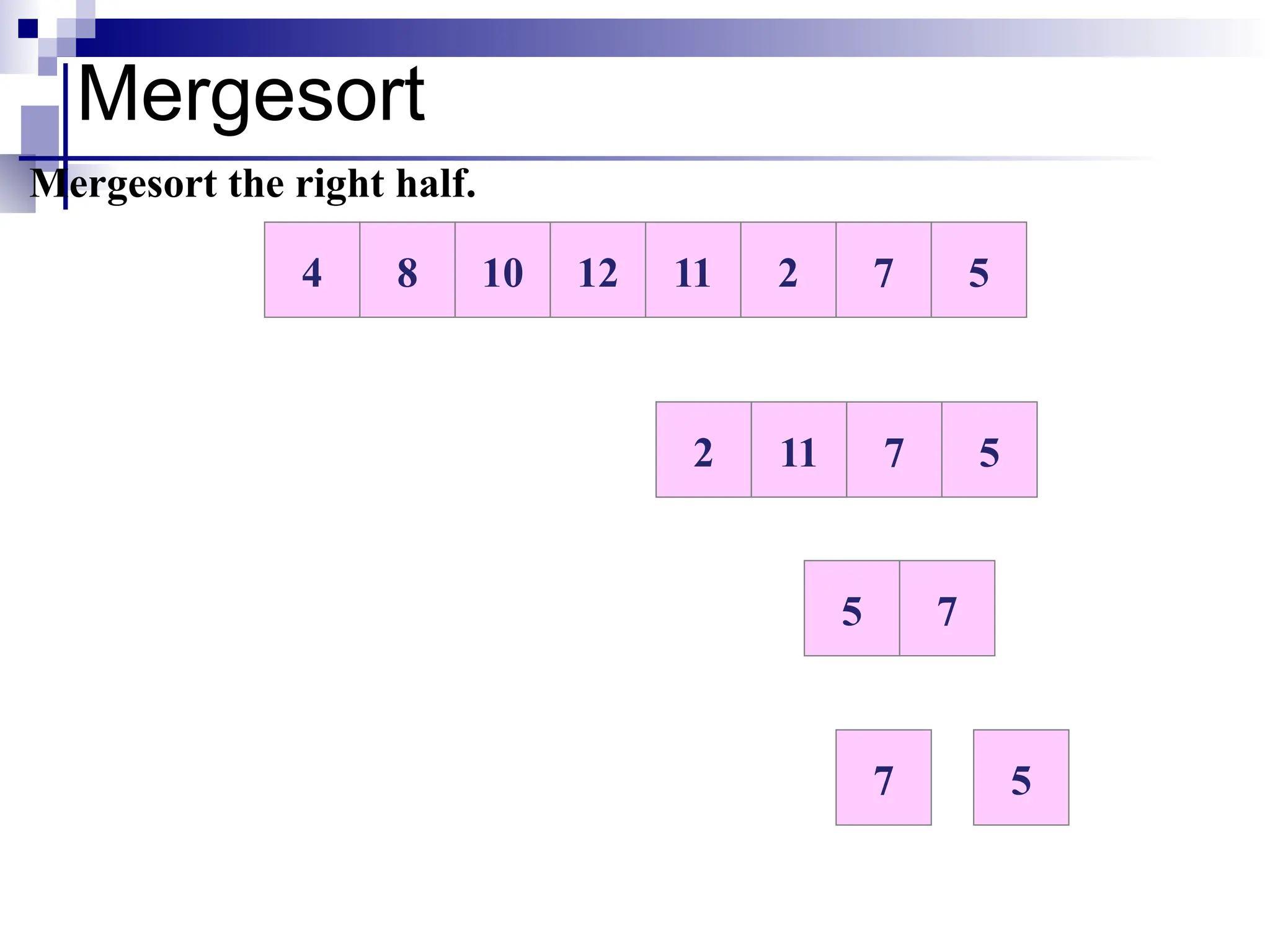
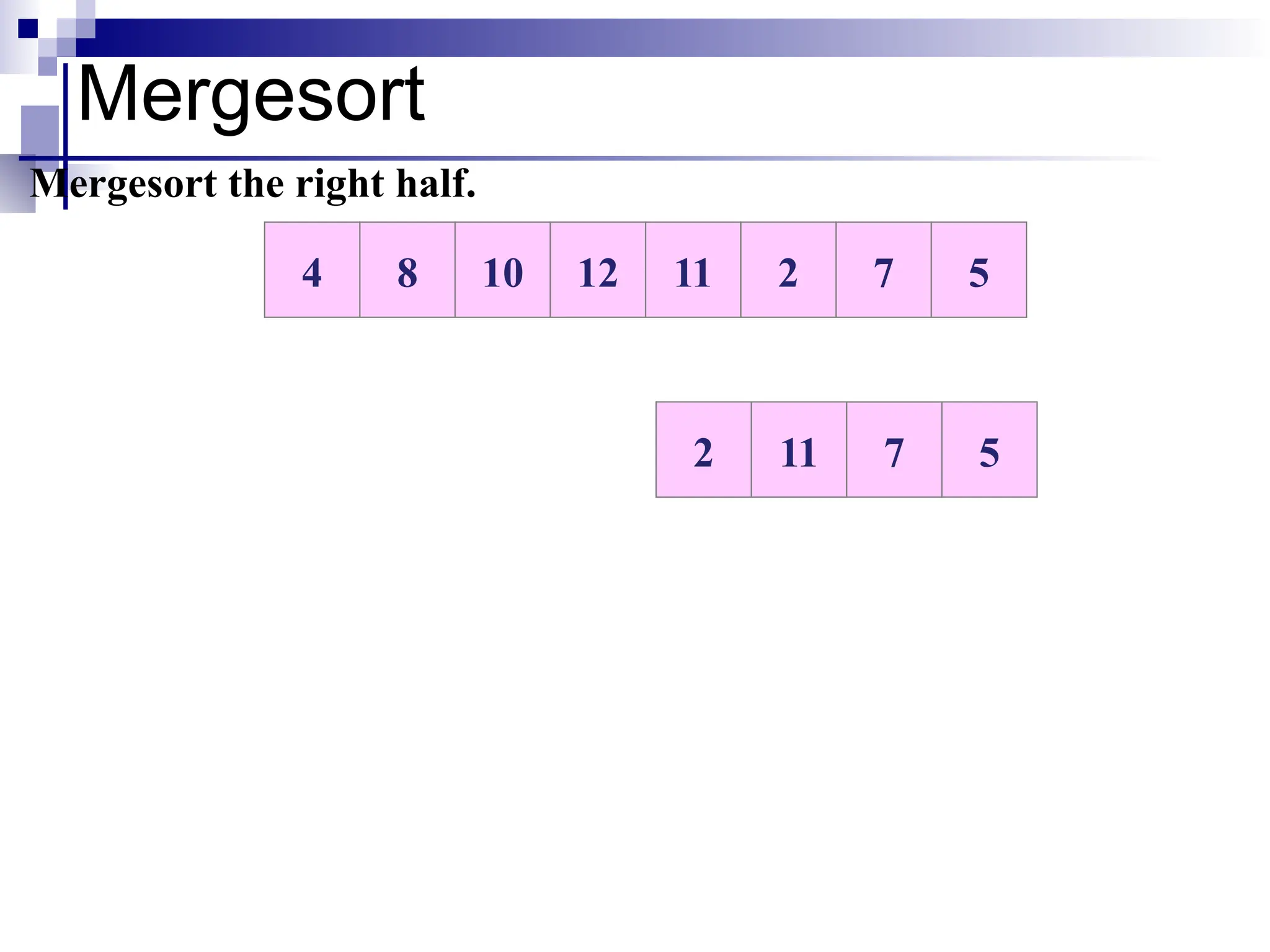
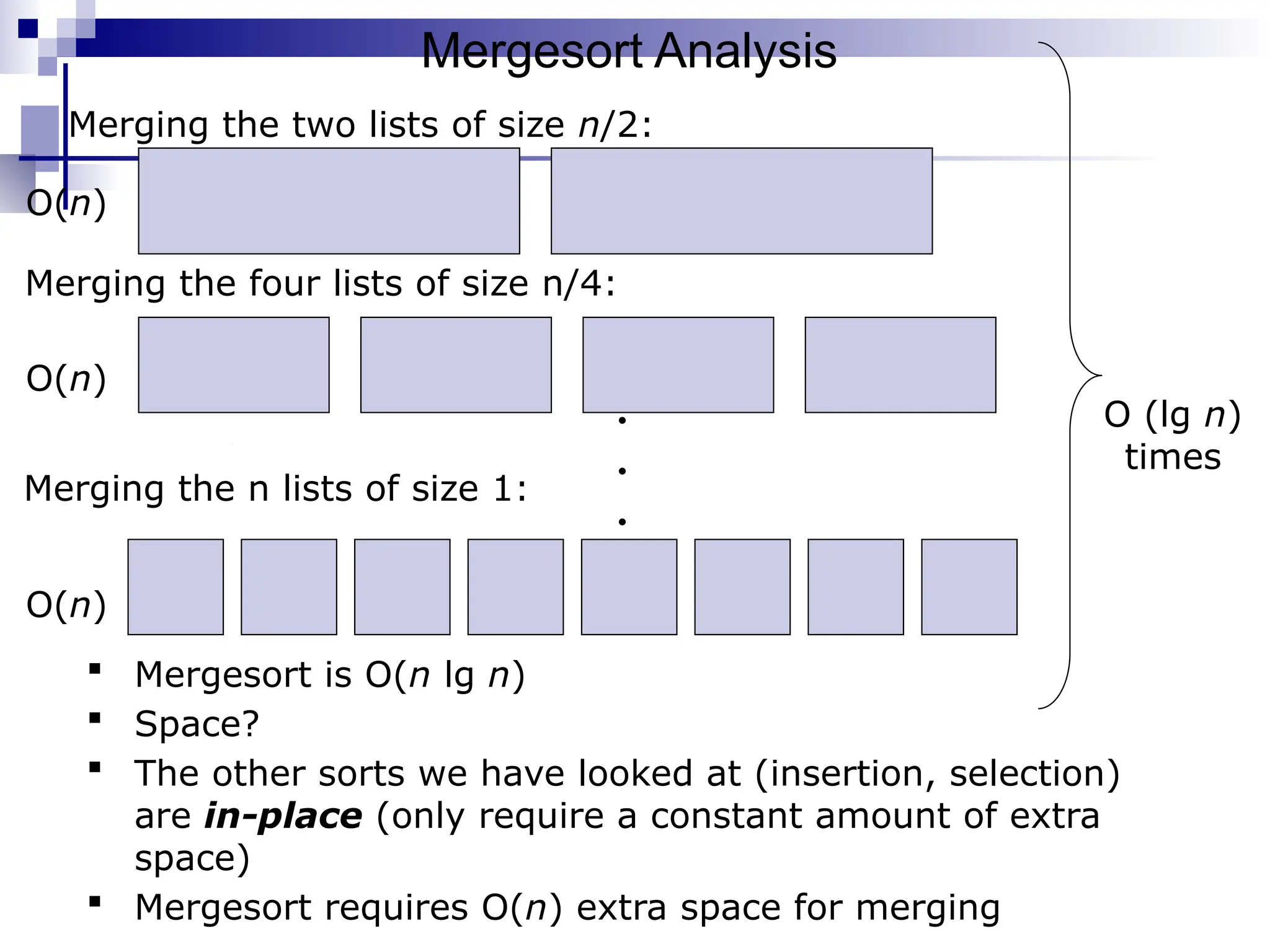
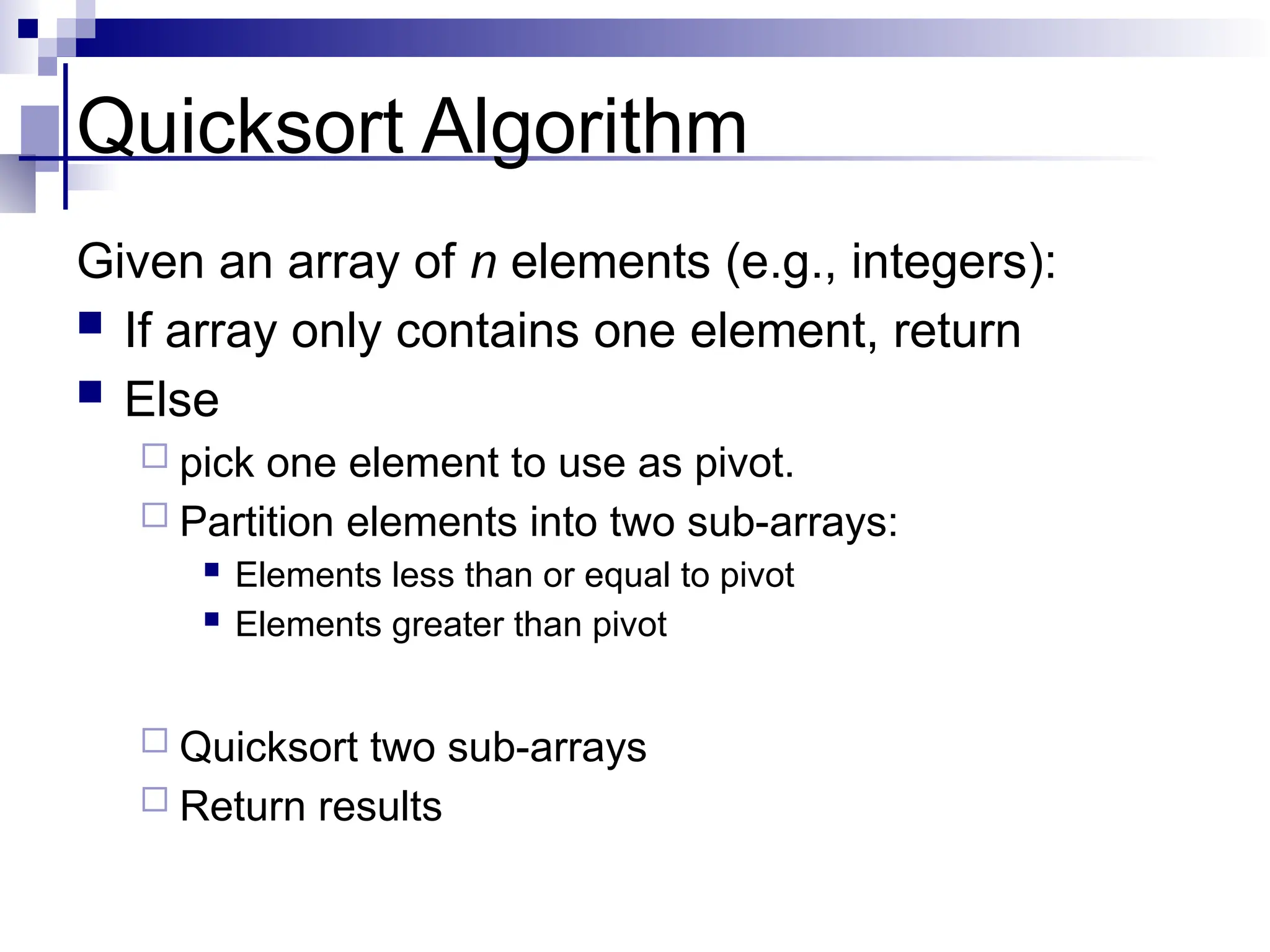
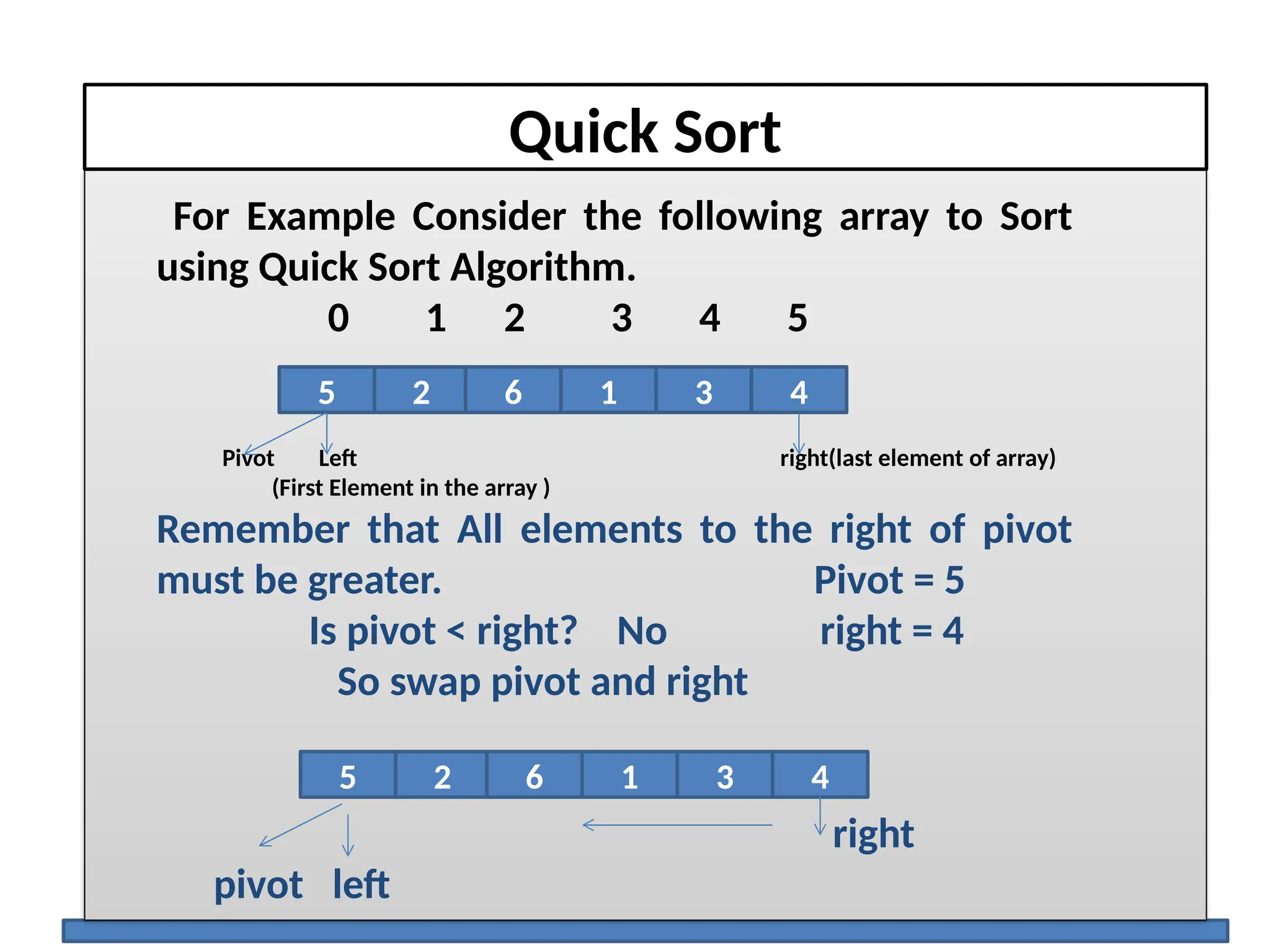
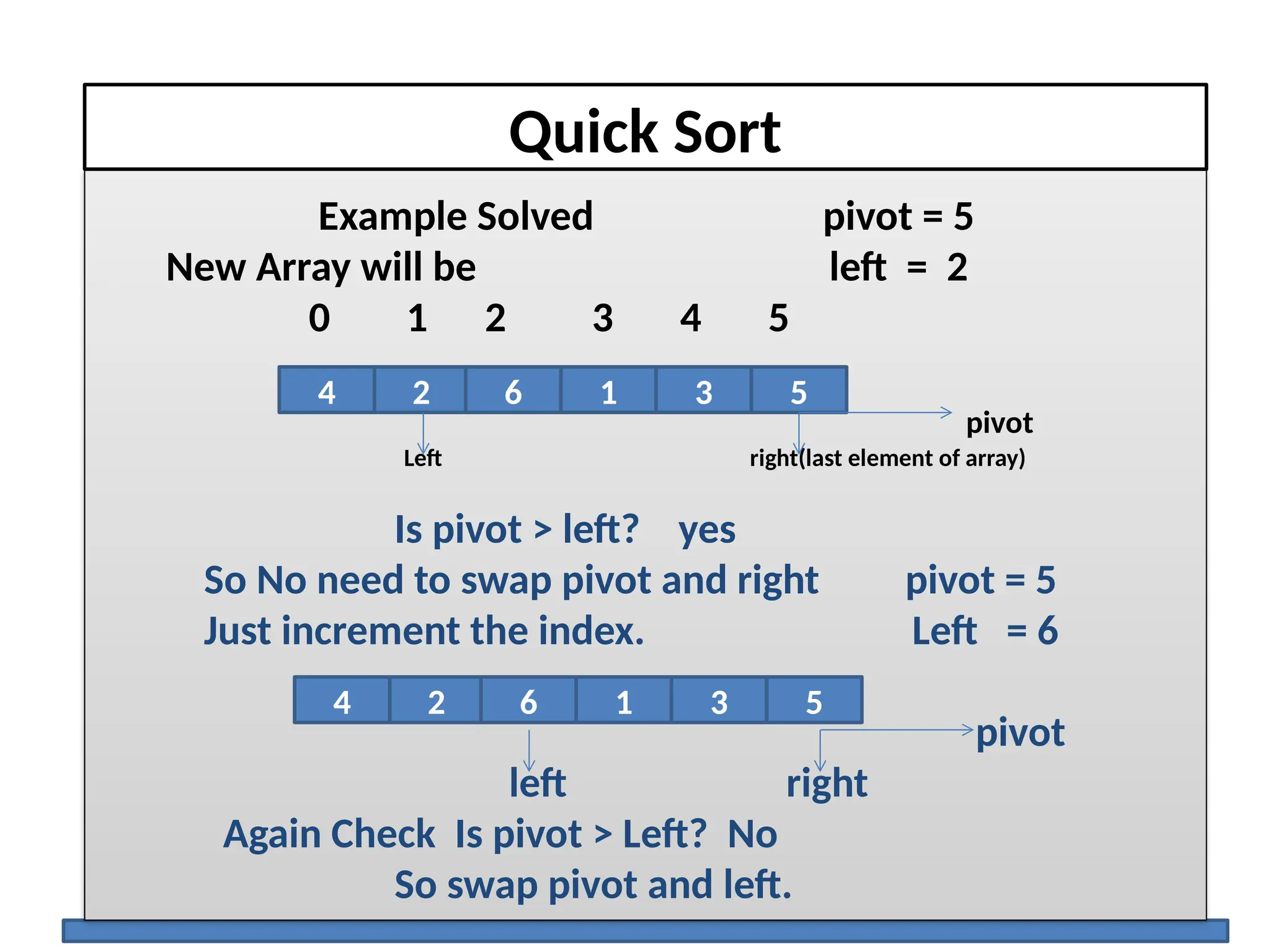
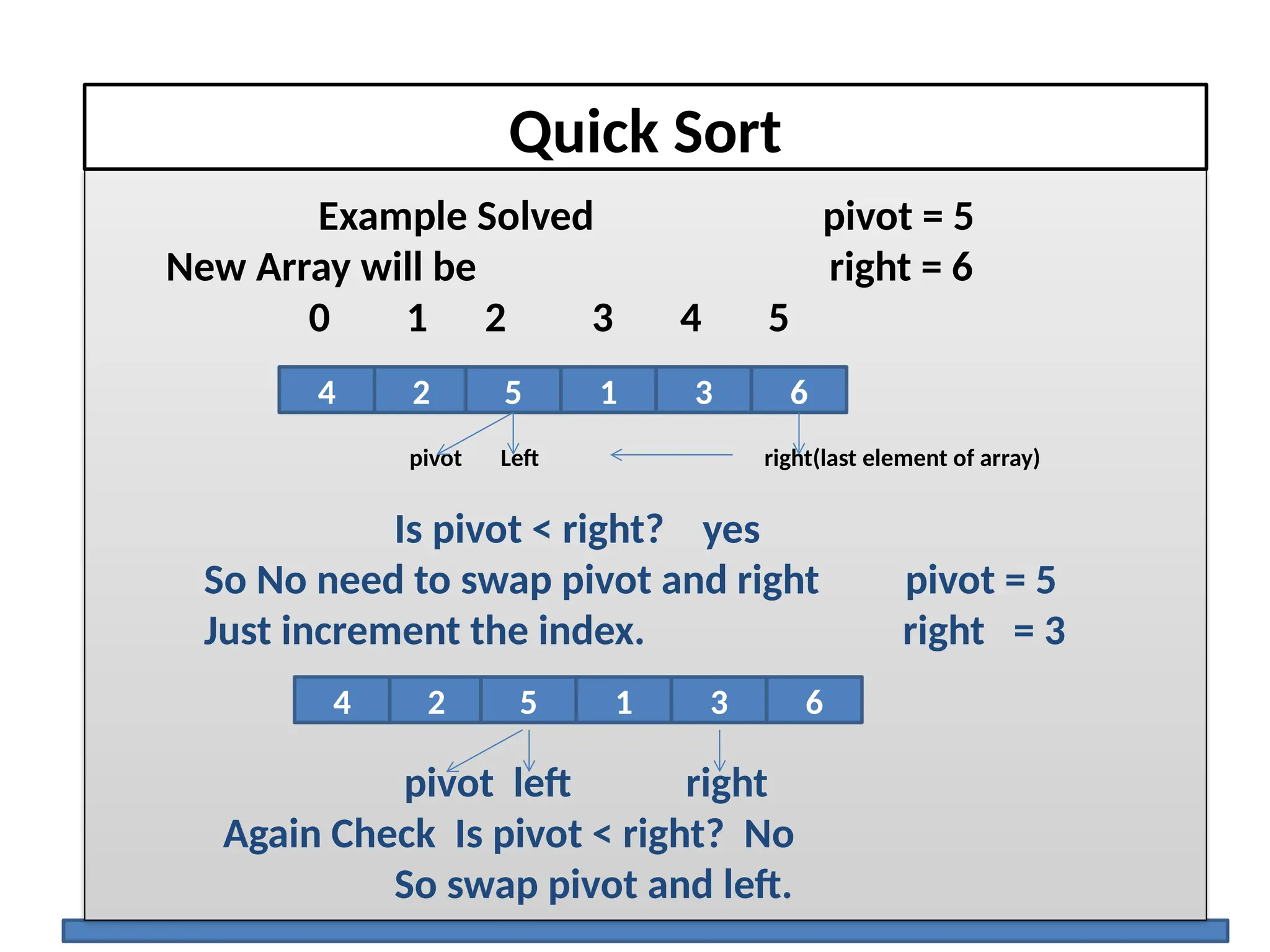
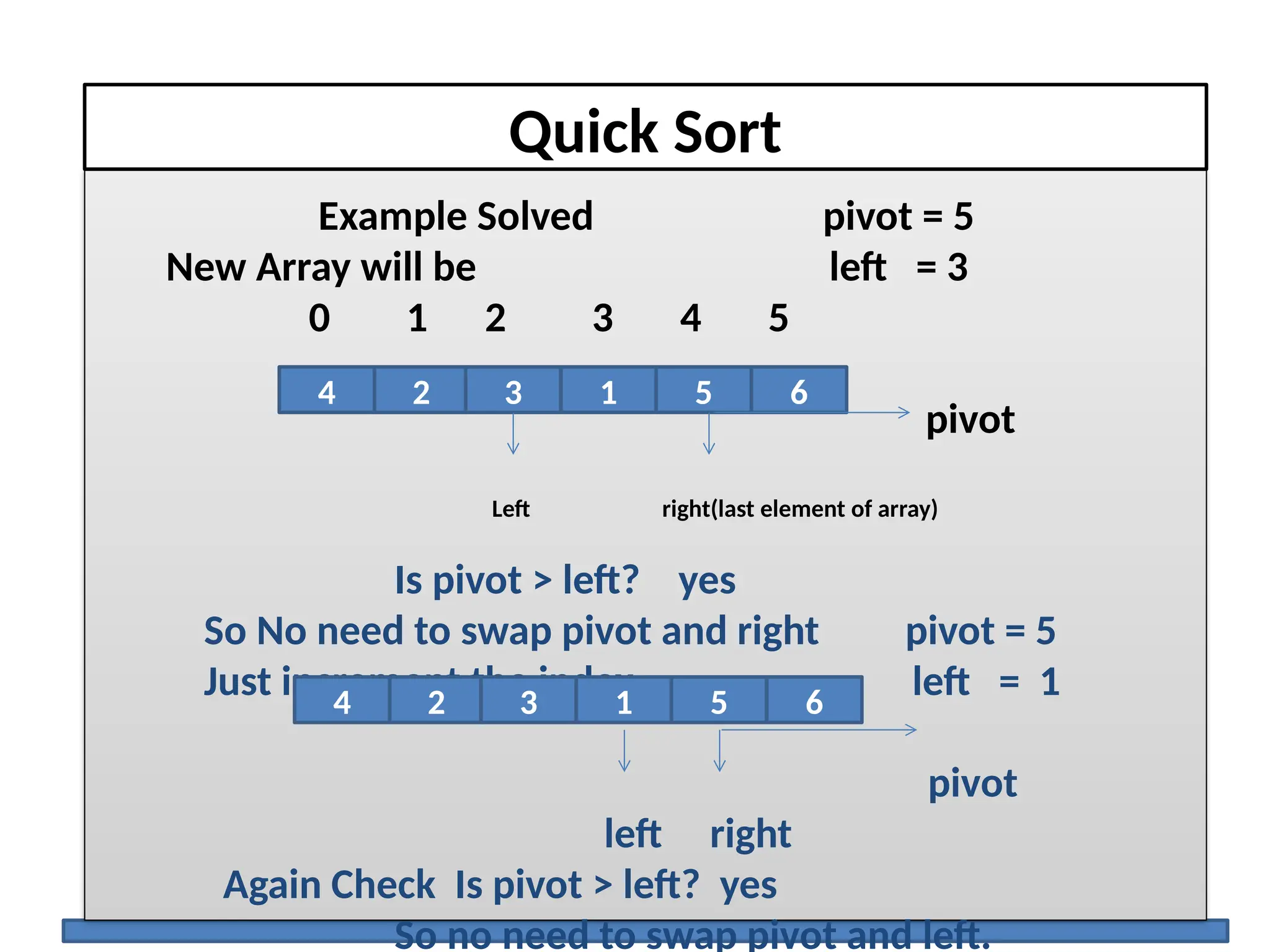
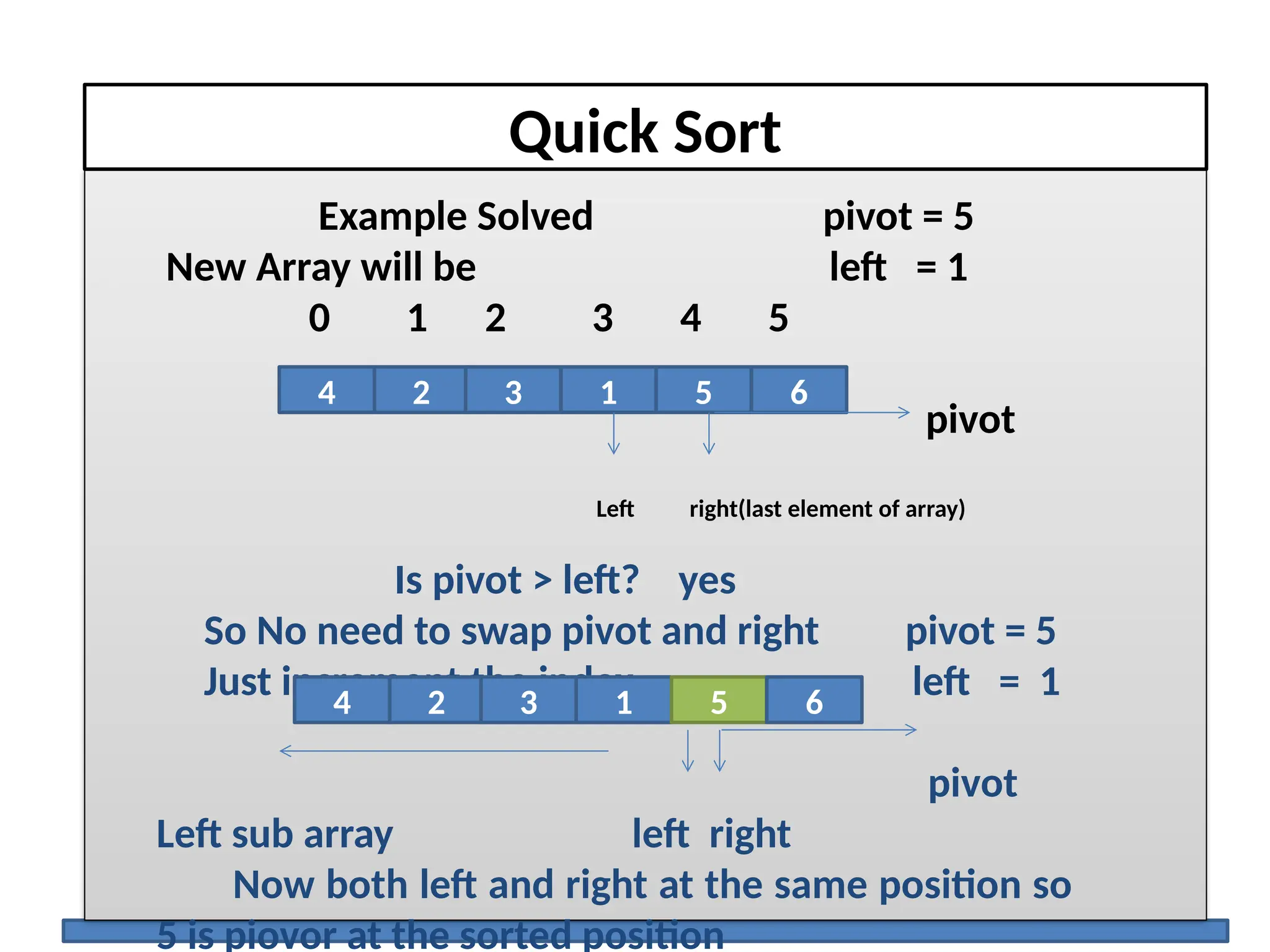
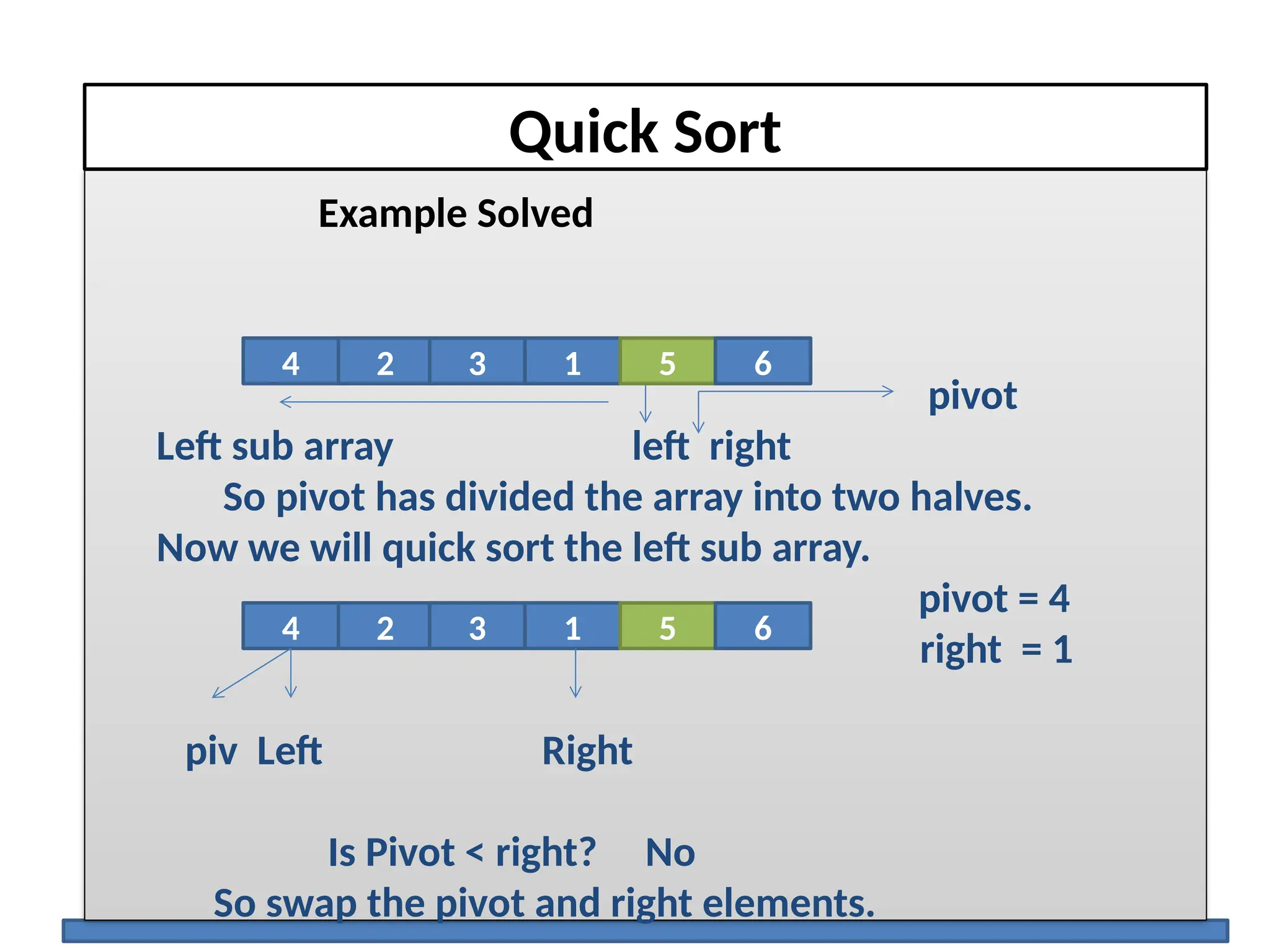
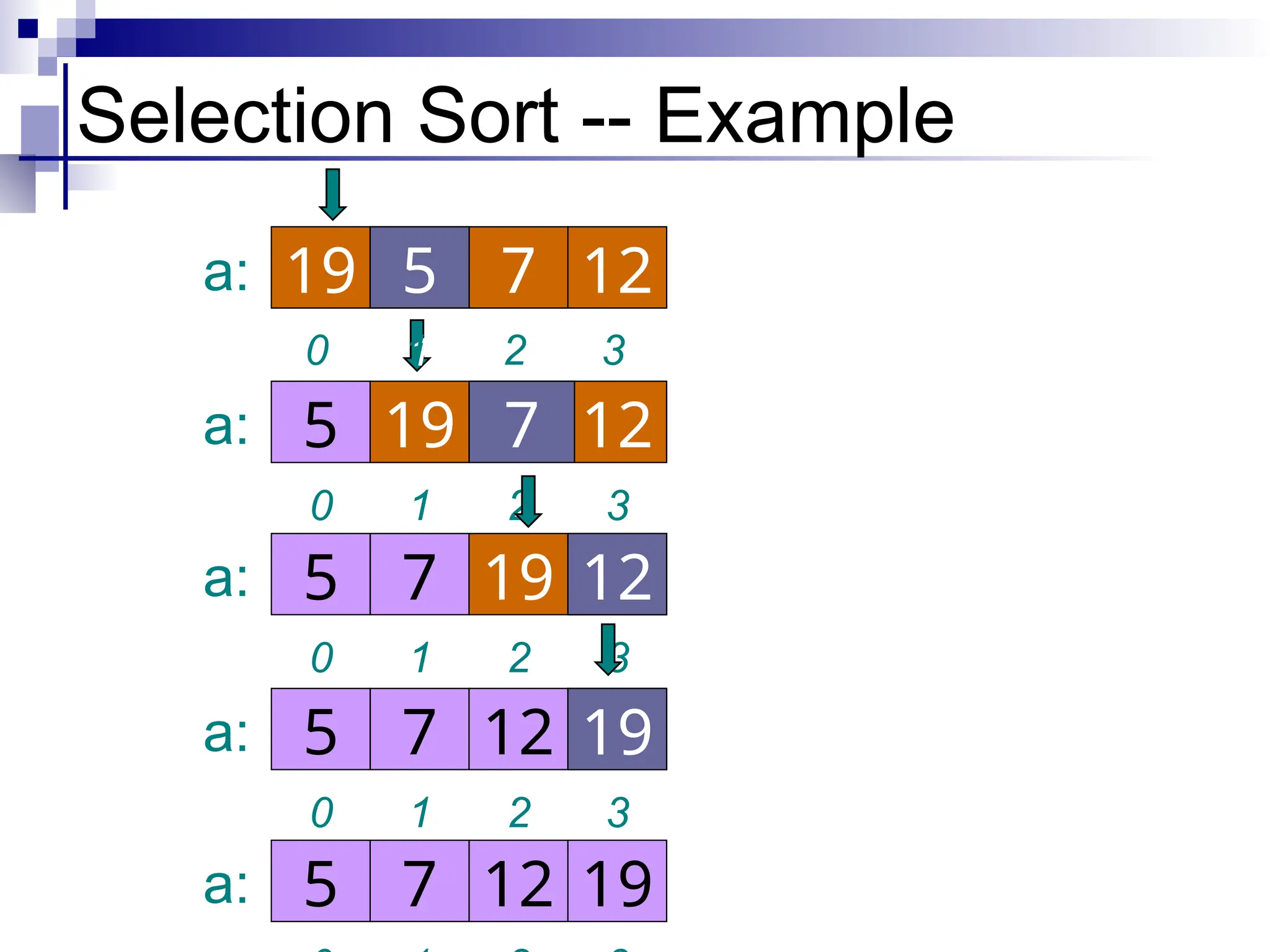
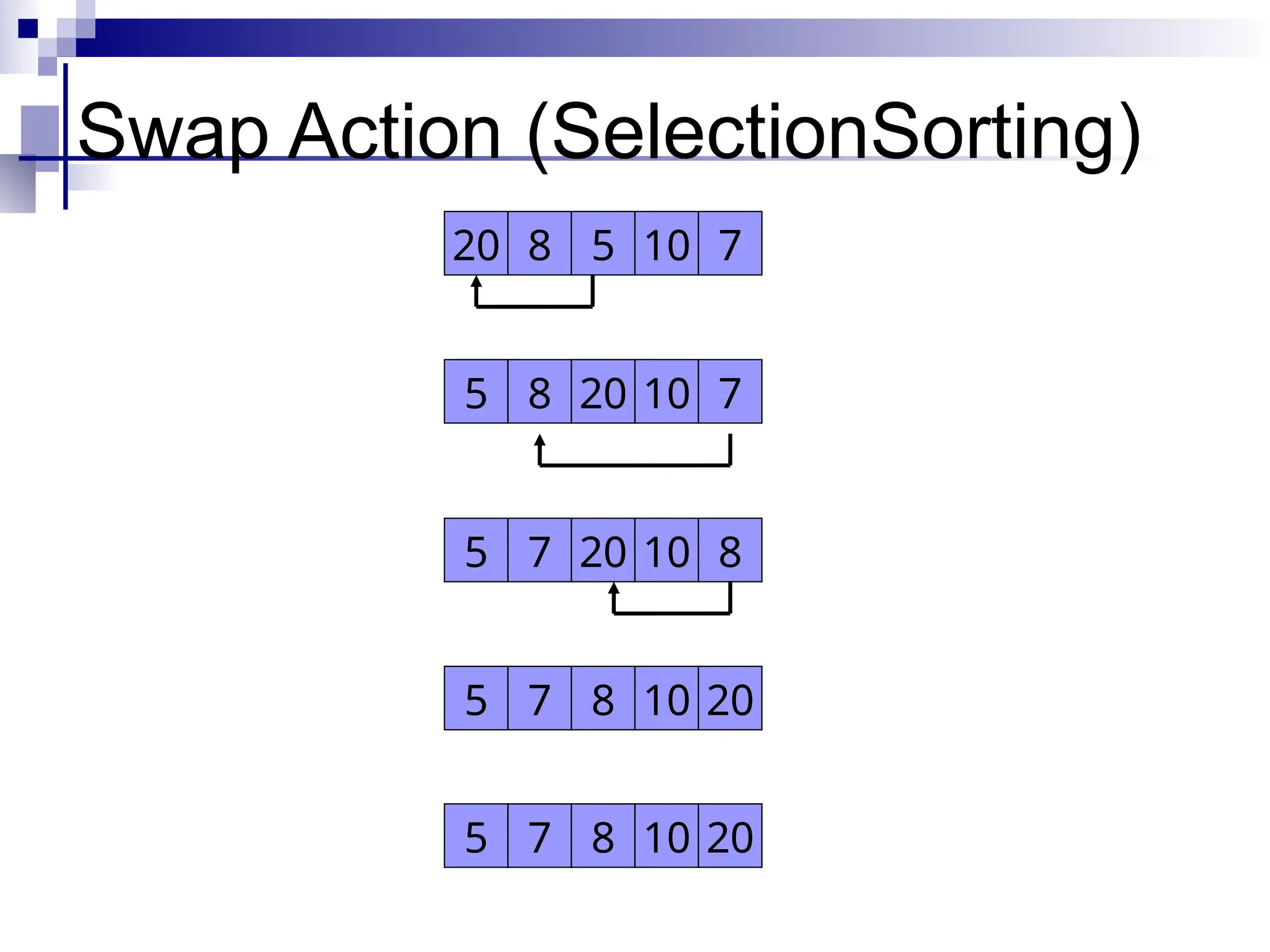
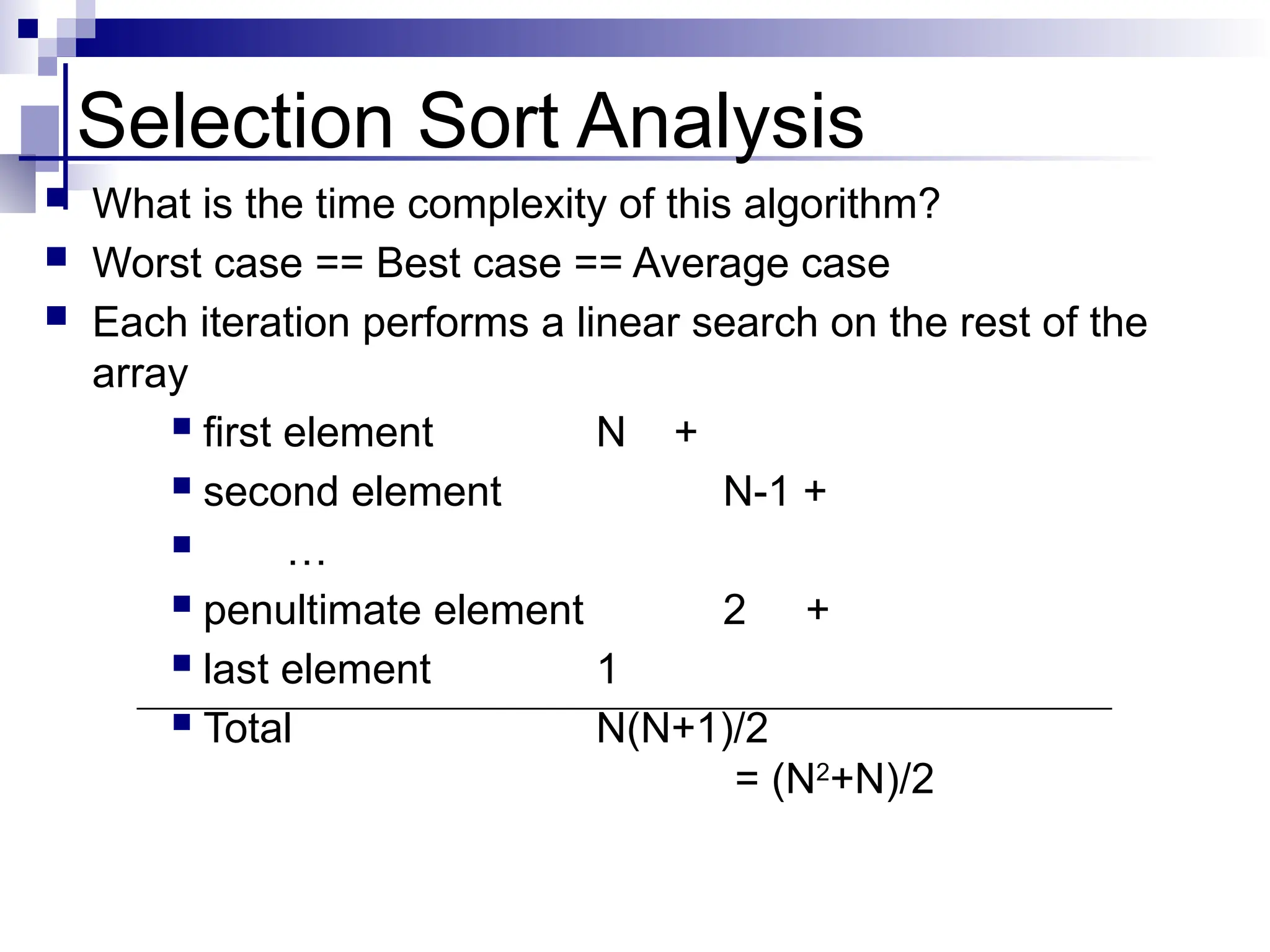
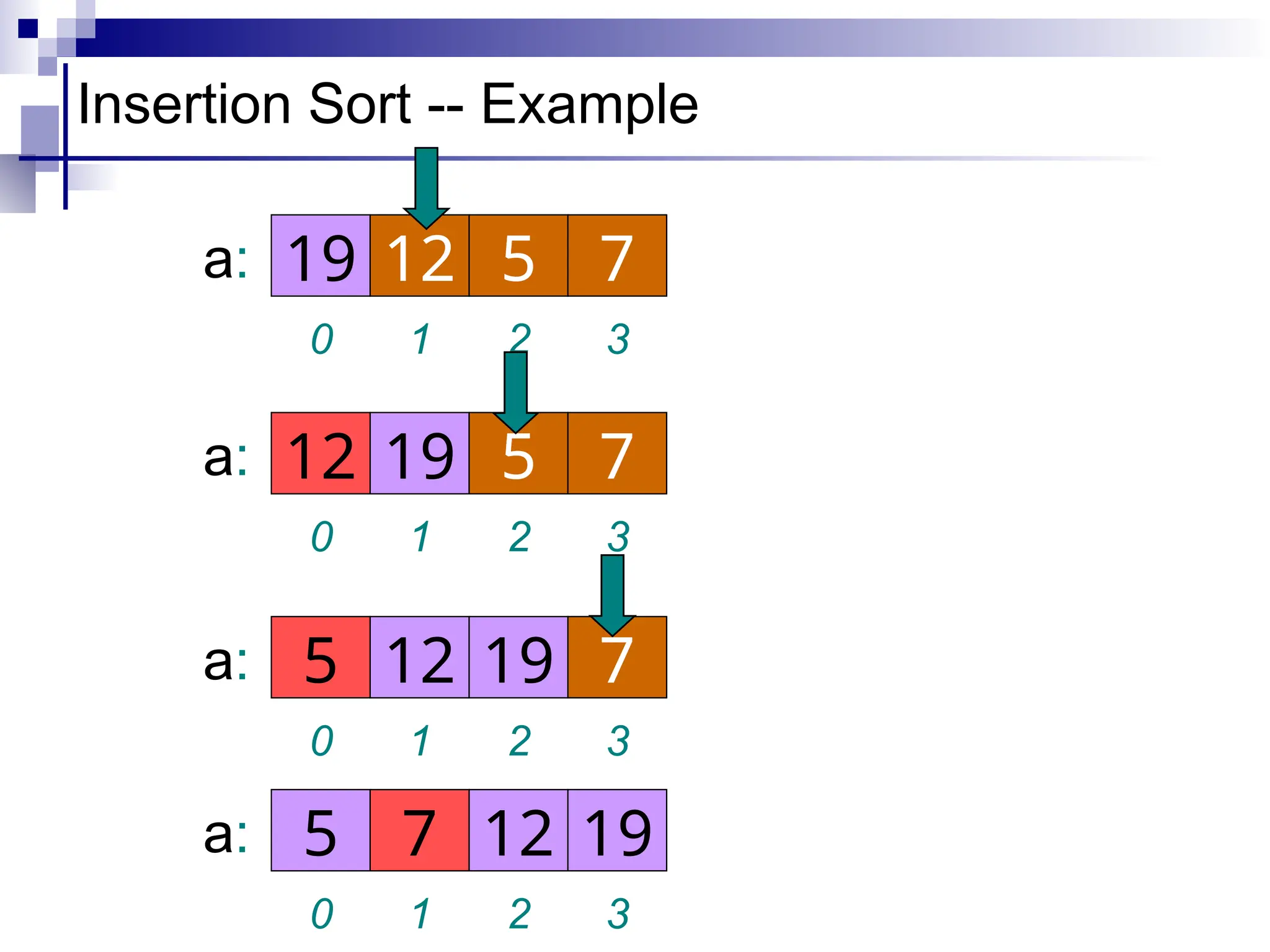
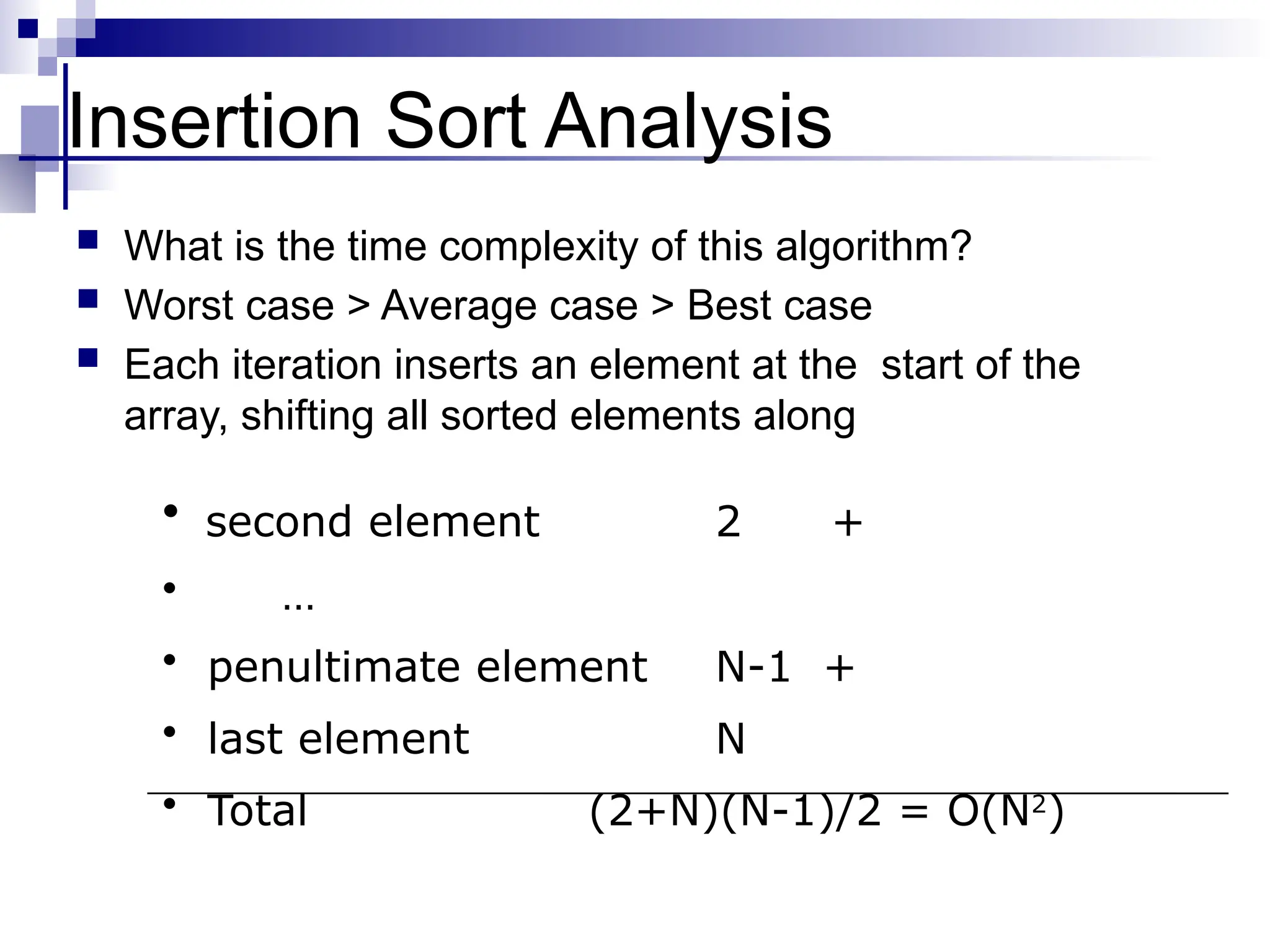
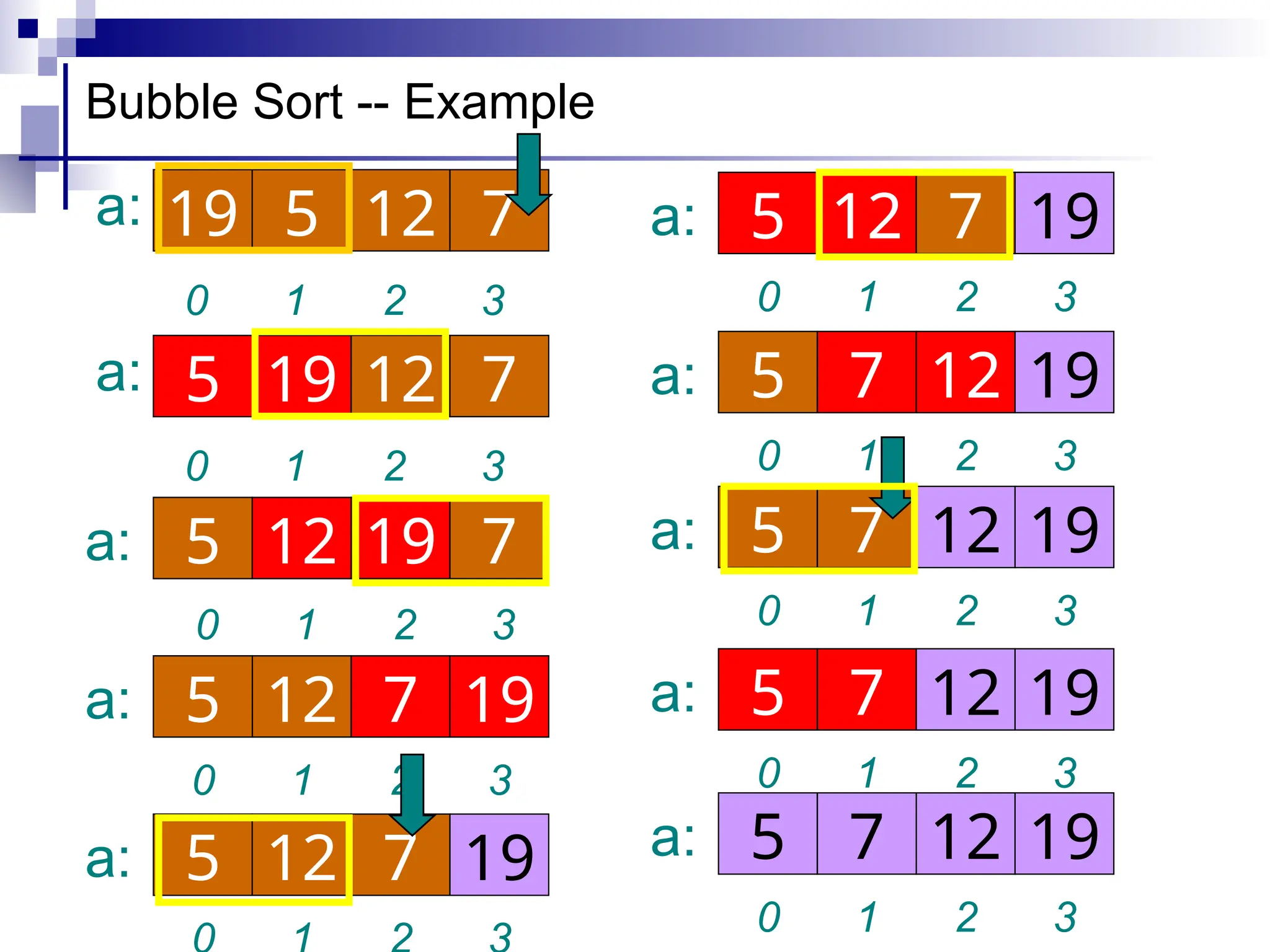
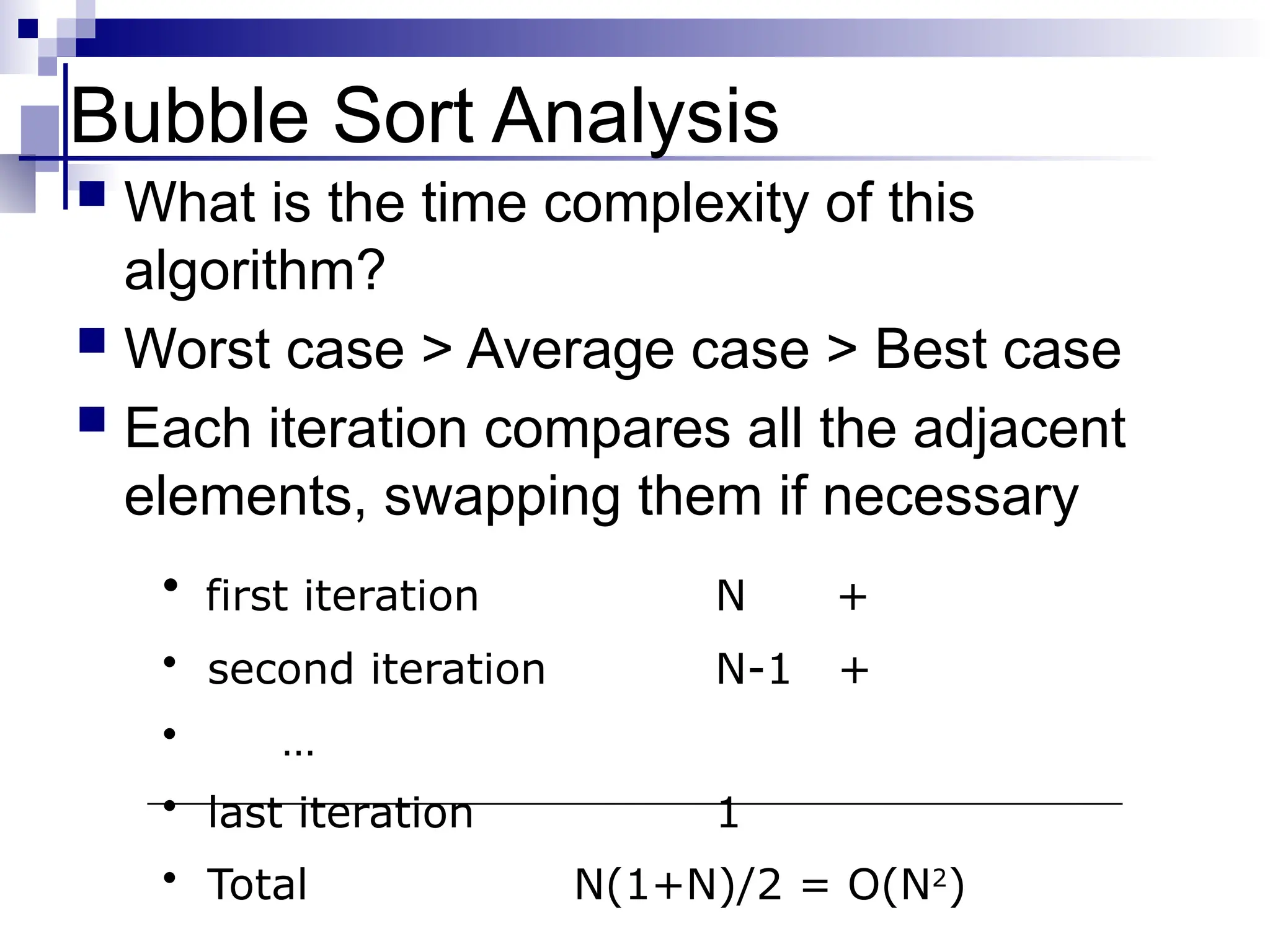
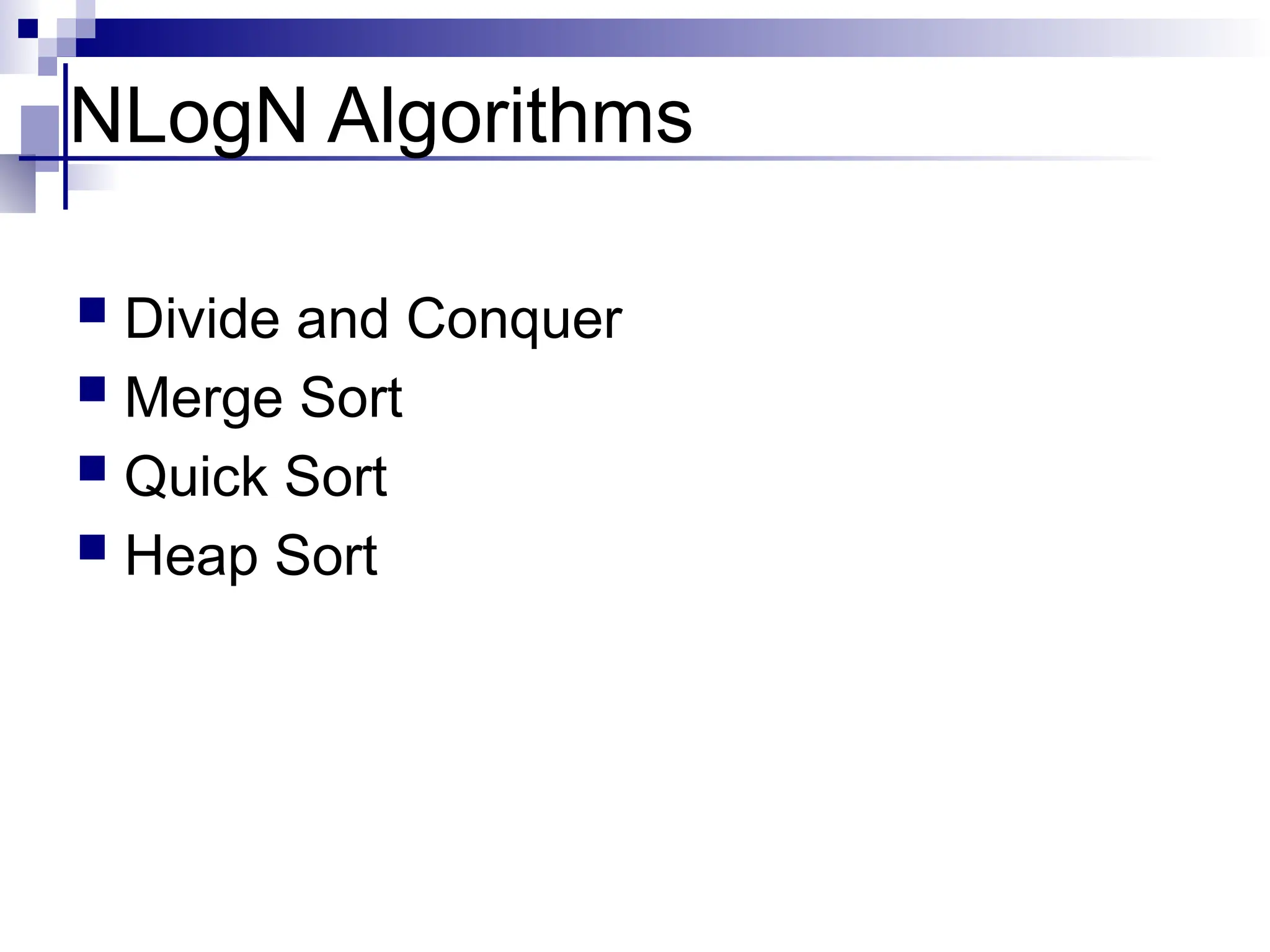
The document discusses several elementary sorting algorithms including selection sort, insertion sort, and bubble sort, detailing their mechanics and time complexities. It introduces more efficient algorithms like merge sort and quicksort, explaining their divide and conquer strategies along with their implementation specifics. The overall emphasis is on understanding the complexity and efficiency of various sorting methods.










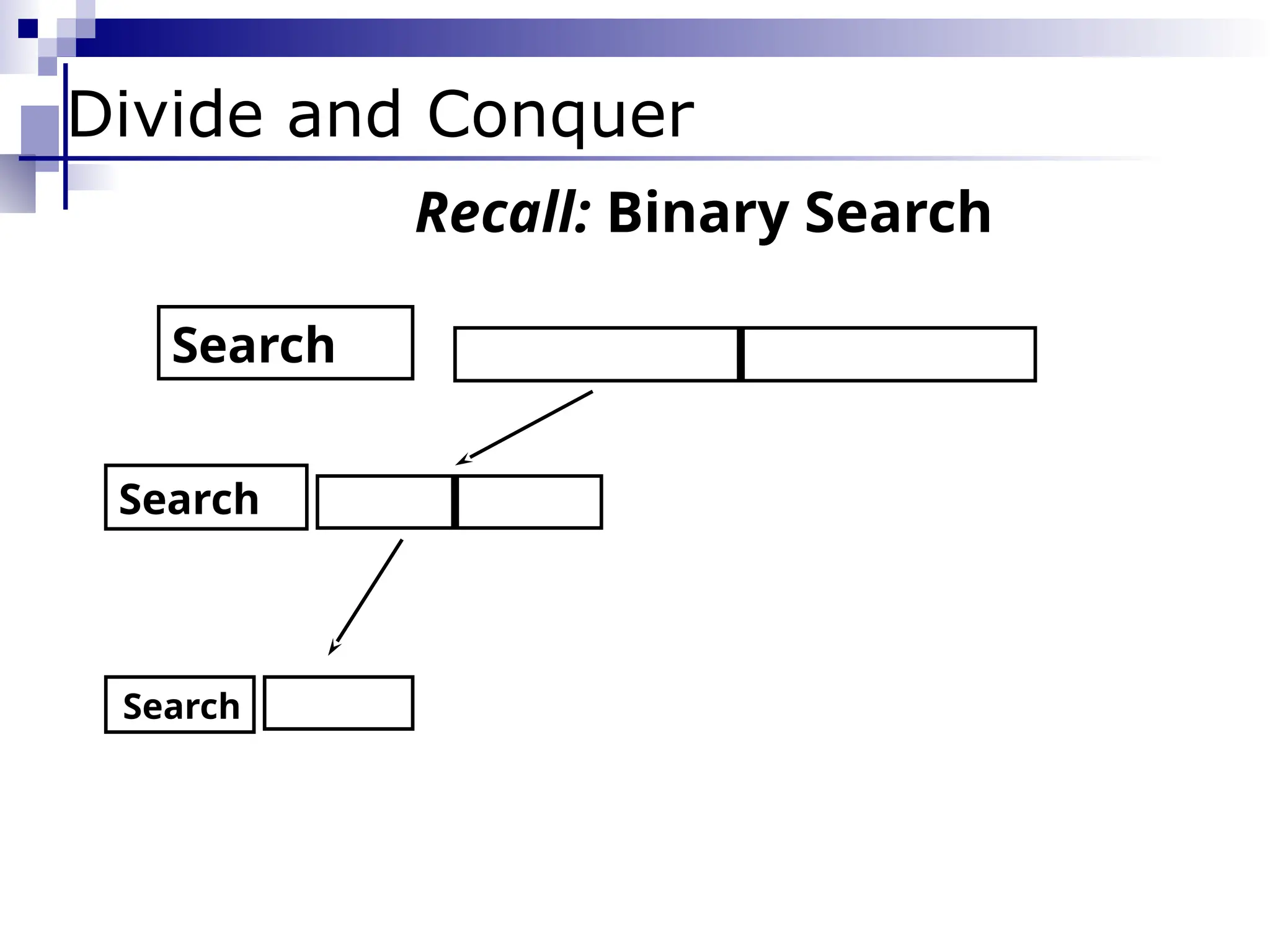
![B_Search(A,value,low,high)
{
if (high < low)
return low
mid = (low + high) / 2
if (A[mid] >= value)
return B_Search (A, value, low, mid-1)
else
return B_Search (A, value, mid+1, high)
}
displayArray(A[], p, r)
{
if(p<r)
show A[p]
displayArray(A,p+1,end);
}
Divide & Conquer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weak11-12sortingupdate-250102045859-cede7d03/75/Weak-11-12-Sorting-update-pptxbhjiiuuuuu-20-2048.jpg)

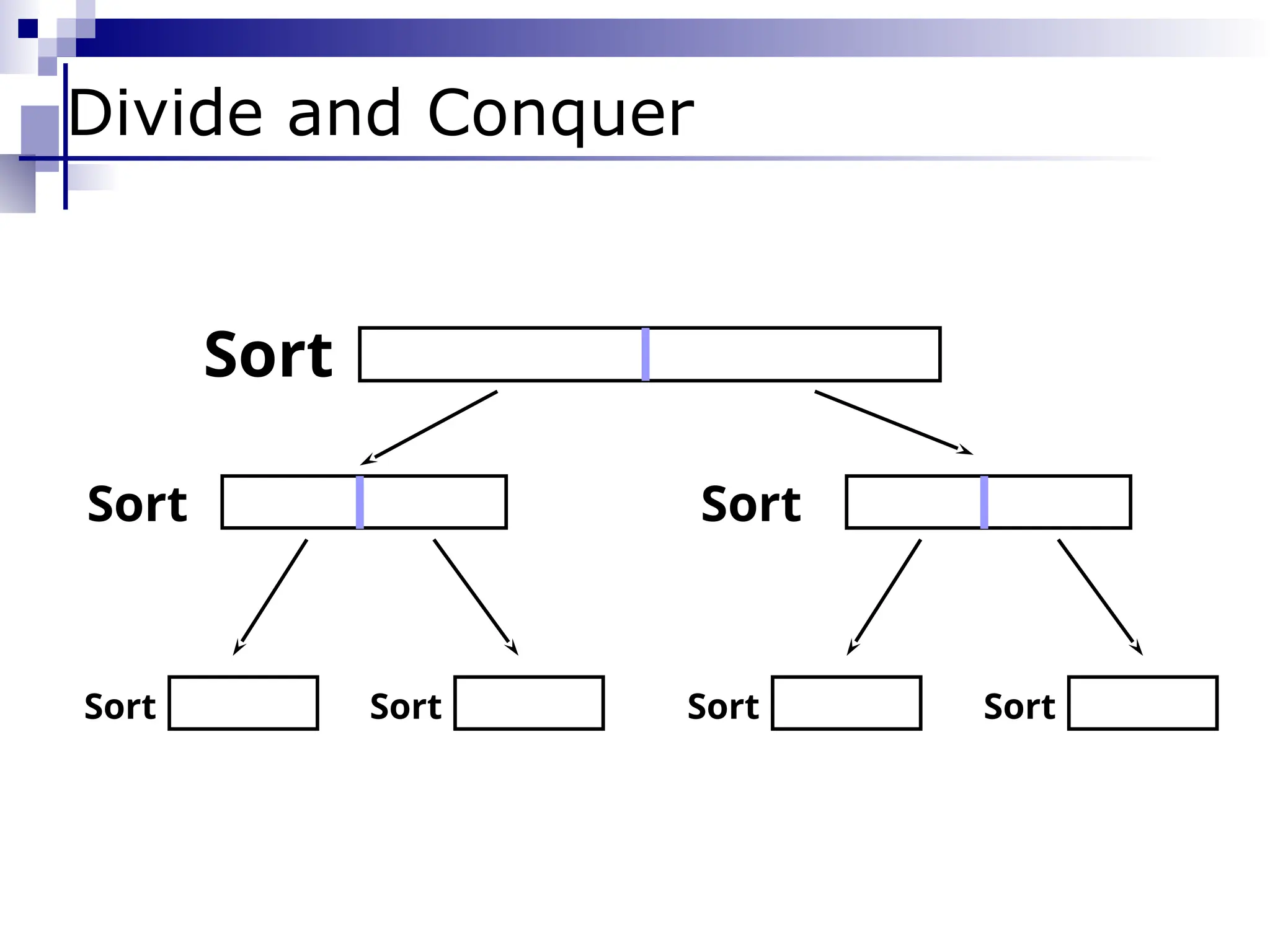



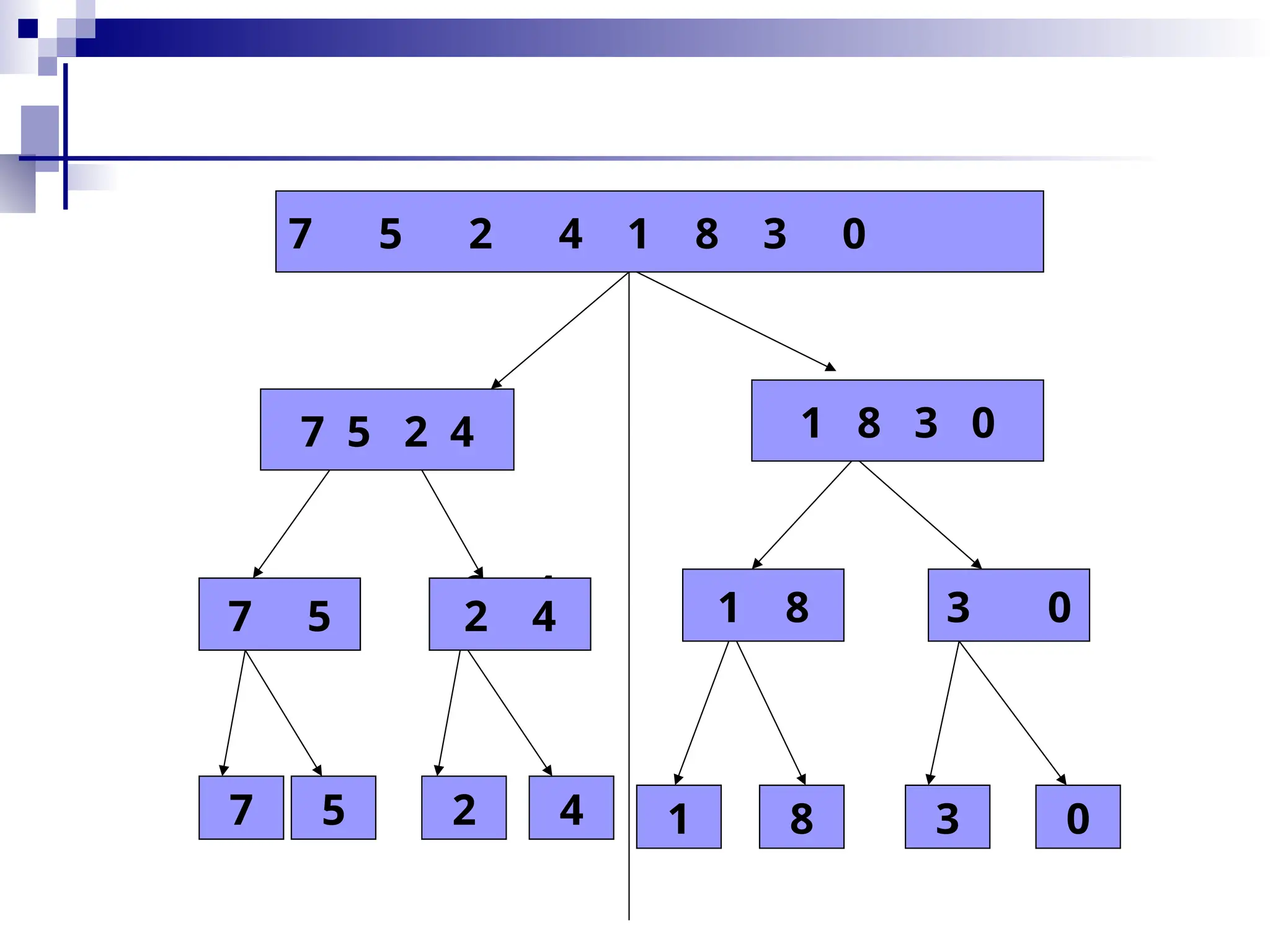
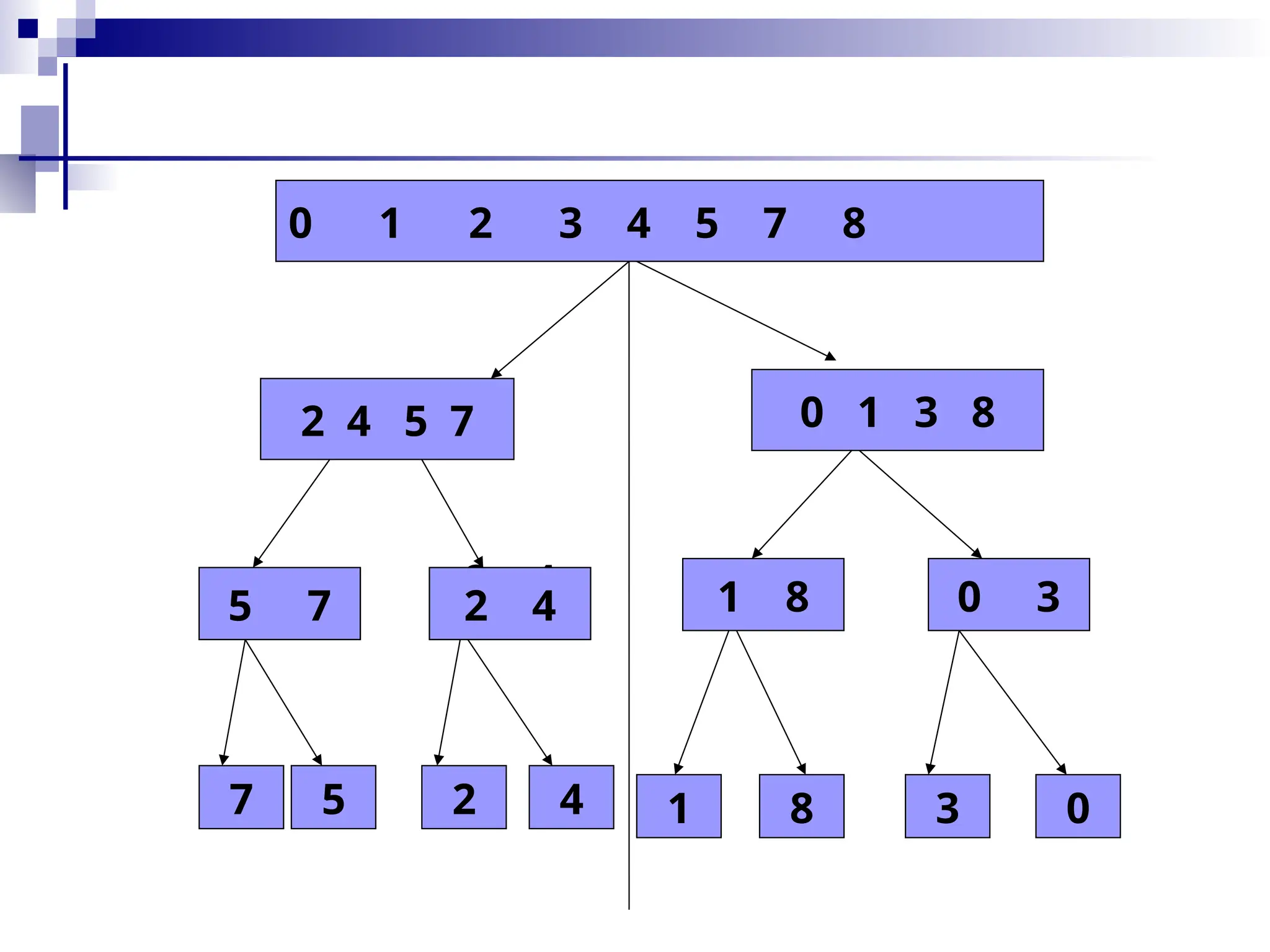
![Algorithm Merge-sort
Merge-sort(array A, int p, int r)
If (p<r)
q ‹— (p+r)/2
Merge-sort(A,p,q) //sort A[p…
q]
Merge-sort(A,q+1,r)//sort
A[q+1..r]
Merge(A,p,q,r)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weak11-12sortingupdate-250102045859-cede7d03/75/Weak-11-12-Sorting-update-pptxbhjiiuuuuu-30-2048.jpg)
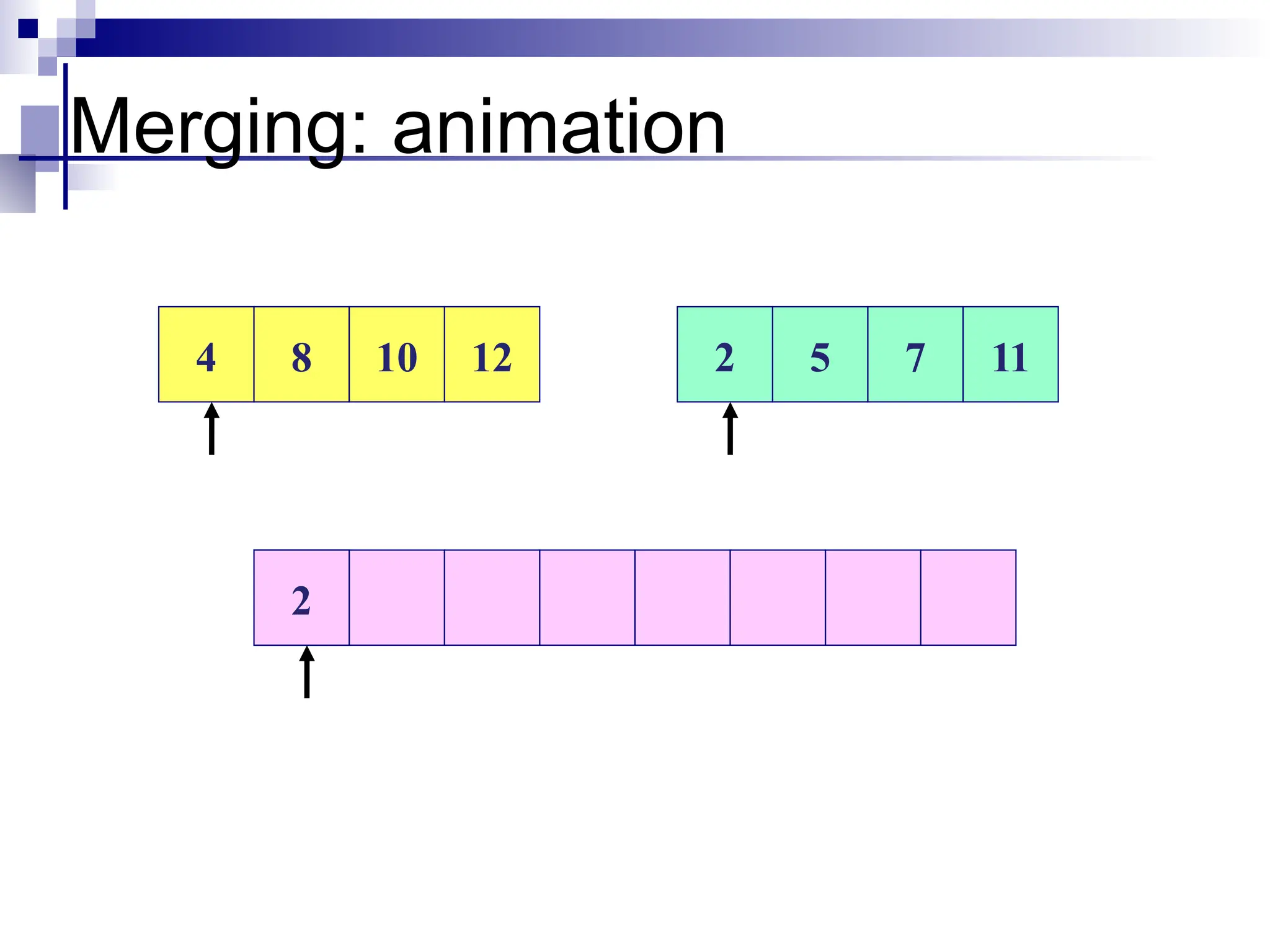
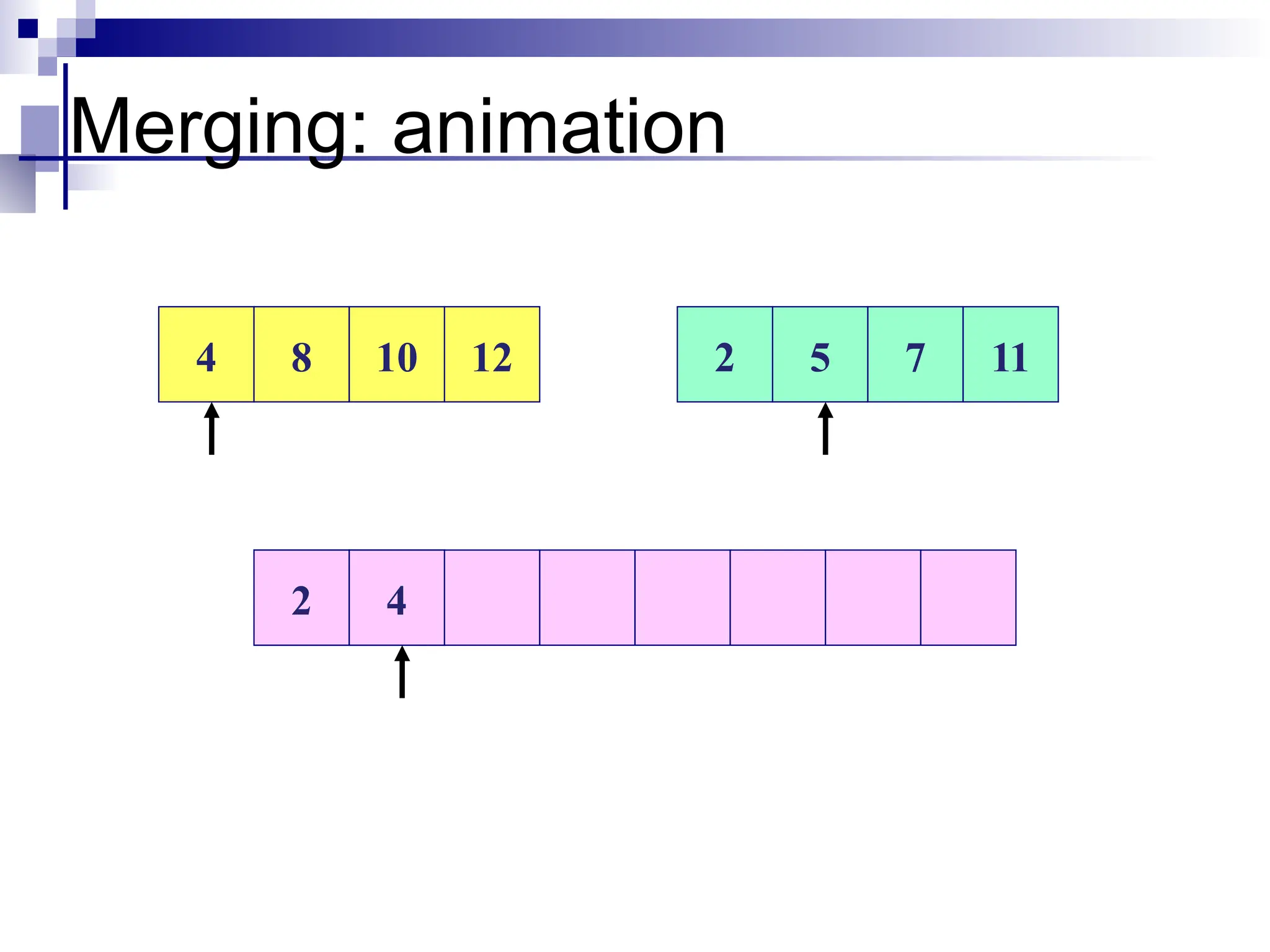
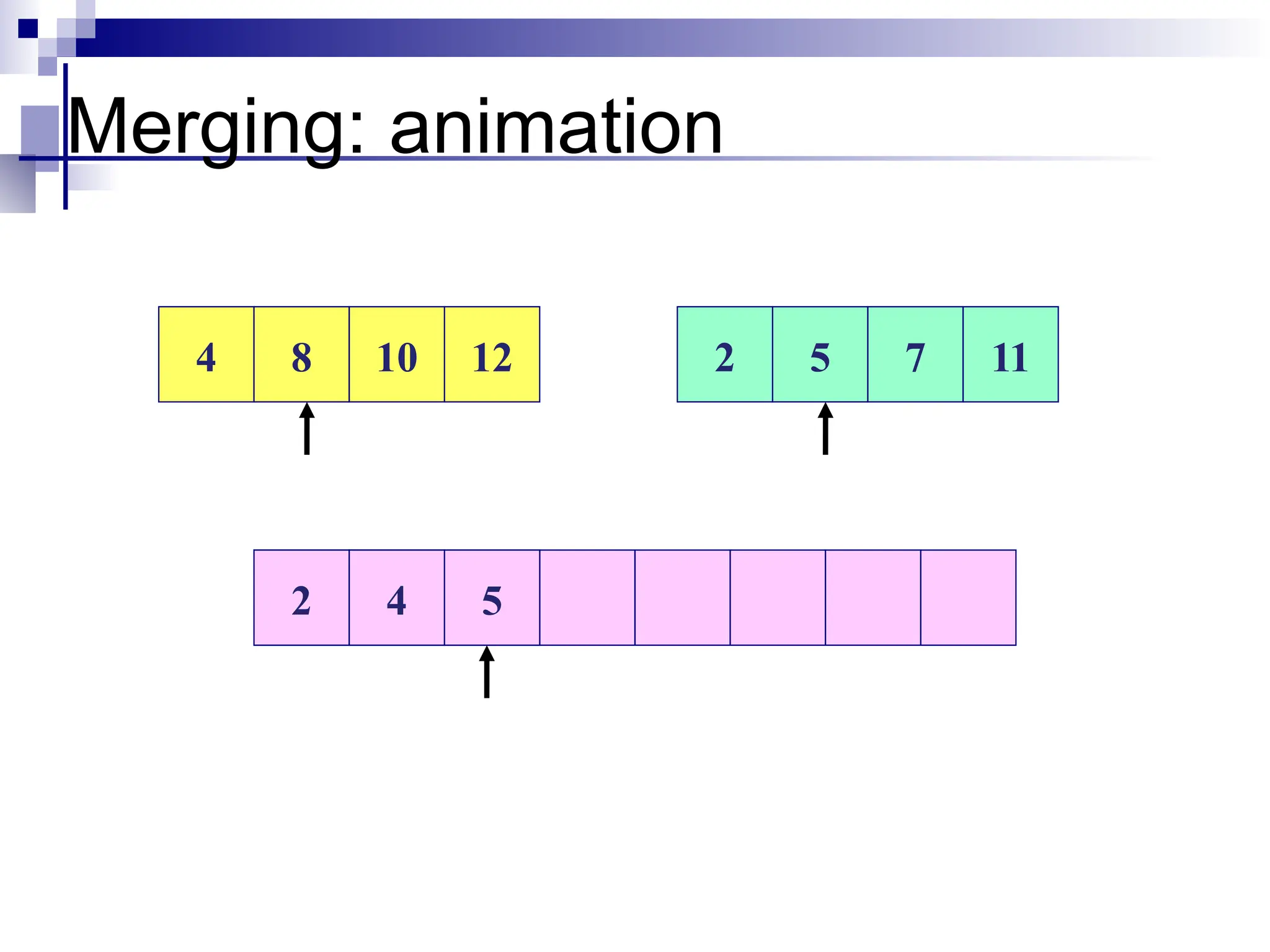
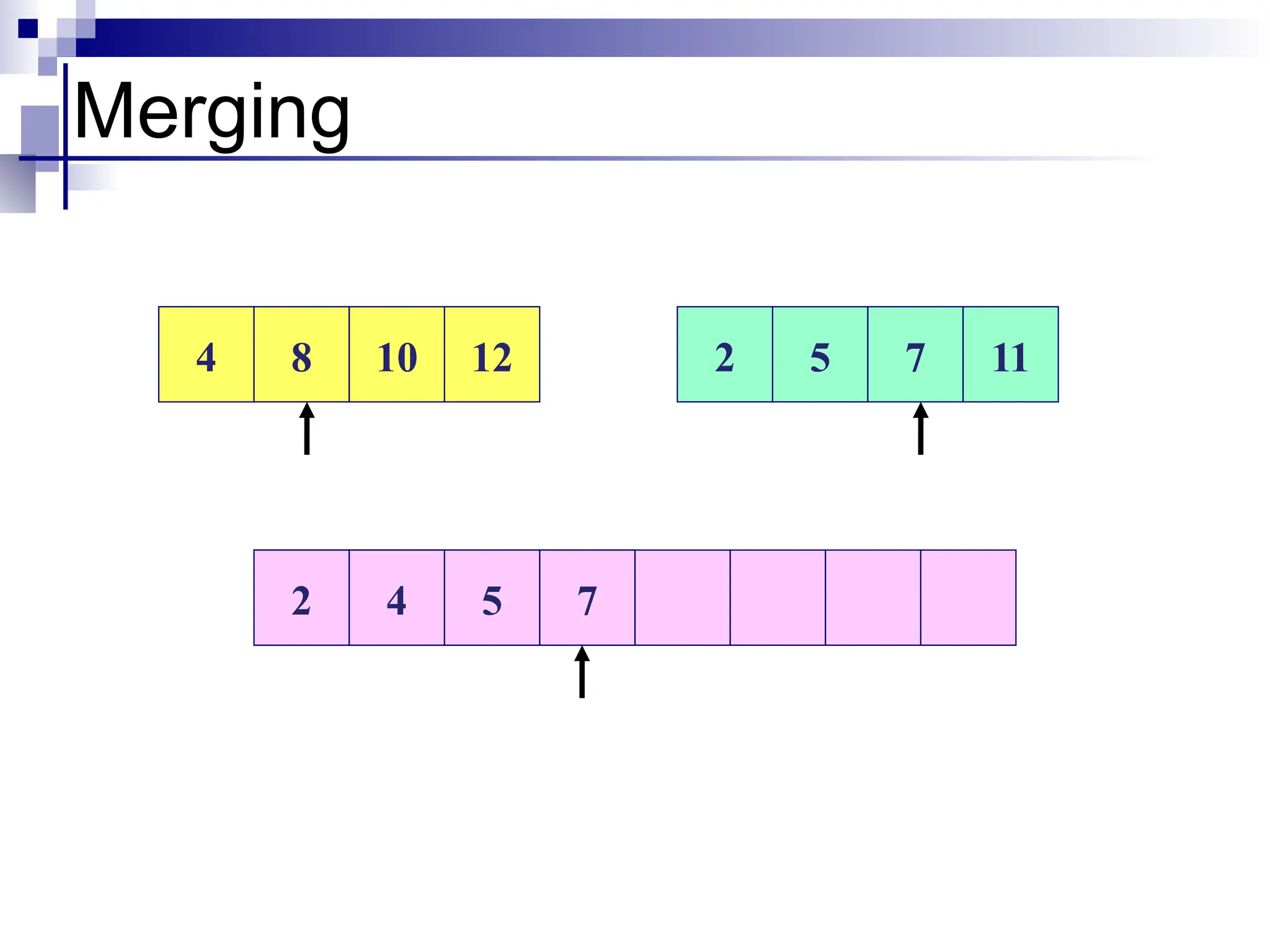
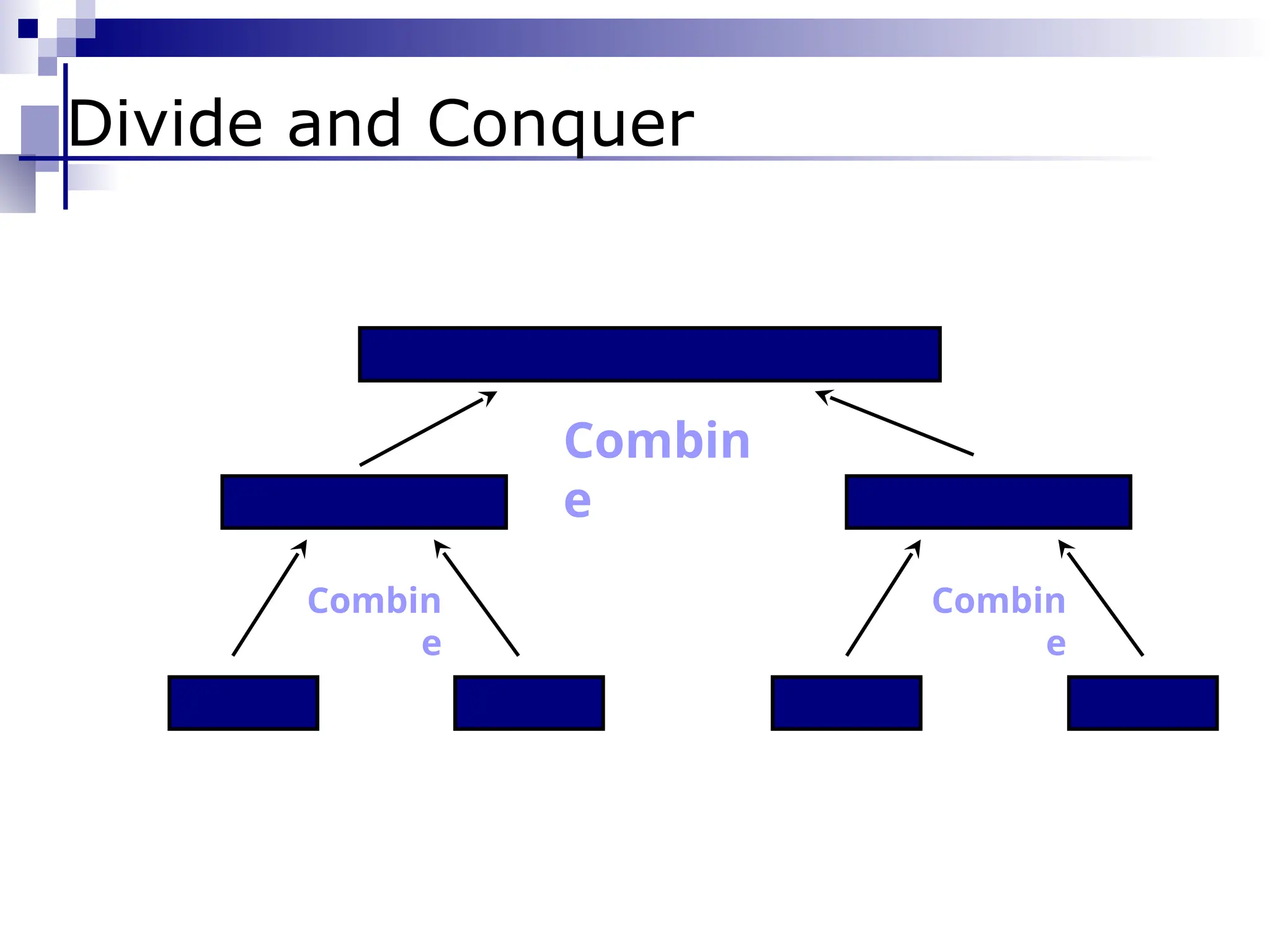
![Merge Algorithm
merge(array A, int p, int q,int r)
1. int B[p…r];
2. int i =k =p;
3. int j =q+1
4. while(i<=q) and (j<=r)
5. do if(A[i] <= A[j])
6. then B[k++] =A[i++]
7. else B[k++] =A[j++]
8. while(i<=q)
9. do B[k++] =A[i++]
10.while(j<=r)
11. do B[k++] = A[j++]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weak11-12sortingupdate-250102045859-cede7d03/75/Weak-11-12-Sorting-update-pptxbhjiiuuuuu-31-2048.jpg)